Ad
Database systems
- 1. Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management Eighth Edition Chapter 1 Database Systems
- 2. Database Systems, 8th Edition 2 Objectives • The differences between data and information • What a database is • What the various types of databases are • Why they are valuable assets for decision making • The importance of database design
- 3. Database Systems, 8th Edition 3 Objectives (continued) • How modern databases evolved from file systems • About flaws in file system data management • What the database system’s main components are • How a database system differs from a file system • The main functions of a database management system (DBMS)
- 4. Database Systems, 8th Edition 4 Introduction • Good decisions require good information derived from raw facts • Data managed most efficiently when stored in a database • Databases evolved from computer file systems • Understanding file system characteristics is important
- 5. Database Systems, 8th Edition 5 Data vs. Information • Data are raw facts • Information is the result of processing raw data to reveal meaning • Information requires context to reveal meaning • Raw data must be formatted for storage, processing, and presentation • Data are the foundation of information, which is the bedrock of knowledge
- 6. Database Systems, 8th Edition 6 Data vs. Information (continued) • Data: building blocks of information • Information produced by processing data • Information used to reveal meaning in data • Accurate, relevant, timely information is the key to good decision making • Good decision making is the key to organizational survival
- 7. Database Systems, 8th Edition 7 Introducing the Database and the DBMS • Database: shared, integrated computer structure that stores a collection of data – End-user data: raw facts of interest to the end user – Metadata: data about data • Metadata provides description of data characteristics and relationships in data – Complements and expands value of data • Database management system (DBMS): collection of programs – Manage structure and control access to data
- 8. Database Systems, 8th Edition 8 Role and Advantages of the DBMS • DBMS is the intermediary between the user and the database • Database structure stored as file collection • Access database through the DBMS • DBMS enables data to be shared • DBMS integrates many users’ views of the data
- 10. Database Systems, 8th Edition 10 Role and Advantages of the DBMS (continued) • Advantages of a DBMS: – Improved data sharing – Improved data security – Better data integration – Minimized data inconsistency – Improved data access – Improved decision making – Increased end-user productivity
- 11. Database Systems, 8th Edition 11 Types of Databases • Databases can be classified according to: – Number of users – Database location(s) – Expected type and extent of use • Single-user database supports only one user at a time – Desktop database – single-user, runs on PC • Multiuser database supports multiple users at the same time – Workgroup database supports a small number – Enterprise database supports a large number
- 12. Database Systems, 8th Edition 12 Types of Databases (continued) • Centralized database: data located at a single site • Distributed database: data distributed across several different sites • Operational database: supports a company’s day-to-day operations – Transactional or production database • Data warehouse: stores data used for tactical or strategic decisions
- 13. Database Systems, 8th Edition 13 Types of Databases (continued) • Unstructured data exist in their original state • Structured data result from formatting – Structure applied based on type of processing to be performed • Semistructured data have been processed to some extent • Extensible Markup Language (XML) represents data elements in textual format • XML database supports semistructured XML data
- 15. Database Systems, 8th Edition 15 Why Database Design is Important • Database design focuses on design of database structure used for end-user data – Designer must identify database’s expected use • Well-designed database: – Facilitates data management – Generates accurate and valuable information • Poorly designed database: – Causes difficult-to-trace errors
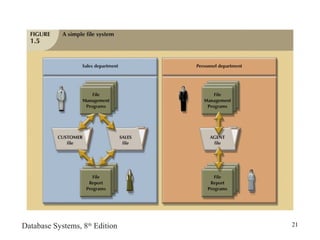
- 16. Database Systems, 8th Edition 16 Historical Roots: Files and File Systems • Reasons for studying file systems: – Complexity of database design easier to understand – Understanding file system problems helps to avoid problems with DBMS systems – Knowledge of file system useful for converting file system to database system • File systems typically composed of collection of file folders, each tagged and kept in cabinet – Organized by expected use
- 17. Database Systems, 8th Edition 17 Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) • Contents of each file folder logically related • Manual system served as a data repository for small data collections – Cumbersome for large collections • Data processing (DP) specialist converted computer file structure from manual system – Wrote software that managed the data – Designed the application programs • Initially, computer files systems resembled manual systems
- 18. Database Systems, 8th Edition 18 Historical Roots: Files and File Systems (continued) • As number of files increased, file systems evolved – Each file used its own application program to store, retrieve, modify data – Each file owned by individual or department that commissioned its creation • Data processing (DP) manager supervised the DP department • DP department’s primary activity remained programming
- 19. Database Systems, 8th Edition 19 FIELD RECORD : a logically connected set of one or more fields that describe person, place or thing
