Ad
Convolution discrete and continuous time-difference equaion and system properties (1)
- 1. Discrete Time Signals Convolution of Discrete Time Signals Properties of the Systems B.S. Panwar Convolve: It is latin word which means fold over or twisting together
- 3. Properties of Unit Impulse Function f ( t ) ( t ) = f ( 0 ) ( t ) f ( t ) ( t - T ) = f ( T ) ( t - T) Multiplication Properties In this case the amplitude of (t) may be 1 / 2 and its duration may be 2 secs. Making the area to be unity. In this case you will have the pulse of amplitude { f(0) / 2 } and its duration of 2 sec. Since, the pulse is of finite duration, so its response will be affected by the pulse response.
- 4. Sampling Properties of Unit Impulse Sampling Properties = ∫ - ∞ f ( t ) (t) dt ∞ = ∫ - ∞ (t) dt ∞ f ( 0 ) f ( 0 ) = ∫ - ∞ f ( t ) ( t - T) dt ∞ = ∫ - ∞ ( t – T ) dt ∞ f ( T ) f ( T ) When you do sampling, we are going to get the sample value at unique time t = T and it will have the sample value f (T).
- 5. Sampling Property of Discrete Impulse [ n ] = 1 For n = 0 0 For n ≠ 0 [ n - no] = 1 For n = no 0 For n ≠ no x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ] Sample magnitude and location x [ n ] [ n - no ] = x [ no ] [ n - no] Sampling Property
- 6. Interpretation of u[n] and u[ n – k ] n u [ n ] 0 1 2 k u [ - k ] 0-4 -2 The function u [n ] = 1 for n > 0 = 0 for n < 1 The function u [n – k ] = 1 for [n – k ] 0 or n k = 0 for [n – k ] < 0 or n < k u [ - k ] = 1 for (k-n) ≤ 0 or n k now put n= 0 we get 0 k or k 0 = 0 for k > 0 Let us consider the function for n = 0. The function will be u [-k]. Now this function has independent variable as “k” This is signal u [n] delayed by k samples Here independent parameter is n and k is the search parameter
- 7. Interpretation of u[n-k] and u[ – k +n ] Here independent parameter is “n” and “k” is the search parameter So the dependence of discrete time signal x[n[ is seen on “n” the independent parameter, which is the first term in the brackets and “k” is the search parameter. Here u [ n – k ] is seen the signal delayed by “k” samples as shown below. This corresponds to delay of “k “ samples of u [n]. Here u [n – k ] signal is viewed as “k” sampled delayed u[n] signal. n u [ n – k ] 0 1 2 The function u [n ] = 1 for n k = 0 for n < k k n u [ n ] 0 1 2 The function u [n ] = 0 for n < 0 = 1 for n > 1 Interpretation of u[n-k]
- 8. Interpretation of u[n-k] and u[ – k +n ] k u [ - k ] 0-4 -2 u [ - k ] = 1 for or k 0 = 0 for k > 0 Here “k” is the is the independent variable. Here independent parameter is “k” and “n” is the search parameter So the dependence of discrete time signal x[k[ is seen on “k” the independent parameter, which is the first term in the brackets and “n” is the search parameter. Here u [ - k + n ] is seen the signal advanced by “n” samples as shown below. So we first visualize first u [- k] and than visualize u [ - k + n] Interpretation of u[- k + n] k u [ - k + n ] -2 0 The function u [-k + n ] = 1 for k n = 0 for k < n n- 4
- 9. Interpretation of u[n] and u[ n – k ] u [ 1 - k ] = 1 for k 1 ( ( 1 – k ) 0 or 1 k ) = 0 for k > 1 Let us consider the function for n = 1. The function will be u [ 1- k] k u [ 1 - k ] 0-4 -2 1 k u [ n - k ] 0-4 -2 1 For n > 0. That is n is a positive real number u [ n - k ] = 1 for k < n { ( n – k ) 0 or n k or k n} = 0 for k > n k 0-4 -2 1 For n > 0 u [ n - k ] = 1 for k n For n < 0 For n < 0. That is n is a negative real number u [ n - k ] = 1 for k n { ( n – k ) 0 or n k or k n} u [n-k] = 1 for k n
- 10. Discrete Time Signal Linear Combination of Weighted Shifted Unit Impulse x [ n ] [ n +1] = x [ -1 ] [ n +1 ] x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ] x [ n ] [ n - 1 ] = x [ 1 ] [ n - 1 ] x [ n ] [ n -2 ] = x [ 2 ] [ n -2 ] -k ]k-n[]k[x[n]x A discrete signal is linear combination of weighted shifted impulses
- 11. Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution y [ n ] = x [ n ] [ n ] x [ n ] ]n[x]k-n[δ[k]x[n]y n -k That means if we input [n] to the system being characterized by x [n] . Than w get x [ n ] [ n +1] = x [ -1 ] [ n +1 ] = y[-1] x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ] = y[0] x [ n ] [ n - 1 ] = x [ 1 ] [ n - 1 ] = y [1] x [ n ] [ n -2 ] = x [ 2 ] [ n -2 ] = y[2] This uniquely characterizes the system response which is x[n]. This is the response to an impulse. That means the response [n] uniquely characterizes the system.
- 12. Specific Case when x [n] = 1 for n 0 ]n[u]k-n[δ[n]y 0k y [ n ] = [ n ] * x [n] = u [n] y [ n ] = x [ n ] [ n ] x [ n ] That means, if I want to know about the system. I start an impulse from [ n + k ], That means k starts from - and varies up to infinity. In this process I can now about the system. Let us assume x [ n ] = u [n]. In this case x [k] = 1 for k 0. So the expression we will get is: ]n[x]k-n[δ[k]x[n]y n -k If x [ n] =1 for n 0 than That means if we input [n] to
- 13. y [ n ] [ n ] h [ n ] ]n[h]k-n[δ[k]h[n]y n -k Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution y [ n ]x [ n ] h [ n ] n -k k n][h[k]x[n]y This implies that output of the system for an input x [ n ] will be superposition of the scaled version of delayed shifted impulses [ n – k ]. Let the response for [n- k] is hk [ n ]
- 14. Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution n -k k n][h[k]x[n]y Let h0[n] is the response to [n] 0 1 1 ho [ n ] n2 Than h-1[n] is the response to [n+1]which is the response for unit advanced impulse. So the response h-1[n] will be unit advanced response as shown 1 1 h-1 [ n ] n0 1 0 2 1 h2 [ n ] n 3 4 1 Let h1[n] is the response to [n-1]which is the response for unit delayed impulse. So the response h1[n] will be unit delayed response of ho[n] as shown 3 0 1 1 h1 [ n ] n2 Identically h2[n] is the response to [n-2],which is the response for two unit delayed impulse. So the response h2[n] will be two unit delayed response of ho[n] as shown h-1[n], h0[n], h1[n], h2[n] Is the response to [n = 1], [n], [n-1] and identified as hk[n] than y [n] can be written as:
- 15. Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution n -k k n][h[k]x[n]y In general h-1[n], ho[n], h1[n] and so on are the responses for [n +1], [n ] [n -1]. That means the most general form defining hk[n] is the responses for an input [n-k]. These responses may not be same as the time shifted version of h0[n] (if the system is not LTI), for the leading or delaying behaviours. But the system is considered to be time invariant. Therefore, hk[n] are the time shifted version of h [n] which are obtained for the input [ n – k ]. Therefore, these will be h [ n – k] as shown in the figure of earlier slide.
- 16. Concept of Discrete Time convolution n0 1 x [ n ]0.5 2.0 n0 1 2 h [ n ] -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] y[n] = 0.5 h[n] + 2 h [n-1] When the input x[n] is applied we get the output x[0] h[n]. Than we get the input x[1]. This is the way sequence is going to flow in. This is implied that we will get the response h[n] delayed by unit pulse. In this case we have taken the input x[- k] This will e multiplied by h [n-1]. That is x[1] h [n-1]. y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] Physically it means that input will be x[o] than x[1] First sample no. at n=0 Last sample no at n=3 Duration of convolved output = (2+3) – 1 = 4 1.0 n0 1 2 y[ n ] 0.5 2.5 2.5 2..0 -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y Let us find the response for x [ n ] which has only two samples
- 17. Discrete Time Convolution: Concept 0 1 0. 5 2x [ k ] k 1]-n[h]1[x[n]h[0]x]k-n[h]k[x[n]y 1 0k = 0.5 h [n] + 2 h [n-1] 0 1 1h [ k ] k2 x [ n ] 0 1 1 h [ k ] k2 2 multiplied 0.5 multiplying to h [n] + + 2 multiplying to h [n] after 1 unit delay that is h [n-1] 0.5 multiplied 1 2 1 h [ k -1 ] k30 1 2 2.5 y [ n ] k3 0.5 2.0 So the output starts at 0 and goes up to sample no. 3
- 18. Total no. of Sample in Convolution Output n1 2 x [ n ]0.5 2.0 k 0 1 2 h [ k ] 3 n 0-2 x [-k ] 0.5 2.0 -1 So the no. of samples in the convolved output will be : 5 – 2 + 1= 4 The last sample value in the convolved output is n = xh + h h Here xh and h h are the values in the un-inverted pattern So the no. of samples are: ( xh – xl) + ( h h - hl) + 1 : (N1 – 1)+ (N2 – 1) + 1 = N1 + N2 -1 So the convolved output extends from sample no.: = ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) So the no. of samples are: ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) + 1 The first sample value in the convolved output is n = xl + h l Here xl and h l are the values in the un-inverted pattern
- 20. First and Last Sample Value in the Convolved Output
- 21. Total no. of Sample in Convolution Output n1 2 x [ n ]0.5 2.0 k 0 1 2 h [ k ] 3 n 0-2 x [-k ] 0.5 2.0 -1 So the no. of samples in the convolved output will be : 5 – 2 + 1= 4 The last sample value in the convolved output is n = xh + h h Here xh and h h are the values in the un-inverted pattern So the no. of samples are: ( xh – xl) + ( h h - hl) + 1 : (N1 – 1)+ (N2 – 1) + 1 = N1 + N2 -1 So the convolved output extends from: = ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) So the no. of samples are: ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) + 1 The first sample value in the convolved output is n = xl + h l Here xl and h l are the values in the un-inverted pattern
- 22. Concept of Discrete Time convolution n0 1 x [ n ]0.5 2.0 n0 1 2 h [ n ] -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] y[n] = 0.5 h[n] + 2 h[n-1] When the input x[n] is applied we get the output x[0] h[n]. Than we get the input x[1]. This is the way sequence is going to flow in. This is implied that we will get the response h[n] delayed by unit pulse. In this case we have taken the input x[- k] This will e multiplied by h [n-1]. That is x[1] h [n-1]. y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] Physically it means that input will be x[o] than x[1] First sample no. at n=0 Last sample no at n=3 Duration of convolved output = (2+3) – 1 = 4 1.0 n0 1 2 y[ n ] 0.5 2.5 2.5 2..0 -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
- 23. Discrete Time Convolution: Concept: Alternate way of looking at it -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y The sum can be carried out on the number of samples in x [ n ] 0 1 0. 5 2x [ k ] k Now we can find the convolution for x [k]. That means we take the contribution of 2 samples. x [0] and x[1] 1]-n[h]1[x[n]h[0]x]k-n[h]k[x[n]y 1 0k This implies that we multiply h [n] containing 3 samples by x [0]. This gives h[0], h[1], h[2] all 0.5. Now we multiply h[n-1] one sample shifted version of h[n] by x[1]. This gives h[-1], h[-2] h [-3] all multiplied by 2. So the response extends from n = 0 to n = 3, which is ( N1 + N2 -1) = 0.5 h [n] + 2 h [n-1] 0 1 1 h [ k ] k 2
- 24. 0 1 2 3 x[n] n 1 2 1 -1 0 1 h[n] n 2 2 0 1 2 3 y[n] n-1 4 5 6 2 4 2 2 -2 Convolution of Two Discrete Time Signals The lower starting sample will be sum of lowest sample points of two signals -k k]-n[h[k]x[n]y Commutative property y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] + x[2] h[n-2] + x[3] h[n-3] -k k]-n[x[k]h[n]y This will give the output y [n] as: y[n] = x[n+1] h[-1] + h[1] x [n-1] The highest sample point will be sum of highest sample points of two signals Total no. of samples will be the sum of samples in both the signals -1. That is N1 + N2 -1
- 25. Examples on Discrete Time Convolution
- 26. n h[n] =u [ n ] 0 h [ n ] = u [n] k h [ 0 - k ] 0 k u [ 1 - k ] 0 k u [-1 – k ] 0 n0 1 2 x [ n ] -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y Here h[-k] is the mirror image of h [n]. And h[- 1-k] is the value for n= - 1 and h [+1-k] for n=1 Example Convolved Output for x[n] = n and h[n] = u[n] We see that output is 0 for n < 0 and we get output for n 0. So the summation is; [n]u α-1 α-1 α[n]y 1nn 0k k The output vale will start from zero and for k the value saturates at ( 1 / ( 1 - ) x [ n ] = n Where 0 < < 1 For k and If = 1 /2 than y[n] = 2
- 27. k h [ - k ] 0 k 0-1-2 x [ k ] Convolved Output for x[n] = 2n u[-n] and h[n] = u[n] 0 -k k 2[n]y If we change the variable k = -m. We get the integral from 0 to . This is when we are computing only for n ranging from - to 0 2 1/2)-1( 1 2 1 [n]y 0k k However we need to compute the integral in the entire range of “n” for which we get: n -k k 2[n]y If k we replace k by k = - k n-k k 2 1 [n]y If k we replace k by k + n = m, we get 2 1 2 2 1 [n]y 0m m n 0m n-m 1n 2[n]yor x[k] starts the output at - and h[k] leads the output until . So the output is from - to Now considering the complete output from - to n, where will also tend to infinity The summation taken from - to 0 will show that the output it must saturate at n=0
- 28. n h [ n ] 0 h [ n ] = u [ - n] k h [ -k ] 0 k u [ 1 - k ] 0 k0 1 2 x [ k ] -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y Here h[-k] is the mirror image of h [n]. And h[- 1-k] is the value for n= - 1 and h [+1-k] for n=1 Example Convolved Output for x[n] = n and h[n] = u[-n] We see that output is 0 for n < 0 and we get output for n 0. So the summation is; [n]u α-1 α-1 α[n]y 1nn 0k k The output vale will start from zero and for k the value saturates at ( 1 / ( 1 - ) x [ n ] = n Where 0 < < 1 k0
- 29. Example of Convolved Output x[n] = 1 for 0 n 4 = 0 h[n] = n 0 n 6 = 0 elsewhere -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y The convolved output will be from n=0 to n=10 and the total no. of samples will be: (5+7 ) -1 = 11 Region #1: n < 0 y[n] = 0 n 0 1 2 x [ n ] 3 4 n h [ n ] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 The starting sample will be n=0 The stop sample will be n=10 This is because of the fact that there is no overlap So the convolved output will have 11 samples
- 30. Example Convolved Output where x[n] is of finite duration x[n] = 1 for 0 n 4 = 0 -k ]k-n[h]k[x[n]y In this case x[n-k] will keep moving below h[k] and the complete fill up will be obtained for n = 4. In this region 0 ≤ n ≤ 4. In this region k will also vary from 0 to 4. In this region if n=1, than we summing over n from 0 to 1 for the product of x [ n-k] and h [k]. Region #2: n = 0 to n= 4. That is the region 0 n 4. n 0k k-n α[n]y n 0r r α[n]y α1 α1 [n]y 1n n 0 1 2 x [ n ] 3 4 n h [ n ] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 h[n] = n 0 n 6 = 0 elsewhere If we put n – k = r. For k=0 : n = r and for k =n : r = 0. So the summation on “r” changes from n to 0. Which is same as r changing from 0 n. It is like u[n] * h[n]. Here we will get y[n] for n=0 to n=4
- 31. k h [ k ] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Visualization of Region #3 k x [n -k ] 4 3 2 1 0 This is the where region 2 ends This is where region 3 starts This is the where region 3 stops. Last sample of h[k] still overlaps In this region 4 < n ≤ 6. That is the signal h [k] remains completely filled only for two values of n, which are n=5 and 6. But during this period the summation for each value of n is to be carried for all values of “k”, which varies from 0 to 4. In region 3 In this region 4 < n ≤ 6. The summation integral will be for k= 0 to k = 4. and the output will be for n=5, and 6 4 0k k-n α[n]y Here we get output for y[n] for n =5 and 6 4 0k k-n αα[n]y )/1(-1 )/1(-1 α[n]y 5 n k x [n -k ] 4 3 2 1 0 k x [n -k ] 4 3 2 1 0
- 32. k h [ k ] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Visualization of Region #4 region 3 stops In this region 6 < n ≤ 10. That is the signal x [n- k] starts coming out. So far y[n] has reached at y[6], making the output as 7 samples In region 4: This is the region we are considering n > 6. Now for n-6 ≤ k, the fist sample will come out for n = 7 and the output will be obtained until all sample get out that is upto k+4. So the value of k will vary from : n-6 ≤ k ≤ 4 4 6-nk k-n α[n]y Region 5 we get when n > 10 than the output is zero n-10 0r 6r- α[n]y )/1(-1 )/1(-1 α[n]y n-11 6 k x [n -k ] 4 3 2 1 0 Now if we put : k – (n – 6 ) = r The limits of summation are from r=0 to r= 10 – n . And n – k = - r + 6 n-10 0r r-6 αα
- 33. Correlation / Correlation Between Two Signals (continuous time)
- 34. f1() f2() T ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( ) d Definition of Correlation Generally Followed The above integral show that there is no similarity between two signals. For finding similarity we shift the waveform f2() towards left by time “t”. This shift is towards left which is negative axis. So we take the value of “t” to be negative and integrate over “ “ . This is contradictory to the convention of giving the leading shift to f2(t). In this case we perform the integral over for a given shift of time “t”, which provides the value of integral ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( - t) d 12 ( t ) = 12 (t) is defined as: f1() is stationary we advance f2() by towards left by different “t” and compute the integral. f2() T t The sign on the shift in “t” is determined by the direction of the axis (rather than delay or lead behaviour of signal) in this case moving towards left is –ve axis. Here the search parameter is “t”
- 35. Example of Correlation of two pulses f1 () 1 0 1 f2 () 1 2 3 Correlation This is in reference with the starting point of the signal f2()The term “t“ is –ve if we move along the -ve direction of X- axis. This automatically decreases the delay. t1 32 12 ( t ) This is same as: ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( - t) d 12 ( t ) = ∫-∞ ∞ f1 (x+t ) f2 (x) d x12 ( t ) = ∫-∞ ∞ f1 (+t ) f2 () d 12 ( t ) = The variable x can be replaced by This states that signal f2() can be kept constant and we can move f1() towards right side, which is positive direction of x- axis. Here also for every shift the integration is taking place on for different values of “t“ .
- 36. Correlation of a Returned Echo to a Radar ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( - t ) d12 ( t ) = That means we move f2( ) towards left for different values of time t , called as the scanning parameter. Since we are moving along the –ve direction of x-axis the value of t is taken to be negative. In this process we get the integral value for a given shift of time “t”
- 37. Cross-correlation Functions Similarity ∞ ∫-∞ f1 ( t + ) f1 ( + T) d 11 ( t ) = ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( - t) d12 ( t ) = ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( t + ) f2 ( ) d12 ( t ) = ∞ ∫-∞ f1 ( t + k –T) f1 ( k) dk11 ( t ) = Replace + T = k = 11 ( t - T) If f2(t) = f1 (t + T)
- 38. Signal Comparison : Correlation ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( - t ) d12 ( t ) = dthxtncorrelatioCross dthhtncorrelatioAuto xh hh )()()( )()()(
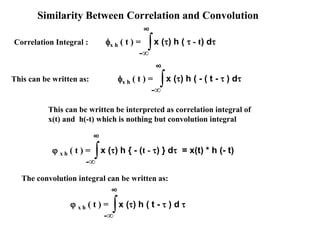
- 39. Similarity Between Correlation and Convolution Correlation Integral : ∫-∞ ∞ x () h ( - t) dx h ( t ) = ∞ ∫-∞ x () h { - (t - ) } d = x(t) * h (- t) x h ( t ) = ∞ ∫-∞ x () h ( t - ) d x h ( t ) = This can be written as: ∞ ∫-∞ x () h ( - ( t - ) dx h ( t ) = This can be written be interpreted as correlation integral of x(t) and h(-t) which is nothing but convolution integral The convolution integral can be written as:
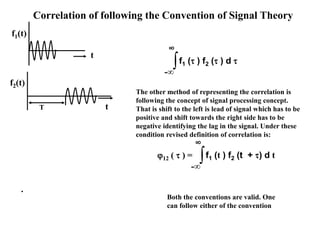
- 40. t f1(t) t f2(t) T ∫-∞ ∞ f1 ( ) f2 ( ) d Correlation of following the Convention of Signal Theory The other method of representing the correlation is following the concept of signal processing concept. That is shift to the left is lead of signal which has to be positive and shift towards the right side has to be negative identifying the lag in the signal. Under these condition revised definition of correlation is: ∫-∞ ∞ f1 (t ) f2 (t + ) d t12 ( ) = . Both the conventions are valid. One can follow either of the convention
- 42. Defining a Pulse for Zero Order Hold If we multiply by T(t) to any signal x(t) and it is a sample and hold circuit. Than it will hold the value of x(t) at x(0) for a duration t +T, and it will also reduce the sample value by 1 /T. Therefore to preserve the original sample value at t = 0, we need to multiply the x(t) by the value T. So t T(t) 1/T T T(t) = 1/T for 0 t T Otherwise0 We are defining the pulse as: x / (0) = x ( 0 ) T ( t ) T x / (1) = x ( T ) T ( t –T ) T x / (2) = x ( 2T ) T ( t -2T ) T TkT)-(t(kT)x(t)x -k T / We can approach to x ( t ) from x / (t) in the limiting case T tends to zero x / (-1) = x ( -T ) T ( t + T ) T
- 43. t T(t) 1/T T TkT)-(t(kT)x(t)x -k T / When T 0 than we are approaching very close to the original signal. The physical interpretation is that we are passing the signal through a wide band bandwidth. So we will get the original signal. Representation of continuous time signal in terms of Impulse Zero Order Hold (t)xTkT)-(t(kT)x(t)x -k T0Tlim / t x ( t ) T 2T0 3T-T Further as T 0 than the function x /(t) x(t) and summation approaches to integral
- 44. Defining a Pulse for Zero Order Hold Originally the pulse was T (-), which is shifted towards right side by “t” such that the centre of pulse is integer multiple of T. That is = mT, where m is an integer T( - ) 1/T - T T(t - ) 1/T - T tt –T mT Shifted towards right side by time “t” T() 1/T T T(t) = 1/T for 0 t 1/T Otherwise0 We are defining the pulse as: lim 𝑻 →𝟎 𝜹 𝑻 𝒕 → 𝜹 (𝒕)
- 45. Sampling the signal x ( ) at T (t - ) T(t - ) 1/T tt –T mT x ( )T(t - ) Shift in T ( ) by “t” Which is sample value of x ( ) at t = mT. Because the pulse duration is T and the amplitude is ( 1 /T). d)-t()(x(t)x - Under this condition we value of x(t) corresponding to m = k. Other values are zero. That means we get the value of x(t) for t = (t)x TkT)-(t(kT)x(t)x -k T0Tlim / The shaded region has the area: x (mT) x T x ( 1 / T) = x (mT) The area under the curve x ( ) T(t - ) will also approach to x( m T) is T 0. In the limiting case as T 0 the function
- 46. Sampling the signal x ( ) at T (t - ) T(t - ) 1/T - T tt –T mT x ( )T(t - ) Shift in T ( ) by “t” The shaded region has the area: x (mT) x T x ( 1 / T) = x (mT) x (mT). Which is sample value of x ( ) at t= mT. Because the pulse duration is T and the amplitude is ( 1 /T). The area under the curve x ( ) T(t - ) will also approach to x( m T) is T 0. d)-t()(x(t)x - While finding the area if we consider linear variation from t – T ≤ ≤ t, We get the sampled value of x( ) ( t--T/2). This the value at the centre. This value approaches to x(mT). For this value of x() is x (mT) when it is sampled by a pulse T(t-mT). Further the pulse T(t) also becomes an impulse if T 0 (t)x TkT)-(t(kT)x(t)x -k T0Tlim /
- 47. Continuous Time Unit Step and Unit Impulse Function t u ( t ) 1 h ( t ) = u(t) Ideal Unit Step Function t 0 aτ- τde(t)y x ( ) e – a t u(t) x( t ) = e – a t u(t) u ( - ) 1 Region #1 The output will increase as a function of t from 0 < ≤ t As “t” tends to infinity y(t) = ( 1 /a) Region #1 t 0τ τa- |)e() a 1 -((t)y )e-1() a 1 ((t)y ta- For all values of t the y(t) = ( 1 /a) ( 1 – e –a t ) u(t)
- 48. Continuous Time Unit Step and Unit Impulse Function t u ( t ) 1 h ( t ) = u(t) Ideal Unit Step Function t aτ τde(t)y x( t ) = e a t u( -t) u ( - ) 1 Region #1 The output will increase as a function of t from - < ≤ t Region #1 t τ τa |)e() a 1 ((t)y t x( t ) 1 e a t u ( -t) y (t ) = ( 1 /a) e at for t ≤ 0 Region #2 The output will remain constant as function of t from < 0 ≤ t Region #2 y ( t ) = 1 /a
- 49. Sampling the signal x ( ) at T (t - ) d)-t()(x(t)x - This represents the convolution of x(t) with impulse (t) In case x(t) is u(t) than we get the integral as: d)-t()(u(t)u - d)-t((t)u 0
- 52. System Without Memory A system is said to be memoryless, if its output at any instant of time Dependents only the value of input at that instant of time. That is y[n]only depends on the input x[n]. This is only possible when h [n] exists only at n=0 otherwise it is zero. Such an impulse response could only be unit step function [n]. The amplitude of [n] may not be unity. It may have the arbitrary value k. x [ n ] K [ n ] y [ n ] = k x [ n ] x [ n ] K h [ n ] y [ n ] = k ( x [ n ] * h[n] )
- 53. System Without Memory y [ n ]x [ n ] K [ n ] y [ n ] = k x [ n ] ]k-n[[k]k x[n]y -k If k=1 than it becomes an identity system d)-t(h)(xx(t) -
