Ad
Dc ch11 : routing in switched networks
- 1. 1 1 1 1 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ DATA COMMUNICATION Routing in Switched Networks Data Communications and Networking Routing in Packet-Switching Network Performance Criteria Example Network Configuration Decision Time and Place Network Information Source and Update Timing Routing Strategies Fixed Routing Fixed Routing Tables Flooding Random Routing Adaptive Routing Reading: Book Chapter 11 Data and Computer Communications, 8th edition By William Stallings Least Cost Algorithms Dijkstra's Algorithm Belman Ford Algorithm
- 2. Data Communications and Networking Chapter 11 Routing in Switched Networks References: Book Chapters 12.1, 12.3 Data and Computer Communications, 8th edition By William Stallings
- 3. 3 3 3 3 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 3 Routing in Packet-Switching Network • Recall the function of a packet-switching network — To accept packets from a source station and deliver them to a destination station. • To accomplish this, a path or route through the network must be determined. • In general terms, routing seeks to design routes through the network for individual pairs of communicating end nodes such that the network is used efficiently. — Routing is one of the most complex and crucial design aspects of switched data networks. • Required characteristics of routing function: — Correctness — Simplicity — Robustness: the ability to deliver packets via some route in the face of localized failures and overloads — Stability — Fairness — Optimality — Efficiency: routing involves processing overhead & transmission overhead
- 4. 4 4 4 4 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 4 Performance Criteria • The selection of a route is generally based on some performance criterion. • The simplest criterion: —Minimum-hop (the least number of nodes) • A generalization of minimum-hop criterion: —Least-cost routing: a cost is associated with each link • E.g., in minimum-hop, each link has a cost of 1 • The route that accumulates the least cost is sought.
- 5. 5 5 5 5 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 5 Example Network Configuration Least-cost path from node 1 to 6
- 6. 6 6 6 6 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 6 Decision Time and Place • Two characteristics of routing decision: — Time and place that the decision is made • Decision time — Datagram: a routing decision is made individually for each packet — Virtual circuit: a routing decision is made at the time the virtual circuit is established • Decision place: which node or nodes are responsible for the routing decision? — Distributed routing • Each node has the responsibility of selecting an output link for routing packets as they arrive — Centralized routing • Decision is made by some designated node — Source routing • Decision is made by the source station
- 7. 7 7 7 7 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 7 Network Information Source and Update Timing • Routing decisions usually are based on knowledge of network (not always): topology, traffic load, link cost • Distributed routing —Nodes use local knowledge —May collect info from adjacent (directly connected) nodes —May collect info from all nodes on any potential route of interest • Centralized routing —Collect info from all nodes • Timing for node information update —Fixed strategy – the info is never updated —Adaptive strategy – the info is regularly updated
- 8. 8 8 8 8 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 8 Routing Strategies • Many routing strategies have evolved in packet-switching networks. Four of them will be introduced here: —Fixed routing —Flooding —Random routing —Adaptive routing
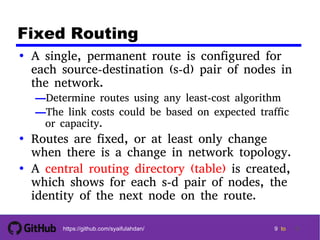
- 9. 9 9 9 9 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 9 Fixed Routing • A single, permanent route is configured for each source-destination (s-d) pair of nodes in the network. —Determine routes using any least-cost algorithm —The link costs could be based on expected traffic or capacity. • Routes are fixed, or at least only change when there is a change in network topology. • A central routing directory (table) is created, which shows for each s-d pair of nodes, the identity of the next node on the route.
- 10. 1010 10 10 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 10 Fixed Routing Tables Using the figure on Slide 4. It is not necessary to store the complete central routing directory for each pair of nodes.
- 11. 1111 11 11 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 11 Flooding • Flooding requires no network info. • A packet is sent by a source node to every neighbor. • At each node, an incoming packet is forwarded to all outgoing links except the incoming link. • Eventually a number of copies will arrive at destination. • Each packet is uniquely numbered so duplicates can be discarded. • Nodes can remember the identity of those packets it has already retransmitted. • Another technique: include a hop count field with each packet. Each time a node passes on a packet, it decrements the hop count by one. When the count reaches zero, the packet is discarded. — The hop count is sometimes called “time-to-live” (TTL) — Recall that TTL is also used in IP header which has nothing to do with flooding!
