Ad
Cvpr2010 open source vision software, intro and training part v open cv and ros - unknown - unknown - 2010
- 1. OpenCV TutorialCVPR 2010ItseezGary BradskiSenior Scientist, Willow GarageConsulting Professor: Stanford CS Dept.Vadim PisarevskyPrinciple Engineer, OpenCVItseez Corporationhttp://opencv.willowgarage.comwww.willowgarage.comwww.itseez.com
- 2. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 20092
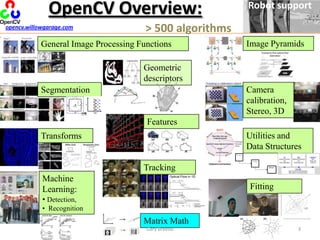
- 3. OpenCV Overview: Robot support> 500 algorithmsopencv.willowgarage.comImage PyramidsGeneral Image Processing FunctionsGeometric descriptorsCamera calibration,Stereo, 3DSegmentationFeaturesUtilities and Data StructuresTransformsTrackingMachine Learning:Detection,
- 4. RecognitionFittingMatrix Math3Gary Bradski
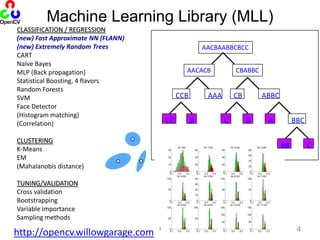
- 5. Machine Learning Library (MLL)AACBAABBCBCCAACACBCBABBCAAACCBABBCCBBCCBCABBCCBBCLASSIFICATION / REGRESSION(new) Fast Approximate NN (FLANN)(new) Extremely Random TreesCARTNaïve BayesMLP (Back propagation)Statistical Boosting, 4 flavorsRandom ForestsSVMFace Detector(Histogram matching)(Correlation)CLUSTERINGK-MeansEM(Mahalanobis distance)TUNING/VALIDATIONCross validationBootstrappingVariable importanceSampling methods44http://opencv.willowgarage.com
- 7. Accelerate the field by lowering the bar to computer vision
- 8. Find compelling uses for the increasing MIPS out in the market
- 9. Timeline:
- 10. Staffing:
- 11. Climbed in 1999 to average 7 first couple of years
- 12. Starting 2003 support declined between zero and one with exception of transferring the machine learning from manufacturing work I led (equivalent of 3 people).
- 13. Support to zero the couple of years before Willow.
- 14. 5 people over the last yearWillowBeta 1 Release, support for LinuxAlpha Release at CVPR’00Beta 2 ReleaseBeta 3 ReleaseBeta 4 ReleaseBeta 5 ReleaseOpenCV StartedRelease 1.0Release 1.1Release 2.01019992000200120032004200520062007200820092010200250Gary Bradski55
- 15. New Directory StructureRe-Organized in terms of processing pipelinesCode site: https://code.ros.org/gf/project/opencv/CoreCalibration, features, I/O, img processingMachine Learning, Obj. RecPython~2.5M downloads
- 16. OpenCV Conceptual StuctureUser ContribModulesPythonSSETBBGPUMPUObjectRecog.Features2dCalib3dStereoVOSLAMStitchingLuaOtherLanguagesffmpegimgprocML ,FLANNCOREHighGUI
- 17. OpenCV Tends Towards Real Timehttp://opencv.willowgarage.com
- 18. Software EngineeringWorks on: Linux, Windows, Mac OSLanguages: C++, Python, COnline documentation:Online reference manuals: C++, C and Python. We’ve been expanding Unit test codeWill soon standarize on cxx or Google’s test system.TEST COVERAGE:
- 19. LicenseBased on BSD license
- 20. Free for commercial or research use
- 21. In whole or in part
- 22. Does not force your code to be open
- 23. You need not contribute back
- 24. We hope you will contribute back, recent contribution, C++ wrapper class used for Google Street Maps** Thanks to Daniel FilipGary Bradski (c) 20081010Gary Bradski, 2009