- 54. System Without Memory A system is said to be memoryless, if its output at any instant of time Dependents only the value of input at that instant of time. That is y[n] only depends on the input x[n]. Such a system is called as identity system. Because the input is same as output This is being visualized as if the input is [n] and system is characterized by The impulse response x [n]. For such a system the output will be x [ n ] y [ n ]x [ n ] h [ n ] y [ n ] = x [ n ] * h [n] This is only possible when the input x [n] = [n] y [ n ] = h [ n ] * x [n] y [ n ]h [ n ] x [ n ] It is analogus to
- 55. Identity Systems That means h [ n ] = [n] For an identity system h [ n ] = [ n ] n -k ]k-n[[k]x[n]x And - τd)τ-t(δ)τ(x(t)x y [ n ] = [ n ] * x [n] y [ n ] [ n ] x [ n ]
- 56. System With Memory 1-n -k [n]x[n]x[n]y The summation term gives the accumulated sum to which the Current value x [n] is added Discrete Time: An accumulator In continuous time: Capacitor Charging An example of a system with the memory is charging of capacitor. The capacitor charges to the previous value. t - τd)τ(x C 1 (t)y The charging of a capacitor by an Input current x(t) keeps charging The capacitor to a voltage y(t) An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds the current value to the previous values n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y
- 57. System With Memory y [n] = x [n -1] Here the value of y [n] at any instant n = no depends on the earlier value of x [n]. System With memory A system with memory stores the information about the value of input value other than current time. For example a delay must retain the previous . Here x[n] already exists and we give a unit delay than it becomes y [n] y [n] = x [n -1]x [n] Here y [n] is response to the signal which was existing. Therefore the system is causal y [n] = x [n-1] DELAY x [n] Delay
- 58. Invertibility / Inverse of Systems
- 59. Invertible System / Inverse System A system is invertible: Than an inverse system exists, which when cascaded with the original system yields the output, which is same as the input y [n] = 0 It is a noninvertible system because the output is zero for all inputs y (t) = x2 (t) is a noninvertible system, because we can not determine determine the sign from the knowledge of output signal
- 60. Invertibility and Inverse System for Continuous Time A system is said to be INVERTIBLE if distinct inputs lead to distinct output If a system is invertible than a inverse system exists that, when cascade With the original system yields the output, which is basically input signal Continuous Time System y(t) = 2 x(t) x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t ) w ( t ) = x ( t )2 1w (t) = y (t) system x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t ) w ( t ) = x ( t )Inverse system
- 61. Invertibility and Inverse System: Discrete time If a system is invertible than a inverse system exists that, when cascade With the original system yields the output, which is basically input signal Discrete Time System x [ n ] y [ n ] w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ] w [n] [k]x[n]y n -k [n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y 1-n 0k n -k [n]x]1-n[y[n]y w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ]
- 63. Three basic Operators to Perform a Function in Discrete Time [n]xb]1-n[ya[n]y y [n] a y [n] a multiplier y [n] y [n -1]Delay Delay +y [n] y [n-1] y[n] + y [n-1] Summation The delay element can be considered as a simple RS flip-flop
- 64. Discrete time Accumulator If a system is invertible than a inverse system exists that, when cascade With the original system yields the output, which is basically input signal Discrete Time System x [ n ] y [ n ] [k]x[n]y n -k [n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y 1-n 0k n -k [n]x]1-n[y[n]y First system can be obtained by passing x[n] through u[n] and its system representation is shown
- 65. System Implementation of Discrete Time Accumulator Convolution of x[n] with h[n] Discrete Time: An accumulator 1-n -k [n]x[n]x[n]y n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y So this can be expressed as : -k ]k-n[u[n]x[n]y n -k ]k-n[u[n]x[n]y h[n] = u [n] x [n] y [n] y [n] = x[n] * u[n] In accumulator we add present value in the previous value. y[n] = y [n-1] + x[n]
- 66. System Implementation of Discrete Time Accumulator Discrete Time Accumulator System n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y -k ]k-n[u[n]x[n]y h[n] = u [n] x [n] y [n] y [n] = x[n] * u[n] Unit Delay x [n] y [n] y [n - 1] Integrator should have feed-back. That is what is reflected
- 67. Impulse Response of Discrete Time Accumulator Unit Delay x [n] y [n] y [n - 1] If we assume system to be causal. That is y[n-1]=0. And the input is [n]. Than the output will be u [n] y [n] = y [ n – 1 ] + x [n] Input is [n]: Output is u[n]: If we multiply the feed-back by “a” after the delay. The output will be: 1 + a + a2+ ….. The output is: y [ n ] = an u[n] The system has recursion. Therefore, we called as the recursive system. Further the impulse response is infinite. So we call it as infinite Impulse Response System
- 68. Recursive Response : I I R : all Pole System The output depends on present and past values of input x [ n ] b0 D -a1 -a2 D -ak D y [ n ] The difference equation is: y [n] = b0 x [ n ] - a1 y [ n – 1 ] - a2 y [ n – 2 ] - ….. - ak y [ n – k] N 1k 0k ]n[xb]kn[ya]n[y y [n] = y [ n – 1 ] + x [n] If we consider that coefficients ak and b0 are normalized value w.r.t. to a0. Than the above equation can be written as: N 0k 0k ]n[xb]kn[ya
- 70. Invertibility and Inverse System: Discrete time The system is invertible if the output of accumulator is fed through a first order differentiator. Here the second block is the differentiator Discrete Time System x [ n ] y [ n ] w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ] w [n] [k]x[n]y n -k [n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y 1-n k n k 1]-[ny]n[y]n[x
- 71. Impulse response of a differentiator and invertible System The impulse response of the differentiator is: [n] - [ n – 1] Discrete Time Differentiator x [ n ] y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ] y [n] Impulse response of an integrator and differentiator u [n] * { [n] - [ n – 1]} = u [n] [n] – u [n-1 ] [ n – 1]} u [n] - u [n-1 ] = [ n ] This establishes the invertiability of the system
- 72. System Implementation of Differentiator Discrete Time Differentiator x [ n ] y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ] y [n] y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ] y [n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ] Unit Delay x [n] The impulse response such as system is : [ n ] - [ n -1]. Since it is a feed-forward So the response will be of finite duration. These are non-recursive systems
- 73. Differentiator: Non recursive System y[n] y [n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ] D x [n] The impulse response such as system is : [ n ] - [ n -1]. Since it is a feed-forward .So the response will be of finite duration. These are non-recursive systems D D bo -b1 -bk -b2 y [n] = box [n] + b1 x [ n – 1 ]+ b2 x [ n – 1 ]+…… bk x [ n – k ] ]kn[xb[n]y k M 0k
- 74. System With Memory: Discrete Time Discrete Time: An accumulator An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds the current value to the previous values n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y This is feed-forward so it is no-recursive type of system Difference Equation y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1] This equation has the feed-back. This reflects the recursive nature
- 75. Impulse Response of a Reversible System Discrete Time Accumulator n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y Verification of Associative Property Differentiator y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1] Unit Delay x [n] y [n] y [n - 1] h[n] = u [n] Unit Delay x [n] h[n] = [n] - [n-1] y[n] = u [ n ] * { [n] - [n-1] } y[n] = { [n] - [n-1] } * u [n]
- 76. General Form of a Discrete Time System It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator n -k [n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator As such both are called as first order difference equation D x [n] b0 - b1 y [n] D - a1 y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1] y1 [n] Differentiator Integrator y [n] = y1 [n-1] – a1 y[n-1]
- 77. General Form of a Discrete Time System It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator n -k [n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator As such both are called as first order difference equation D x [n] b0 - b1 y [n] D - a1 y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1] y1 [n] Differentiator Integrator y [n] = y1 [n-1] – a1 y[n-1]
- 78. General Form of a Discrete Time System y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = y1 [n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1] If we consider all the coefficients were initially normalized to some constant coefficient a0. That means a1 was actually a1/a0, b0 was b0/a0 andb1 was b1 / a0 M 0k k N 0k k ]k-n[yb]k-n[ya D x [n] b0 - b1 y [n] D - a1 y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1] y1 [n] Differentiator Integrator y [n] = y1 [n] – a1 y[n-1]
- 79. Inverse System for Continuous and Discrete Time A system is said to be INVERTIBLE if the complete system functions As an Identity system h1 (t) x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t ) w ( t ) = x ( t )h2 ( t) h1 (t) * h2 ( t ) = (t) h1 [n] x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ] w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ] h1 [ n ] * h2 [ n ] = [ n ]
- 80. Inverse System for Continuous Time A system is said to be INVERTIBLE if the complete system functions As an Identity system h1 (t) x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t ) w ( t ) = x ( t )h2 ( t) y ( t ) = x (t) * h1(t) = x ( t – to ) That means y (t) is nothing but delay x (t) by time t0. h1 (t) x ( t ) y ( t ) = x ( t – t0) y ( t ) = x ( t – t0) If y (t) = x (t) than it is a memoryless system and the impulse response Has to be (t). Now x ( t - t0 ) is x(t) shifted by t0. That means the impulse response is ( t - t0 ), this is because that the output now exists at t = to
- 81. Inverse System for Continuous Time A system is said to be INVERTIBLE if the complete system functions As an Identity system h1 (t) x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t ) w ( t ) = x ( t )h2 ( t) y ( t ) = x ( t – to ) h ( t ) = ( t – to) If t – to > 0 than the output at time “t” is what the input is at time t - to To get w( t ) = x( t ), we should advance the response y (t) by time to That means the impulse response h1(t) = ( t + to ) h1( t ) * h2 ( t ) = ( t – to ) * ( t + to ) = ( t )
- 82. Inverse System in Discrete Time: Identity System h1 [n] x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ] w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ] y [ n ] = x [ n – no ] h1 [ n ] = [ n – no ] w [ n ] = y [ n+ no ] h2 [ n ] = [ n + no ] k [ n - k + no ] 0 no -k oo ]nk-[n]-n[k[n]h k [ k – no ] no0 h1 [k] k [ k + no ] no0 h2 [k]
- 83. Inverse System in Discrete Time: Identity System h1 [n] x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ] w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ] h [ n ] = h1 [ n ] * h2 [ n ] = [ n - no] * [ n + no] = [n] y [ n ] = x [ n – no ] h1 [ n ] = [ n – no ] w [ n ] = y [ n+ no ] h2 [ n ] = [ n + no ] k [ k – no ] no0 k [ n - k + no ] 0 no -k oo ]nk-[n]-n[k[n]h
- 84. Stability of the System
- 85. Stability for LTI System : Discrete Time A system is said to be stable if bounded input has the bounded output Let the input x [ n ] is a bounded in magnitude. | x ( t ) | < B for all values of n |τd)τ-t(x)τ(h||)t(y| - τd|)τ-t(x||)τ(h||)t(y| - Since, | x ( t ) | < B for all values of t τd|)τ(h|B|)t(y| - That means for a system to be stable τd|)τ(h| -
- 86. Stability for LTI System: Continuous Time A system is said to be stable if bounded input has the bounded output Let the input x [ n ] is a bounded in magnitude. | x [ n ] | < B for all values of n |]k-[nx||[k]h||]k-[nx[k]h||[n]y| -k-k -k |[k]h|B|[n]y| Since | x [ n – k ] | < B for all values of k and n This requires that the impulse response is absolutely summable |[k]h| -k for all values of n We take the magnitude because the swing +ve and negative values may tend to infinity but still the average value may be zero. This summation may be zero
- 88. Time Invariance System A system is said to be time invariant if the behavior and characteristic of the system are fixed over time. A system is said to be time invariant if the time shift in the Input signal results in time shift in the output signal In a continuous time system if y (t) is the output for an input x (t) Than y ( t – t0 ) is the output when input is x ( t – t 0 ) For a discrete time system if y [n] is the output for an input x [n] Than y [ n – n0 ) is the output when input is x [ n – n 0 ) If we take a R, C circuit and the values of the elements do not change with time (characteristic remains fixed with time). It is a time invariant system. If the values of the elements changes with time than it is time variant system.
- 89. Checking a System for Time Invariance Let us consider a system y ( t ) = sin [ x1 ( t ) ] Let x1 (t) is the input at any time t y1(t) = sin [ x1(t) ] Now if we look at the response delayed time t0. That is for the input x1( t - t0 ) x2 ( t ) = x1 ( t – t0) Y2 ( t ) = sin [ x1 ( t – t 0 ) Now if we find y1 (t) at time = t - t0 y1( t – t0 ) = sin [ x1( t – t0) ] So the system is time invariant The time invariance should be checked for any input and any time delay.
- 90. Some Useful Signal Operation : Time Scaling t f1 (t) T1 2 T2 2 Case (1) f1 ( t) = g (2 t) For a > 1 there is A time compression. In the present case a = 2 t f2 (t) 2T1 2T2 Case (2) For a < 1 there is A time expansion. In the present case a = 0.5 Original Signal g ( t ) t g (t) T1 T2 Signal f ( t ) = g ( a t ) g (a t ) t = T /a = g ( T )
- 91. Checking a System for Time Invariance t x1 (t) 1 - 2 2 y ( t ) = x ( 2 t ) t y1 (t) -1 1 Time compression x2 ( t ) = x1 ( t – 2 ) t x2 (t) 1 4 t y2 (t) 2 y1 ( t ) = x1 ( 2 t ) y2 ( t ) = x1 ( 2 t - 2 ) Since we have delayed x1 ( t ) by 2, we would expect that y1 ( t ) should also be delayed by 2 and output should be: t y2 (t) 1 3 Expected from Time invariant system So the system is not time Invariant Any time shift also leads time compression in output. So it is a time VARIANT SYSTEM
- 93. Causality of a System A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System Output depends on present and past values of input signals. h(t) = 0 for t <0 A typical is charging of a capacitor. The voltage on capacitor Depends on present past and past values of source voltage h [n] = 0 for n <0 For a discrete time system For a continuous system
- 94. Causality of a System for discrete System A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System Output depends on present and past values of input signals. Therefore the criteria of present and past value of x[n] states that for any shift in x[n] the h[n] must shift so: ]k-[nh[k]x[n]y -k n Since h [n] , for n < 0. The above expression can also be written in alternate form by using commutative property ]k-[nh[k]x[n]y 0k h [ n ] = 0 for n < 0
- 95. Causality of a System for Continuous Time System A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System Output depends on present and past values of input signals. Therefore the criteria of present and past value of x ( t ) states that for any shift in x (t) the h ( t ) must shift so: Since h ( t ) , for t < 0. The above expression can also be written in alternate form by using commutative property h (t) = 0 for t < 0 τd)τ-t(h)τ(x)t(y t - τd)τ(h)τ-t(x)t(y t -
- 96. Causality of a System A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System Output depends on present and past values of input signals. The system y [ n ] = x [ n – 1 ] is causal system The system y ( t ) = x ( t – t0 ) is causal System A typical is charging of a capacitor. The voltage on capacitor Depends on present past and past values of source voltage If a signal is defined at t = to. Than we can determine the output at any instant later t > to.
- 97. Causality of a System A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System Output depends on present and past values of input signals. The system y [ n ] = x [ n ] + x [ n + 1 ] is NON causal system The system y ( t ) = x ( t + t0 ) is NON Causal System Any memory less system is Causal system, because it depends Only current value of the input signal
- 98. Checking Causality of a System y [ n ] = x [ - n ] The values at n = n0 for some positive time n0 depends on past values of signal x [ - n0 ]. System seems to be Causal But if n is negative say n = - 4. Than y [ - 4 ] = x [ 4 ]. That means output depends on a future value of input signal. So system is not Causal y ( t ) = x ( t ) cos ( t + 1 ) Here cos ( t + 1) indicates that system is not causal But the output is multiplications of x(t) which defines That the system is casual
- 99. Causality not an Essential Parameter If Time is not Independent Parameter This finds application in meteorological signals, predicting the stock Market. In such cases it is the average value taken over an interval say – M to M and predict the value at some instant of time M Mk M][kx 12M 1 [n]y This can be used to predict the dynamic behavior f the market
- 101. System With Memory: Discrete Time [n]xb]1-n[ya[n]y y [n] a y [n] a multiplier y [n] y [n -1]Delay Delay +y [n] y [n-1] y[n] + y [n-1] Summation The delay element can be considered as a simple RS flip-flop In this the information Q = 1 gets tranf
- 102. System With Memory: Discrete Time Discrete Time: An accumulator An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds the current value to the previous values n -k [n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y This is feed-forward so it is no-recursive type of system Difference Equation y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1] This equation has the feed-back. This reflects the recursive nature
- 103. General Form of a Discrete Time System It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator n -k [n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator As such both are called as first order difference equation y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = b0 x[n] +b1 x[n-1] D x [n] b0 - b1 y1 [n] D - a1 y [n] y1[n] = b0 x[n] + b1 x[n-1] y[n] = y1[n] - a1 y[n-1]
- 104. General Form of a Discrete Time System D x [n] b0 - b1 y [n] D - a1 If we consider all the coefficients were initially normalized to some constant coefficient a0. That means a1 was actually a1/a0, b0 was b0/a0 andb1 was b1 / a0 M 0k k N 0k k ]k-n[yb]k-n[ya y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = b0 x[n] +b1 x[n-1]
- 105. N th Order linear constant Coefficient Difference Equation M 0k k N 0k k ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya M 0k k N 1k k0 ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya[n]ya This equation can be expressed as: }]k-n[ya-]k-n[xb{) a 1 ([n]y N 1k k M 0k k 0 This equation states that for computing the present output value. We need the information of the previous output value. From this we must realize that we need the auxiliary conditions. That is the initial conditions. To compute y [n] we need the information on y [n-1], ……..y [ n – N]
- 106. N th Order linear constant Coefficient Difference Equation M 0k k N 0k k ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya In this equation if we assume that N=0. That means K =0. For this the above equation gets modified as M 0k 0k ]k-n[x)a/b([n]y M 0k k0 ]k-n[xb[n]ya or In this case the output depends on the present and past (previous) values of the input. That means we do not recursively use previously computed values of the output to compute the present value of output
- 107. N th Order linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equation M 0k 0k ]k-n[x)a/b([n]y M 0k ]k-n[xk)h([n]y Now if we compare the above two equations we find that the impulse response of the system is: h [n] = bn / ao for 0 n M 0 otherwise The above equation is convolution sum of the input x [n] with the impulse response ( bn /ao). Since we are not using the previously computed value to compute the present value, therefore we do not need the auxiliary conditions. That is the status of the system whether It is initially at rest.
- 108. PRACTICAL EXAMPLE y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n] Now we want to find the output for x [n] = K [n]. This forces the condition that x [n ] = 0 for n -1. The condition of initial rest implies that y [n] = 0 for n -1 In the process we take the Causal LTI system. The causal system dictates that x [n] = 0 for n < 0. Identically y[n] = 0 for n<0 From the above equation we can y[n] for an input x [n] = K [n] y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 } k
- 109. PRACTICAL EXAMPLE y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n] Now we want to find the output for x [n] = K [n]. This forces the condition that x [n ] = 0 for n -1. The condition of initial rest implies that y [n] = 0 for n -1 In the process we take the Causal LTI system. The causal system dictates that x [n] = 0 for n < 0. Identically y[n] = 0 for n<0 From the above equation we can y[n] for an input x [n] = K [n] y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 } k
- 110. PRACTICAL EXAMPLE y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n] y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 ) k y [2] = ( 1 /2 ) y [1] + x [2] = ( 1 / 2 ) 2 k y [3] = ( 1 /2 ) y [2] + x [3] = ( 1 / 2 ) 3 k So y [n] = ( 1 / 2) n k Since the system is completely characterized by an impulse response The impulse response can be found from putting k=1 So h [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) n u[n]
- 112. Miscellaneous Slides
- 113. Some Mathematical Functions cos ( A + B ) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B cos ( A - B ) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B sin ( A + B ) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B sin ( A - B ) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B sin A sin B = 1 / 2 { cos ( A- B) - cos (A + B) } cos A cos B = 1 / 2 { cos ( A- B) + cos (A + B) } sin A cos B = 1 / 2 { sin ( A+ B)+ sin (A - B) } cos A sin B = 1 / 2 { sin ( A+ B) - sin (A - B) } sin2 = 2sin cos cos2 = cos2 – sin2
- 114. Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equation
- 115. Formation of Difference Equation an Impulse Response Delay x [ n ] y [ n ] a y [ n -1 ] a y [n] = x [ n ] + a y [ n – 1 ] Now let us assume that it is a causal system y [ n ] = for n < 0 The system response for [ n ] is: y [0] = x [ 0 ] + a y [– 1 ] = 1 Since x [ n ] is [ n ] so x [ o ] = 1 and y [ 0 ] =1 y [1] = x [ 1 ] + a y [0] = a y [2] = x [ 2 ] + a y [1] = a2 Or y [n] = x [ n ] + a y [n-1] = an u [n] The impulse response of the system is: a n u [ n ]
- 116. The output depends on present and past values of input Summation x [ n ] y [ n ] b k D D D D b0 b1 b2 X ( z) = ∑ - ∞ ∞ x [n] z - n X/ ( z)= ∑ - ∞ ∞ x [ n - 1 ] z - n X/ ( z)= z – 1 X [ z ] zb)z(Y k- k M ok )z(X)zb..........zbzbb( -k k -2 2 1- 1o )z(X )z(Y k k 2-k 2 1-k 1 k o Z )b..........zbzbzb( Basically it is a all zero filter. It has all the poles lying at z =0. Origin Non Recursive Response : F IR : all Zero System
- 117. Recursive Response : I I R : all Pole System The output depends on present and past values of input y [ n ] Y ( z) )z(X)za..........zaza(1)z(Y -k k -2 2 1- 1 Basically it is a all pole filter. It has all the zeros lying at z =0. Origin Y [ n - 1 ] z – 1 Y ( z) x [ n ] 1 D -a1 -a2 D -ak D y [ n ] The difference equation is: y [n] + a1 y [ n – 1 ] + a2 y [ n – 2 ] + ….. ak y [ n – k] = x [ n ] )za..........zaza(1 1 )z(X )z(Y k- k 2- 2 1- 1
- 118. Time Integration Property Problem 2: Addition of any constant to x (t) does not change the value of f (t). That means for given f (t), x (t) can have many possible solutions. That means we need to find the unique function x (t), which relates uniquely the integral of function f (t). LTI System with The response f (t) Input (t) ∫- ∞ t y ( t ) = f ( ) ( t - ) d = f ( t ) LTI System with the response f (t) Input (t) f ( t ) ∫- ∞ t x (t) = f ( ) d Integrator LTI System with the response f (t) Input (t) ∫- ∞ t x (t) = f ( ) u ( t - ) d Integrator u(t) (Using associative property)




