Contextual Dependency Injection for Apachecon 2010
- 1. Getting started with Java Contexts and Dependency Injection in Java EE6 Rohit Kelapure Apache Open Web Beans IBM WebSphere Application Server http://twitter.com/#!/rkela http://www.linkedin.com/in/rohitkelapure
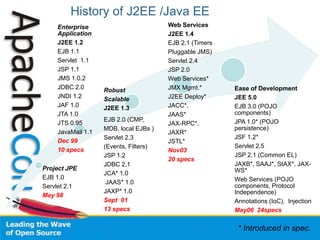
- 2. History of J2EE /Java EE Project JPE EJB 1.0 Servlet 2.1 May 98 Enterprise Application J2EE 1.2 EJB 1.1 Servlet 1.1 JSP 1.1 JMS 1.0.2 JDBC 2.0 JNDI 1.2 JAF 1.0 JTA 1.0 JTS 0.95 JavaMail 1.1 Dec 99 10 specs Robust Scalable J2EE 1.3 EJB 2.0 (CMP, MDB, local EJBs ) Servlet 2.3 (Events, Filters) JSP 1.2 JDBC 2.1 JCA* 1.0 JAAS* 1.0 JAXP* 1.0 Sept 01 13 specs Web Services J2EE 1.4 EJB 2.1 (Timers Pluggable JMS) Servlet 2.4 JSP 2.0 Web Services* JMX Mgmt.* J2EE Deploy* JACC*, JAAS* JAX-RPC*, JAXR* JSTL* Nov03 20 specs Ease of Development JEE 5.0 EJB 3.0 (POJO components) JPA 1.0* (POJO persistence) JSF 1.2* Servlet 2.5 JSP 2.1 (Common EL) JAXB*, SAAJ*, StAX*, JAX- WS* Web Services (POJO components, Protocol Independence) Annotations (IoC), Injection May06 24specs * Introduced in spec.
- 3. JSF 1.2 Shortcomings • No integration with EJBs • No templating support (before JSF 1.2) • Transparent to HTTP Requests • Difficult to create custom components • Lacks – conversation scope – advanced components (tabbed panes, menus, trees) • Weak page oriented support • Overly complex lifecycle • JSP & JSF inherent mismatch
- 4. EJB 2 Shortcomings • Sheer amount of code – Boilerplate code • Glutton for XML (deployment descriptors) • Broken Persistence Model • Difficult Unit Test • Rigid API interfaces • Needs IDE Tooling
- 5. Emergence of SEAM • Bind EJBs directly to JSF-View using EL • Contextual Components • Page flow & Navigation Rules • Interceptors • Conversation Scope, Persistence • Dependency Injection (Bijection) • Security • Ajax Support • Seam-gen • Integration testing contextual name Component stateless SB stateful SB Entity Bean Java Bean Context Event Page Conversation Process Stateless Application Session instance variable in a component realized by means of bijection Role 1..* 0..* 1..* *picture source: Steffen Ryll Conversation Stack Servlet Session mapping contextual name Component stateless SB stateful SB Entity Bean Java Bean Context 1..* 0..* Event Page Conversation Process Stateless Application Session instance variable in a component realized by means of bijection 1..* long-running Conversation - long-running flag = true temporary Conversation - long-running flag = false Conversation - ID - description - long-running flag - initiator component - start time - last access time - timeout duration inner conversation outer conversation 0..1
- 6. • Lightweight dependency injection • Aspect oriented • Layered application & container framework • Well defined modules on top of the core container • NOT an all-or-nothing solution Spring Framework
- 7. Java EE6 to the rescue
- 8. Evolution of J2EEJava EE6 (Dec 09) • New specs (JAX-RS, DI, CDI, Bean Validation) • Prune dead wood – EJB 2.x, JAX-RPC, JAXR, JEE App. Deploy, JEE App mgmt. • Extensibility – Easy Framework Pluggability (web fragments & CDI Extensions) • Enhanced ease of development – POJO annotation based Servlets, – Async processing (Servlet 3.0 & EJB 3.1) – EJB 3.1 • EJB-in-WAR, No-interface view, Singleton, EJB-lite, Timers, Standalone-container – Contextual Dependency Injection (CDI) – RESTful services, Portable JNDI names – JSF2.0 • Facelets, built-in-AJAX, Skins, Annotations, Resource handling • Simplified Navigation, Easier custom components, View & Page scopes • Bookmarkable pages, Project Stage, Expanded event model – JPA 2.0 • Mapping enhancements, JPAQL, Criteria Query API, Pessimistic locking • Profiles reduce platform size - Web Profile 12 specs
- 9. Java EE Platform & the Web Profile
- 10. Java EE6 Dependency Injection JSR 330 • Dependency Injection for Java • Foundation for CDI – CDI provides EE context to Injection • Standardizes annotations – @Inject, @Named, @Qualifier, @Scope, @Singleton • Abstract – Does NOT specify how applications are configured • Implementations – Apache Geronimo – Spring Source tc Server – Google Guice (Java SE) – Apache Open Web Beans (Java EE & SE) – JBoss Weld (Java EE & SE) – Resin CanDI (Java EE & SE)