- 25. Where is OpenCV Used?Google Maps, Google street view, Google Earth, BooksAcademic and Industry ResearchSafety monitoring (Dam sites, mines, swimming pools)Security systemsImage retrievalVideo searchStructure from motion in moviesMachine vision factory production inspection systemsRobotics Well over 2M downloads2M downloadsScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 2005
- 26. Useful OpenCV Links1212OpenCV Wiki:http://opencv.willowgarage.com/wikiOpenCV Code Repository:svn co https://code.ros.org/svn/opencv/trunk/opencvNew Book on OpenCV:http://oreilly.com/catalog/9780596516130/Or, direct from Amazon:http://www.amazon.com/Learning-OpenCV-Computer-Vision-Library/dp/0596516134Code examples from the book:http://examples.oreilly.com/9780596516130/Documentationhttp://opencv.willowgarage.com/documentation/index.htmlUser Group (39717 members):http://tech.groups.yahoo.com/group/OpenCV/joinGary Bradski, 2009
- 27. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 200913
- 28. Main Structures
- 34. Histogram
- 35. I/O
- 38. GUI (“HighGUI”)
- 39. Camera Calibration, Pose, Stereo
- 41. samples/c27In ...\opencv_incomp\samples\cbgfg_codebook.cpp - Use of a image value codebook for background detection for collectin objectsbgfg_segm.cpp - Use of a background learning engineblobtrack.cpp - Engine for blob tracking in imagescalibration.cpp - Camera Calibrationcamshiftdemo.c - Use of meanshift in simple color trackingcontours.c - Demonstrates how to compute and use object contoursconvert_cascade.c - Change the window size in a recognition cascadeconvexhull.c - Find the convex hull of an objectdelaunay.c - Triangulate a 2D point clouddemhist.c - Show how to use histograms for recognitiondft.c - Discrete fourier transformdistrans.c - distance map from edges in an imagedrawing.c - Various drawing functionsedge.c - Edge detectionfacedetect.c - Face detection by classifier cascadeffilldemo.c - Flood filling demofind_obj.cpp - Demo use of SURF featuresfitellipse.c - Robust elipse fittinghoughlines.c - Line detectionimage.cpp - Shows use of new image class, CvImage();inpaint.cpp - Texture infill to repair imagerykalman.c - Kalman filter for trackignkmeans.c - K-Meanslaplace.c - Convolve image with laplacian. letter_recog.cpp - Example of using machine learning Boosting, Backpropagation (MLP) and Random forestslkdemo.c - Lukas-Canada optical flowminarea.c - For a cloud of points in 2D, find min bounding box and circle. Shows use of Cv_SEQmorphology.c - Demonstrates Erode, Dilate, Open, Closemotempl.c - Demonstrates motion templates (orthogonal optical flow given silhouettes)mushroom.cpp - Demonstrates use of decision trees (CART) for recognitionpyramid_segmentation.c - Color segmentation in pyramidsquares.c - Uses contour processing to find squares in an imagestereo_calib.cpp - Stereo calibration, recognition and disparity map computationwatershed.cpp - Watershed transform demo.