- 12. 1212 12 12 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 12 Flooding Example The TTL value decreases by one after each hop.
- 13. 1313 13 13 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 13 Properties of Flooding • All possible routes are tried —A packet will always get through if at least one path between source and destination exists. • At least one copy of the packet will have taken the minimum-hop-count route —Can be used to set up the virtual circuit • All nodes that are directly or indirectly connected to the source node are visited. —Useful to broadcast information (e.g. routing information) • Disadvantage: high traffic load
- 14. 1414 14 14 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 14 Random Routing • Random routing has the simplicity and robustness of flooding, with far less traffic load. • A node selects only one outgoing path to forward the incoming packet —The outgoing link can be selected at random, excluding the link on which the packet arrived. • A refinement is to select outgoing path based on probability calculation • Like flooding, no network info needed • Disadvantage: route is typically not least-cost nor minimum-hop
- 15. 1515 15 15 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 15 Adaptive Routing • Routing decisions change as conditions on the network change —Failure: node or link fails —Congestion: a portion of the network is heavily congested • Requires info about the state of the network • Drawbacks, compared to fixed routing —Routing decision is more complex; the processing burden on nodes increases —A tradeoff between quality of network info and the cost of updating such info • Advantages —Improved performance —Can aid in congestion control, because an adaptive routing strategy tends to balance loads.
- 16. 1616 16 16 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 16 Least Cost Algorithms • Virtually all packet-switching networks base their routing decisions on some form of lest-cost criterion. —Can minimize hop with each link cost 1 —Can have link value inversely proportional to capacity • Least-cost routing problem —Given a network of nodes connected by bi-directional links, where each link has a cost associated with it in each direction, define the cost of a path between two nodes as the sum of costs of links traversed. For each pair of nodes, find a path with the least cost. • Two common algorithms —Dijkstra’s algorithm —Bellman-Ford algorithm
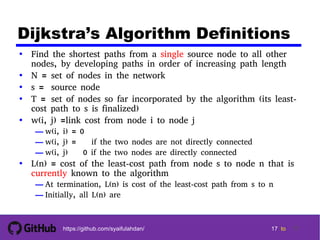
- 17. 1717 17 17 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 17 Dijkstra’s Algorithm Definitions • Find the shortest paths from a single source node to all other nodes, by developing paths in order of increasing path length • N = set of nodes in the network • s = source node • T = set of nodes so far incorporated by the algorithm (its least- cost path to s is finalized) • w(i, j) =link cost from node i to node j — w(i, i) = 0 — w(i, j) = if the two nodes are not directly connected — w(i, j) 0 if the two nodes are directly connected • L(n) = cost of the least-cost path from node s to node n that is currently known to the algorithm — At termination, L(n) is cost of the least-cost path from s to n — Initially, all L(n) are
- 18. 1818 18 18 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 18 Dijkstra’s Algorithm Method • Step 1 [Initialization] —T = {s}: the set of nodes so far incorporated consists of only the source node —L(n) = w(s, n) for n ≠ s: the initial path costs to neighboring nodes are simply the link costs • Step 2 [Get Next Node] —Find the neighboring node not in T with the least-cost path from s (smallest L(n) ) —Incorporate that node into T —Also incorporate the edge that is incident on that node and a node in T that contributes to the path • Step 3 [Update Least-Cost Paths] —L(n) = min[L(n), L(x) + w(x, n)] for all n Ï T —If the latter term is smaller, the path from s to n is now updated as the path from s to x extended with the edge from x to n