- 11. Example Generic Injection JSR330 // injection-point; no get/set needed... @Inject private BusinessService service; // Provide an implementation public class DefaultBusinessService implements BusinessService{ … } import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.* import java.lang.annotation.*; import javax.inject.Qualifier; @Qualifier @Target( { TYPE, METHOD, FIELD }) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface FancyService { } // Use Qualifier to inject a more meaningful implementaion of the service: @Inject @FancyService private BusinessService fancyService;
- 12. Java EE6 Managed Beans 1.0 spec. • Common Bean Definition – POJO that is treated as managed component by the Java EE container • Annotating POJOs with @javax.annotation,ManagedBean • Standard annotations @PostConstruct & @PreDestroy can be applied to methods in managed bean – perform resource initialization, cleanup etc • Bean can be injected in Servlet or managed JEE component – Using @Resource, @Inject , InitialContext.lookup(“java:module/”) • Component specs (EJB, CDI, JSF, JAX-RS ) add characteristics to managed bean. • EJB, CDI are defined as managed beans too and so; are implicitly managed beans as well @javax.annotation.ManagedBean(value="mybean") public class MyManagedBean { ... }
- 13. Contextual Dependency Injection JSR299 • Future of JEE • Loose Coupling – Server & Client, Components, Concerns & Events • Design pattern Specific type of IoC – Don’t call us, we will call you – No hard coded dependencies • Inspirations SEAM, Spring, Guice • Spec. lead SEAM Gavin King – Reference Implementation Weld • Dramatic reduction in LOC • Goes far beyond what was possible with Java EE5 • Not only an API but also a SPI – Seam 3 to be released as CDI extensions
- 14. CDI Services • Contextual State and lifecycle mgmt. • Typesafe dependency injection • Interceptors and decorators – extend behavior with typesafe interceptor bindings • SPI enables portable extensions – integrates cleanly with Java EE • Adds the Web conversation context – + to standard contexts (request, session, application) • Unified component model – Integration with the Unified EL • Enables use of EJB 3.0 components as JSF managed beans • Events decouple producers and consumers
- 16. Relationship to other Java EE Specs • Contextual lifecycle mgmt. for EJBs – Session bean instances obtained via DI are contextual • Bound to a lifecycle context • Available to others that execute in that context • Container creates instance when needed • Container Destroys instance when context ends • Contextual lifecycle mgmt. for Managed Beans • Associate Interceptors with beans using typesafe interceptor bindings • Enhances JSF with a sophisticated context & DI model – Allows any bean to be assigned an unique EL name
- 17. What is a CDI Managed Bean • Concrete POJO – No argument constructor – Constructor annotated with @Inject • Objects returned by producers • Additional types defined by CDI SPI • Defined to be a managed bean by its EE specification – EJB session beans (local or remote) – Message Driven Beans – JEE Resources (DataSources, JMS Destinations) – Persistent Unit, Persistent Contexts – Web Service References – Servlets, Filters, JSF Managed Beans, Tag Libraries … • Built-in Beans • JTA User Transaction – Security Principal representing caller identity – Bean Validator & Validation Factory
- 18. CDI Packaging • Bean classes packaged in a Bean Deployment Archive • To activate CDI create a beans.xml file (can be empty) – META-INF – WEB-INF/classes • Container searches for beans in all bean archives in application classpath • http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/beans_1_0.xsd * Picture source Norman Richards
- 19. Types of CDI Injection • Field Injection • Parameter Injection – Observer, producer & disposer methods – Initializer methods @ConversationScoped public class Order { @Inject @Selected Product product; //field injection @Inject //Initializer method void setProduct(@Selected Product product) { this.product = product; } }
- 20. Bean Definition Bean Type Qualifier Scope EL Name Interceptors Implementation
