Ad
[D2 COMMUNITY] Open Container Seoul Meetup - 마이크로 서비스 아키텍쳐와 Docker kubernetes
- 1. Microservice, Docker & Kubernetes 조대협, Google Cloud Sales Engineer [email protected]
- 2. Google Cloud Platform 2 발표자 소개 조 대 협 본명: 조병욱 회원 13만명 온라인 개발자 커뮤니티 자바스터디(www.javastudy.co.kr) 운영자.. (기억의 저편..)한국 자바 개발자 협회 부회장,서버사이드 아키텍트 그룹 운영자벤쳐 개발자BEA 웹로직 기술 지원 엔지니어장애 진단, 성능 튜닝NHN 잠깐오라클 컨설턴트 (SOA,EAI,ALM,Enterprise 2.0,대용량 분산 시스템)MS APAC 클라우드 수석 아키텍트프리렌서 (잘나가는 사장님)삼성전자 무선 사업부 B2B팀 Chief Architect피키캐스트 CTO 구글 클라우드 엔지니어
- 3. Google Cloud Platform 3 목차 ● Micro Service Architecture ● Docker ● Kubernetes ● DEMO
- 4. Google Cloud Platform 4 Micro Service Architecture 의 기본 개념
- 5. Google Cloud Platform 5 전통적인 아키텍쳐 스타일 • 모노리틱 아키텍쳐 (통서버) • 하나의 서버에 모든 비지니스 로직이 들어가 있는 형태 • 하나의 중앙 집중화된 데이타 베이스에 모든 데이타가 저장됨
- 6. Google Cloud Platform 6 전통적인 아키텍쳐 스타일의 장단점 • 단점 • 여러개의 기술을 혼용해서 사용하기 어려움 (node.js , Ruby, Python etc) • 배포 및 재기동 시간이 오래 걸림 • 수정이 용이하지 않음 (타 컴포넌트 의존성) • 장점 • 기술 단일화 • 관리 용이성
- 7. Google Cloud Platform 7 마이크로서비스 아키텍쳐란? • 시스템을 여러개의 독립된 서비스로 나눠서, 이 서비스를 조합함으로서 기능을 제공하는 아키텍쳐 디자인 패턴 • SOA의 경량화 버전 (실패한다면 실패하는 이유도 같음) 서비스란? – 단일된 기능 묶음으로 개발된 서비스 컴포넌트 – REST API등을 통하여 기능을 제공 – 데이타를 공유하지 않고 독립적으로 가공 저장 사용자 관리 인터페이스 • REST • Thrift,Protocol buffer • AMQP • :사용자 데이타
- 8. Google Cloud Platform 8 서비스 조합 • 하나의 기능을 구현 하는데, 여러개의 서비스를 조합하여 기능을 제공 예) 주문 하기 : 사용자 정보 조회, 상품 정보 조회, 신규 주문 생성 사용자 관리 상품 관리 주문 관리 쇼핑몰 웹 API CALL 사용자정보 상품정보 주문정보 사용자 관리 상품 관리 주문 관리 사용자 정보 상품 정보 주문 정보 쇼핑몰 웹 API CALL 모노리틱 아키텍쳐 마이크로 서비스 아키텍쳐
- 9. Google Cloud Platform 9 기술 스택 • 마이크로 서비스 아키텍쳐는 서비스 별로 다른 기술 스택을 사용할 수 있음 사용자 관리 (JAVA) 상품 관리 (node.js) 주문 관리 (JAVA) 사용자 정보 (Cassandra) 상품 정보 (MySQL) 주문 정보 (CouchBase) 쇼핑몰 웹 API CALL 장점일까? • 운영 관점에서 여러가지 기술을 동시에 다뤄야 함 (Devops – You build, You run) • 사람이 떠나면 보수 불가 (Product not a project) 단점일까? • 적절한 기술을 적절하게 배치 가능 o 복잡한 데이타 RDBMS, 양이 많은 고속 데이타 NoSQL o C10K NoSQL, 빠른 개발 스크립트 언어, 튼튼한 시스템은 자바 …
- 10. Google Cloud Platform 10 팀 모델 • 컨웨이의 법칙 • 뼈저리게 느낌 “소프트웨어의 구조는 그 소프트웨어를 만드는 팀의 구조와 일치한다.” 설계 백날 잘해야 소용없음 제대로 된 팀 구조를 만드는 것이 설계 (그 다음은 알아서 됨 ?) • 친한팀 컴포넌트끼리는 개발이 잘됨. 그러다 보니 그쪽으로 기능이 몰림 • 잘하는 팀한테 자꾸 중요 기능이 몰림 서비스 컴포넌트들이 균등하게 디자인 되지 않음
- 11. Google Cloud Platform 11 팀모델 • 분산형 거버넌스 (각 팀이 알아서. 적합한 기술, 스스로 하기) • You build & You run!! • Self Organized Team • Product vs Project • Cross functional team • Alignment (소통!!)