![Sampling Property of Discrete Impulse
[ n ] =
1 For n = 0
0 For n ≠ 0
[ n - no] =
1 For n = no
0 For n ≠ no
x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ] Sample magnitude and location
x [ n ] [ n - no ] = x [ no ] [ n - no]
Sampling Property](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-5-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of u[n] and u[ n – k ]
n
u [ n ]
0 1 2
k
u [ - k ]
0-4 -2
The function u [n ] = 1 for n > 0
= 0 for n < 1
The function u [n – k ] = 1 for [n – k ] 0 or n k
= 0 for [n – k ] < 0 or n < k
u [ - k ] = 1 for (k-n) ≤ 0 or n k now put n= 0
we get 0 k or k 0
= 0 for k > 0
Let us consider the function for n = 0. The
function will be u [-k]. Now this function
has independent variable as “k”
This is signal u [n]
delayed by k samples
Here independent
parameter is n and k is
the search parameter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-6-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of u[n-k] and u[ – k +n ]
Here independent parameter is “n” and “k” is the search parameter
So the dependence of discrete time signal x[n[ is seen on “n” the independent parameter,
which is the first term in the brackets and “k” is the search parameter. Here u [ n – k ] is
seen the signal delayed by “k” samples as shown below. This corresponds to delay of “k “
samples of u [n]. Here u [n – k ] signal is viewed as “k” sampled delayed u[n] signal.
n
u [ n – k ]
0 1 2
The function u [n ] = 1 for n k
= 0 for n < k
k
n
u [ n ]
0 1 2
The function u [n ] = 0 for n < 0
= 1 for n > 1
Interpretation of u[n-k]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-7-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of u[n-k] and u[ – k +n ]
k
u [ - k ]
0-4 -2
u [ - k ] = 1 for or k 0
= 0 for k > 0
Here “k” is the is the
independent variable.
Here independent parameter is “k” and “n” is the search parameter
So the dependence of discrete time signal x[k[ is seen on “k” the independent parameter,
which is the first term in the brackets and “n” is the search parameter. Here u [ - k + n ]
is seen the signal advanced by “n” samples as shown below. So we first visualize first u [-
k] and than visualize u [ - k + n]
Interpretation of u[- k + n]
k
u [ - k + n ]
-2 0
The function
u [-k + n ] = 1 for k n
= 0 for k < n
n- 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-8-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of u[n] and u[ n – k ]
u [ 1 - k ] = 1 for k 1 ( ( 1 – k ) 0 or 1 k )
= 0 for k > 1
Let us consider the function for n = 1.
The function will be u [ 1- k]
k
u [ 1 - k ]
0-4 -2 1
k
u [ n - k ]
0-4 -2 1
For n > 0. That is n is a positive real number
u [ n - k ] = 1 for k < n { ( n – k ) 0 or
n k or k n}
= 0 for k > n
k
0-4 -2 1
For n > 0
u [ n - k ] = 1 for k n
For n < 0
For n < 0. That is n is a negative real number
u [ n - k ] = 1 for k n { ( n – k ) 0 or
n k or k n}
u [n-k] = 1 for k n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-9-320.jpg)
![Discrete Time Signal Linear Combination
of Weighted Shifted Unit Impulse
x [ n ] [ n +1] = x [ -1 ] [ n +1 ]
x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ]
x [ n ] [ n - 1 ] = x [ 1 ] [ n - 1 ]
x [ n ] [ n -2 ] = x [ 2 ] [ n -2 ]
-k
]k-n[]k[x[n]x
A discrete signal is linear combination of weighted shifted impulses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-10-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution
y [ n ] = x [ n ] [ n ]
x [ n ]
]n[x]k-n[δ[k]x[n]y
n
-k
That means if we input [n] to the system being characterized by x [n] . Than w get
x [ n ] [ n +1] = x [ -1 ] [ n +1 ] = y[-1]
x [ n ] [ n ] = x [ 0 ] [ n ] = y[0]
x [ n ] [ n - 1 ] = x [ 1 ] [ n - 1 ] = y [1]
x [ n ] [ n -2 ] = x [ 2 ] [ n -2 ] = y[2]
This uniquely characterizes the system response which is x[n]. This
is the response to an impulse. That means the response [n]
uniquely characterizes the system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-11-320.jpg)
![Specific Case when x [n] = 1 for n 0
]n[u]k-n[δ[n]y
0k
y [ n ] = [ n ] * x [n] = u [n]
y [ n ] = x [ n ] [ n ]
x [ n ]
That means, if I want to know about the system. I start an impulse from [ n + k ], That
means k starts from - and varies up to infinity. In this process I can now about the system.
Let us assume x [ n ] = u [n]. In this case x [k] = 1 for k 0. So the expression we will get is:
]n[x]k-n[δ[k]x[n]y
n
-k
If x [ n] =1 for n 0 than
That means if we input [n] to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-12-320.jpg)
![y [ n ] [ n ]
h [ n ]
]n[h]k-n[δ[k]h[n]y
n
-k
Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution
y [ n ]x [ n ]
h [ n ]
n
-k
k n][h[k]x[n]y
This implies that output of the system for an input x [ n ] will be superposition of
the scaled version of delayed shifted impulses [ n – k ]. Let the response for [n-
k] is hk [ n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-13-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution
n
-k
k n][h[k]x[n]y
Let h0[n] is the response to [n]
0 1
1 ho [ n ]
n2
Than h-1[n] is the response to [n+1]which is the
response for unit advanced impulse. So the response
h-1[n] will be unit advanced response as shown
1
1 h-1 [ n ]
n0 1
0 2
1
h2 [ n ]
n
3 4
1
Let h1[n] is the response to [n-1]which is the
response for unit delayed impulse. So the response
h1[n] will be unit delayed response of ho[n] as shown
3
0 1
1
h1 [ n ]
n2
Identically h2[n] is the response to [n-2],which is the
response for two unit delayed impulse. So the response
h2[n] will be two unit delayed response of ho[n] as shown
h-1[n], h0[n], h1[n], h2[n]
Is the response to [n = 1], [n], [n-1]
and identified as hk[n] than y [n] can be
written as:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-14-320.jpg)
![Interpretation of Discrete Time Convolution
n
-k
k n][h[k]x[n]y
In general h-1[n], ho[n], h1[n] and so on are the responses for [n +1], [n ]
[n -1]. That means the most general form defining hk[n] is the responses
for an input [n-k]. These responses may not be same as the time shifted
version of h0[n] (if the system is not LTI), for the leading or delaying
behaviours. But the system is considered to be time invariant. Therefore,
hk[n] are the time shifted version of h [n] which are obtained for the input
[ n – k ]. Therefore, these will be h [ n – k] as shown in the figure of earlier
slide.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-15-320.jpg)
![Concept of Discrete Time convolution
n0 1
x [ n ]0.5
2.0
n0 1 2
h [ n ]
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1]
y[n] = 0.5 h[n] + 2 h [n-1]
When the input x[n] is applied we get the output x[0] h[n].
Than we get the input x[1]. This is the way sequence is going
to flow in. This is implied that we will get the response h[n]
delayed by unit pulse. In this case we have taken the input x[-
k] This will e multiplied by h [n-1]. That is x[1] h [n-1].
y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1]
Physically it means that input will be x[o] than x[1]
First sample no. at n=0 Last sample no at n=3
Duration of convolved output = (2+3) – 1 = 4
1.0
n0 1 2
y[ n ]
0.5
2.5
2.5
2..0
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
Let us find the response for x [ n ] which has only two samples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-16-320.jpg)
![Discrete Time Convolution: Concept
0 1
0. 5
2x [ k ]
k
1]-n[h]1[x[n]h[0]x]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
1
0k
= 0.5 h [n] + 2 h [n-1]
0 1
1h [ k ]
k2
x [ n ]
0 1
1
h [ k ]
k2
2 multiplied
0.5 multiplying to h [n]
+
+ 2 multiplying to h [n] after 1 unit delay that is h [n-1]
0.5 multiplied
1 2
1 h [ k -1 ]
k30
1 2
2.5 y [ n ]
k3
0.5
2.0
So the output starts at 0 and goes up to sample no. 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-17-320.jpg)
![Total no. of Sample in Convolution Output
n1 2
x [ n ]0.5
2.0
k
0 1 2
h [ k ]
3
n
0-2
x [-k ]
0.5
2.0
-1
So the no. of samples in the convolved output will be
: 5 – 2 + 1= 4
The last sample value in the convolved output is n = xh + h h
Here xh and h h are the values in the un-inverted pattern
So the no. of samples are: ( xh – xl) + ( h h - hl) + 1
: (N1 – 1)+ (N2 – 1) + 1 = N1 + N2 -1
So the convolved output extends from sample no.:
= ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l )
So the no. of samples are: ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) + 1
The first sample value in the convolved output is n = xl + h l
Here xl and h l are the values in the un-inverted pattern](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-18-320.jpg)