- 21. Bean Type: Set of Java Types a Bean Provides public class BookShop extends Business implements Shop<Book>{ ... } • Client visible Bean types – BookShop, Business, Shop<Book>, Object. @Stateful public class BookShopBean extends Business implements BookShop, Auditable { ... } • Bean types – BookShop, Auditable , Object • Restricted using the @Typed annotation – @Typed(Shop.class) public class BookShop
- 22. Qualifiers Distinguish between beans of the same Type @ASynchronous class AsynchronousPaymentProcessor implements PaymentProcessor { ... } @Synchronous class SynchronousPaymentProcessor implements PaymentProcessor { ... } //Qualifier type @Qualifier @Target({TYPE, METHOD, PARAMETER, FIELD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Synchronous{} Specifying qualifiers on an injected bean aka Client • @Inject @Synchronous PaymentProcessor paymentProcessor
- 23. Qualifiers • Bean can define multiple qualifier types – Injection Point only needs enough qualifiers to uniquely identify a bean • Every bean – Built-in qualifier @Any – Default qualifier @Default when one is not explicitly declared • Producer methods and fields can also use qualifiers @Produces @Asynchronous public PaymentProcessor createAsynchronousProcessor() { return new AsynchronousPaymentProcessor(); } • Qualifiers with members @Target({FIELD, PARAMETER}) @Retention(RUNTIME) @Qualifier public @interface Currency { public String code(); } // client @Inject @Currency(code=“USD”) PaymentProcessor processor;
- 24. Scope: Lifecycle & Visibility of Instances • Scoped Objects exist a lifecycle context – Each bean aka contextual instance is a singleton in that context – Contextual instance of the bean shared by all objects that execute in the same context // Session scoped bean shared by all requests // that execute in the context of that session public @SessionScoped class ShoppingCart implements Serializable { ... } @Produces @RequestScoped @Named("orders") List<Order> getOrderSearchResults() { ... } @ConversationScoped public class Order { ... } @Produces @SessionScoped User getCurrentUser() { ... }
- 25. Scope: Lifecycle & Visibility of Instances • Normal Scopes – @RequestScoped DTO/Models, JSF Backing beans – @ConversationScoped Multi-step workflow, Shopping Cart – @SessionScoped User login credentials – @ApplicationScoped Data shared by entire app, Cache • Pseudo scope – @Dependent (default scope) makes sense for majority • Bound to the lifecycle of the object they were injected • Qualifier – @New (new instance will be created) • Not bound to the declared scope • Has had DI performed • Custom scopes provided by Extensions – OpenWebBeans provides @ViewScoped through the Jsf2ScopesExtension
- 26. EL Name: Lookup beans in Unified EL • Binding components to JSF Views Specified using the @Named annotation public @SessionScoped @Named("cart“) class ShoppingCart implements Serializable { ... } Now we can easily use the bean in any JSF or JSP page <h:dataTable value="#{cart.lineItems}" var="item"> ... </h:dataTable> • Container derives default name in absence of @Named – Unqualified short class name of the bean class • @Named is a built-in Qualifier
- 27. Interceptors • Separate cross-cutting concerns from business logic • Associate Interceptors to managed beans using Interceptor Bindings @Inherited @InterceptorBinding //Interceptor Binding Type definition @Target({TYPE, METHOD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Transactional {} //Declaring Interceptor Bindings of an Interceptor @Transactional @javax.interceptor.Interceptor public class TransactionInterceptor { @AroundInvoke public Object manageTransaction(InvocationContext ctx) throws Exception { ... } } //Binding Interceptor to Bean @Transactional public class ShoppingCart { ... } public class ShoppingCart { @Transactional public void placeOrder() { ... } }
- 28. Interceptors • Enabled manually in the beans.xml • Order defined in beans.xml • @Dependent object of the object it intercepts <beans> <interceptors> <class>org.mycompany.TransactionInterceptor</class> <class>org.mycompany.LoggingInterceptor</class> </interceptors> </beans>
- 29. Implementation & Design Patterns • Bean Implementation provided by – Developer … Java class – Container … Java EE env. Resource beans • Contextual Singleton • All Normal scoped beans are proxied – Contextual Reference implies a proxy for a contextual instance • Dynamic Proxies – Passivation of contextual instances – Scope Management • Narrower scope injected into a wider scope • Chaining of Dynamic Proxies – Interceptor and Decorator chaining