- 42. samples/C++28
- 43. Samples/python
- 44. Book ExamplesGary Bradski, 200930ch2_ex2_1.cpp Load image from disk ch2_ex2_2.cpp Play video from diskch2_ex2_3.cpp Add a slider controlch2_ex2_4.cpp Load, smooth and dsiplay imagech2_ex2_5.cpp Pyramid down samplingch2_ex2_6.cpp CvCanny edge detectionch2_ex2_7.cpp Pyramid down and Canny edgech2_ex2_8.cpp Above program simplifiedch2_ex2_9.cpp Play video from camera or filech2_ex2_10.cpp Read and write video, do Logpolarch3_ex3_1.txt Matrix structurech3_ex3_2.txt Matrix creation and releasech3_ex3_3.cpp Create matrix from data listch3_ex3_4.cpp Accessing matrix data CV_MAT_ELEM()ch3_ex3_5.cpp Setting matrix CV_MAT_ELEM_PTR()ch3_ex3_6.txt Pointer access to matrix data ch3_ex3_7.txt Image and Matrix Element access functionsch3_ex3_8.txt Setting matrix or image elementsch3_ex3_9.cpp Summing all elements in 3 channel matrixch3_ex3_10.txt IplImage Headerch3_ex3_11.cpp Use of widthstepch3_ex3_12.cpp Use of image ROIch3_ex3_13.cpp Implementing an ROI using widthstepch3_ex3_14.cpp Alpha blending examplech3_ex3_15.cpp Saving and loading a CvMatch3_ex3_16.txt File storage democh3_ex3_17.cpp Writing configuration files as XMLch3_ex3_19.cpp Reading an XML filech3_ex3_20.cpp How to check if IPP acceleration is on
- 45. Book ExamplesGary Bradski, 200931ch4_ex4_1.cpp Use a mouse to draw boxesch4_ex4_2.cpp Use a trackbar as a buttonch4_ex4_3.cpp Finding the video codecch5_ex5_1.cpp Using CvSeq ch5_ex5_2.cpp cvThreshold examplech5_ex5_3.cpp Combining image planesch5_ex5_4.cpp Adaptive threshioldingch6_ex6_1.cpp cvHoughCircles examplech6_ex6_2.cpp Affine transformch6_ex6_3.cpp Perspective transformch6_ex6_4.cpp Log-Polar conversionch6_ex6_5.cpp 2D Fourier Transformch7_ex7_1.cpp Using histogramsch7_ex7_2.txt Earth Mover’s Distance interfacech7_ex7_3_expanded.cpp Earth Mover’s Distance set upch7_ex7_4.txt Using Earth Mover’s Distancech7_ex7_5.cpp Template matching /Cross Corr.ch7_ex7_5_HistBackProj.cpp Back projection of histogramsch8_ex8_1.txt CvSeq structurech8_ex2.cpp Contour structurech8_ex8_2.cpp Finding contoursch8_ex8_3.cpp Drawing contours
- 46. Book ExamplesGary Bradski, 200932ch9_ex9_1.cpp Sampling from a line in an imagech9_watershed.cpp Image segmentation using Watershed transformch9_AvgBackground.cpp Background model using an average imagech9_backgroundAVG.cpp Background averaging using a codebook compared to just an averagech9_backgroundDiff.cpp Use the codebook method for doing background differencingch9_ClearStaleCB_Entries.cpp Refine codebook to eliminate stale entriescv_yuv_codebook.cpp Core code used to design OpenCV codebookch10_ex10_1.cpp Optical flow using Lucas-Kanade in an image pyramidch10_ex10_1b_Horn_Schunck.cpp Optical flow based on Horn-Schunck block matchingch10_ex10_2.cpp Kalman filter example codech10_motempl.cpp Using motion templates for segmenting motion.ch11_ex11_1.cpp Camera calibration using automatic chessboard finding using a camerach11_ex11_1_fromdisk.cpp Doing the same, but read from diskch11_chessboards.txt List of included chessboards for calibration from disk examplech12_ex12_1.cpp Creating a bird’s eye view of a scene using homographych12_ex12_2.cpp Computing the Fundamental matrix using RANSACch12_ex12_3.cpp Stereo calibration, rectification and correspondencech12_ex12_4.cpp 2D robust line fittingch12_list.txt List of included stereo L+R image pair datach13_dtree.cpp Example of using a decision treech13_ex13_1.cpp Using k-meansch13_ex13_2.cpp Creating and training a decision tree ch13_ex13_3.cpp Training using statistical boostingch13_ex13_4.cpp Face detection using Viola-Jonescvx_defs.cpp Some defines for use with codebook segmentatio
