Data models
Download as PPS, PDF5 likes19,090 views
This document discusses different types of data models, including object based models like entity relationship and object oriented models, physical models that describe how data is stored, and record based logical models. It specifically mentions hierarchical, network, and relational models as examples of record based logical data models. The purpose of data models is to represent and make data understandable by specifying rules for database construction, allowed data operations, and integrity.
1 of 10
Downloaded 761 times









Ad
Recommended
Date warehousing concepts



Date warehousing conceptspcherukumalla The document provides an overview of key concepts in data warehousing and business intelligence, including:
1) It defines data warehousing concepts such as the characteristics of a data warehouse (subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, non-volatile), grain/granularity, and the differences between OLTP and data warehouse systems.
2) It discusses the evolution of business intelligence and key components of a data warehouse such as the source systems, staging area, presentation area, and access tools.
3) It covers dimensional modeling concepts like star schemas, snowflake schemas, and slowly and rapidly changing dimensions.
Data models



Data modelsUsman Tariq This document provides an overview of data modeling concepts. It discusses the importance of data modeling, the basic building blocks of data models including entities, attributes, and relationships. It also covers different types of data models such as conceptual, logical, and physical models. The document discusses relational and non-relational data models as well as emerging models like object-oriented, XML, and big data models. Business rules and their role in database design are also summarized.
Data preprocessing in Data Mining



Data preprocessing in Data MiningDHIVYADEVAKI Data is often incomplete, noisy, and inconsistent which can negatively impact mining results. Effective data cleaning is needed to fill in missing values, identify and remove outliers, and resolve inconsistencies. Other important tasks include data integration, transformation, reduction, and discretization to prepare the data for mining and obtain reduced representation that produces similar analytical results. Proper data preparation is essential for high quality knowledge discovery.
Entity relationship modelling



Entity relationship modellingDr. C.V. Suresh Babu This document provides an overview of entity-relationship modeling as a first step for designing a relational database. It describes how to model entities, attributes, relationships, and participation constraints. Key aspects covered include using boxes to represent entity types, diamonds for relationship types, and labeling relationships with degrees. The document also discusses handling multi-valued attributes and deciding whether to model concepts as attributes or entity types.
Dimensional Modelling



Dimensional ModellingPrithwis Mukerjee The document discusses dimensional modeling and data warehousing. It describes how dimensional models are designed for understandability and ease of reporting rather than updates. Key aspects include facts and dimensions, with facts being numeric measures and dimensions providing context. Slowly changing dimensions are also covered, with types 1-3 handling changes to dimension attribute values over time.
DBMS and its Models



DBMS and its ModelsAhmadShah Sultani The document discusses database management systems and data modeling. It begins by defining key terms like data, databases, database management systems, and data models. It then provides a brief history of database development from the 1960s to the 1980s. The rest of the document discusses database concepts in more detail, including components of a DBMS, types of database users, database administration responsibilities, data modeling techniques, and the evolution of different data models.
Data preprocessing



Data preprocessingGajanand Sharma This presentation gives the idea about Data Preprocessing in the field of Data Mining. Images, examples and other things are adopted from "Data Mining Concepts and Techniques by Jiawei Han, Micheline Kamber and Jian Pei "
Relational Database Design



Relational Database DesignArchit Saxena The document provides an overview of databases and database design. It defines what a database is, what databases do, and the components of database systems and applications. It discusses the database design process, including identifying fields, tables, keys, and relationships between tables. The document also covers database modeling techniques, normalization to eliminate redundant or inefficient data storage, and functional dependencies as constraints on attribute values.
Data Modeling Basics



Data Modeling Basicsrenuindia Data modeling is the first step in creating a database and involves creating a conceptual representation of the required data structures. A data model focuses on what data is needed and how it should be organized rather than operations performed on the data. There are three levels of data modeling: conceptual, logical, and physical. The conceptual model identifies high-level relationships between entities while the logical model describes the data and relationships in detail without regard to implementation. The physical model represents how the data will be implemented in the database. Entities, attributes, relationships, cardinality, and ordination are key concepts in data modeling.
Data preprocessing ng



Data preprocessing ngdatapreprocessing This document discusses various techniques for data preprocessing, including data cleaning, integration, transformation, and reduction. It describes why preprocessing is important for obtaining quality data and mining results. Key techniques covered include handling missing data, smoothing noisy data, data integration and normalization for transformation, and data reduction methods like binning, discretization, feature selection and dimensionality reduction.
Data modelling 101



Data modelling 101Christopher Bradley Data Modelling 101 half day workshop presented by Chris Bradley at the Enterprise Data and Business Intelligence conference London on November 3rd 2014.
Chris Bradley is a leading independent information strategist.
Contact [email protected]
data modeling and models



data modeling and modelssabah N This document provides an overview of data modeling, including definitions of key concepts like data models and data modeling. It describes the evolution of popular data models from hierarchical to network to relational to entity-relationship to object-oriented models. For each model, it outlines the basic concepts, advantages, and disadvantages. The document emphasizes that newer data models aimed to address shortcomings of previous approaches and capture real-world data and relationships.
Dimensional Modeling