- 31. Alternatives • Deploy time selection of bean implementation • Alternate implementation of bean – Explicitly enabled in the beans.xml – Overrides the original bean @Alternative // annotate bean class, producer method or field @Specializes public class MockOrder extends Order { ... // alternative implementation } <beans> <alternatives> <class>org.example.MockOrder</class> </alternatives> </beans> • @Specializes – Alternate inherits the metadata (name, qualifiers ) etc of the parent
- 32. Stereotypes • Meta-annotation that bundles multiple annotations • Stereotype bundles – Scope – Interceptor Bindings – @Named – @Alternative • Bean annotated with a stereotype inherits all annotations of the stereotype @RequestScoped @Secure @Transactional @Named @Stereotype @Target(TYPE) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Action {} • Built-in Stereotypes – @Model – @Decorator – @Interceptor • @Alternative applied to a stereotype – ALL beans with that stereotype are enabled/disabled as a group
- 33. Producers • Application control of bean instance creation & destruction • Producer Fields public class Shop { @Produces @ApplicationScoped @Catalog @Named("catalog") List<Product> products = ....; } • Producer Methods public class Shop { @Produces @ApplicationScoped @Catalog @Named("catalog") List<Product> getProducts(CatalogID cID) { ... } } • Disposer Methods – Customized cleanup of object returned by a producer method public class Shop { public void close(@Disposes @Catalog List<Product> products) { products.clear(); } }
- 34. Injecting Java EE Resources • When injecting EJBs – Use @Inject to get Contextual Injection – Use @EJB ONLY for remote session beans • Define producers making EE types available for injection… non contextual injection @Produces @WebServiceRef(lookup="java:app/service/PaymentService") PaymentService paymentService; @Produces @PersistenceContext(unitName="CustomerDatabase") @CustomerDatabase EntityManager customerDatabasePersistenceContext; • Consume the Injected types in other CDI Beans @Inject @CustomerDatabase EntityManager myEntityManager @Inject PaymentService myPaymentService
- 35. Decorators • Implements one or more bean types – Can be abstract – Implements the interface it is decorating • Extend bean types with function specific to that type • Called after interceptors • Explicitly enabled in the beans.xml public interface Htmlable { String toHtml(); } //interface public class HtmlDate extends Date implements Htmlable { public String toHtml() { //date class that knows its HTML representation return toString(); } } @Decorator public class StrongDecorator implements Htmlable { @Inject @Delegate @Any private Htmlable html; public String toHtml() { //decorator that puts the HTML inside <strong> tags return "<strong>" + html.toHtml() + "</strong>"; } }
- 36. Events: Observer Pattern // Event is a POJO public class MyEvent { String data; Date eventTime; .... } // Event<MyEvent> is injected automatically by the container @Stateless @Named (“producer”) public class EventProducer { @Inject @My Event<MyEvent> event; //@My is a Qualifier public void doSomething() { event.fire(new MyEvent()); } } // Declare method that takes a parameter with @Observes annotation @Stateless // Transactional, Conditional observer public class EventConsumer { public void afterMyEvent( @Observes(during=AFTER_SUCCESS receive=IF_EXISTS) @My MyEvent event) { // .. Do something with MyEvent } } <h:form> // Fire the event from a JSF 2.0 Page <h:commandButton value="Fire!" action="#{producer.doSomething}"/> </h:form>
- 37. CDI Extensions • Portable – Activated by dropping jars on the application classpath – Loaded by the java.util.ServiceLoader • Service provider of the service javax.enterprise.inject.spi.Extension declared in META-INF/services • Code to javax.enterprise.inject.spi .* interfaces • Integrate with container through container lifecycle events by – Providing its own beans, interceptors and decorators – Injecting dependencies into its own objects – Providing a context implementation for a custom scope – Augmenting or overriding the annotation-based metadata with other source