- 47. Python Face Detector Node: 133The Setup#!/usr/bin/python"""This program is demonstration python ROS Node for face and object detection using haar-like features.The program finds faces in a camera image or video stream and displays a red box around them. Python implementation by: Roman Stanchak, James Bowman"""import roslibroslib.load_manifest('opencv_tests')import sysimport osfrom optparse import OptionParserimport rospyimport sensor_msgs.msgfrom cv_bridge import CvBridgeimport cv# Parameters for haar detection# From the API:# The default parameters (scale_factor=2, min_neighbors=3, flags=0) are tuned # for accurate yet slow object detection. For a faster operation on real video # images the settings are: # scale_factor=1.2, min_neighbors=2, flags=CV_HAAR_DO_CANNY_PRUNING, # min_size=<minimum possible face sizemin_size = (20, 20)image_scale = 2haar_scale = 1.2min_neighbors = 2haar_flags = 0
- 48. Python Face Detector Node: 234The Coreif __name__ == '__main__': pkgdir = roslib.packages.get_pkg_dir("opencv2") haarfile = os.path.join(pkgdir, "opencv/share/opencv/haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt.xml") parser = OptionParser(usage = "usage: %prog [options] [filename|camera_index]") parser.add_option("-c", "--cascade", action="store", dest="cascade", type="str", help="Haar cascade file, default %default", default = haarfile) (options, args) = parser.parse_args() cascade = cv.Load(options.cascade) br = CvBridge() def detect_and_draw(imgmsg): img = br.imgmsg_to_cv(imgmsg, "bgr8") # allocate temporary images gray = cv.CreateImage((img.width,img.height), 8, 1) small_img = cv.CreateImage((cv.Round(img.width / image_scale), cv.Round (img.height / image_scale)), 8, 1) # convert color input image to grayscale cv.CvtColor(img, gray, cv.CV_BGR2GRAY) # scale input image for faster processing cv.Resize(gray, small_img, cv.CV_INTER_LINEAR) cv.EqualizeHist(small_img, small_img) if(cascade): faces = cv.HaarDetectObjects(small_img, cascade, cv.CreateMemStorage(0), haar_scale, min_neighbors, haar_flags, min_size) if faces: for ((x, y, w, h), n) in faces: # the input to cv.HaarDetectObjects was resized, so scale the # bounding box of each face and convert it to two CvPoints pt1 = (int(x * image_scale), int(y * image_scale)) pt2 = (int((x + w) * image_scale), int((y + h) * image_scale)) cv.Rectangle(img, pt1, pt2, cv.RGB(255, 0, 0), 3, 8, 0) cv.ShowImage("result", img) cv.WaitKey(6) rospy.init_node('rosfacedetect') image_topic = rospy.resolve_name("image") rospy.Subscriber(image_topic, sensor_msgs.msg.Image, detect_and_draw) rospy.spin()
- 49. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 200935
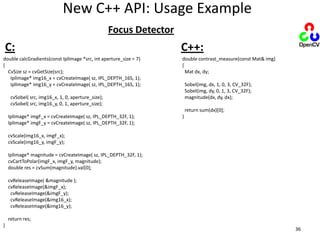
- 50. New C++ API: Usage ExampleFocus DetectorC:C++:double calcGradients(const IplImage *src, int aperture_size = 7){ CvSize sz = cvGetSize(src); IplImage* img16_x = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_16S, 1); IplImage* img16_y = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_16S, 1); cvSobel( src, img16_x, 1, 0, aperture_size); cvSobel( src, img16_y, 0, 1, aperture_size); IplImage* imgF_x = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); IplImage* imgF_y = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); cvScale(img16_x, imgF_x); cvScale(img16_y, imgF_y); IplImage* magnitude = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); cvCartToPolar(imgF_x, imgF_y, magnitude); double res = cvSum(magnitude).val[0]; cvReleaseImage( &magnitude ); cvReleaseImage(&imgF_x); cvReleaseImage(&imgF_y); cvReleaseImage(&img16_x); cvReleaseImage(&img16_y); return res;}double contrast_measure(const Mat& img){ Mat dx, dy; Sobel(img, dx, 1, 0, 3, CV_32F); Sobel(img, dy, 0, 1, 3, CV_32F); magnitude(dx, dy, dx); return sum(dx)[0];}36
- 51. Pyramid/* * Make an image pyramid with levels of arbitrary scale reduction (0,1) * M Input image * reduction Scaling factor 1>reduction>0 * levels How many levels of pyramid * pyr std vector containing the pyramid * sz The width and height of blurring kernel, DEFAULT 3 * sigma The standard deviation of the blurring Gaussian DEFAULT 0.5 * RETURNS Number of levels achieved */int buildGaussianPyramid(const Mat &M, double reduction, int levels, vector<Mat> &pyr, int sz = 3, float sigma = 0.5){ if(M.empty()) return 0; pyr.clear(); //Clear it up if((reduction <= 0.0)||(reduction >=1.0)) return 0; Mat Mblur, Mdown = M; pyr.push_back(Mdown); Size ksize = Size(sz,sz); int L=1; for(; L<=levels; ++L) { if((reduction*Mdown.rows) <= 1.0 || (reduction*Mdown.cols) <= 1.0) break; GaussianBlur(Mdown,Mblur, ksize, sigma, sigma); resize(Mblur,Mdown, Size(), reduction, reduction); pyr.push_back(Mdown); } return L;}
- 52. Laplacian/* * Make an image pyramid with levels of arbitrary scale reduction (0,1) * M Input image * reduction Scaling factor 1>reduction>0 * levels How many levels of pyramid * pyr std vector containing the pyramid * int sz The width and height of blurring kernel, DEFAULT 3 * float sigma The standard deviation of the blurring Gaussian DEFAULT 0.5 * RETURNS Number of levels achieved */int buildGaussianPyramid(const Mat &M, double reduction, int levels, vector<Mat> &pyr, int sz = 3, float sigma = 0.5){if(M.empty()) return 0; pyr.clear(); //Clear it up if((reduction <= 0.0)||(reduction >=1.0)) return 0; Mat Mblur, Mdown = M; pyr.push_back(Mdown); Size ksize = Size(sz,sz); int L=1; for(; L<=levels; ++L) { if((reduction*Mdown.rows) <= 1.0 || (reduction*Mdown.cols) <= 1.0) break; GaussianBlur(Mdown,Mblur, ksize, sigma, sigma); resize(Mblur,Mdown, Size(), reduction, reduction); pyr.push_back(Mdown); } return L;}
- 53. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 200939
- 55. Distance TransformDistance field from edges of objectsFlood Filling41
- 56. Hough TransformGary Bradski, Adrian Kahler 200842
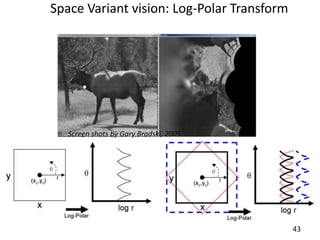
- 57. Space Variant vision: Log-Polar TransformScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 200543
- 58. Scale SpaceChart by Gary Bradski, 2005void cvPyrUp( IplImage* src, IplImage* dst, IplFilter filter = IPL_GAUSSIAN_5x5);void cvPyrDown( IplImage* src, IplImage* dst, IplFilter filter = IPL_GAUSSIAN_5x5);44
- 59. ThresholdsScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 200545
- 60. Histogram EqualizationScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 200546
- 61. Contours 47
- 62. Morphological Operations ExamplesMorphology - applying Min-Max. Filters and its combinationsDilatation IBOpening IoB= (IB)BErosion IBImage IClosing I•B= (IB)BTopHat(I)= I - (IB)BlackHat(I)= (IB) - IGrad(I)= (IB)-(IB)
- 63. Image textures Inpainting:Removes damage to images, in this case, it removes the text.