![Total no. of Sample in Convolution Output
n1 2
x [ n ]0.5
2.0
k
0 1 2
h [ k ]
3
n
0-2
x [-k ]
0.5
2.0
-1
So the no. of samples in the convolved output will be
: 5 – 2 + 1= 4
The last sample value in the convolved output is n = xh + h h
Here xh and h h are the values in the un-inverted pattern
So the no. of samples are: ( xh – xl) + ( h h - hl) + 1
: (N1 – 1)+ (N2 – 1) + 1 = N1 + N2 -1
So the convolved output extends from:
= ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l )
So the no. of samples are: ( xh + hh ) - ( x l + h l ) + 1
The first sample value in the convolved output is n = xl + h l
Here xl and h l are the values in the un-inverted pattern](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-21-320.jpg)
![Concept of Discrete Time convolution
n0 1
x [ n ]0.5
2.0
n0 1 2
h [ n ]
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1]
y[n] = 0.5 h[n] + 2 h[n-1]
When the input x[n] is applied we get the output x[0] h[n].
Than we get the input x[1]. This is the way sequence is going
to flow in. This is implied that we will get the response h[n]
delayed by unit pulse. In this case we have taken the input x[-
k] This will e multiplied by h [n-1]. That is x[1] h [n-1].
y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1]
Physically it means that input will be x[o] than x[1]
First sample no. at n=0 Last sample no at n=3
Duration of convolved output = (2+3) – 1 = 4
1.0
n0 1 2
y[ n ]
0.5
2.5
2.5
2..0
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-22-320.jpg)
![Discrete Time Convolution: Concept: Alternate way of looking at it
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
The sum can be carried out on the number of samples in x [ n ]
0 1
0. 5
2x [ k ]
k
Now we can find the convolution for x [k]. That means
we take the contribution of 2 samples. x [0] and x[1]
1]-n[h]1[x[n]h[0]x]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
1
0k
This implies that we multiply h [n] containing 3
samples by x [0]. This gives h[0], h[1], h[2] all 0.5.
Now we multiply h[n-1] one sample shifted
version of h[n] by x[1]. This gives h[-1], h[-2]
h [-3] all multiplied by 2. So the response extends
from n = 0 to n = 3, which is ( N1 + N2 -1)
= 0.5 h [n] + 2 h [n-1]
0 1
1
h [ k ]
k
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-23-320.jpg)
![0 1
2 3
x[n]
n
1
2
1
-1 0 1
h[n]
n
2
2
0 1 2
3
y[n]
n-1
4 5 6
2
4
2 2
-2
Convolution of Two Discrete Time Signals
The lower starting sample will be sum of
lowest sample points of two signals
-k
k]-n[h[k]x[n]y
Commutative property
y[n] = x[0] h[n] + x[1] h [n-1] + x[2] h[n-2] + x[3] h[n-3]
-k
k]-n[x[k]h[n]y
This will give the output y [n] as:
y[n] = x[n+1] h[-1] + h[1] x [n-1]
The highest sample point will be sum of
highest sample points of two signals
Total no. of samples will be the
sum of samples in both the
signals -1. That is N1 + N2 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-24-320.jpg)

