Cyber Security PPT and how to be aware from hackers
- 1. Ms.Dipali A. Awasekar, (Assistant Professor) CSI Cyber Security Influencer Awardee Walchand Institute of Technology , Solapur. Maharashtra – India Cyber Security Awareness: Protecting Yourself in the Digital Age
- 2. Learning Objectives End of this session, you will be able to: • Learn what cybercrime is and appreciate the importance of cybercrime as a topic. • Understand the different types cybercrime. • Understand the difference between cybercrime and cyberfraud. • Learn about different types of cybercriminals and the motives behind them • Get an overview of cybercrime scenario in India and global • Understand legal perspective on cybercrime.
- 3. 1.1 INTRODUCTION • The internet in India is growing rapidly. It has given rise to new opportunities in every field we can think of be it entertainment, business, sports or education. • There’re two sides to a coin. Internet also has it’s own disadvantages is Cyber crime- illegal activity committed on the internet.
- 4. Alternative definitions for cybercrime • Any illegal act where a special knowledge of computer technology is essential for its perpetration, investigation or prosecution • Any traditional crime that has acquired a new dimension or order of magnitude through the aid of a computer, and abuses that have come into being because of computers • Any financial dishonesty that takes place in a computer environment. • Any threats to the computer itself, such as theft of hardware or software, sabotage and demands for ransom
- 5. Another definition • “Cybercrime (computer crime) is any illegal behavior, directed by means of electronic operations, that target the security of computer systems and the data processed by them”. • Hence cybercrime can sometimes be called as computer-related crime, computer crime, E-crime, Internet crime, High-tech crime….
- 6. • A crime committed using a computer and the internet to steal a person’s identity(identity theft) or sell contraband or stalk victims or disrupt operations with malevolent programs. • Crimes completed either on or with a computer • Any illegal activity through the Internet or on the computer. • All criminal activities done using the medium of computers, the Internet, cyberspace and the WWW.
- 7. • Cybercrime refers to the act of performing a criminal act using cyberspace as communication vehicle. • Two types of attacks are common: ⚬Techno- crime : Active attack ■ Techno Crime is the term used by law enforcement agencies to denote criminal activity which uses (computer) technology, not as a tool to commit the crime, but as the subject of the crime itself. Techno Crime is usually pre-meditated and results in the deletion, corruption, alteration, theft or copying of data on an organization's systems. ■ Techno Criminals will usually probe their prey system for weaknesses and will almost always leave an electronic 'calling card' to ensure that their pseudonym identity is known. ⚬Techno – vandalism: Passive attack ■ Techno Vandalism is a term used to describe a hacker or cracker who breaks into a computer system with the sole intent of defacing and or destroying its contents. ■ Techno Vandals can deploy 'sniffers' on the Internet to locate soft (insecure) targets and then execute a range of commands using a variety of protocols towards a range of ports. If this sounds complex - it is! The best weapon against such attacks is a firewall which will hide and disguise your organization's presence on the Internet.
- 9. 1.3 Cybercrime and information security • Lack of information security give rise to cybercrime • Cybersecurity: means protecting information, equipment, devices, computer, computer resource, communication device and information stored therein from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification or destruction.
- 10. 1.4 Who are Cybercriminals? • Are those who conduct acts such as: ⚬Child pornography ⚬Credit card fraud ⚬Cyberstalking ⚬Defaming another online ⚬Gaining unauthorized access to computer systems ⚬Ignoring copyrights ⚬Software licensing and trademark protection ⚬Overriding encryption to make illegal copies ⚬Software piracy ⚬Stealing another’s identity to perform criminal acts
- 11. Categorization of Cybercriminals • Type 1: Cybercriminals- hungry for recognition ⚬Hobby hackers ■ A person who enjoys exploring the limits of what is possible, in a spirit of playful cleverness. May modify hardware/ software ⚬IT professional(social engineering): ■ Ethical hacker ⚬Politically motivated hackers : ■ promotes the objectives of individuals, groups or nations supporting a variety of causes such as : Anti globalization, transnational conflicts and protest ⚬Terrorist organizations ■ Cyberterrorism ■ Use the internet attacks in terrorist activity ■ Large scale disruption of computer networks , personal computers attached to internet via viruses
- 12. Type 2: Cybercriminals- not interested in recognition ⚬Psychological perverts ■ Express sexual desires, deviates from normal behavior ■ Poonam panday ⚬Financially motivated hackers ■ Make money from cyber attacks ■ Bots-for-hire : fraud through phishing, information theft, spam and extortion ⚬State-sponsored hacking ■ Hacktivists ■ Extremely professional groups working for governments ■ Have ability to worm into the networks of the media, major corporations, defense departments
- 13. Type 3: Cybercriminals- the insiders ⚬Disgruntled or former employees seeking revenge ⚬Competing companies using employees to gain economic advantage through damage and/ or theft.