- 40. Apache Open Web Beans • 1.0.0 release … October 2010 – http://www.apache.org/dist/openwebbeans/1.0.0/ • Apache License v2 • Running in production web sites • 14 Committers (Looking for more ) • Active developer mailing list • Well defined hook points for integration with JEE containers • Works in Java SE & Java EE – Container agnostic • Consumers – Servlet Containers • Jetty • Apache Tomcat 6, 7 – Apache Open EJB – Apache Geronimo – WebSphere Application Server 8 • Now in beta, Developer license is FREE – WebSphere Community Edition
- 41. Apache Open Web Beans Getting Started Ensure Subversion and Maven binaries are on the PATH svn co http://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/openwebbeans/trunk openwebbeans mvn package Install Eclipse plugins for maven and subversion http://m2eclipse.sonatype.org/sites/m2e http://subclipse.tigris.org/update_1.6.x Eclipse File Import Existing Maven Projects Samples Downloaded /samples/conversation-sample /samples/ejb-sample /samples/ejb-telephone /samples/guess /samples/jms-sample /samples/jsf2sample /samples/reservation /samples/standalone-sample /samples/tomcat7-sample Running samples New m2 Maven Build Base Directory: ${workspace_loc:/reservation} Goals: org.mortbay.jetty:maven-jetty-plugin:6.1.21:run Profiles: jetty Using Apache Open Web Beans with Tomcat http://java.dzone.com/articles/using-apache-openwebbeans Debugging :Using the Jetty plugin inside Eclipse: http://bit.ly/4VeDqV
- 42. Troubleshooting CDI Exception How to Fix AmbiguousResolutionException More than one bean eligible for injection. Add qualifiers or alternatives to @Inject to narrow bean resolution. Disable alternatives. Annotate class with @Typed UnproxyableResolutionException bean type cannot be proxied by the container Ensure that bean types are legal. Check if class is declared final, has final methods or private CTOR with no parameters UnsatisfiedResolutionException No bean eligible for injection Remove qualifiers from injection point or add qualifiers to existing types. Enable alternatives BusyConversationException Rejected request b/c concurrent request is associated with the same conversation context. Before starting a conversation check if one already exists using Conversation.isTransient() NonexistentConversationException Conversation context could not be restored Check if conversation is being propagated with the cid GET request parameter ContextNotActiveException Bean invocation in inactive context Ensure that methods on the injected bean are called in a context that is active as defined by the scope of the bean. ObserverException Exception is thrown while handling event Fix observer method code that throws the exception.
- 43. Future of CDI • Closer integration between EJB and CDI beans • Transactions, Security, Concurrency etc delivered as Interceptors that can be applied to any CDI bean • Popular CDI portable extensions rolled into the core spec.
- 44. CDI/Java EE vs Spring • Similar programming models – Spring AOP vs JEE6 Interceptors & Decorators – @Component vs @Stateless – @Autowired vs @Inject – ApplicationContext vs BeanManager • Spring supports JSR330 style annotations • Spring does NOT provide support for CDI/JSR 299 • SPRING + CDI/JEE6 DON’T MIX – Too much overlap – Support and Migration cost • For start-to-scratch projects CDI is the right choice Spring Framework Java EE 6/ CDI Flexible, best-of-breed, mix-and-match Full package Vendor lock-in Standards based
- 45. Links/References • JSR 299 spec http://bit.ly/cbh2Uj • Weld Reference Implementation http://bit.ly/aLDxUS • Spring to Java EE http://bit.ly/9pxXaQ • WebSphere Application Server 8 Beta http://bit.ly/aKozfM • Apache Open Web Beans dev mailing list http://bit.ly/b8fMLw • Weld Blog http://relation.to/ • CDI Reference card http://bit.ly/7mWtYO • CDI, Weld and the Future of SEAM: http://slidesha.re/9nODL2 • Reza Rahman Articles on CDI – http://bit.ly/aIhCD6 – http://bit.ly/adHGKO – http://bit.ly/d4BHTd – http://bit.ly/dcufcQ – http://bit.ly/d0kO9q
- 46. DEMO
- 48. CDI Portable Extensions Resources • https://cwiki.apache.org/EXTCDI/ • https://cwiki.apache.org/EXTCDI/core-usage.html • http://bit.ly/botJKZ • http://bit.ly/9cVdKg • http://bit.ly/axmKob