![n
h[n] =u [ n ]
0
h [ n ] = u [n]
k
h [ 0 - k ]
0
k
u [ 1 - k ]
0
k
u [-1 – k ]
0
n0 1 2
x [ n ]
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
Here h[-k] is the mirror image of h [n]. And h[-
1-k] is the value for n= - 1 and h [+1-k] for n=1
Example Convolved Output for x[n] = n
and h[n] = u[n]
We see that output is 0 for n < 0 and we get
output for n 0. So the summation is;
[n]u
α-1
α-1
α[n]y
1nn
0k
k
The output vale will start from zero and for
k the value saturates at ( 1 / ( 1 - )
x [ n ] = n Where 0 < < 1
For k and
If = 1 /2 than y[n] = 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-26-320.jpg)
![k
h [ - k ]
0
k 0-1-2
x [ k ]
Convolved Output for x[n] = 2n
u[-n] and h[n] = u[n]
0
-k
k
2[n]y
If we change the variable k = -m. We get the
integral from 0 to . This is when we are
computing only for n ranging from - to 0
2
1/2)-1(
1
2
1
[n]y
0k
k
However we need to compute
the integral in the entire range
of “n” for which we get:
n
-k
k
2[n]y If k we replace k by k = - k
n-k
k
2
1
[n]y If k we replace k by
k + n = m, we get
2
1
2
2
1
[n]y
0m
m
n
0m
n-m
1n
2[n]yor
x[k] starts the output at - and
h[k] leads the output until . So
the output is from - to
Now considering the complete output from -
to n, where will also tend to infinity
The summation taken from - to 0 will show
that the output it must saturate at n=0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-27-320.jpg)
![n
h [ n ]
0
h [ n ] = u [ - n]
k
h [ -k ]
0
k
u [ 1 - k ]
0
k0 1 2
x [ k ]
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
Here h[-k] is the mirror image of h [n]. And h[-
1-k] is the value for n= - 1 and h [+1-k] for n=1
Example Convolved Output for x[n] = n
and h[n] = u[-n]
We see that output is 0 for n < 0 and we get
output for n 0. So the summation is;
[n]u
α-1
α-1
α[n]y
1nn
0k
k
The output vale will start from zero and for
k the value saturates at ( 1 / ( 1 - )
x [ n ] = n Where 0 < < 1
k0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-28-320.jpg)
![Example of Convolved Output
x[n] = 1 for 0 n 4
= 0
h[n] = n 0 n 6
= 0 elsewhere
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
The convolved output will be from n=0 to n=10 and
the total no. of samples will be: (5+7 ) -1 = 11
Region #1: n < 0 y[n] = 0
n
0 1 2
x [ n ]
3 4
n
h [ n ]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
The starting sample will be n=0
The stop sample will be n=10
This is because of the fact that there is no overlap
So the convolved output will have 11 samples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-29-320.jpg)
![Example Convolved Output where x[n] is of finite duration
x[n] = 1 for 0 n 4
= 0
-k
]k-n[h]k[x[n]y
In this case x[n-k] will keep moving below h[k] and
the complete fill up will be obtained for n = 4. In this
region 0 ≤ n ≤ 4. In this region k will also vary
from 0 to 4. In this region if n=1, than we summing
over n from 0 to 1 for the product of x [ n-k] and h
[k].
Region #2: n = 0 to n= 4. That
is the region 0 n 4.
n
0k
k-n
α[n]y
n
0r
r
α[n]y
α1
α1
[n]y
1n
n
0 1 2
x [ n ]
3 4
n
h [ n ]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
h[n] = n 0 n 6
= 0 elsewhere
If we put n – k = r. For k=0 : n = r and for k =n :
r = 0. So the summation on “r” changes from n
to 0. Which is same as r changing from 0 n. It is
like u[n] * h[n].
Here we will get y[n] for n=0 to n=4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-30-320.jpg)
![k
h [ k ]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Visualization of Region #3
k
x [n -k ]
4 3 2 1 0
This is the where
region 2 ends
This is where
region 3 starts
This is the where region 3
stops. Last sample of h[k]
still overlaps
In this region 4 < n ≤ 6. That is the signal h [k]
remains completely filled only for two values of n,
which are n=5 and 6. But during this period the
summation for each value of n is to be carried for
all values of “k”, which varies from 0 to 4.
In region 3
In this region 4 < n ≤ 6. The summation integral will be
for k= 0 to k = 4. and the output will be for n=5, and 6
4
0k
k-n
α[n]y
Here we get output for y[n] for n =5 and 6
4
0k
k-n
αα[n]y
)/1(-1
)/1(-1
α[n]y
5
n
k
x [n -k ]
4 3 2 1 0
k
x [n -k ]
4 3 2 1 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-31-320.jpg)
![k
h [ k ]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Visualization of Region #4
region 3
stops
In this region 6 < n ≤ 10. That is the signal x [n-
k] starts coming out. So far y[n] has reached at
y[6], making the output as 7 samples
In region 4: This is the region we are considering
n > 6. Now for n-6 ≤ k, the fist sample will come
out for n = 7 and the output will be obtained until
all sample get out that is upto k+4. So the value of
k will vary from : n-6 ≤ k ≤ 4
4
6-nk
k-n
α[n]y
Region 5 we get when n > 10 than the output is zero
n-10
0r
6r-
α[n]y )/1(-1
)/1(-1
α[n]y
n-11
6
k
x [n -k ]
4 3 2 1 0
Now if we put : k – (n – 6 ) = r The
limits of summation are from r=0
to r= 10 – n . And n – k = - r + 6
n-10
0r
r-6
αα](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-32-320.jpg)

