- 14. Motives behind cybercrime • Greed • Desire to gain power • Publicity • Desire for revenge • A sense of adventure • Looking for thrill to access forbidden information • Destructive mindset • Desire to sell network security services
- 15. 1.5 Classification of cybercrimes • Cybercrime against an individual • Cybercrime against property • Cybercrime against organization • Cybercrime against Society • Crimes emanating from Usenet newsgroup
- 16. 1. Cybercrime against an individual • Electronic mail spoofing and other online frauds • Phishing, spear phishing • spamming • Cyberdefamation • Cyberstalking and harassment • Computer sabotage • Pornographic offenses • passwordsniffing
- 17. 2.Cybercrime against property • Credit card frauds • Intellectual property( IP) crimes • Internet time theft
- 18. 3.Cybercrime against organization • Unauthorized accessing of computer • Password sniffing • Denial-of-service attacks • Virus attack/dissemination of viruses • E-Mail bombing/mail bombs • Salami attack/ Salami technique • Logic bomb • Trojan Horse • Data diddling • Industrial spying/ industrial espionage • Computer network intrusions • Software piracy
- 19. 4.Cybercrime against Society • Forgery • Cyberterrorism • Web jacking
- 20. 5.Crimes emanating from Usenet newsgroup • Usenet groups may carry very offensive, harmful, inaccurate material • Postings that have been mislabeled or are deceptive in another way • Hence service at your own risk
- 21. History of Usenet groups • In 1979 it was developed by two graduate student • s from Duke University in North Carolina (UNC) as a network that allowed users to exchange quantities of information too large for mailboxes • Usenet was designed to facilitate textual exchanges between scholars. • Slowly, the network structure adapted to allow the exchange of larger files such as videos or images.
- 22. Usenet groups as a “safe” place? • Usenet newsgroups constitute one o the largest source of child pornography available in cyberspace • This source useful for observing other types of criminal or particular activities: online interaction between pedophiles, adult pornographers and writers of pornographic stories. • Usenet for sharing illegal content
- 23. Criminal activity on Oracle USENET Newsgroups • This interesting SearchOracle article on Oracle security bloopers, we see the risks with engaging the unsavory inhabitants of the Oracle USENET newsgroup, a forum laced with profanity, pornography and, according to this note, criminal Oracle hackers: • “I subscribe to several Usenet groups so I can keep my skills current. Well, a few years ago a DBA needed some assistance and posted a question in which he shared his tnsnames.ora file and wondered why he could not connect to SQL*Plus with the following syntax: • sqlplus system/SecurePswd@prod • Almost immediately several people connected to this person’s production system and was able to fish around the system. Numerous people emailed the DBA back and pointed out that he just broadcasted to the world his production connection string and password. How crazy is that?”
- 24. E-Mail Spoofing • E-mail spoofing is the forgery of an e-mail header so that the message appears to have originated from someone or somewhere other than the actual source. • To send spoofed e-mail, senders insert commands in headers that will alter message information. • It is possible to send a message that appears to be from anyone, anywhere, saying whatever the sender wants it to say. • Thus, someone could send spoofed e-mail that appears to be from you with a message that you didn't write. • Classic examples of senders who might prefer to disguise the source of the e-mail include a sender
- 25. E-Mail Spoofing • Although most spoofed e-mail falls into the "nuisance" category and requires little action other than deletion, the more malicious varieties can cause serious problems and security risks. • For example, spoofed e-mail may purport to be from someone in a position of authority, asking for sensitive data, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other personal information -- any of which can be used for a variety of criminal purposes. • The Bank of America, eBay, and Wells Fargo are among the companies recently spoofed in mass spam mailings. • One type of e-mail spoofing, self-sending spam, involves messages that appear to be both to and from the recipient.
- 26. Spamming • People who create electronic spam : spammers • Spam is abuse of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately • Spamming may be ⚬E-Mail Spam ⚬Instant messaging spam ⚬Usenet group spam ⚬Web search engine spam ⚬Spam in blogs, wiki spam ⚬Online classified ads spam ⚬Mobile phone messaging spam ⚬Internet forum spam ⚬Junk fax spam ⚬Social networking spam ……..