Dimensional ModelingSunita Sahu The document discusses dimensional modeling concepts used in data warehouse design. Dimensional modeling organizes data into facts and dimensions. Facts are measures that are analyzed, while dimensions provide context for the facts. The dimensional model uses star and snowflake schemas to store data in denormalized tables optimized for querying. Key aspects covered include fact and dimension tables, slowly changing dimensions, and handling many-to-many and recursive relationships.
Dbms classification according to data models



Dbms classification according to data modelsABDUL KHALIQ CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO DATA MODELS
Hierarchal Model
In a hierarchical data model, data are organized into a tree-like structure.
Network Model
based on an enlargement of the concept of hierarchical data bases.
Relational Model
Data are stored in tables
Object Oriented model
Object oriented data base systems are the most recent development in data base technology.
Introduction
Definations
Advantages and Disadvantages
PowerPoint Presentation
PowerPoint Presentation for free
Star schema



Star schemaChandanapriya Sathavalli A data warehouse stores current and historical data for analysis and decision making. It uses a star schema with fact and dimension tables. The fact table contains measures that can be aggregated and connected to dimension tables through foreign keys. Dimensions describe the facts and contain descriptive attributes to analyze measures over time, products, locations etc. This allows analyzing large volumes of historical data for informed decisions.
Data preprocessing



Data preprocessingksamyMCA This document discusses various techniques for data preprocessing including data cleaning, integration, transformation, reduction, and discretization.
Data cleaning involves filling in missing values, smoothing noisy data, identifying outliers, and resolving inconsistencies. Data integration combines data from multiple sources by integrating schemas and resolving value conflicts. Data transformation techniques include normalization, aggregation, generalization, and smoothing.
Data reduction aims to reduce the volume of data while maintaining similar analytical results. This includes data cube aggregation, dimensionality reduction by removing unimportant attributes, data compression, and discretization which converts continuous attributes to categorical bins.
Advanced Dimensional Modelling



Advanced Dimensional ModellingVincent Rainardi This is my presentation at SQLBits 8, Brighton, 9th April 2011. This session is about advanced dimensional modelling topics such as Fact Table Primary Key, Vertical Fact Tables, Aggregate Fact Tables, SCD Type 6, Snapshotting Transaction Fact Tables, 1 or 2 Dimensions, Dealing with Currency Rates, When to Snowflake, Dimensions with Multi Valued Attributes, Transaction-Level Dimensions, Very Large Dimensions, A Dimension With Only 1 Attribute, Rapidly Changing Dimensions, Banding Dimension Rows, Stamping Dimension Rows and Real Time Fact Table. Prerequisites: You need have a basic knowledge of dimensional modelling and relational database design.
My name is Vincent Rainardi. I am a data warehouse & BI architect. I wrote a book on SQL Server data warehousing & BI, as well as many articles on my blog, www.datawarehouse.org.uk. I welcome questions and discussions on data warehousing on [email protected]. Enjoy the presentation.
Data Warehousing and Data Mining



Data Warehousing and Data Miningidnats This document discusses data warehousing and OLAP (online analytical processing) technology. It defines a data warehouse as a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and nonvolatile collection of data to support management decision making. It describes how data warehouses use a multi-dimensional data model with facts and dimensions to organize historical data from multiple sources for analysis. Common data warehouse architectures like star schemas and snowflake schemas are also summarized.
Data Models



Data ModelsRituBhargava7 A data model is a set of concepts that define the structure of data in a database. The three main types of data models are the hierarchical model, network model, and relational model. The hierarchical model uses a tree structure with parent-child relationships, while the network model allows many-to-many relationships but is more complex. The relational model - which underlies most modern databases - uses tables with rows and columns to represent data, and relationships are represented by values in columns.
Data Warehouse Modeling



Data Warehouse Modelingvivekjv This document provides an overview of data warehousing concepts including dimensional modeling, online analytical processing (OLAP), and indexing techniques. It discusses the evolution of data warehousing, definitions of data warehouses, architectures, and common applications. Dimensional modeling concepts such as star schemas, snowflake schemas, and slowly changing dimensions are explained. The presentation concludes with references for further reading.
Different type of databases



Different type of databasesShwe Yee Databases are the prime technique used to develop any information system used in modern business. There are many different types of database available used for different purposes.
Importance of data model



Importance of data modelyhen06 Data models can facilitate communication between designers, programmers, and users. A well-developed data model can improve understanding of an organization. Data models are a communication tool that represent different types of relationships in a database. Common data models include hierarchical, network, relational, entity-relationship, and object-oriented models. Each model has advantages like conceptual simplicity and flexibility as well as disadvantages like complexity and implementation limitations.
Data Warehouse Fundamentals