![System Without Memory
A system is said to be memoryless, if its output at any instant of time
Dependents only the value of input at that instant of time. That is y[n]only
depends on the input x[n].
This is only possible when h [n] exists only at n=0 otherwise it is zero.
Such an impulse response could only be unit step function [n]. The
amplitude of [n] may not be unity. It may have the arbitrary value k.
x [ n ] K [ n ]
y [ n ] = k x [ n ]
x [ n ] K h [ n ]
y [ n ] = k ( x [ n ] * h[n] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-52-320.jpg)
![System Without Memory
y [ n ]x [ n ]
K [ n ] y [ n ] = k x [ n ]
]k-n[[k]k x[n]y
-k
If k=1 than it becomes an identity system
d)-t(h)(xx(t)
-
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-53-320.jpg)
![System Without Memory
A system is said to be memoryless, if its output at any instant of time
Dependents only the value of input at that instant of time. That is y[n]
only depends on the input x[n].
Such a system is called as identity system. Because the input is same as output
This is being visualized as if the input is [n] and system is characterized by
The impulse response x [n]. For such a system the output will be x [ n ]
y [ n ]x [ n ]
h [ n ] y [ n ] = x [ n ] * h [n]
This is only possible when the input x [n] = [n]
y [ n ] = h [ n ] * x [n]
y [ n ]h [ n ]
x [ n ]
It is analogus to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-54-320.jpg)
![Identity Systems
That means h [ n ] = [n]
For an identity system h [ n ] = [ n ]
n
-k
]k-n[[k]x[n]x
And
-
τd)τ-t(δ)τ(x(t)x
y [ n ] = [ n ] * x [n]
y [ n ] [ n ]
x [ n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-55-320.jpg)
![System With Memory
1-n
-k
[n]x[n]x[n]y
The summation term gives the
accumulated sum to which the
Current value x [n] is added
Discrete Time: An accumulator
In continuous time: Capacitor Charging
An example of a system with the memory is charging of capacitor. The
capacitor charges to the previous value.
t
-
τd)τ(x
C
1
(t)y
The charging of a capacitor by an
Input current x(t) keeps charging
The capacitor to a voltage y(t)
An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds
the current value to the previous values
n
-k
[n]x[n]y
[n]x]1-n[y[n]y ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-56-320.jpg)
![System With Memory
y [n] = x [n -1]
Here the value of y [n] at any instant n = no
depends on the earlier value of x [n]. System
With memory
A system with memory stores the information about the value of input value
other than current time. For example a delay must retain the previous .
Here x[n] already exists and we give a unit delay than it becomes y [n]
y [n] = x [n -1]x [n]
Here y [n] is response to the signal which
was existing. Therefore the system is causal
y [n] = x [n-1]
DELAY
x [n]
Delay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-57-320.jpg)