- 27. Spamming • Spamming is difficult to control • Advertisers have no operating costs beyond the management of their mailing lists • It is difficult to hold senders accountable for their mass mailings • Spammers are numerous
- 28. Avoid the following web publishing techniques: • Repeating keywords • Use of keywords that do not relate to the content on the site • Use of fast meta refresh ⚬change to the new page in few seconds. • Redirection • IP cloaking: ⚬ including related links, information, and terms. • Use of colored text on the same color background • Tiny text usage • Duplication of pages with different URLs • Hidden links
- 29. Cyber defamation
- 30. Cyber defamation • The tort of cyber defamation is considered to be the act of defaming, insulting, offending or otherwise causing harm through false statements pertaining to an individual in cyberspace. • Example: someone publishes defamatory matter about someone on a website or sends an E-mail containing defamatory information to all friends of that person.
- 31. It may amount to defamation when- • If imputation to a deceased person would harm the reputation of that person, and is intended to be hurtful to the feelings of his family or other near relatives • An imputation is made concerning a company or an association or collection of people as such. • An imputation in the form of an alternative or expressed ironically • An imputation that directly or indirectly, in the estimation of others, lowers the moral or intellectual character of that person, or lowers the character of that person in respect of his caste or of his calling, or lowers the credit of that person.
- 32. Types of defamation • Libel : written defamation • Slander: oral defamation • The plaintiff must have to show that the defamatory statements were unlawful and would indeed injure the person’s or organization’s reputation. • When failed to prove, the person who made the allegations may still be held responsible for defamation.
- 33. Cyber defamation cases • In first case of cyber defamation in India (14 dec 2009), ⚬ the employee of a corporate defamed its reputation was sending derogatory and defamatory emails against the company and its managing directo ⚬ In this case the Court(delhi court) had restrained the defendant from sending derogatory, defamatory, obscene, vulgar, humiliating and abusive emails. ⚬The court passed as important ex-parte injunction. • In another case, accused posted obscene, defamatory and annoying message about a divorcee woman and also sent emails to the victim. ⚬ The offender was traced and was held guilty of offences under section 469, 509 IPC and 67 of IT Act, 2000. • Other defamation cases: ⚬ A malicious customer review by a competitor could destroy a small business. ⚬ A false accusation of adultery on a social networking site could destroy a marriage. ⚬ An allegation that someone is a “crook” could be read by a potential employer or business partner
- 34. Internet Time Theft • Occurs when an unauthorized person uses the Internet hours paid for by another person • Comes under hacking • The person get access to someone else’s ISP user ID and password, either by hacking or by gaining access to it by illegal means • And uses the internet without the other person’s knowledge • This theft can be identified when Internet time is recharged often, despite infrequent usage. • This comes under “identity theft”
- 35. Salami attack/ salami technique • Are used for committing financial crimes. • The alterations made are so insignificant that in a single case it would go completely unnoticed. • Example: a bank employee inserts a program, into the bank’s serve, that deduces a small amount from the account of every customer every month, • The unauthorised debit goes unnoticed by the customers, but the employee will make a sizable amount every month.
- 36. Salami attack: real life examples • Small “shavings” for Big gains! • The petrol pump fraud
- 37. Data diddling • Data diddling involves changing data input in a computer. • In other words, information is changed from the way it should be entered by a person typing in the data. • Usually, a virus that changes data or a programmer of the database or application has pre-programmed it to be changed. • For example, a person entering accounting may change data to show their account, or that or a friend or family member, is paid in full. By changing or failing to enter the information, they are able to steal from the company.
- 38. • To deal with this type of crime, a company must implement policies and internal controls. • This may include performing regular audits, using software with built-in features to combat such problems, and supervising employees.
- 39. Real life example: Doodle me Diddle • Electricity board in India have been victims to data diddling programs inserted when private parties computerized their systems.
- 40. Forgery • The act of forging something, especially the unlawful act of counterfeiting a document or object for the purposes of fraud or deception. • Something that has been forged, especially a document that has been copied or remade to look like the original. • Counterfeit currency notes, postage, revenue stamps, marksheets, etc., can be forged using sophisticated computers, printers and scanners.