- 19. 1919 19 19 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 19 Dijkstra’s Algorithm Notes • Terminate when all nodes have been added to T • At termination, value L(n) associated with each node n is the cost of least-cost path from s to n. • In addition, algorithm defines the least-cost path from s to each other node • One iteration of steps 2 and 3 adds one new node to T, and defines the least-cost path from s to that node
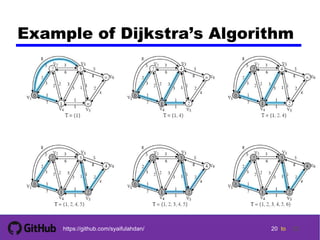
- 20. 2020 20 20 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 20 Example of Dijkstra’s Algorithm
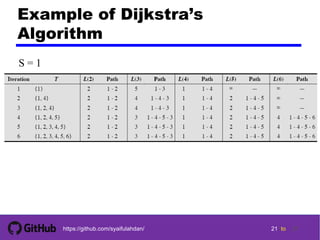
- 21. 2121 21 21 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 21 Example of Dijkstra’s Algorithm S = 1
- 22. 2222 22 22 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 22 Bellman-Ford Algorithm Definitions • Find the least-cost paths from a given source node subject to constraint that the paths contain at most one link, then find the shortest paths with a constraint of paths of at most two links, and so on. • Finally, this algorithm returns the least-cost paths between any pairs of nodes. • s = source node • w(i, j) = link cost from node i to node j —w(i, i) = 0 —w(i, j) = if the two nodes are not directly connected —w(i, j) 0 if the two nodes are directly connected • h = maximum number of links in a path at the current stage of the algorithm • Lh(n) = cost of the least-cost path from s to n under the constraint of no more than h links
- 23. 2323 23 23 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 23 Bellman-Ford Algorithm Method • Step 1 [Initialization] —L0(n) = , for all n s —Lh(s) = 0, for all h • Step 2 [Update] —For each successive h 0 • For each n ≠ s, compute Lh+1(n)=min{ Lh(n), minj[Lh(j)+w(j,n)] } • It means “the least-cost path from s to n of length h+1 is the least-cost path of length h, or it is actually a length h+1 path, and before it reaches n, it passes through j”
- 24. 2424 24 24 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 24 Example of Bellman-Ford Algorithm
- 25. 2525 25 25 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 25 Example of Bellman-Ford Algorithm S = 1
- 26. 2626 26 26 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 26 Comparison • What information needs to be gathered? • Bellman-ford —Each node can maintain a set of costs and associated paths for every other node and exchange this information with its direct neighbors from time to time —Each node can update its costs and paths using only the information from its neighbors and knowledge of its link costs. • Dijkstra’s algorithm —Each node must have complete topological information about the network
















![1818
18 18 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 18
Dijkstra’s Algorithm Method
• Step 1 [Initialization]
—T = {s}: the set of nodes so far incorporated consists of only
the source node
—L(n) = w(s, n) for n ≠ s: the initial path costs to
neighboring nodes are simply the link costs
• Step 2 [Get Next Node]
—Find the neighboring node not in T with the least-cost path
from s (smallest L(n) )
—Incorporate that node into T
—Also incorporate the edge that is incident on that node and
a node in T that contributes to the path
• Step 3 [Update Least-Cost Paths]
—L(n) = min[L(n), L(x) + w(x, n)] for all n Ï T
—If the latter term is smaller, the path from s to n is now
updated as the path from s to x extended with the edge
from x to n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-ch11routinginswitchednetworks-190925071354/85/Dc-ch11-routing-in-switched-networks-18-320.jpg)


![2323
23 23 tohttps://github.com/syaifulahdan/ 23
Bellman-Ford Algorithm Method
• Step 1 [Initialization]
—L0(n) = , for all n s
—Lh(s) = 0, for all h
• Step 2 [Update]
—For each successive h 0
• For each n ≠ s, compute
Lh+1(n)=min{ Lh(n), minj[Lh(j)+w(j,n)] }
• It means “the least-cost path from s to n of length h+1
is the least-cost path of length h, or it is actually a
length h+1 path, and before it reaches n, it passes
through j”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-ch11routinginswitchednetworks-190925071354/85/Dc-ch11-routing-in-switched-networks-23-320.jpg)


























































































