Distributed systems
- 1. Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Distributed Systems EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS Homework number: 1 Group number: EEDC-30 Group members: Javier Álvarez [email_address] Francesc Lordan [email_address] Roger Rafanell [email_address]
- 2. Content Distributed Systems Part 1: Definition Part 2: Evolution Part 3: Fields of application Part 4: Questions
- 3. Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Part 1 Definition EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS
- 4. Definition “ A distributed system is a set of autonomous computational resources, communicated through a computer network, that cooperate to achieve a common goal.”
- 5. Key Concepts Cooperation Nodes work together to achieve a common goal. Autonomous Each node has a limited knowledge of the whole system. Communication Nodes communicate by passing messages. Homogeneity/Heterogeneity Many types of computers. Many network scopes (LAN/WAN). Many networks topologies.
- 6. Advantages Reliability Fault tolerance mechanisms, replication of processes, … Resource sharing Many users interacting with the same resource at the same time. Resource aggregation computing power, disk space, network bandwidth, … Scalability Ease to modify the amount of computing resources. Openness Easy integration of a part of another system. Price No need to purchase resources if remote ones are used.
- 7. Disadvantages Security Data, processes and computational resources are exposed through the network. Relies on network latencies Message passing is slower than just reading from local memory. Complexity Access, configuration and programming.
- 8. Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Part 2 Evolution and Architectures EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS
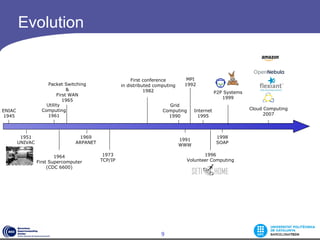
- 9. Evolution 1951 UNIVAC Internet 1995 Packet Switching & First WAN 1965 1969 ARPANET 1973 TCP/IP ENIAC 1945 First conference in distributed computing 1982 Utility Computing 1961 1996 Volunteer Computing Cloud Computing 2007 1964 First Supercomputer (CDC 6600) MPI 1992 P2P Systems 1999 1998 SOAP Grid Computing 1990 1991 WWW
- 10. Architectures Master-worker A master node orchestrates the execution of an application among a set of workers. Client-server Simple clients contacts the server asking for data / process. 3-tier A new node between the client and the server is added to the previous architecture. This middle layer contents the complex logic to interpret the result obtained from the server. The client logic is simplified.
- 11. Architectures N-tier 3-tier but with many levels. The request is forwarded through n-layers and the response is treated by each one. Tightly coupled Resources that closely work together (Clusters). Peer-to-Peer There is no special machine. The responsibility is uniformly divided through all the nodes. Space based Create the illusion of a single address-space even it is distributed.
- 12. Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Part 3 Fields of application EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS
- 13. Fields of application Everywhere!
- 14. Applications Computer science Distributed Databases (Hbase, Cassandra, …) Distributed file systems (GlusterFS, HDFS, Lustre, … ) Ad-hoc networks Sensor networks Mobile apps Transport Aeronautics VANET: Vehicular ad-hoc networks Entertainment: Multiplayer Online Games Gaming/Media-On-Demand
- 15. Applications Science & Engineering Forecasting models Simulators Data Analysis Medics Electronic medical history Remote exploration, therapy Business Business Intelligence Accounting Virtual shops Public administration Services based on OpenData …
- 16. Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Part 4 Questions EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS
- 17. Questions
![Execution Environments for Distributed Computing Distributed Systems EEDC 34330 Master in Computer Architecture, Networks and Systems - CANS Homework number: 1 Group number: EEDC-30 Group members: Javier Álvarez [email_address] Francesc Lordan [email_address] Roger Rafanell [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributedsystems-120223105732-phpapp01/85/Distributed-systems-1-320.jpg)