- 41. Real life case: • Stamp Paper Scam – a racket that flourished on loopholes in the system • Abdul Karim Telgi, the mastermind of the multi-crore counterfeiting, printed fake stamp papers worth thousands of crores of rupees using printing machines purchased illegally with the help of some conniving officials of the Central Govt.’s Security Printing Press (India Security Press) located in Nasik. These fake stamp papers penetrated in more than 12 states through a widespread network of vendors who sold the counterfeits without any fear and earned hefty commissions. • Amount swindled Rs. 172 crores • Telgi is in jail serving his 13 plus 10 years term
- 42. Web jacking • This term is derived from the term hi jacking. • In these kinds of offences the hacker gains access and control over the web site of another. • He may even change the information on the site. • The first stage of this crime involves “password sniffing”. • The actual owner of the website does not have any more control over what appears on that website • This may be done for fulfilling political objectives or for money
- 43. Real life examples • recently the site of MIT (Ministry of Information Technology) was hacked by the Pakistani hackers and some obscene matter was placed therein. • Further the site of Bombay crime branch was also web jacked. • Another case of web jacking is that of the ‘gold fish’ case. In this case the site was hacked and the information pertaining to gold fish was changed.
- 44. Industrial spying/ Industrial Espionage • Industrial espionage is the covert and sometimes illegal practice of investigating competitors to gain a business advantage. • The target of investigation might be a trade secret such as a proprietary product specification or formula, or information about business plans. • In many cases, industrial spies are simply seeking any data that their organization can exploit to its advantage.
- 45. Real life case • A Chinese Trojan horse email campaign targeted some 140 senior Israeli defense corporation employees (2013) involved in highly classified, sensitive security projects. • The email was made to appear as if it came from a known German company that regularly works with the Israeli defense industry. • However, it turned out to contain a Trojan horse, which, according to the report, attempted to funnel information from the recipients' computers. • The Trojan horse was noticed by computer defense systems and shut down. • The defense establishment then realized how many Israelis received the email, and reportedly tracked the malicious program down to Chinese defense industries. • The incident led security companies to reiterate to employees computer security guidelines.
- 46. Hacking Every act committed toward breaking into a computer and/ or network is hacking. Purpose • Greed • Power • Publicity • Revenge • Adventure • Desire to access forbidden information • Destructive mindset
- 47. History of hacking • hacking is any technical effort to manipulate the normal behavior of network connections and connected systems. • A hacker is any person engaged in hacking. • The term "hacking" historically referred to constructive, clever technical work that was not necessarily related to computer systems. • M.I.T. engineers in the 1950s and 1960s first popularized the term and concept of hacking. • the so-called "hacks" perpetrated by these hackers were intended to be harmless technical experiments and fun learning activities. • Later, outside of M.I.T., others began applying the term to less honorable pursuits. for example, several hackers in the U.S. experimented with methods to modify telephones for making free long-distance calls over the phone network illegally. • As computer networking and the Internet exploded in popularity, data networks became by far the most common target of hackers and hacking.
- 48. Hacking vs. Cracking • Malicious attacks on computer networks are officially known as cracking , • while hacking truly applies only to activities having good intentions. • Most non-technical people fail to make this distinction, however. • Outside of academia, its extremely common to see the term "hack" misused and be applied to cracks as well.
- 49. There are 3 types of modern hackers • Black Hats: Criminal Hackers. ⚬Possess desire to destruction ⚬Hack for personal monetary gains : Stealing credit card information, transferring money from various bank accounts to their own account, extort money from corporate giant by threatening. • White Hats: Ethical Hackers. ⚬Network Security Specialist. • Grey Hats: Deals in both of the above (jack of all trades, master of none).