Data Warehouse FundamentalsRashmi Bhat The document discusses dimensional modeling concepts for data warehousing. It defines dimensional modeling as a technique to design database tables optimized for analytical tasks in a data warehouse. Dimensional models consist of fact tables that contain metrics/measurements and dimension tables that provide context for the facts. The document provides examples of star schemas where the fact table is at the center connected to various dimension tables, and explains how dimensional modeling supports analysis of data through queries along different dimensions.
Dbms slides



Dbms slidesrahulrathore725 This document discusses the key components of a database system including applications, file systems, data views, query processors, users and administrators, data languages, transaction management, and storage managers. It provides examples of common database applications and describes how data is abstracted at the physical, logical, and view levels. It also explains the roles of DDL, DML, transactions, and storage managers in database design and management.
Dbms Notes Lecture 4 : Data Models in DBMS



Dbms Notes Lecture 4 : Data Models in DBMSBIT Durg Data Models, Hierarchical data models, Network data model, Relational data model, Entity relationship model, Object oriented data models
Data quality and bi



Data quality and bijeffd00 The document discusses business intelligence (BI) tools, data warehousing concepts like star schemas and snowflake schemas, data quality measures, master data management (MDM), and business intelligence competency centers (BICC). It provides examples of BI tools and industries that use BI. It defines what a BICC is and some of the typical jobs in a BICC like business analyst and BI programmer.
Data warehouse physical design



Data warehouse physical designEr. Nawaraj Bhandari Data Warehouse Physical Design,Physical Data Model, Tablespaces, Integrity Constraints, ETL (Extract-Transform-Load) ,OLAP Server Architectures, MOLAP vs. ROLAP, Distributed Data Warehouse ,
Relational databases vs Non-relational databases



Relational databases vs Non-relational databasesJames Serra There is a lot of confusion about the place and purpose of the many recent non-relational database solutions ("NoSQL databases") compared to the relational database solutions that have been around for so many years. In this presentation I will first clarify what exactly these database solutions are, compare them, and discuss the best use cases for each. I'll discuss topics involving OLTP, scaling, data warehousing, polyglot persistence, and the CAP theorem. We will even touch on a new type of database solution called NewSQL. If you are building a new solution it is important to understand all your options so you take the right path to success.
DBMS OF DATA MODEL Deepika 2



DBMS OF DATA MODEL Deepika 2Rai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj This document provides an overview of different data models, including object-based models like the entity-relationship model and object-oriented model, and record-based models like the relational, network, and hierarchical models. It describes the key features of each model, such as how data and relationships are represented, and highlights some of their advantages and disadvantages. The presentation aims to guide students in understanding different approaches to database design and modeling.
DBMS



DBMSRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj This document provides an overview of different data models, including object-based models like the entity-relationship model and object-oriented model, and record-based models like the relational, network, and hierarchical models. It describes the key features of each model, such as how data and relationships are represented, and highlights some advantages and disadvantages. The presentation is intended to guide students in understanding different approaches to database design and logical data modeling.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Data Modeling Basics



Data Modeling Basicsrenuindia Data modeling is the first step in creating a database and involves creating a conceptual representation of the required data structures. A data model focuses on what data is needed and how it should be organized rather than operations performed on the data. There are three levels of data modeling: conceptual, logical, and physical. The conceptual model identifies high-level relationships between entities while the logical model describes the data and relationships in detail without regard to implementation. The physical model represents how the data will be implemented in the database. Entities, attributes, relationships, cardinality, and ordination are key concepts in data modeling.
Data preprocessing ng



Data preprocessing ngdatapreprocessing This document discusses various techniques for data preprocessing, including data cleaning, integration, transformation, and reduction. It describes why preprocessing is important for obtaining quality data and mining results. Key techniques covered include handling missing data, smoothing noisy data, data integration and normalization for transformation, and data reduction methods like binning, discretization, feature selection and dimensionality reduction.
Data modelling 101



Data modelling 101Christopher Bradley Data Modelling 101 half day workshop presented by Chris Bradley at the Enterprise Data and Business Intelligence conference London on November 3rd 2014.
Chris Bradley is a leading independent information strategist.
Contact [email protected]
data modeling and models



data modeling and modelssabah N This document provides an overview of data modeling, including definitions of key concepts like data models and data modeling. It describes the evolution of popular data models from hierarchical to network to relational to entity-relationship to object-oriented models. For each model, it outlines the basic concepts, advantages, and disadvantages. The document emphasizes that newer data models aimed to address shortcomings of previous approaches and capture real-world data and relationships.
Dimensional Modeling