- 12. Google Cloud Platform 12 팀 모델 • 팀간 조율이 핵심 • 새로운 조율자 ROLE이 요구됨 프로그램 메니져 : 팀간 일정 조율 치프 아키텍트 : 서비스간 흐름 정의, 표준 정의, 에러 추적/처리 방법 정의
- 13. Google Cloud Platform 13 MSA Reference Architecture
- 14. Google Cloud Platform 14 마이크로 서비스 아키텍쳐 토폴로지 • 일반적인 마이크로 서비스 아키텍쳐 스택 구조 API gateway Service orchestration (mediation, aggregation) CommonAPIs CommonAPIs CommonAPIs CommonAPIs CommonAPIs CommonAPIs 생략 가능 영역 • API 게이트 웨이 : API의 single end point • Common APIs : 범용 API • Orchestration : 여러 API를 묶어서, 요구 사항에 맞는 로직을 구현 • Service Orchestration 규모가 커질 수 록 추가되는 계층들 (오케스트레이션, API 게이트 웨이) 1단계 2단계 3단계
- 15. Google Cloud Platform 15 쇼핑몰 API 서버 서비스 오케스트레이션 계층의 활용 사용자 관리 상품 관리 주문 관리 사용자 정보 상품 정보 주문 정보 앱 또는 자바스크립트 클라이언트 API CALL 사용자 관리 상품 관리 주문 관리 사용자 정보 상품 정보 주문 정보 API CALL 클라이언트 API CALL 클라이언트에서 직접 서비스를 조합 하는 방식 별도의 조합 계층(Orchestration or Mediation) 을 넣는 방식 다른 프로토콜 사용 가능 ex)내부 PB, 외부 REST • API가 범용적으로 잘 짜야 있어야함 • 클라이언트 팀이 모든 컴포넌트팀과 조율이 필요 규모가 크지 않은 구조에서 효과적 • 중간에 API를 커스터마이제이션 또는 조합 하는 계층을 별도로 둠 • 클라이언트팀은 조합 API 개발팀과 커뮤니케이션만 하면 됨 • 클라이언트 요구 사항에 기민하게 대처 • 그러나 계층은 하나 더 늘어남 (성능, 디버깅,배포) 일정 규모 이상. 특히 클라이언트가 여러개인 구조에
- 16. Google Cloud Platform 16 API 게이트 웨이 • 클라이언트와 API 서버 앞에서 일종의 프록시 처럼 위치 하여 다양한 기능을 수행함 • API 인증/인가 • 로깅 • 라우팅 • 메시지 변환 • 메시지 프로토콜 변환 : API 서버 API 서버 API 서버 데이타 데이타 데이타 API 게이트 웨이
- 17. Google Cloud Platform 17 API 게이트 웨이 • SOA ESB (Enterprise Service Bus)의 단순화 버전 • 있으면 좋음. 없어도 됨 • 만들 수 있는 실력있으면, 쓰는게 좋음 • 잘못 쓰면 망하는 지름길
- 18. Google Cloud Platform 18 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #1 • 인증,인가의 단일화 IDM (계정관리) API 토큰 관리 클라이언트 API 게이트 웨이 API 서버 1. API 토큰 발급 요청 2. 사용자 인증/인가 3. API 호출 5. API 호출 4. API 토큰 인증
- 19. Google Cloud Platform 19 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #2 • 멀티 앤드포인트와 멀티 프로토콜 제공 <그림. 다양한 디바이스로 부터 정보를 수집하는 IOT시스템에 타입별 앤드 포인트 제공하는 예제>
- 20. Google Cloud Platform 20 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #3 • 오케스트레이션 • ESB 기반 SOA 프로젝트가 실패한 대부분의 원인 (안하는게 좋음) • 오케스트레이션 서버를 별도로 두는게 좋음
- 21. Google Cloud Platform 21 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #4 • 메세지 기반 라우팅 • 글로벌 배포 시스템에 유용함 • 멀티 버전 시스템 (레거시 업그레이드)에 유용
- 22. Google Cloud Platform 22 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #5 • Cross Cutting Concern (공통 기능) 처리 • 인증,로깅등 공통 기능 처리 • API 개발팀은 비지니스 로직에 집중할 수 있도록 해줌
- 23. Google Cloud Platform 23 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #6 • 다중 API 게이트 웨이 패턴 • 내부,외부용 API 게이트웨이 분리
- 24. Google Cloud Platform 24 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #7 • API 호출용 엔드포인트와 스트리밍 (파일)용 엔드포인트 분리