- 65. Here: WatershedScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 20055050
- 66. Recent Algorithms: GrabCutGraph Cut based segmentationImages by Gary Bradski, © 201051
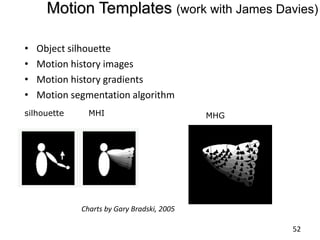
- 67. Motion Templates (work with James Davies)Object silhouette
- 70. Motion segmentation algorithmsilhouetteMHIMHGCharts by Gary Bradski, 200552
- 71. Segmentation, Motion TrackingandGesture RecognitionMotionSegmentationMotionSegmentationPoseRecognitionGestureRecognitionScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 2005
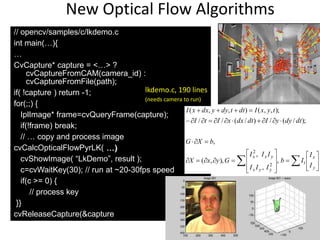
- 72. New Optical Flow Algorithms// opencv/samples/c/lkdemo.cint main(…){…CvCapture* capture = <…> ? cvCaptureFromCAM(camera_id) : cvCaptureFromFile(path);if( !capture ) return -1;for(;;) { IplImage* frame=cvQueryFrame(capture); if(!frame) break; // … copy and process imagecvCalcOpticalFlowPyrLK( …) cvShowImage( “LkDemo”, result ); c=cvWaitKey(30); // run at ~20-30fps speed if(c >= 0) { // process key }}cvReleaseCapture(&capture);} lkdemo.c, 190 lines(needs camera to run)
- 73. Tracking with CAMSHIFTControl game with headScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 2005
- 74. ProjectionsScreen shots by Gary Bradski, 2005
- 75. Stereo … Depth from TriangulationInvolved topic, here we will just skim the basic geometry.Imagine two perfectly aligned image planes:Depth “Z” and disparity “d” are inversly related:57
- 76. StereoIn aligned stereo, depth is from similar triangles:Problem: Cameras are almost impossible to alignSolution: Mathematically align them:58All: Gary Bradski and Adrian Kaehler: Learning OpenCV
- 77. Stereo RectificationAlgorithm steps are shown at right:Goal:Each row of the image contains the same world points“Epipolar constraint”Result: Epipolar alignment of features:59All: Gary Bradski and Adrian Kaehler: Learning OpenCV
- 78. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 200960
- 79. New Object Rec. Pipelines ComingObject RecRecog. FusionPoseAttentionPose RefineObject TrainInput Image list
- 81. Score
- 82. Segment.
- 84. Score list
- 86. Segment.
- 88. Depth list
- 89. Segment.Output PoseInput Image list
- 90. Depth listOutputMaskInput Image list
- 91. Depth list
- 92. Segment.Output PoseInput Image list
- 93. Depth listOutputModelsRecognitionHand tracking + Gradient Histogram:
- 94. Features2d contentsDetectors availableSIFTSURFFASTSTARMSERGFTT (Good Features To Track)Descriptors availableSIFTSURFOne wayCalonder(under construction)FERNS
- 95. Detector interfaceclass CV_EXPORTS FeatureDetector{public:void detect( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const {detectImpl( image, mask, keypoints ); } virtual void read(const FileNode& fn) {}; virtual void write(FileStorage& fs) const {};protected:virtual void detectImpl( const Mat& image, const Mat& mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints ) const = 0;static void removeInvalidPoints( const Mat& mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints );};
- 96. Creating a detectorStaticallySurfFeatureDetector detector;Or by using class factory:cv::Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = createDetector(“SURF”);
- 97. Running detectorSurfFeatureDetector detector;Mat img = imread(“test.jpg”);std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;detector.compute(img, keypoints);
- 98. Descriptor interfacesFor descriptors that can be represented as vectors in multidimensional space: DescriptorExtractor and DescriptorMatcherMore general interface (one way, decision-tree-based descriptors): GenericDescriptorMatch
- 99. DescriptorExtractorPtr<FeatureDetector> detector = createDetector( “FAST” ); Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptorExtractor = createDescriptorExtractor( “SURF );Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> descriptorMatcher = createDescriptorMatcher( "BruteForce" );vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;detector->detect( img1, keypoints );Mat descriptors;descriptorExtractor->compute( img, keypoints, descriptors );
- 100. Descriptor MatcherdescriptorExtractor->compute( img1, keypoints1, descriptors1 );descriptorExtractor->compute( img2, keypoints2, descriptors2 );vector<int> matches;descriptorMatcher->add( descriptors2 );descriptorMatcher->match( descriptors1, matches );