Dimensional ModelingSunita Sahu The document discusses dimensional modeling concepts used in data warehouse design. Dimensional modeling organizes data into facts and dimensions. Facts are measures that are analyzed, while dimensions provide context for the facts. The dimensional model uses star and snowflake schemas to store data in denormalized tables optimized for querying. Key aspects covered include fact and dimension tables, slowly changing dimensions, and handling many-to-many and recursive relationships.
Dbms classification according to data models



Dbms classification according to data modelsABDUL KHALIQ CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO DATA MODELS
Hierarchal Model
In a hierarchical data model, data are organized into a tree-like structure.
Network Model
based on an enlargement of the concept of hierarchical data bases.
Relational Model
Data are stored in tables
Object Oriented model
Object oriented data base systems are the most recent development in data base technology.
Introduction
Definations
Advantages and Disadvantages
PowerPoint Presentation
PowerPoint Presentation for free
Star schema



Star schemaChandanapriya Sathavalli A data warehouse stores current and historical data for analysis and decision making. It uses a star schema with fact and dimension tables. The fact table contains measures that can be aggregated and connected to dimension tables through foreign keys. Dimensions describe the facts and contain descriptive attributes to analyze measures over time, products, locations etc. This allows analyzing large volumes of historical data for informed decisions.
Data preprocessing



Data preprocessingksamyMCA This document discusses various techniques for data preprocessing including data cleaning, integration, transformation, reduction, and discretization.
Data cleaning involves filling in missing values, smoothing noisy data, identifying outliers, and resolving inconsistencies. Data integration combines data from multiple sources by integrating schemas and resolving value conflicts. Data transformation techniques include normalization, aggregation, generalization, and smoothing.
Data reduction aims to reduce the volume of data while maintaining similar analytical results. This includes data cube aggregation, dimensionality reduction by removing unimportant attributes, data compression, and discretization which converts continuous attributes to categorical bins.
Advanced Dimensional Modelling



Advanced Dimensional ModellingVincent Rainardi This is my presentation at SQLBits 8, Brighton, 9th April 2011. This session is about advanced dimensional modelling topics such as Fact Table Primary Key, Vertical Fact Tables, Aggregate Fact Tables, SCD Type 6, Snapshotting Transaction Fact Tables, 1 or 2 Dimensions, Dealing with Currency Rates, When to Snowflake, Dimensions with Multi Valued Attributes, Transaction-Level Dimensions, Very Large Dimensions, A Dimension With Only 1 Attribute, Rapidly Changing Dimensions, Banding Dimension Rows, Stamping Dimension Rows and Real Time Fact Table. Prerequisites: You need have a basic knowledge of dimensional modelling and relational database design.
My name is Vincent Rainardi. I am a data warehouse & BI architect. I wrote a book on SQL Server data warehousing & BI, as well as many articles on my blog, www.datawarehouse.org.uk. I welcome questions and discussions on data warehousing on [email protected]. Enjoy the presentation.
Data Warehousing and Data Mining



Data Warehousing and Data Miningidnats This document discusses data warehousing and OLAP (online analytical processing) technology. It defines a data warehouse as a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and nonvolatile collection of data to support management decision making. It describes how data warehouses use a multi-dimensional data model with facts and dimensions to organize historical data from multiple sources for analysis. Common data warehouse architectures like star schemas and snowflake schemas are also summarized.
Data Models



Data ModelsRituBhargava7 A data model is a set of concepts that define the structure of data in a database. The three main types of data models are the hierarchical model, network model, and relational model. The hierarchical model uses a tree structure with parent-child relationships, while the network model allows many-to-many relationships but is more complex. The relational model - which underlies most modern databases - uses tables with rows and columns to represent data, and relationships are represented by values in columns.
Data Warehouse Modeling



Data Warehouse Modelingvivekjv This document provides an overview of data warehousing concepts including dimensional modeling, online analytical processing (OLAP), and indexing techniques. It discusses the evolution of data warehousing, definitions of data warehouses, architectures, and common applications. Dimensional modeling concepts such as star schemas, snowflake schemas, and slowly changing dimensions are explained. The presentation concludes with references for further reading.
Different type of databases



Different type of databasesShwe Yee Databases are the prime technique used to develop any information system used in modern business. There are many different types of database available used for different purposes.
Importance of data model



Importance of data modelyhen06 Data models can facilitate communication between designers, programmers, and users. A well-developed data model can improve understanding of an organization. Data models are a communication tool that represent different types of relationships in a database. Common data models include hierarchical, network, relational, entity-relationship, and object-oriented models. Each model has advantages like conceptual simplicity and flexibility as well as disadvantages like complexity and implementation limitations.
Data Warehouse Fundamentals



Data Warehouse FundamentalsRashmi Bhat The document discusses dimensional modeling concepts for data warehousing. It defines dimensional modeling as a technique to design database tables optimized for analytical tasks in a data warehouse. Dimensional models consist of fact tables that contain metrics/measurements and dimension tables that provide context for the facts. The document provides examples of star schemas where the fact table is at the center connected to various dimension tables, and explains how dimensional modeling supports analysis of data through queries along different dimensions.
Dbms slides



