Copy of G10 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonic Theory and Formation of Continents.pptx
- 1. PLATE Marc Rodel C. Mesa TECTONICS UNIT 1
- 2. CONTENT STANDARDS Demonstrate an understanding relationship among the locations of volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and mountain ranges
- 3. PERFORMANCE STANDARDS 1. Demonstrate ways to ensure disaster preparedness during earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions 2. suggest ways by which he/she can contribute to government efforts in reducing damage due to earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions
- 4. LEARNING COMPETENCIES • describe the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts;
- 5. LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Explain the theory of continental movement and plate tectonics; • Use logic and evidence to reconstruct the position of large islands as they appeared 220 million years ago; • Describe how scientists use different kinds of evidence to form theories about the formation of the continents.
- 6. HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE EARTH? BASED ON PHYSICAL PROPERTIES?
- 7. LESSON 1: THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS AND THE FORMATION OF CONTINENTS FIRST GRADING
- 8. LET’S HAVE A GAME!!! FIRST GRADING
- 9. During its billion years of evolution, Earth has gone through a series of major biological and geographical changes such as volcanic eruptions
- 10. During its billion years of evolution, Earth has gone through a series of major biological and geographical changes such as volcanic eruptions, collision of plate boundaries.
- 11. THE EARTH Our home planet Earth is a rocky, terrestrial planet. It has a solid and active surface with mountains, valleys, canyons, plains and so much more https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/earth/overview/
- 12. THE EARTH 70.8% of the planet is covered with water 29.2% percent is composed of land.
- 13. THE EARTH The Earth is composed of 4 “Spheres” • the atmosphere • the hydrosphere • the biosphere • the geosphere
- 14. GEOSPHERE This portion of Earth includes the planet’s interior structure, rocks, minerals, landforms, and other processes that shape its surface
- 15. PLATE TECTONICS
- 16. MAIN LESSON ◦In the beginning of 20th century, many scientist explained the physical attributes of Earth using Raisin Theory.
- 17. MAIN LESSON According to this theory, Earth is like a grape that contracted into a raisin due to the cooling process that occurred on Earth after the Big Bang about 13.77 Billion yrs. ago.
- 18. MAIN LESSON ◦The contracting Earth concept was further explained when an American seismologist and geologist, Clarence Edward Dutton, proposed the term “isostasy” in 1889.
- 19. MAIN LESSON
- 20. MAIN LESSON Tectonic plates = lithospheric plates Are massive, irregular slabs of solid rock that envelope the surface of the Earth.
- 21. MAIN LESSON Tectonic is a term derived from a Greek word tekton, “carpenter or builder”. Tectonic plates have been used by scientists to describe the movement of the lithosphere.
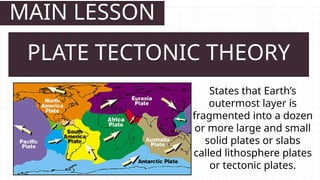
- 22. MAIN LESSON States that Earth’s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more large and small solid plates or slabs called lithosphere plates or tectonic plates. PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
- 23. MAIN LESSON Earth is generally compose d of 58 crustal plates.
- 24. MAIN LESSON • Pacific Plate is the largest of all the lithospheric plates. • North American Plate • Eurasian Plate • African Plate • Antarctic Plate • Indo-Australian Plate • South American Plate 7 MAJOR LITHOSPHERIC PLATES
- 25. MAIN LESSON Plates fit together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle and the movement ranges from less than 1 to more than 15 cm per year. Resulting to the opening and closure of bodies of water.
- 26. MAIN LESSON Foundational works that gave rise to this theory is the first world atlas “Theatrum Obris Terrarum,” which was developed and published by Abraham Ortelius.
- 28. ABRAHAM ORTELIUS He suggested that America was originally connected to Europe and Africa and that the projecting parts of the two continents would fit the recesses of America.
- 29. RECAP • Earth is a rocky, terrestrial planet. It has a solid and active surface with mountains, valleys, canyons, plains and so much more • 70.8% of the planet is covered with water while 29.2% percent is composed of land • The Earth is composed of 4 “Spheres” ⚬ the atmosphere ⚬ the hydrosphere ⚬ the biosphere ⚬ the geosphere • According to Raisin Theory is that Earth is like a grape that contracted into a raisin due to the cooling process • Clarence Edward Dutton, proposed the term “isostasy” ⚬ isostasy = theory describing the mass balance in the Earth’s crust
- 30. RECAP • Tectonic is a term derived from a Greek word tekton, = “carpenter or builder”. • Tectonic plates have been used by scientists to describe the movement of the lithosphere. • Plate Tectonic Theory states that Earth’s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more large and small solid plates or slab • First Published World Atlas - “Theatrum Obris Terrarum,” which was developed and published by Abraham Ortelius.
- 32. ALFRED WEGENER • Austrian climatologist, proposed the Continental Drift Theory. • In his book, The Origins of Continents and Oceans in 1915, Wegener explained that about 1,100 million years ago (1.1 B), there was a supercontinent named Rodinia, which predated as Pangaea.
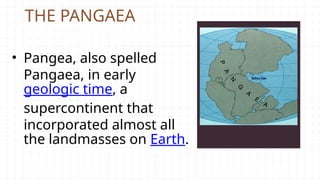
- 33. THE PANGAEA • Pangea, also spelled Pangaea, in early geologic time, a supercontinent that incorporated almost all the landmasses on Earth.
- 34. THE PANTHALASSA • Pangea was surrounded by a global ocean called Panthalassa
- 35. LAURASIA AND GONDWANALAND • During the late Triassic Period, Pangaea began to break up into two smaller supercontinents called Laurasia and Gondwanaland • which moved to the northern and southern extremes of the planet, respectively.
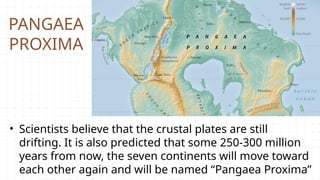
- 37. PANGAEA PROXIMA • Scientists believe that the crustal plates are still drifting. It is also predicted that some 250-300 million years from now, the seven continents will move toward each other again and will be named “Pangaea Proxima”
- 40. 7 CONTINENTS
- 41. 2 TYPES OF CRUST
- 43. CONTINENTAL CRUST • The solid ground where you stand upon is called the CONTINENTAL CRUST • formed through volcanic eruption, which are foundation of Earth’s crust
- 44. CRATONS • Cratons often survive the cycles of merging and rifting of continents and are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates.
- 45. OCEANIC CRUST • Like continental crust it is also formed by magma, when volcanic eruption occurs
- 46. RECAP • Alfred Wegener proposed the Continental Drift Theory. • in 1915, Wegener explained that about 1,100 million years ago (1.1 B), there was a supercontinent named Rodinia, which predated as Pangaea. ⚬ Pangaea began to break up into two smaller supercontinents called Laurasia and Gondwanaland • It is also predicted that some 250-300 million years from now, the seven continents will move toward each other again and will be named “Pangaea Proxima” • There are 2 types of Crusts ⚬ Continental Crust ⚬ Oceanic Crust
- 47. I hope you learn smething new today! THANK YOU!