- 101. Visualize keypointsMat img_points;drawKeypoints(img, keypoints, img_points);namedWindow(“keypoints”, 1);imshow(“keypoints”, img_points);waitKey();
- 102. Visualize matchesMat img_matches;drawMatches(img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, img_matches);namedWindow(“matches”, 1);imshow(“matches”, img_matches);waitKey();
- 103. Detector testbenchMeasures of detector repeatability are taken from K.Mikolajczyk, CordeliaSchmid, “Scale & Affine Invariant Interest Point Detectors”, IJCV 60(1), 63–86, 2004.K.Mikolajczyk et al, A Comparison of Affine Region Detectors, IJCV 65(1/2):43-72, 2005.Test images are taken from http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/data-aff.htmlTestbench is located in opencv_extra/testdata/cv/detectors_descriptors_evaluation/detectorsDescriptor testbench is on the way
- 104. Examples of testbench output
- 105. Running the sampleDownload OpenCV from TBD linkCompile Run matcher_simple: bin/matcher_simple ../../opencv/samples/c/box.png ../../opencv/samples/c/box_in_scene.pngSelect a detector that gives the maximum number of keypointsSwitch SIFT and SURF descriptors
- 106. Calculating inliers (planar objects case)Detect keypointsFind matches using descriptorsCalculate best homographyFilter outliersRun bin/descriptor_extractor_matcher SURF SURF ../../opencv/samples/c/box.png ../../opencv/samples/c/box_in_scene.png 3
- 107. The last parameter is the reprojection threshold for ransacFeatures Use: HomographyIf you have a known planar object on the ground plane, you can use it to map any other ground pt in the image to its (X,Y,Z) point on the groundGary Bradski, CS223A, Into to Robotics76We used this in the DARPA Grand Challenge to map the image road segmentation to a bird’s eye view obsticle map:Parking a robotgetPerspectiveTransform(objPts,imgPts,H); //This learns ground_pts->image_pts invert(H,H_invt); //So we need to invert this to get img_pts->ground_ptsGary Bradski and Adrian Kaehler: Learning OpenCVGary Bradski and Adrian Kaehler: Learning OpenCV
- 108. Robot Race
- 110. OutlineOpenCV OverviewCheatsheetSimple ProgramsTourFeatures2DObj RecGary Bradski, 200979
- 111. Milestone 2:Gary Bradski80Milestone 2Wim Meeussen*, Melonee Wise, Stuart Glaser, Sachin Chitta, Conor McGann, Patrick Mihelich, Eitan Marder-Eppstein, Marius Constantin Muja, Victor Eruhimov, Tully Foote, john hsu, Radu Bogdan Rusu, Bhaskara Marthi, Gary Bradski, Kurt Konolige, Brian Gerkey, Eric BergerAutonomous Door Opening and Plugging In with a Personal Robot, ICRA 2010
- 112. Binary Gradient GridWe organize gradients in a way that allows extremely rapid searchThis allows us to directly scale recognition with compute cycles(Similar to Stefan Hinterstoisser’s DOT at this conference)RawGradient GridRecognizedGary Bradski, 2010
- 113. 82Use of BiGG for ManipulationCS 324: Perception for Manipulation
- 115. Working on: Object Database> 200 ObjectsTextured, transparent, opaque, translucent3D ModelsStereo depth mapsAnnotated with grasping pointsGary Bradski84
- 116. Working on: Computer Vision challengesThere are many data set challenges:PASCAL VOC, CalTech101CalTech256 …CVPR semantic robot vision challenge All of these explore the “False Positive” region of the ROC curveGary Bradski, 200985True PositiveFalse Positive
- 117. I want to publically establish solved problems in visionThis corresponds to exploring the True Positive part of the curveAnd push it to: “solved” for increasing classes of data:Gary Bradski, 200986Working on: Computer Vision challengesTrue PositiveFalse PositiveTrue PositiveFalse PositiveStart with “easy” problems, advance from there
- 118. Working on: Solved Problems in Vision ContestGive people 3D ModelsLots of imageryStereo scansLimited object types (Lambertian, rigid)Can the community solve the recognition problem at 100%?If yes, declare victory, post code and move onIf no, try again next timeGary Bradski87