Dbms slidesrahulrathore725 This document discusses the key components of a database system including applications, file systems, data views, query processors, users and administrators, data languages, transaction management, and storage managers. It provides examples of common database applications and describes how data is abstracted at the physical, logical, and view levels. It also explains the roles of DDL, DML, transactions, and storage managers in database design and management.
Dbms Notes Lecture 4 : Data Models in DBMS



Dbms Notes Lecture 4 : Data Models in DBMSBIT Durg Data Models, Hierarchical data models, Network data model, Relational data model, Entity relationship model, Object oriented data models
Data quality and bi



Data quality and bijeffd00 The document discusses business intelligence (BI) tools, data warehousing concepts like star schemas and snowflake schemas, data quality measures, master data management (MDM), and business intelligence competency centers (BICC). It provides examples of BI tools and industries that use BI. It defines what a BICC is and some of the typical jobs in a BICC like business analyst and BI programmer.
Data warehouse physical design



Data warehouse physical designEr. Nawaraj Bhandari Data Warehouse Physical Design,Physical Data Model, Tablespaces, Integrity Constraints, ETL (Extract-Transform-Load) ,OLAP Server Architectures, MOLAP vs. ROLAP, Distributed Data Warehouse ,
Relational databases vs Non-relational databases



Relational databases vs Non-relational databasesJames Serra There is a lot of confusion about the place and purpose of the many recent non-relational database solutions ("NoSQL databases") compared to the relational database solutions that have been around for so many years. In this presentation I will first clarify what exactly these database solutions are, compare them, and discuss the best use cases for each. I'll discuss topics involving OLTP, scaling, data warehousing, polyglot persistence, and the CAP theorem. We will even touch on a new type of database solution called NewSQL. If you are building a new solution it is important to understand all your options so you take the right path to success.
Similar to Data models (20)
DBMS OF DATA MODEL Deepika 2



DBMS OF DATA MODEL Deepika 2Rai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj This document provides an overview of different data models, including object-based models like the entity-relationship model and object-oriented model, and record-based models like the relational, network, and hierarchical models. It describes the key features of each model, such as how data and relationships are represented, and highlights some of their advantages and disadvantages. The presentation aims to guide students in understanding different approaches to database design and modeling.
DBMS



DBMSRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj This document provides an overview of different data models, including object-based models like the entity-relationship model and object-oriented model, and record-based models like the relational, network, and hierarchical models. It describes the key features of each model, such as how data and relationships are represented, and highlights some advantages and disadvantages. The presentation is intended to guide students in understanding different approaches to database design and logical data modeling.
Dbms notes



Dbms notesProf. Dr. K. Adisesha The document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS). It can be summarized as follows:
1. A DBMS allows for the storage and retrieval of large amounts of related data in an organized manner. It removes data redundancy and allows for fast retrieval of data.
2. Key components of a DBMS include the database engine, data definition subsystem, data manipulation subsystem, application generation subsystem, and data administration subsystem.
3. A DBMS uses a data model to represent the organization of data in a database. Common data models include the entity-relationship model, object-oriented model, and relational model.
CBSE XII Database Concepts And MySQL Presentation



CBSE XII Database Concepts And MySQL PresentationGuru Ji The document provides an introduction to database concepts and the relational model. It defines what a database is and discusses the purpose of databases, including reducing data redundancy and maintaining data integrity. It also describes different data models like relational, network, and hierarchical models. The relational model is then explained in detail, covering terminology, keys, views, and relational algebra operations like select, project, cartesian product. The document provides examples to illustrate database concepts and the relational model.
Data Modeling Training.pptx



Data Modeling Training.pptxssuser23b3eb Data Modeling Training.pptxData Modeling Training.pptxData Modeling Training.pptxData Modeling Training.pptx
data modeling data modeling and its context .pptx



data modeling data modeling and its context .pptxssuser2690b8 data modeling Representing information and a simplified explanation of its forms
data modelingEntity-Relationship (E-R) Models UML (unified modeling language)...



data modelingEntity-Relationship (E-R) Models UML (unified modeling language)...ssuser2690b8 Entity-Relationship (E-R) Models
UML (unified modeling language)
types of data modeling tecnologyesy.pptx



types of data modeling tecnologyesy.pptxssuser2690b8 Entity-Relationship (E-R) Models
UML (unified modeling language)
types of data modelingEntity-Relationship (E-R) Models UML .pptx



types of data modelingEntity-Relationship (E-R) Models UML .pptxssuser2690b8 Entity-Relationship (E-R) Models
UML (unified modeling language)
1.1 Data Modelling - Part I (Understand Data Model).pdf