- 50. Real life case:dec 2009 NASA site hacked via SQL Injection • Two NASA sites recently were hacked by an individual wanting to demonstrate that the sites are susceptible to SQL injection. • The websites for NASA's Instrument Systems and Technology Division and Software Engineering Division were accessed by a researcher, who posted to his blog screen shots taken during the hack. • The researcher, using the alias "c0de.breaker," used SQL injection to hijack the sites. • SQL injection is an attack process where a hacker adds additional SQL code commands to a page request and the web server then tries to execute those commands within the backend database • The NASA hack yielded the credentials of some 25 administrator accounts. • The researcher also gained access to a web portal used for managing and editing those websites. • In this particular case, the researcher found the vulnerabilities, made NASA aware of them, then published findings after the websites had been fixed. • An attacker, however, could have tried to use that web server as an entry point into other systems NASA might control or edit the content of the
- 51. Nadya Suleman’s Website Hacked, feb 2009
- 52. The story.. • LOS ANGELES, CA – Octuplet mom Nadya Suleman launched a website to solicit donations for her family, but it was immediately hacked by a group of vigilante mothers! • The website originally featured photos of all eight octuplets, a thank you note from Suleman, images of children’s toys and a large donation button for viewers to send money through. Suleman also provided an address where people can send items such as diapers and formula. • Suleman was perhaps not prepared for the backlash she was to receive, as the site was hacked and brought down within hours. The original homepage
- 53. • The site was tagged by the famous hacker group MOD, also known as the Mothers of Disappointment. The mysterious group has a history of attacking personal sites they disapprove of, including Britney Spears when she infamously hung dry her sons on a clothes line after a bath, and Angelina Jolie for being Angelina Jolie. • Weekly World News could not reach any members for comment, however reporters did receive a short note from an anonymous e-mail address: • mod will not tolerate the selfish acts of bad parenting we will remain true to our mission despite any setbacks viva la maternity (call your mother, she misses you) • The site has since been restored, and Suleman’s PR
- 54. Online frauds • Fraud that is committed using the internet is “online fraud.” Online fraud can involve financial fraud and identity theft. • Online fraud comes in many forms. ⚬ viruses that attack computers with the goal of retrieving personal information, to email schemes that lure victims into wiring money to fraudulent sources, ⚬ “phishing” emails that purport to be from official entities (such as banks or the Internal Revenue Service) that solicit personal information from victims to be used to commit identity theft, ⚬ to fraud on online auction sites (such as Ebay) where perpetrators sell fictional goods. ⚬E-Mail spoofing to make the user to enter the personal information : financial fraud ⚬Illegal intrusion: log-in to a computer illegally by having previously obtained actual password. Creates a new identity fooling the computer that the hacker is the genuine operator. Hacker commits innumerable number of frauds.
- 55. Pornographic offenses: Child pornography • Means any visual depiction, including but not limited to the following: • Any photograph that ca be considered obscene and/ or unsuitable for the age of child viewer. • Film ,video, picture; • Obscene Computer generated image or picture
- 56. How do they Operate • Pedophiles use false identity to trap the children/teenagers • Pedophiles contact children/teens in various chat rooms which are used by children/teen to interact with other children/teen. • Befriend the child/teen. • Extract personal information from the child/teen by winning his confidence. • Gets the e-mail address of the child/teen and starts making contacts on the victims e-mail address as well. • Starts sending pornographic images/text to the victim including child pornographic images in order to help child/teen shed his inhibitions so that a feeling is created in the mind of the victim that what is being fed to him is normal and that everybody does it. • Extract personal information from child/teen • At the end of it, the pedophile set up a meeting with the child/teen out of the house and then drag him into the net to further sexually assault him or to use him as a sex object.
- 57. Software piracy • Theft of software through the illegal copying of genuine programs or the counterfeiting and distribution of products intended to pass for the original. • End-user copying • Hard disk loading with illicit means • Counterfeiting • Illegal downloads from internet
- 58. Buying Pirated software have a lot to lose: • Getting untested software that may have been copied thousands of times. • Potentially contain hard-ware infecting viruses • No technical support in case of software failure • No warranty protection • No legal right to use the product
- 59. Computer sabotage • Computer sabotage involves deliberate attacks intended to disable computers or networks for the purpose of disrupting commerce, education and recreation for personal gain, committing espionage, or facilitating criminal conspiracie. • Through viruses, worms, logic bombs • Chernobyl virus ■The Chernobyl virus is a computer virus with a potentially devastating payload that destroys all computer data when an infected file is executed., • Y2K virus ⚬Y2K bug, also called Year 2000 bug or Millennium Bug, a problem in the coding of computerized systems that was projected to create havoc in computers and computer networks around the world at the beginning of the
- 60. E-mail bombing/mail bombs • In Internet usage, an email bomb is a form of net abuse consisting of sending huge volumes of email to an address in an attempt to overflow the mailbox or overwhelm the server where the email address is hosted in a denial-of-service attack. • Construct a computer to repeatedly send E-mail to a specified person’s E-mail address. • Can overwhelm the recipient’s personal account and potentially shut down the entire system.