- 119. Working on: FeaturesVery fast, binarized grid of gradient featuresTogether with branch and boundOcclusion weighting over the grid.Circular Foveal/log-polar sampling gridPairs of these for recognition and pose (“Barbells”)Have ideas about using this for Transparent objects(captures the object in a grid) Flexible objects (pairs of barbells)Sound perception (using a spectrogram)Gary Bradski88
- 120. Working on: Scalable Machine learning. Philosophy:Engineer algorithm to have properties that you need:Features can drop outFeatures can go away permanently (discontinue a sensor)New features can appear (new sensor)Massive data, want online response, offline refinementIntrinsically DistributedAnytime, but with guarenteesPossibly useExtremely Random Trees (due to distributed and independence)Vocabulary treeFast approximate k-means.Question: Do like Google and have each server node “own” as many objects as it can handle in a given response time? Or completely distribute?Gary Bradski89










































![Python Face Detector Node: 234The Coreif __name__ == '__main__': pkgdir = roslib.packages.get_pkg_dir("opencv2") haarfile = os.path.join(pkgdir, "opencv/share/opencv/haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt.xml") parser = OptionParser(usage = "usage: %prog [options] [filename|camera_index]") parser.add_option("-c", "--cascade", action="store", dest="cascade", type="str", help="Haar cascade file, default %default", default = haarfile) (options, args) = parser.parse_args() cascade = cv.Load(options.cascade) br = CvBridge() def detect_and_draw(imgmsg): img = br.imgmsg_to_cv(imgmsg, "bgr8") # allocate temporary images gray = cv.CreateImage((img.width,img.height), 8, 1) small_img = cv.CreateImage((cv.Round(img.width / image_scale), cv.Round (img.height / image_scale)), 8, 1) # convert color input image to grayscale cv.CvtColor(img, gray, cv.CV_BGR2GRAY) # scale input image for faster processing cv.Resize(gray, small_img, cv.CV_INTER_LINEAR) cv.EqualizeHist(small_img, small_img) if(cascade): faces = cv.HaarDetectObjects(small_img, cascade, cv.CreateMemStorage(0), haar_scale, min_neighbors, haar_flags, min_size) if faces: for ((x, y, w, h), n) in faces: # the input to cv.HaarDetectObjects was resized, so scale the # bounding box of each face and convert it to two CvPoints pt1 = (int(x * image_scale), int(y * image_scale)) pt2 = (int((x + w) * image_scale), int((y + h) * image_scale)) cv.Rectangle(img, pt1, pt2, cv.RGB(255, 0, 0), 3, 8, 0) cv.ShowImage("result", img) cv.WaitKey(6) rospy.init_node('rosfacedetect') image_topic = rospy.resolve_name("image") rospy.Subscriber(image_topic, sensor_msgs.msg.Image, detect_and_draw) rospy.spin()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvpr2010opensourcevisionsoftwareintroandtrainingpart-vopencvandros-unknown-unknown-2010-110515235222-phpapp02/85/Cvpr2010-open-source-vision-software-intro-and-training-part-v-open-cv-and-ros-unknown-unknown-2010-48-320.jpg)

![New C++ API: Usage ExampleFocus DetectorC:C++:double calcGradients(const IplImage *src, int aperture_size = 7){ CvSize sz = cvGetSize(src); IplImage* img16_x = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_16S, 1); IplImage* img16_y = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_16S, 1); cvSobel( src, img16_x, 1, 0, aperture_size); cvSobel( src, img16_y, 0, 1, aperture_size); IplImage* imgF_x = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); IplImage* imgF_y = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); cvScale(img16_x, imgF_x); cvScale(img16_y, imgF_y); IplImage* magnitude = cvCreateImage( sz, IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); cvCartToPolar(imgF_x, imgF_y, magnitude); double res = cvSum(magnitude).val[0]; cvReleaseImage( &magnitude ); cvReleaseImage(&imgF_x); cvReleaseImage(&imgF_y); cvReleaseImage(&img16_x); cvReleaseImage(&img16_y); return res;}double contrast_measure(const Mat& img){ Mat dx, dy; Sobel(img, dx, 1, 0, 3, CV_32F); Sobel(img, dy, 0, 1, 3, CV_32F); magnitude(dx, dy, dx); return sum(dx)[0];}36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvpr2010opensourcevisionsoftwareintroandtrainingpart-vopencvandros-unknown-unknown-2010-110515235222-phpapp02/85/Cvpr2010-open-source-vision-software-intro-and-training-part-v-open-cv-and-ros-unknown-unknown-2010-50-320.jpg)