1.1 Data Modelling - Part I (Understand Data Model).pdfRakeshKumar145431 Data modeling is the process of creating a data model for data stored in a database. It ensures consistency in naming conventions, default values, semantics, and security while also ensuring data quality. There are three main types of data models: conceptual, logical, and physical. The conceptual model establishes entities, attributes, and their relationships. The logical model defines data element structure and relationships. The physical model describes database-specific implementation. The primary goal is accurately representing required data objects. Drawbacks include requiring application modifications for even small structure changes and lacking a standard data manipulation language.
ppt_rdbms.pdfuvuguvuvugycycyctcucuvyvvuvuvy



ppt_rdbms.pdfuvuguvuvugycycyctcucuvyvvuvuvyvk5985399 The document provides information about the course "Relational Database Management Systems" including its 5 units of study. Unit I provides an introduction to database concepts like data models, DBMS architecture, and Entity Relationship modeling. Unit II covers the relational model, SQL, queries, views, constraints, and database design. Unit III discusses transaction processing, concurrency control, and recovery concepts. Unit IV focuses on file operations, indexing techniques like B+ trees. Unit V examines special purpose databases for objects, XML, temporal, mobile and spatial data. The textbook and reference books are also listed.
Data models



Data modelsKIRANPREET KAUR The document discusses different types of data models including logical, physical, and record-based models. It describes key concepts of data models like entities, attributes, relationships and different relationship types. Specific models covered are hierarchical, network, and relational with details on their structure, advantages and disadvantages.
Methodology logical database design for the relational



Methodology logical database design for the relationaluniversity of the punjab The document outlines the steps for building and validating a logical data model from a conceptual data model for a relational database:
1. Derive relationships and map entities to tables.
2. Validate relations through normalization to minimize redundancy and update issues.
3. Validate relations can support required transactions.
4. Include integrity constraints like required fields, data types, relationships.
5. Review the logical model with users.
6. Merge individual models into a single global logical data model.
7. Consider future growth and changes the model may need to accommodate.
Methodology conceptual databases design roll no. 99 & 111



Methodology conceptual databases design roll no. 99 & 111Manoj Nolkha The document describes the methodology for conceptual database design. It outlines the objectives of database design which include determining information requirements, having a distinct structure, minimizing redundancy, and allowing for flexibility. The methodology involves three phases - conceptual, logical, and physical design. Conceptual design involves building a conceptual data model by identifying entities, relationships, attributes, domains, and keys. The model is checked for redundancy and validated against user requirements.
BAB 7 Pangkalan data new



BAB 7 Pangkalan data newNur Salsabila Edu The document discusses database concepts including:
1) The key concepts of a database including data, information, fields, records, files, and how a database improves over traditional file-based systems.
2) The functions of a database management system (DBMS) including database development, application development, and maintenance.
3) The database development process including planning, requirement specification, conceptual design, logical design, and physical design.
database-model group presentation.pptx



database-model group presentation.pptxRuksanKarki A database model refers to the structure of a database and determines how the data within the database can be organized and manipulated. Let’s explore some common types of database models:
Relational Model: The most popular example, the relational model, organizes data into tables (also known as relations). Each table contains rows representing records and columns representing attributes. Relationships between tables are established using keys.
Hierarchical Model: Developed by IBM for IMS (Information Management System), this model arranges data in a tree-like structure. Each record is a tree node, and relationships follow a one-to-many pattern. It’s predictable and efficient for data access.
Network Model: This model allows many-to-many relationships between records. It’s more flexible than the hierarchical model but less common.
Entity–Relationship Model (ER Model): It represents entities, their attributes, and the relationships between them. ER diagrams visually depict these components.
Object Model: Used in object-oriented databases, it treats data as objects with properties and methods. It’s suitable for complex data structures.
Document Model: Commonly used in NoSQL databases, it stores data as documents (e.g., JSON or XML). Each document can have varying attributes.
Entity–Attribute–Value (EAV) Model: A flexible model where data is stored in a sparse matrix. It’s useful for handling dynamic attributes.
Star Schema: Primarily used in data warehousing, it simplifies complex data structures into a central fact table connected to dimension tables.
Information Technology 104



Information Technology 104'Vladimir Medina Mga dapat paagaralan...
Upang may matutunan...
At may mapulot na kaalaman...
At ang pagsusulit ay mapaghandaan...
Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled Intelligence 



Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled Intelligence dannyijwest World Wide Web has revolutionized the means of data availability, but with its current structure model , it
is becoming increasingly difficult to retrieve relevant information, with reasonable precision and recall,
using the major search engines. However, with use of metadata, combined with the use of improved
searching techniques, helps to enhance relevant information retrieval .The design of structured,
descriptions of Web resources enables greater search precision and a more accurate relevance ranking of
retrieved information .One such efforts towards standardization is , Dublin Core standard, which has been
developed as Metadata Standard and also other standards which enhances retrieval of a wide range of
information resources. This paper discuses the importance of metadata, various metadata schemas and
elements, and the need of standardization of Metadata. This paper further discusses how the metadata can
be generated using various tools which assist intelligent agents for efficient retrieval.
Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled Intelligence