![Invertible System / Inverse System
A system is invertible: Than an inverse system exists, which when cascaded
with the original system yields the output, which
is same as the input
y [n] = 0 It is a noninvertible system because the output is zero for all inputs
y (t) = x2
(t) is a noninvertible system, because we can not determine
determine the sign from the knowledge of output signal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-59-320.jpg)

![Invertibility and Inverse System: Discrete time
If a system is invertible than a inverse system exists that, when cascade
With the original system yields the output, which is basically input signal
Discrete Time System
x [ n ] y [ n ]
w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ]
w [n]
[k]x[n]y
n
-k
[n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y
1-n
0k
n
-k
[n]x]1-n[y[n]y
w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-61-320.jpg)

![Three basic Operators to Perform a Function in Discrete Time
[n]xb]1-n[ya[n]y
y [n] a y [n]
a
multiplier
y [n] y [n -1]Delay
Delay
+y [n]
y [n-1]
y[n] + y [n-1] Summation
The delay element can be considered as a simple RS flip-flop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-63-320.jpg)
![Discrete time Accumulator
If a system is invertible than a inverse system exists that, when cascade
With the original system yields the output, which is basically input signal
Discrete Time System
x [ n ] y [ n ]
[k]x[n]y
n
-k
[n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y
1-n
0k
n
-k
[n]x]1-n[y[n]y
First system can be obtained by passing x[n]
through u[n] and its system representation is shown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-64-320.jpg)
![System Implementation of Discrete Time Accumulator
Convolution of x[n] with h[n]
Discrete Time: An accumulator
1-n
-k
[n]x[n]x[n]y
n
-k
[n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y
So this can be expressed as :
-k
]k-n[u[n]x[n]y
n
-k
]k-n[u[n]x[n]y
h[n] = u [n]
x [n] y [n]
y [n] = x[n] * u[n]
In accumulator we add present value in the previous value. y[n] = y [n-1] + x[n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-65-320.jpg)
![System Implementation of Discrete Time Accumulator
Discrete Time Accumulator System
n
-k
[n]x[n]y
[n]x]1-n[y[n]y
-k
]k-n[u[n]x[n]y
h[n] = u [n]
x [n] y [n]
y [n] = x[n] * u[n]
Unit
Delay
x [n] y [n]
y [n - 1]
Integrator should have feed-back. That is what is reflected](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-66-320.jpg)
![Impulse Response of Discrete Time Accumulator
Unit
Delay
x [n] y [n]
y [n - 1]
If we assume system to be
causal. That is y[n-1]=0. And the
input is [n]. Than the output
will be u [n]
y [n] = y [ n – 1 ] + x [n]
Input is [n]: Output is u[n]:
If we multiply the feed-back by “a” after the delay. The
output will be: 1 + a + a2+ ….. The output is: y [ n ] = an u[n]
The system has recursion. Therefore, we called as the
recursive system. Further the impulse response is infinite.
So we call it as infinite Impulse Response System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-67-320.jpg)
![Recursive Response : I I R : all Pole System
The output depends on present
and past values of input
x [ n ] b0
D
-a1
-a2
D
-ak
D
y [ n ]
The difference equation is:
y [n] = b0 x [ n ] - a1 y [ n – 1 ] - a2 y [ n – 2 ] - ….. - ak y [ n – k]
N
1k
0k ]n[xb]kn[ya]n[y
y [n] = y [ n – 1 ] + x [n]
If we consider that coefficients ak and b0 are normalized value w.r.t.
to a0. Than the above equation can be written as:
N
0k
0k ]n[xb]kn[ya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-68-320.jpg)

![Invertibility and Inverse System: Discrete time
The system is invertible if the output of accumulator
is fed through a first order differentiator. Here the
second block is the differentiator
Discrete Time System
x [ n ] y [ n ]
w [n] = y [n] – y [ n – 1 ]
w [n]
[k]x[n]y
n
-k
[n]x[k]x[k]x]n[y
1-n
k
n
k
1]-[ny]n[y]n[x ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-70-320.jpg)
![Impulse response of a differentiator
and invertible System
The impulse response of the differentiator is: [n] - [ n – 1]
Discrete Time Differentiator
x [ n ]
y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ]
y [n]
Impulse response of an integrator and differentiator
u [n] * { [n] - [ n – 1]} = u [n] [n] – u [n-1 ] [ n – 1]}
u [n] - u [n-1 ] = [ n ]
This establishes the invertiability of the system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-71-320.jpg)
![System Implementation of
Differentiator
Discrete Time Differentiator
x [ n ]
y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ]
y [n]
y[n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ]
y [n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ]
Unit
Delay
x [n]
The impulse response such as system is : [ n ] - [ n -1]. Since it is a feed-forward
So the response will be of finite duration. These are non-recursive systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-72-320.jpg)
![Differentiator: Non recursive System
y[n]
y [n] = x [n] – x [ n – 1 ]
D
x [n]
The impulse response such as system is : [ n ] - [ n -1].
Since it is a feed-forward .So the response will be of finite
duration. These are non-recursive systems
D
D
bo
-b1
-bk
-b2
y [n] = box [n] + b1 x [ n – 1 ]+ b2 x [ n – 1 ]+…… bk x [ n – k ]
]kn[xb[n]y k
M
0k
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-73-320.jpg)
![System With Memory: Discrete Time
Discrete Time: An accumulator
An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds
the current value to the previous values
n
-k
[n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y
This is feed-forward so it is no-recursive type of system
Difference Equation
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]
This equation has the feed-back. This reflects the recursive nature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-74-320.jpg)
![Impulse Response of a Reversible System
Discrete Time Accumulator
n
-k
[n]x[n]y
[n]x]1-n[y[n]y
Verification of Associative Property
Differentiator
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]
Unit
Delay
x [n] y [n]
y [n - 1] h[n] = u [n]
Unit
Delay
x [n]
h[n] = [n] - [n-1]
y[n] = u [ n ] * { [n] - [n-1] }
y[n] = { [n] - [n-1] } * u [n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-75-320.jpg)
![General Form of a Discrete Time System
It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator
n
-k
[n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator
As such both are called as first
order difference equation
D
x [n]
b0
- b1
y [n]
D
- a1
y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1]
y1 [n]
Differentiator
Integrator
y [n] = y1 [n-1] – a1 y[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-76-320.jpg)
![General Form of a Discrete Time System
It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator
n
-k
[n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator
As such both are called as first
order difference equation
D
x [n]
b0
- b1
y [n]
D
- a1
y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1]
y1 [n]
Differentiator
Integrator
y [n] = y1 [n-1] – a1 y[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-77-320.jpg)
![General Form of a Discrete Time System
y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = y1 [n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1]
If we consider all the coefficients were initially normalized to some
constant coefficient a0. That means a1 was actually a1/a0, b0 was b0/a0
andb1 was b1 / a0
M
0k
k
N
0k
k ]k-n[yb]k-n[ya
D
x [n]
b0
- b1
y [n]
D
- a1
y1[n] = b0 x[n] – b1 x[n-1]
y1 [n]
Differentiator
Integrator
y [n] = y1 [n] – a1 y[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-78-320.jpg)
![Inverse System for Continuous and Discrete Time
A system is said to be INVERTIBLE if the complete system functions
As an Identity system
h1 (t)
x ( t ) y ( t ) w ( t )
w ( t ) = x ( t )h2 ( t)
h1 (t) * h2 ( t ) = (t)
h1 [n]
x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ]
w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ]
h1 [ n ] * h2 [ n ] = [ n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-79-320.jpg)


![Inverse System in Discrete Time: Identity System
h1 [n]
x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ]
w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ]
y [ n ] = x [ n – no ] h1 [ n ] = [ n – no ]
w [ n ] = y [ n+ no ] h2 [ n ] = [ n + no ]
k
[ n - k + no ]
0 no
-k
oo ]nk-[n]-n[k[n]h
k
[ k – no ]
no0
h1 [k]
k
[ k + no ]
no0
h2 [k]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-82-320.jpg)
![Inverse System in Discrete Time: Identity System
h1 [n]
x [ n ] y [n] w [ n ]
w [ n ] = x [ n ]h2 [ n ]
h [ n ] = h1 [ n ] * h2 [ n ]
= [ n - no] * [ n + no] = [n]
y [ n ] = x [ n – no ] h1 [ n ] = [ n – no ]
w [ n ] = y [ n+ no ] h2 [ n ] = [ n + no ]
k
[ k – no ]
no0
k
[ n - k + no ]
0 no
-k
oo ]nk-[n]-n[k[n]h ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-83-320.jpg)