- 22. Database Systems, 8th Edition 22 Problems with File System Data Management • File system an improvement over manual system – File systems used for more than two decades – Understanding the shortcomings of file systems aids in development of modern databases – Many problems not unique to file systems • Even simple file system retrieval task required extensive programming – Ad hoc queries impossible – Changing existing structure difficult
- 23. Database Systems, 8th Edition 23 Problems with File System Data Management (continued) • Security features difficult to program – Often omitted in file system environments • Summary of file system limitations: – Requires extensive programming – Can not perform ad hoc queries – System administration complex and difficult – Difficult to make changes to existing structures – Security features likely to be inadequate
- 24. Database Systems, 8th Edition 24 Structural and Data Dependence • Structural dependence: access to a file dependent on its own structure – All file system programs must be modified to conform to a new file structure • Structural independence: change file structure without affecting data access • Data dependence: data access changes when data storage characteristics change • Data independence: data storage characteristics do not affect data access penggunaan sistem yang merubah struktur capaian data. Contoh: keluarkan duit Tabung Haji cara manual dan juga dengan menggunakan ATM. perubahan tidak menjejaskan capaian data cara capaian data berubah apabila data berubah perubahan data tidak menjejaskan cara capaian data
- 25. Database Systems, 8th Edition 25 Structural and Data Dependence (continued) • Practical significance of data dependence is difference between logical and physical format • Logical data format: how human views the data • Physical data format: how computer must work with data • Each program must contain: – Lines specifying opening of specific file type – Record specification – Field definitions
- 26. Database Systems, 8th Edition 26 Field Definitions and Naming Conventions • Storing customer name as single field is a liability – Better record definition breaks fields into component parts • Selecting proper field names important; field names are descriptive – With proper naming conventions, file structure becomes self-documenting – Some software places restrictions on length of field names • Each record should have unique identifier
- 28. Database Systems, 8th Edition 28 Data Redundancy • File system structure makes it difficult to combine data from multiple sources – Vulnerable to security breaches • Organizational structure promotes storage of same data in different locations – Islands of information • Data stored in different locations unlikely to be updated consistently • Data redundancy: same data stored unnecessarily in different places
- 29. Database Systems, 8th Edition 29 Data Redundancy (continued) • Data inconsistency: different and conflicting versions of same data occur at different places • Data anomalies: abnormalities when all changes in redundant data not made correctly – Update anomalies – Insertion anomalies – Deletion anomalies
- 30. Database Systems, 8th Edition 30 Database Systems • Database system consists of logically related data stored in a single logical data repository – May be physically distributed among multiple storage facilities • DBMS eliminates most of file system’s problems • Current generation stores data structures, relationships between structures, access paths – Takes care of defining, storing, managing all access paths and components
- 32. Database Systems, 8th Edition 32 The Database System Environment • Database system: defines and regulates the collection, storage, management, use of data • Five major parts of a database system: – Hardware – Software – People – Procedures – Data
- 34. Database Systems, 8th Edition 34 The Database System Environment (continued) • Hardware: all the system’s physical devices • Software: three types of software required: – Operating system software – DBMS software – Application programs and utility software • People: all users of the database system: – System and database administrators – Database designers – Systems analysts and programmers – End users
- 35. Database Systems, 8th Edition 35 The Database System Environment (continued) • Procedures: instructions and rules that govern the design and use of the database system • Data: the collection of facts stored in the database • Database systems created and managed at different levels of complexity • Database solutions must be cost-effective as well as tactically and strategically effective • Database technology already in use affects selection of a database system
- 36. Database Systems, 8th Edition 36 DBMS Functions • Most functions transparent to end users – Can only be achieved through the DBMS • Data dictionary management – DBMS stores definitions of data elements and relationships (metadata) in a data dictionary – DBMS looks up required data component structures and relationships – Changes automatically recorded in the dictionary – DBMS provides data abstraction, removes structural and data dependency ciri ciri kepada sesuatu data
- 38. Database Systems, 8th Edition 38 DBMS Functions (continued) • Data storage management – DBMS creates and manages complex structures required for data storage – Also stores related data entry forms, screen definitions, report definitions, etc. – Performance tuning: activities that make the database perform more efficiently – DBMS stores the database in multiple physical data files
- 40. Database Systems, 8th Edition 40 DBMS Functions (continued) • Data transformation and presentation – DBMS transforms data entered to conform to required data structures – DBMS transforms physically retrieved data to conform to user’s logical expectations • Security management – DBMS creates a security system that enforces user security and data privacy – Security rules determine which users can access the database, which items can be accessed, etc.
