Digital Image File Formats
- 1. A Programme Under the compumitra Series Copyright 2010-2015 © Sunmitra Education Technologies Limited, India "A Picture is worth a thousand words." An Old Proverb. DIGITAL IMAGE FEATURES AND FILE FORMATS
- 2. Outline About Images. Image Types. Image Features. Image File Format Categorisation. Raster Formats. Vector Formats. Special Formats.
- 3. About Images
- 4. From Cave Paintings to Digital Images Visual representation of anything displayed on a medium such as paper, screen etc is called an IMAGE. Modern 3D holograms may however be displayed without a base medium. Digital Images are those which are used on computers and other digital devices and are formed by using a series of 1's and 0's . While Images have been there since millions of years as man-made cave- paintings or naturally formed art forms, Digital images are just about 50+ years old. .
- 5. Image Formation The primary concept of image formation signify the presence of dots. In digital mediums these dots are often called PIXELS (Picture Elements) for 2-D medium or VOXELS (Volumetric Picture Elements ) for 3- D images. Pixels can be of single colour in an entire image drawing or may be of primary colours in a multi-colour drawing. The proximity of pixels (DPI - Dots Per Inch) and the count over a given dimension represent the Image Resolution which is the primary measure of Visual Quality of an Image.
- 6. Image Types
- 7. Types of Digital Images (Based on Drawing Units) RASTER IMAGES: Images made of pixels or dots. A Raster means a frame of Screen which is made using scanning of entire screen line by line. Raster images are resolution dependent and can not be scaled up or down without loss of quality. VECTOR IMAGES: Images made using lines and curves that are drawn using mathematical equations. These images are not related to resolution and they can be scaled up or down to any size. While drawing on a medium vector images are also drawn using pixels, but they retain their scaling quality and redrawn again when resized. Both Raster and Vector Images can have Colours. In case of Raster Images, colours is a pixel property while in case of Vector Images Colours are given as another mathematical property.
- 8. Types of Digital Images (Based On Dimensions) 2-D IMAGES: Images that are seen on X and Y axis only. 3-D IMAGES on 2-D Medium: Images that are displayed on 2-D medium but still have feeling of depth associated with it. These images might require a viewer to wear special glasses to feel the 3D effect. 3-D IMAGES on 3-D Medium: Images that are produced in all 3- Dimensions of space such as 3-D holographic images, 3-D Laser Images.
- 10. Features List Resolution and DPI Colour/Bit Depth Compression Transparency Alpha Channels Gamma Correction Anti-Aliasing Interlacing Palletes Half Tone/ Duotone Animation Support
- 11. Resolution and DPI Resolution represents the number of pixels required to draw a raster based image. It is given by pixel count in its width (Horizontal Resolution) and the pixel count in its height (Vertical Resolution). Images also has a related property called DPI (dots per inch) that combined with its resolution governs the size it will take on screen. The visible quality of an image will also depend on the display resolution property. Common computer display resolutions are – 800 x 600 Pixels (SVGA resolution) 1024 x 768 Pixels (XGA resolution) 1280 x 1024 Pixels (SXGA resolution) 2048 x 1080 Pixels (2K resolution)
- 12. Colour Depth/Bit Depth 2 Colour: This is mostly a black and white image. It may however be any other two colour image also. It requires just 1 bit for colour information. 16 Colour: These are very basic image types used on old machines. The colour information here is encoded in 4 bits only. 256 Color: These are 8 Bit images often used in BMP and GIF formats. 16 Bit: This is also known as HI-COLOR setting. These have more than 64 Thousand colours and are suitable for most picture related work on computers. 24 Bit: This is known as TRUE COLOR Setting. These have a better colour depth of more than 16.7 Million Colours and are visually excellent. 32 Bit: These have even better picture quality to show excellent picture shading effects and shades of special colours like silver, gold, colours across a glass etc. This quality is also available on modern computers.
- 13. Image Compression. With the advent of faster computers the technology of reducing the image file size gained momentum. It is possible to reduce file size of a pixel based image to the tune of 1/10 using modern compression techniques without much loss in image quality. Image compression can be either completely lossless like in case of GIF and PNG standards, while in case of lossy compression even more size reduction can be achieved as in the case of JPG formats (commonly used for photographs). 5.6KB File Size 112KB File Size Watch the minor loss of image quality near the Cat's nose.