- 25. Google Cloud Platform 25 API 게이트웨이를 이용한 설계 패턴 #6 • 비 기능 요소 제어 • QoS 제어 • Metering & Charging (상용 API 서비스 과금) • API 모니터링
- 26. Google Cloud Platform 26 분산 트렌젝션의 추적 • 여러개의 서비스 컴포넌트를 조합하여 움직이는 트렌젝션에 대한 추적 디자인 패턴 • 원리 (XA 분산 트렌젝션과 유사) • 초기 API에서 GTXID와 LTXID를 생성 • 서버를 넘어갈때 마다 같은 GTXID를 사용, LTXID는 하나씩 증가 • 구현시 • 서버간에는 HTTP 헤더로 TXID 전달 • 서버내에서는 Thread Local (Java)등의 컨택스트 변수 활용 → 초기 표준 설계가 중요함
- 27. Google Cloud Platform 27 Docker
- 28. Google Cloud Platform 28 Container ● Linux Container (LxC)기반의 컨테이너 기술 ● 애플리케이션 코드를 컨테이너로 패키징 해서, 개발에서 운영 환경으로 배포
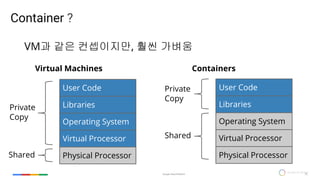
- 29. Google Cloud Platform 29 Google for Mobile Container ? VM과 같은 컨셉이지만, 훨씬 가벼움 Physical Processor Virtual Processor Operating System Libraries User Code Physical Processor Virtual Processor Operating System Libraries User Code Private Copy Shared Private Copy Shared Virtual Machines Containers
- 30. Google Cloud Platform 30 Container vs VM ● 비교 Virtual machine Docker container 이미지 크기 큼 작음 부팅 속도 분단위 초단위 이미지 생성 시간 느림 (+10분) 빠름 (수분) 윈도우 지원여부 가능 불가(?) 호환성 하이퍼바이져에 종속 Docker 지원 환경이면 사용 가능
- 31. Google Cloud Platform 31 Large scale container service ● 컨테이너를 어느 서버(물리)에 배포하지? Node Container Node Node Node Node …... Container 2 CPU, 4GB Where ?
- 32. Google Cloud Platform 32 스케쥴러 ● Docker Swarm ● Apache Mesos ● Kubernetes
- 33. Google Cloud Platform 33 스케쥴링 만으로 충분한가? ● Load balancing ● Health check ● Rolling upgrade ● Container Image management (repository) :
- 34. Google Cloud Platform 34 Kubernetes
- 35. Google Cloud Platform 35 Each week Google launches over 2 billion containers
- 36. Google Cloud Platform 36 Kubernetes ● 구글의 오랜 컨테이너 서비스 운영 경험의 산물 ● 오픈소스 ● public, private 거의 모든 인프라에서 사용 가능 ● 넒은 에코 시스템 (파트너, 클라우드 서비스 제공자등)
- 37. Google Cloud Platform 37 Virtual Network Compute Engine Instances Container Engine Kubernetes Master Zone Cluster Node Pod Container Container Pod Container Container Service Proxy Scheduler Cluster Node Pod Container Container Pod Container Container
- 38. Google Cloud Platform 38 Cluster Resources Pods are ephemeral units that are used to manage one or more tightly coupled containers. They enable data sharing and communication among their constituent components. Pods Replication Controller Services Replication controllers create new pod "replicas" from a template and ensure that a configurable number pods are running. Services provide a bridge based on an IP and port pair for non-Kubernetes-native client applications to access backends without needing to write code that is Kubernetes-specific.