- 41. Database Systems, 8th Edition 41 DBMS Functions (continued) • Multiuser access control – DBMS uses sophisticated algorithms to ensure concurrent access does not affect integrity • Backup and recovery management – DBMS provides backup and data recovery to ensure data safety and integrity – Recovery management deals with recovery of database after a failure • Critical to preserving database’s integrity
- 42. Database Systems, 8th Edition 42 DBMS Functions (continued) • Data integrity management – DBMS promotes and enforces integrity rules • Minimizes redundancy • Maximizes consistency – Data relationships stored in data dictionary used to enforce data integrity – Integrity especially important in transaction- oriented database systems
- 43. Database Systems, 8th Edition 43 DBMS Functions (continued) • Database access languages and application programming interfaces – DBMS provides access through a query language – Query language is a nonprocedural language – Structured Query Language (SQL) is the de facto query language • Standard supported by majority of DBMS vendors
- 44. Database Systems, 8th Edition 44 DBMS Functions (continued) • Database communication interfaces – Current DBMSs accept end-user requests via multiple different network environments – Communications accomplished in several ways: • End users generate answers to queries by filling in screen forms through Web browser • DBMS automatically publishes predefined reports on a Web site • DBMS connects to third-party systems to distribute information via e-mail
- 45. Database Systems, 8th Edition 45 Managing the Database System: A Shift in Focus • Database system provides a framework in which strict procedures and standards enforced – Role of human changes from programming to managing organization’s resources • Database system enables more sophisticated use of the data • Data structures created within the database and their relationships determine effectiveness
- 46. Database Systems, 8th Edition 46 Managing the Database System: A Shift in Focus (continued) • Disadvantages of database systems: – Increased costs – Management complexity – Maintaining currency – Vendor dependence – Frequent upgrade/replacement cycles
- 47. Database Systems, 8th Edition 47 Summary • Data are raw facts • Information is the result of processing data to reveal its meaning • Accurate, relevant, timely information is the key to good decision making • Data usually stored in a database • DBMS implements a database and manages its contents
- 48. Database Systems, 8th Edition 48 Summary (continued) • Metadata is data about data • Database design defines the database structure – Well-designed database facilitates data management, generates valuable information – Poorly-designed database leads to bad decision making, organizational failure • Databases evolved from manual and computerized file systems – In a file system, data stored in independent files • Each requires its own management program
- 49. Database Systems, 8th Edition 49 Summary (continued) • Some limitations of file system data management: – Requires extensive programming – System administration complex and difficult – Changing existing structures difficult – Security features likely inadequate – Independent files tend to contain redundant data • Structural and data dependency problems
- 50. Database Systems, 8th Edition 50 Summary (continued) • Database management systems developed to address file system’s inherent weaknesses • DBMS present database to end user as single repository – Promotes data sharing – Eliminates islands of information • DBMS enforces data integrity, eliminates redundancy, promotes security