- 14. Image Transparency. Transparency is a feature of image where a certain colour of image can be replaced by the background. Image Transparency feature is available with certain file formats only. Most common one with transparency features are GIF, PNG and TIFF formats. In some formats multiple levels of transparency is supported by adding additional byte for transparency level. So instead of RGB colours it becomes RGBA colours. Here A stands for Alpha Channel. Typical example of this is the PNG file format. White Background Colour has been made transparent in this case.
- 15. More About Alpha Channel It is a way to produce partial transparency. This often provides perfect smoothening of edges which is otherwise difficult due to rectangular nature of pixels. The drop shadow effect is also correctly possible due to partial transparency feature.
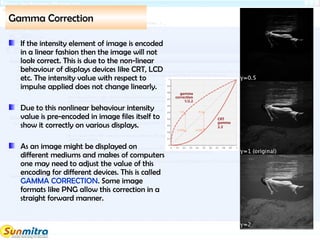
- 16. Gamma Correction If the intensity element of image is encoded in a linear fashion then the image will not look correct. This is due to the non-linear behaviour of displays devices like CRT, LCD etc. The intensity value with respect to impulse applied does not change linearly. Due to this nonlinear behaviour intensity value is pre-encoded in image files itself to show it correctly on various displays. As an image might be displayed on different mediums and makes of computers one may need to adjust the value of this encoding for different devices. This is called GAMMA CORRECTION. Some image formats like PNG allow this correction in a straight forward manner.
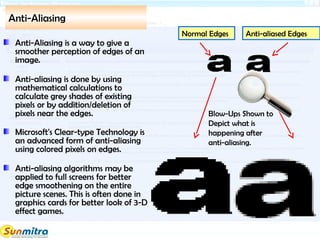
- 17. Anti-Aliasing Anti-Aliasing is a way to give a smoother perception of edges of an image. Anti-aliasing is done by using mathematical calculations to calculate grey shades of existing pixels or by addition/deletion of pixels near the edges. Microsoft's Clear-type Technology is an advanced form of anti-aliasing using colored pixels on edges. Anti-aliasing algorithms may be applied to full screens for better edge smoothening on the entire picture scenes. This is often done in graphics cards for better look of 3-D effect games. Normal Edges Anti-aliased Edges Blow-Ups Shown to Depict what is happening after anti-aliasing.
- 18. Interlacing Interlacing indicates the way an image is drawn on the screen. Interlaced Image: When the image is drawn in a way like it is done on a TV where ODD frame is drawn first and then EVEN frame is drawn, it is called an Interlaced image. In this case the whole image frame is drawn at once and then gradually the other interpolated frames are drawn to give a feel of improving quality. Non-Interlaced Image: In this type the image is drawn from top to bottom pixel by pixel and line by line. The rest portion of image looks blank. Non-Interlacing is also termed as "Progressive Scan". Image Formats Like GIF, JPG and TIFF support interlacing. Interlaced Non-Interlaced
- 19. Image Palettes The set of colour an image is made of is called image palette. A typical digital image may contain an 8 bit palette (256 colours) or a set of more colours like 64K colours or 16.7 Million Colours. A palette based image has an advantage of changing the entire colour set in one go by just switching the palettes. 8-Bit BMP and GIF images are examples of palette based images.
- 20. Half Tone / Duo Tone Half tone is a method where continuous tone perception is generated with the use of dots pitched far from regular dots density. Duotone is produced by superimposing another contrasting colour halftone over halftone drawing in another colour.
- 21. Animation Some Image Formats have limited capability to store multiple raster image frames that can produce animation effects. Major Example is GIF format. Later PNG format was also revised as MNG format (Multiple Image Network Graphics) to support animation. MNG is yet to be supported on common internet browsers. The other most common animation format on internet is SWF (Shock Wave Flash) format that is primarily a vector based image format with fully time-based animation support.
- 22. Popular 2-D Digital Image Formats
- 23. Categorisation of 2-D Image Formats RASTER IMAGE FORMATS Non-Proprietary: JPG, GIF, PNG, TIFF, BMP Proprietary: PSD, PSP VECTOR IMAGE FORMATS Non-Proprietary: CGM, SVG, WMF/EMF, EPS Proprietary: CDR, AI, PDF, SWF
- 24. RASTER FORMATS
- 25. BMP – Bitmap Format Used to store direct pixel colour information. It is mainly used on Windows family of OS. One of its variations is DIB (device independent bitmaps). It has file extensions BMP and DIB. Its 8 bit version can store only 256 colours. It creates a very large file-size as it has no major compression technique in use. Sometimes low compression ratio techniques like RLE (Run Length Encoding) can be used along with BMPs. BMP files may be zipped to reduce file sizes but still BMP format is not suitable for internet transfer. BMP format is however useful for standalone applications and creation of a base file that stores entire image information without any quality loss.