- 61. Computer network intrusions • An intrusion to computer network from any where in the world and steal data, plant viruses, create backdoors, insert trojan horse or change passwords and user names. • An intrusion detection system (IDS) inspects all inbound and outbound network activity and identifies suspicious patterns that may indicate a network or system attack from someone attempting to break into or compromise a system. • The practice of strong password
- 62. Password sniffing • Password sniffers are programs that monitor and record the name and password of network users as they login, jeopardizing security at a site. • through sniffers installed, anyone can impersonate an authorized user and login to access restricted documents.
- 63. Credit card frauds • Credit card fraud is a wide-ranging term for theft and fraud committed using or involving a payment card, such as a credit card or debit card, as a fraudulent source of funds in a transaction. • The purpose may be to obtain goods without paying, or to obtain unauthorized funds from an account. • Credit card fraud is also an adjunct to identity theft.
- 64. Identity theft • Identity theft is a fraud involving another person’s identity for an illicit purpose. • The criminal uses someone else’s identity for his/ her own illegal purposes. • Phishing and identity theft are related offenses • Examples: ⚬Fraudulently obtaining credit ⚬Stealing money from victim’s bank account ⚬Using victim’s credit card number ⚬Establishing accounts with utility companies ⚬Renting an apartment ⚬Filing bankruptcy using the victim’s name
- 65. Real life cases • Dr. Gerald Barnes Gerald Barnbaum lost his pharmacist license after committing Medicaid fraud. He stole the identity of Dr. Gerald Barnes and practiced medicine under his name. A type 1 diabetic died under his care. “Dr. Barnes” even worked as a staff physician for a center that gave exams to FBI agents. He’s currently serving hard time. • Andrea Harris-Frazier Margot Somerville lost her wallet on a trolley. Two years later she was arrested. Andrea Harris-Frazier had defrauded several banks—using Somerville’s identity—out of tens of thousands of dollars. The real crook was caught. • Abraham Abdallah A busboy named Abraham Abdallah got into the bank accounts of Steven Spielberg and other famous people after tricking his victims via computer, getting sufficient data to fake being their financial advisors—then calling their banks…and you know the rest.
- 66. Cybercrime: the legal perspective • Cybercrime possess a mammoth challenge • Computer crime: Criminal Justice Resource Manual(1979) ⚬Any illegal act for which knowledge of computer technology is essential for a successful prosecution. • International legal aspects of computer crimes were studied in 1983 ⚬Encompasses any illegal act for which the knowledge of computer technology is essential for its prepetration
- 67. Cybercrime: the legal perspective • The network context of cyber crime make it one of the most globalized offenses of the present and most modernized threats of the future. • Solution: ⚬Divide information system into segments bordered by state boundaries. ■ Not possible and unrealistic because of globalization ⚬Or incorporate the legal system into an integrated entity obliterating these state boundaries.
- 68. Cybercrimes: An Indian Perspective • India has the fourth highest number of internet users in the world. • 45 million internet users in India • 37% - in cybercafes • 57% are between 18 and 35 years • The Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000, specifies the acts which are punishable. Since the primary objective of this Act is to create an enabling environment for commercial use of I.T.
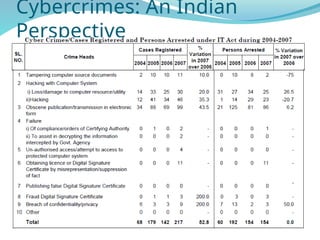
- 69. Cybercrimes: An Indian Perspective • 217 cases were registered under IT Act during the year 2007 as compared to 142 cases during the previous year (2006) • Thereby reporting an increase of 52.8% in 2007 over 2006. • 22.3% cases (49out of 217 cases) were reported from Maharashtra followed by Karnataka (40), Kerala (38) and Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan (16 each).
- 71. Incidence of Cyber Crimes in Cities • 17 out of 35 mega cities did not report any case of Cyber Crime i.e, neither under the IT Act nor under IPC Sections) during the year 2007. • 17 mega cities have reported 118 cases under IT Act and 7 megacities reported 180 cases undervarious section of IPC. • There was an increase of 32.6% (from 89 cases in 2006 to 118 cases in 2007) in cases under IT Act as compared to previous year (2006), • and an increase of 26.8% (from 142 cases in 2006 to 180 cases in 2007) of cases registered under various section of IPC • Bengaluru (40), Pune (14) and Delhi (10) cities have reported high incidence of cases (64 out of 118 cases) registered under IT Act, accounting for more than half of