![Stability for LTI System : Discrete Time
A system is said to be stable if bounded input has the bounded output
Let the input x [ n ] is a bounded in magnitude. | x ( t ) | < B for all values of n
|τd)τ-t(x)τ(h||)t(y|
-
τd|)τ-t(x||)τ(h||)t(y|
-
Since, | x ( t ) | < B for all values of t
τd|)τ(h|B|)t(y|
-
That means for a system to be stable
τd|)τ(h|
-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-85-320.jpg)
![Stability for LTI System: Continuous Time
A system is said to be stable if bounded input has the bounded output
Let the input x [ n ] is a bounded in magnitude. | x [ n ] | < B for all values of n
|]k-[nx||[k]h||]k-[nx[k]h||[n]y|
-k-k
-k
|[k]h|B|[n]y|
Since | x [ n – k ] | < B for all values of k and n
This requires that the impulse response is absolutely summable
|[k]h|
-k
for all values of n
We take the magnitude because the swing +ve and negative values may tend to infinity
but still the average value may be zero. This summation may be zero](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-86-320.jpg)

![Time Invariance System
A system is said to be time invariant if the behavior and
characteristic of the system are fixed over time.
A system is said to be time invariant if the time shift in the
Input signal results in time shift in the output signal
In a continuous time system if y (t) is the output for an input x (t)
Than y ( t – t0 ) is the output when input is x ( t – t 0 )
For a discrete time system if y [n] is the output for an input x [n]
Than y [ n – n0 ) is the output when input is x [ n – n 0 )
If we take a R, C circuit and the values of the elements do not change with
time (characteristic remains fixed with time). It is a time invariant system. If
the values of the elements changes with time than it is time variant system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-88-320.jpg)
![Checking a System for Time Invariance
Let us consider a system y ( t ) = sin [ x1 ( t ) ]
Let x1 (t) is the input at any time t y1(t) = sin [ x1(t) ]
Now if we look at the response delayed time t0.
That is for the input x1( t - t0 )
x2 ( t ) = x1 ( t – t0) Y2 ( t ) = sin [ x1 ( t – t 0 )
Now if we find y1 (t) at time = t - t0
y1( t – t0 ) = sin [ x1( t – t0) ]
So the system is time invariant
The time invariance should be checked for any input and any time delay.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-89-320.jpg)



![Causality of a System
A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System
Output depends on present and past values of input signals.
h(t) = 0 for t <0
A typical is charging of a capacitor. The voltage on capacitor
Depends on present past and past values of source voltage
h [n] = 0 for n <0
For a discrete time system
For a continuous system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-93-320.jpg)
![Causality of a System for discrete System
A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System
Output depends on present and past values of input signals.
Therefore the criteria of present and past value of x[n] states that
for any shift in x[n] the h[n] must shift so:
]k-[nh[k]x[n]y
-k
n
Since h [n] , for n < 0. The above expression can also be
written in alternate form by using commutative property
]k-[nh[k]x[n]y
0k
h [ n ] = 0 for n < 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-94-320.jpg)

![Causality of a System
A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System
Output depends on present and past values of input signals.
The system y [ n ] = x [ n – 1 ] is causal system
The system y ( t ) = x ( t – t0 ) is causal System
A typical is charging of a capacitor. The voltage on capacitor
Depends on present past and past values of source voltage
If a signal is defined at t = to. Than we can determine the output
at any instant later t > to.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-96-320.jpg)
![Causality of a System
A non-anticipative system is called as Causal System
Output depends on present and past values of input signals.
The system y [ n ] = x [ n ] + x [ n + 1 ] is NON causal system
The system y ( t ) = x ( t + t0 ) is NON Causal System
Any memory less system is Causal system, because it depends
Only current value of the input signal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-97-320.jpg)
![Checking Causality of a System
y [ n ] = x [ - n ]
The values at n = n0 for some positive time n0 depends on past
values of signal x [ - n0 ]. System seems to be Causal
But if n is negative say n = - 4. Than y [ - 4 ] = x [ 4 ]. That means
output depends on a future value of input signal. So system is not Causal
y ( t ) = x ( t ) cos ( t + 1 )
Here cos ( t + 1) indicates that system is not causal
But the output is multiplications of x(t) which defines
That the system is casual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-98-320.jpg)
![Causality not an Essential Parameter
If Time is not Independent Parameter
This finds application in meteorological signals, predicting
the stock Market. In such cases it is the average value taken
over an interval say – M to M and predict the value at some
instant of time
M
Mk
M][kx
12M
1
[n]y
This can be used to predict the dynamic behavior f the market](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-99-320.jpg)

![System With Memory: Discrete Time
[n]xb]1-n[ya[n]y
y [n] a y [n]
a
multiplier
y [n] y [n -1]Delay
Delay
+y [n]
y [n-1]
y[n] + y [n-1] Summation
The delay element can be considered as a simple RS flip-flop
In this the information Q = 1 gets tranf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-101-320.jpg)
![System With Memory: Discrete Time
Discrete Time: An accumulator
An example of memory system is an accumulator. It adds
the current value to the previous values
n
-k
[n]x[n]y [n]x]1-n[y[n]y
This is feed-forward so it is no-recursive type of system
Difference Equation
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]
This equation has the feed-back. This reflects the recursive nature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-102-320.jpg)
![General Form of a Discrete Time System
It is a combination of a accumulator and differentiator
n
-k
[n]x[n]y y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n]Accumulator
y[n] = x [ n ] – x [n-1]Differentiator
As such both are called as first
order difference equation
y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = b0 x[n] +b1 x[n-1]
D
x [n] b0
- b1
y1 [n]
D
- a1
y [n]
y1[n] = b0 x[n] + b1 x[n-1]
y[n] = y1[n] - a1 y[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-103-320.jpg)
![General Form of a Discrete Time System
D
x [n] b0
- b1
y [n]
D
- a1
If we consider all the coefficients were initially normalized to some
constant coefficient a0. That means a1 was actually a1/a0, b0 was b0/a0
andb1 was b1 / a0
M
0k
k
N
0k
k ]k-n[yb]k-n[ya
y[n] + a1 y[n-1] = b0 x[n] +b1 x[n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-104-320.jpg)
![N th Order linear constant Coefficient Difference Equation
M
0k
k
N
0k
k ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya
M
0k
k
N
1k
k0 ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya[n]ya
This equation can be expressed as:
}]k-n[ya-]k-n[xb{)
a
1
([n]y
N
1k
k
M
0k
k
0
This equation states that for computing the present output value. We need
the information of the previous output value. From this we must realize
that we need the auxiliary conditions. That is the initial conditions.
To compute y [n] we need the information on y [n-1], ……..y [ n – N]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-105-320.jpg)
![N th Order linear constant Coefficient Difference Equation
M
0k
k
N
0k
k ]k-n[xb]k-n[ya
In this equation if we assume that N=0. That means
K =0. For this the above equation gets modified as
M
0k
0k ]k-n[x)a/b([n]y
M
0k
k0 ]k-n[xb[n]ya or
In this case the output depends on the present and past (previous)
values of the input. That means we do not recursively use previously
computed values of the output to compute the present value of output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-106-320.jpg)
![N th Order linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equation
M
0k
0k ]k-n[x)a/b([n]y
M
0k
]k-n[xk)h([n]y
Now if we compare the above two
equations we find that the impulse
response of the system is:
h [n] =
bn / ao for 0 n M
0 otherwise
The above equation is convolution sum of the input x [n] with the impulse
response ( bn /ao). Since we are not using the previously computed value to
compute the present value, therefore we do not need the auxiliary
conditions. That is the status of the system whether It is initially at rest.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-107-320.jpg)
![PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n]
Now we want to find the output for x [n] = K [n]. This
forces the condition that x [n ] = 0 for n -1. The
condition of initial rest implies that y [n] = 0 for n -1
In the process we take the Causal LTI system. The causal system
dictates that x [n] = 0 for n < 0. Identically y[n] = 0 for n<0
From the above equation we can y[n] for an input x [n] = K [n]
y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k
y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 } k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-108-320.jpg)
![PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n]
Now we want to find the output for x [n] = K [n].
This forces the condition that x [n ] = 0 for n -1.
The condition of initial rest implies that y [n] = 0 for n -1
In the process we take the Causal LTI system. The causal system
dictates that x [n] = 0 for n < 0. Identically y[n] = 0 for n<0
From the above equation we can y[n] for an input x [n] = K [n]
y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k
y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 } k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-109-320.jpg)
![PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
y [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) y [n-1 ] + x [n]
y [0] = ( 1 /2 ) y [-1] + k [n] = k
y [1] = ( 1 /2 ) y [0] + x [1] = ( 1 / 2 ) k
y [2] = ( 1 /2 ) y [1] + x [2] = ( 1 / 2 ) 2 k
y [3] = ( 1 /2 ) y [2] + x [3] = ( 1 / 2 ) 3 k
So y [n] = ( 1 / 2) n k
Since the system is completely characterized by an impulse response
The impulse response can be found from putting k=1
So h [n] = ( 1 / 2 ) n u[n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-110-320.jpg)




![Formation of Difference Equation an Impulse Response
Delay
x [ n ] y [ n ]
a y [ n -1 ]
a
y [n] = x [ n ] + a y [ n – 1 ]
Now let us assume that it is a causal
system y [ n ] = for n < 0
The system response for [ n ] is:
y [0] = x [ 0 ] + a y [– 1 ] = 1 Since x [ n ] is [ n ] so x [ o ] = 1 and y [ 0 ] =1
y [1] = x [ 1 ] + a y [0] = a
y [2] = x [ 2 ] + a y [1] = a2
Or y [n] = x [ n ] + a y [n-1] = an u [n]
The impulse response of the system is: a n
u [ n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-115-320.jpg)
![The output depends on present
and past values of input
Summation
x [ n ]
y [ n ]
b
k
D D D D
b0
b1
b2
X ( z) = ∑
- ∞
∞
x [n] z
- n
X/
( z)= ∑
- ∞
∞
x [ n - 1 ] z
- n
X/
( z)= z
– 1
X [ z ]
zb)z(Y k-
k
M
ok
)z(X)zb..........zbzbb( -k
k
-2
2
1-
1o
)z(X
)z(Y
k
k
2-k
2
1-k
1
k
o
Z
)b..........zbzbzb(
Basically it is a all zero filter. It has all the poles lying at z =0. Origin
Non Recursive Response : F IR : all Zero System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-116-320.jpg)
![Recursive Response : I I R : all Pole System
The output depends on present
and past values of input
y [ n ] Y ( z)
)z(X)za..........zaza(1)z(Y -k
k
-2
2
1-
1
Basically it is a all pole filter. It has all the zeros lying at z =0. Origin
Y [ n - 1 ] z – 1
Y ( z)
x [ n ] 1
D
-a1
-a2
D
-ak
D
y [ n ]
The difference equation is:
y [n] + a1 y [ n – 1 ] + a2 y [ n – 2 ] + ….. ak y [ n – k] = x [ n ]
)za..........zaza(1
1
)z(X
)z(Y
k-
k
2-
2
1-
1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolution-discreteandcontinuoustime-differenceequaionandsystemproperties1-150901060342-lva1-app6891/85/Convolution-discrete-and-continuous-time-difference-equaion-and-system-properties-1-117-320.jpg)
























































