- 39. Google Cloud Platform 39 Pods ● Kubernetes 에서 최소 논리 단위 ● 하나의 애플리케이션을 표현하는 최소 논리 단위 ● 하나의 Pod에는 1..N개의 Container를 가질 수 있음 ● 주로 Tightly Coupled 되는 Container들을 하나의 Pod에 묶음 ○ 예) Nginx + Tomcat ○ 예) Tomcat + memcached ● Pod에 있는 Container는 물리적으로 같은 서버에 생성됨 Cluster Node Pod Container Container Pod Container Container
- 40. Google Cloud Platform 40 Pods ● 같은 Pod에 있는 Container는 Disk Volume을 공유할 수 있음 version: v1beta1 containers: - name: www … volumeMounts: - name: dataShard path: /mnt/shard readOnly: true - name: dataLoader … volumeMounts: - name: dataShard path: /mnt/output volumes: - name: dataShard www dataLoader dataShard
- 41. Google Cloud Platform 41 Replication Controllers ● Pod를 생성하고 관리. ● Pod 생성은 미리 정의된 Template에서 부터 생성 ● Pod의 가동 상태를 체크하고, 죽으면 다시 재기동. version: v1beta1 containers: - name: www image: nginx ports: - name: http hostPort: 8080 containerPort: 80
- 42. Google Cloud Platform 42 Services ● Pod 들의 집합 (예. 웹서버 서비스, 백앤드 서비스, 캐쉬 서비스) ● IP Address가 지정 되고, Pod 간에 로드 밸런싱을 제공
- 43. Google Cloud Platform 43 Cluster Node Services { "kind": "Service", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { "name": "my-service" }, "spec": { "selector": { "app": "MyApp" }, "ports": [ { "protocol": "TCP", "port": 80, "targetPort": 9376 } ] } } Pod 1 labels: app=MyApp port: 9376 Pod 2 labels: app=MyApp port: 9376 Pod 3 labels: app=MyApp port: 9376 kube-proxy Port 80 Port 9376
- 44. Google Cloud Platform 44 FE FE FE FE FE FE BE BE BE BEBE BE BE BE BE Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Kubernetes - Master/Scheduler Labels : Too Many Pods
- 45. Google Cloud Platform 45 labels: role: frontend FE FE FE FE FE FE BE BE BE BEBE BE BE BE BE Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Kubernetes - Master/Scheduler Labels
- 46. Google Cloud Platform 46 labels: role: frontend stage: production Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Machine Host Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Container Agent Kubernetes - Master/Scheduler FE FE FE FE FE FE BE BE BE BEBE BE BE BE BE Labels
- 47. Google Cloud Platform 47 Google for Mobile Kubernetes on Cloud New service for cluster-based compute ● 수초내에 Kubernetes 클러스터 생성 ● 구글 클라우드 뿐 아니라, 타 클라우드 + 자체 데이타 센터를 단일 Kubernetes로 관리 Releases ● Today: General Availability Resources ● Google Container Engine: http://cloud.google.com/container-engine ● Kubernetes: http://kubernetes.io
- 48. Google Cloud Platform 48 DEMO
- 49. Google Cloud Platform 49 감사합니다. Free credit!! 페이스북 구글 클라우드 사용자 그룹 https://www.facebook.com/groups/googlecloudkorea/










































![Google Cloud Platform 43
Cluster Node
Services
{
"kind": "Service",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "my-service"
},
"spec": {
"selector": {
"app": "MyApp"
},
"ports": [
{
"protocol": "TCP",
"port": 80,
"targetPort": 9376
}
]
}
}
Pod 1
labels: app=MyApp
port: 9376
Pod 2
labels: app=MyApp
port: 9376
Pod 3
labels: app=MyApp
port: 9376
kube-proxy
Port 80
Port 9376](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerkubernetes-161207045638/85/D2-COMMUNITY-Open-Container-Seoul-Meetup-Docker-kubernetes-43-320.jpg)






![[215]네이버콘텐츠통계서비스소개 김기영](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/215-161025030904-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[211]대규모 시스템 시각화 현동석김광림](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/211-161025004529-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[233]멀티테넌트하둡클러스터 남경완](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/233-161025011544-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[231]나는서버를썰터이니너는개발만하여라 양지욱](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/231-161025004555-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[221] docker orchestration](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/212dockerorchestration-150915010646-lva1-app6891-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[214] data science with apache zeppelin](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/241datasciencewithapachezeppelin-150915001420-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


![[넥슨] kubernetes 소개 (2018)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/gcdkubernetes-190419130148-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[NDC17] Kubernetes로 개발서버 간단히 찍어내기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ndc-170529041601-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![3.[d2 오픈세미나]분산시스템 개발 및 교훈 n base arc](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/3-140905000012-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[122]네이버의모던웹라이브러리 박재성](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/122-161023161034-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)








![[124]네이버에서 사용되는 여러가지 Data Platform, 그리고 MongoDB](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/124mongodb-181011042943-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)







![[D2 COMMUNITY] Open Container Seoul Meetup - Kubernetes를 이용한 서비스 구축과 openshift](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/kubernetesopenshift-161207045304-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 COMMUNITY] Open Container Seoul Meetup - Running a container platform in ...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/runningacontainerplatforminproductionexperienceatgsshop-161207045420-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[D2 COMMUNITY] Open Container Seoul Meetup - Docker security](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/dockersecurity-161207045539-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