- 26. GIF – Graphics Interchange Format This is also a pixel based format with a good image compression technique called LZW compression. The image quality is not reduced while using this compression. It supports upto 256 colours. It is good for images with lines, curves and solid colours. It is most widely supported on internet and other software. It can support animated images with different set of colours for each frame. It also supports transparency.
- 27. JPG/JPEG – Joint Photographic Expert Group It has been designed under the banner of ISO (International standard Organisation) by Joint Photographic Experts Group. It is a highly compressed raster image format best suited for photographs. It allows for adjustment of degree of compression. It is a lossy compression. Once compressed perfect reproduction of original is impossible. For very little image loss 1:10 compression is often possible. It has an advanced version called JPEG 2000 which is still less used as it is a licensed version. Progressive JPGs allow multipass drawing when loaded.
- 28. PNG – Portable Network Graphics What the GIF format lags, PNG completes. It supports up to 48 Bit Colours. It supports Alpha Channel Based Transparency. PNG is a lossless file format so it is very useful to store base files that can be edited across multiple graphic editors to produce the final outputs.
- 29. TIFF – Tagged Image File Format This format was designed for images for Desktop Publishing Purposes. This format is often the default format in which a scanner saves the file. It can work as an image container along with its editing/cropping status. It can support compression without any loss of quality. It is highly recommended for archival images so that every thing can remain intact along with the image. It can even act as container of lossy JPEG files. Adobe Corp. holds the copyright of this format but for usage purpose license is not required. It is also useful for high precision scientific images. The other option for high precision scientific images such as astronomical images is FITS (Flexible Image Transport System)
- 30. PSD – Photoshop Document It is a application specific proprietary format for Adobe Photoshop. Application specific formats support layered image storage, editing marks, clipping, padding and position storage. It supports colour modes like RGB, CMYK, LAB, GREY, PALLETTED etc. It supports unlimited colours. It produces native bitmap format with RLE compression.
- 31. VECTOR FORMATS
- 32. WMF/EMF – Windows Metafile/Enhanced Meta File It can store both vector and bitmap components. It is the native format for applications like Word, Power-point, Publisher etc. The EMF enhancement has commands for printer graphics also. WMF/EMF have direct function calls for windows GDI – Graphics Device Interface. WMF produces very small size files and is quite suitable for usage in form of clipart libraries. WMZ and EMZ are compressed formats of WMF and EMF respectively.
- 33. CDR - CorelDraw It is native Vector Based Format for Corel Applications. It has capability to store both vector based and bitmap images. It can store multiple pages of data. It stores all editing status and other image configuration data. It produces an extremely low file size. Every Version of CorelDraw has different formats and it is essentially required to convert files to a lower version while transferring to previous version of Corel Application.
- 34. EPS – Encapsulated Postscript This format is frequently used for production quality drawing in printing. This is a vector based format that can contain PostScript Style Description of Drawing. Its purpose is for printing only and EPS files are not meant for Editing. Converted EPS files may only be viewed by special viewers. Regular graphics applications are not able to open these file.
- 35. OTHER FORMATS
- 36. ICO - ICON It is a file format for Windows Icons. One can produce 16x16 16 colour icon to 48x48 16.7 Million Colour Icons using this format. Technically ICO file can even store a 1x1 pixel image. Vista and above supports even the 256x256 pixel icons. Modern systems also supports PNG files to be used as icons. One may require to use a special pixels based editor to create icons.
- 37. SVG – Scalable Vector Graphics It is a modern XML based file for vector graphics, that can be used on internet also. It is an standard from W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) that created standards for HTML, XML etc. It supports standard compression techniques and is saved as SVGZ when compressed. It supports dynamic, interactive drawing using Javascript. It supports Vector Graphics, Raster Graphics and Normal Text.
- 39. Ask and guide me at [email protected] Share this information with as many people as possible. Keep visiting www.sunmitra.com for programme updates.