Metadata: Towards Machine-Enabled Intelligencedannyijwest World Wide Web has revolutionized the means of data availability, but with its current structure model , it is becoming increasingly difficult to retrieve relevant information, with reasonable precision and recall, using the major search engines. However, with use of metadata, combined with the use of improved searching techniques, helps to enhance relevant information retrieval .The design of structured, descriptions of Web resources enables greater search precision and a more accurate relevance ranking of retrieved information .One such efforts towards standardization is , Dublin Core standard, which has been developed as Metadata Standard and also other standards which enhances retrieval of a wide range of information resources. This paper discuses the importance of metadata, various metadata schemas and elements, and the need of standardization of Metadata. This paper further discusses how the metadata can be generated using various tools which assist intelligent agents for efficient retrieval
Ad
More from Anuj Modi (20)
Android Technology



Android TechnologyAnuj Modi This document provides an overview of the Android operating system, including its history and versions. It is owned by Google and is an open-source, Linux-based OS used primarily in mobile devices. The document outlines the major versions of Android from 1.0 in 2008 to the current version, 4.4 KitKat. It also discusses topics like Android rooting, advantages and disadvantages of the OS, market share of smartphones using Android, and the future of Android.
Virtual memory



Virtual memoryAnuj Modi The document discusses the concept of virtual memory. Virtual memory allows a program to access more memory than what is physically available in RAM by storing unused portions of the program on disk. When a program requests data that is not currently in RAM, it triggers a page fault that causes the needed page to be swapped from disk into RAM. This allows the illusion of more memory than physically available through swapping pages between RAM and disk as needed by the program during execution.
Timing and-control-unit



Timing and-control-unitAnuj Modi The document discusses the control unit of a CPU. It describes the functions of the control unit, which include generating timing signals, controlling data flow between the processor and memory/peripherals, and directing the computer to carry out instructions. The control unit can be implemented using either a hardwired or microprogrammed design. A hardwired control unit uses logic circuits to generate signals, while a microprogrammed unit executes a stored program of microinstructions.
Synchronous and-asynchronous-data-transfer



Synchronous and-asynchronous-data-transferAnuj Modi Synchronous data transfer involves sharing a common clock between a CPU and I/O interface so that data transfer is coordinated. Asynchronous transfer has independent clocks, so handshaking methods like strobe control and handshaking are used. Strobe control uses a single strobe pulse to indicate valid data. Handshaking adds a second control signal for acknowledgment between units. This ensures the source knows data was received and the destination knows data is available.
Registers and-common-bus



Registers and-common-busAnuj Modi The document describes the basic registers in a computer including the accumulator, program counter, instruction register, data register, address register, and temporary register. It explains that these registers are used to temporarily store and manipulate data and instructions during program execution. A common bus is used to transfer information between the registers and memory unit.
Ram and-rom-chips



Ram and-rom-chipsAnuj Modi RAM is the main memory that allows bidirectional transfer of data via its data bus. It has a capacity of 128 bytes addressed by a 7-bit address. ROM can only read and can store more data than RAM in the same size chip. A memory address map assigns addresses to RAM and ROM chips. RAM uses address lines 1-7 and is selected by address lines 8-9 through a decoder. ROM uses address lines 1-9 and is selected by address line 10.
Memory



MemoryAnuj Modi The document discusses computer memory and its types. It explains that memory is required to store data and instructions before, during, and after processing by the CPU. There are two main types of memory: primary and secondary. Primary memory (RAM and ROM) is high-speed volatile memory that is used for temporary storage and processing. Secondary memory (hard disks, optical disks, magnetic tapes, etc.) is non-volatile storage for long-term storage and retrieval of data. The document provides details about different types of primary and secondary storage, their characteristics, uses, and examples.
Computer instructions



Computer instructionsAnuj Modi An instruction format consists of bits that specify an operation to perform on data in computer memory. The processor fetches instructions from memory and decodes the bits to execute them. Instruction formats have operation codes to define operations like addition and an address field to specify where data is located. Computers may have different instruction sets.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnuj Modi Cache memory is a small, fast memory located between the CPU and main memory. It stores copies of frequently used instructions and data to accelerate access and improve performance. There are different mapping techniques for cache including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. When the cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU and FIFO are used to determine which content to remove. The cache can write to main memory using either a write-through or write-back policy.
Introduction to-dbms



Introduction to-dbmsAnuj Modi Data is a collection of raw facts and figures that can be processed by computing machines. Information is data that has been converted into a more useful form to help with decision making. A database is an organized collection of related information that can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. Common database operations include inserting, updating, deleting, and retrieving stored information. Manual databases are less efficient than computerized databases as the number of records increases due to issues like redundancy, inconsistency, isolation, security, speed of access and recovery of data.
DBA