![[D2 COMMUNITY] ECMAScript 2015 S67 seminar - 1. primitive](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/1primitive-161207024601-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 COMMUNITY] ECMAScript 2015 S67 seminar - 4. promise](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/4promise-161207024833-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 COMMUNITY] ECMAScript 2015 S67 seminar - 3. generator](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/3generator-161207024803-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 COMMUNITY] ECMAScript 2015 S67 seminar - 2. functions](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2functions-161207024734-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 오픈세미나]1.무한스크롤성능개선](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/1-140804011241-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


![[D2 오픈세미나]5.robolectric 안드로이드 테스팅](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/5-140804011233-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 오픈세미나]4.네이티브앱저장통신](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/4-140804011236-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[D2 오픈세미나]2.모바일웹디버깅](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2-140804011239-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[D2 오픈세미나]3.web view hybridapp](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/3-140804011233-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


















![[2017 AWS Startup Day] 서버리스 마이크로서비스로 일당백 개발조직 만들기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/awsstartupday2017-microservicespiljoong-171101081359-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[211] 인공지능이 인공지능 챗봇을 만든다](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/211chatbot-181106094835-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[233] 대형 컨테이너 클러스터에서의 고가용성 Network Load Balancing: Maglev Hashing Scheduler i...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/233networkloadbalancing-181018151852-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[215] Druid로 쉽고 빠르게 데이터 분석하기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/215druid-181012071910-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[245]Papago Internals: 모델분석과 응용기술 개발](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/245papagointernals1-181012045005-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[236] 스트림 저장소 최적화 이야기: 아파치 드루이드로부터 얻은 교훈](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/236deview2018jihoonson-final-181012031726-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[235]Wikipedia-scale Q&A](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/235deview2018julienperezwikipediaqa12oct2018-181012030613-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[244]로봇이 현실 세계에 대해 학습하도록 만들기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/244deview2018tomisilanderrobotsrealworldfinal11oct2018-181012024720-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[243] Deep Learning to help student’s Deep Learning](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/243deeplearningtohelpstudentsdeeplearning-181012024530-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[234]Fast & Accurate Data Annotation Pipeline for AI applications](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/234fastaccuratedataannotationpipelineforaiapplications1-181012024230-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Old version: [233]대형 컨테이너 클러스터에서의 고가용성 Network Load Balancing](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/233largecontainerclusternetworkloadbalancing-181012024225-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[226]NAVER 광고 deep click prediction: 모델링부터 서빙까지](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/226naveraddeepclickprediction-181012024116-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[225]NSML: 머신러닝 플랫폼 서비스하기 & 모델 튜닝 자동화하기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/225nsmlmachinelearningntuningautomize-181012023407-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[224]네이버 검색과 개인화](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/224naversearchnpersonalizationfinal-181012022631-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[216]Search Reliability Engineering (부제: 지진에도 흔들리지 않는 네이버 검색시스템)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/216sresearchreliabilityengineering-181012022623-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[214] Ai Serving Platform: 하루 수 억 건의 인퍼런스를 처리하기 위한 고군분투기](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/214aiservingplatforminference-181012022603-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[213] Fashion Visual Search](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/213fashionvisualsearchreduced-181012022540-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[232] TensorRT를 활용한 딥러닝 Inference 최적화](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/232dlinferenceoptimizationusingtensorrt1-181012014455-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[242]컴퓨터 비전을 이용한 실내 지도 자동 업데이트 방법: 딥러닝을 통한 POI 변화 탐지](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/242pcdpublic-181012011734-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[212]C3, 데이터 처리에서 서빙까지 가능한 하둡 클러스터](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/212c3-181012011644-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[223]기계독해 QA: 검색인가, NLP인가?](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2232018-181012010149-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)