DBAAnuj Modi The document discusses the role and responsibilities of a database administrator (DBA). A DBA has centralized control over the database and is responsible for its creation, modification, and maintenance. Key responsibilities of a DBA include deciding the database's content and storage structure, providing support to users, defining backup and recovery strategies, setting security and integrity checks, and monitoring performance and making adjustments in response to changing requirements.
Architecture of-dbms-and-data-independence



Architecture of-dbms-and-data-independenceAnuj Modi The document discusses the architecture of a database management system (DBMS). It describes the three levels of DBMS architecture: the external, conceptual, and internal views. The external view represents how individual users see the data. The conceptual view presents a common view of data for all users. The internal view describes the physical storage and organization of data. This three-level architecture provides data independence, where each level is isolated from changes in the other levels.
Central Processing Unit User View



Central Processing Unit User ViewAnuj Modi This document summarizes the central processing unit (CPU) and its organization. The CPU has three main parts: the register set, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and control unit. It describes two common CPU organizations: general register organization and stack organization. General register organization uses multiple registers and a register set with a register file and ALU. The stack organization uses a last-in, first-out stack and stack pointer register. It also discusses addressing modes that provide programming versatility and reduce the number of bits in instruction addresses.
Microprogram Control 



Microprogram Control Anuj Modi A microprogrammed control unit stores control signals for executing instructions in a control memory rather than using dedicated logic. It has four main components: 1) a control memory that stores microinstructions specifying microoperations, 2) a control address register that selects microinstructions, 3) a sequencer that generates the next address, and 4) a pipeline register that holds the selected microinstruction. Microprograms are sequences of microinstructions that are executed to carry out machine-level instructions. Microinstructions can implement conditional branching to alter the control flow.
Graphs In Data Structure



Graphs In Data StructureAnuj Modi A graph G is composed of vertices V connected by edges E. It can be represented using an adjacency matrix or adjacency lists. Graph search algorithms like depth-first search (DFS) and breadth-first search (BFS) are used to traverse the graph and find paths between vertices. DFS recursively explores edges until reaching the end of a branch before backtracking, while BFS explores edges in levels starting from the starting vertex.
Graphs In Data Structure



Graphs In Data StructureAnuj Modi A graph G is composed of vertices V connected by edges E. It can be represented using an adjacency matrix or adjacency lists. Graph search algorithms like depth-first search (DFS) and breadth-first search (BFS) are used to traverse the graph and find paths between vertices. DFS recursively explores edges until reaching the end of a branch before backtracking, while BFS explores all neighbors at each level before moving to the next.
B trees in Data Structure



B trees in Data StructureAnuj Modi B-Trees are tree data structures used to store data on disk storage. They allow for efficient retrieval of data compared to binary trees when using disk storage due to reduced height. B-Trees group data into nodes that can have multiple children, reducing the height needed compared to binary trees. Keys are inserted by adding to leaf nodes or splitting nodes and promoting middle keys. Deletion involves removing from leaf nodes, borrowing/promoting keys, or joining nodes.
Ad
Data models
- 1. Mrs. Maninder Kaur [email protected] Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 1
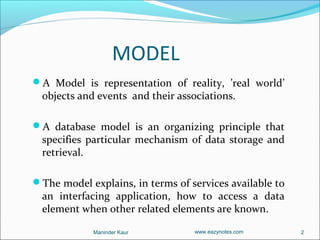
- 2. MODEL A Model is representation of reality, ’real world’ objects and events and their associations. A database model is an organizing principle that specifies particular mechanism of data storage and retrieval. The model explains, in terms of services available to an interfacing application, how to access a data element when other related elements are known. Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 2
- 3. Components of Data Models Structure Part: Consisting of set of rules according to which databases can be constructed. Manipulative Part: Define the types of operation that are allowed on the data. Set of Integrity Rules: Which ensures that data is accurate. Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 3
- 4. Purpose of Data Model To represent data. To make the data understandable. Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 4
- 5. Types of Data Models Object Based Data Models Physical Data Models Record Based Logical Data Models Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 5
- 6. Object Based Data Models It use concepts such as entities, attributes and relationships. Types of Object Based Data Models: * Entity Relationship * Object Oriented * Semantic *Functional Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 6
- 7. Physical Data Models It describe how data is stored in the computer, representing information such as record structures, record ordering and access paths. Less no. of models are there. Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 7
- 8. Record Based Logical Data Models o It is used to specify the overall logical structure of the database and to provide a higher-level description of the implementation. o Structured database in fixed formats. Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 8
- 9. Types of Record Based Data Models Hierarchical Model Network Model Relational Model Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 9
- 10. Types of Record Based Data Models Hierarchical Model Network Model Relational Model Maninder Kaur www.eazynotes.com 9




