Dpdk: rte_security: An update and introducing PDCP
- 1. rte_security: An update and introducing PDCP Akhil Goyal (NXP) Hemant Agrawal (NXP) DPDK Summit – Dublin- 2018
- 2. Agenda Rte_security – A brief recap PDCP - Introduction Rte_security – Updates for PDCP Protocol Error Handling Q&A
- 4. rte_security – A brief recap Framework for management and provisioning of hardware acceleration of security protocols. Generic APIs to manage security sessions. Net/Crypto device PMD initializes a security context which is used to access security operations on that particular device. Rich capabilities discovery APIs Currently IP Security (IPsec) protocol is supported. Could support a wide variety of protocols/applications Enterprise/SMB VPNs — IPsec Wireless backhaul — IPsec, PDCP Data-center — SSL WLAN backhaul — CAPWAP/DTLS Control-plane options for above — PKCS, RNG Net PMD Security Library Crypto PMD
- 5. A multi-deviceAPI (Object Model) <<Interface>> rte_cryptodev APIs rte_device cryptodev_ops rte_cryptodev - device - ops <<Interface>> rte_security APIs <<Interface>> rte_ethdev APIs rte_security_context - device - ops security_ops rte_device eth_dev_ops rte_ethdev - device - ops security_ops rte_security_context - device - ops
- 6. Protocols and actions Select the session Protocol: “rte_security_session_protocol” IPSEC, MACSEC, SSL, PDCP etc. Select the Security Action Type: “rte_security_session_action_type” RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_INLINE_CRYPTO: Inline crypto processing as NIC offload during recv/transmit. RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_INLINE_PROTOCOL: Inline security protocol processing as NIC offload during recv/transmit. RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_LOOKASIDE_PROTOCOL: Security protocol processing including crypto on a crypto accelerator. Action type can be an input for the given application during session creation Based on the action type and other session related information, application configures session parameters for security offload.
- 7. IPSEC - Encrypt Packet Processing Packet Received Flow and SPD/SA Lookup Pre-Protocol Processing • Sequence Number • Random IV generation • Block Cipher Padding • Tunnel Header Preparations (TOS/ECN/DF etc) Crypto Processing • Encryption • Authentication Post-Protocol Processing IP Header Addition L2 process and transmission
- 8. Security APIs /* Security context for crypto/eth devices */ struct rte_security_ctx { void *device; /**< Crypto/ethernet device attached */ const struct rte_security_ops *ops; /**< Pointer to security ops for the device */ uint16_t sess_cnt; /**< Number of sessions attached to this context */ }; /** security session configuration parameters */ struct rte_security_session_conf config = { .action_type = RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_INLINE_CRYPTO, /**< Type of action to be performed on the session */ .protocol = RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_IPSEC, /**< Security protocol to be configured */ .ipsec = { .spi = /**< Security Protocol Index */, .salt = /** Salt value */, .direction = RTE_SECURITY_IPSEC_SA_DIR_INGRESS, .proto = RTE_SECURITY_IPSEC_SA_PROTO_ESP, .mode = RTE_SECURITY_IPSEC_SA_MODE_TUNNEL }, /**< Configuration parameters for security session */ .crypto_xform = /** crypto transforms */ /**< Security Session Crypto Transformations */ .userdata = /** Application specific User data */ }; Get device context void *rte_cryptodev_get_sec_ctx(uint8_t dev_id) void *rte_eth_dev_get_sec_ctx(uint8_t port_id) Create Session struct rte_security_session * rte_security_session_create( struct rte_security_ctx *instance, struct rte_security_session_conf *conf, struct rte_mempool *mp); Update (rte_security_session_update) Destroy (rte_security_session_destroy) Get Stats (rte_security_session_stats_get) Get userdata (rte_security_get_userdata) Set pkt metadata (rte_security_set_pkt_metadata) Attach session with crypto_op (rte_security_attach_session)
- 9. PDCP Packet Data Convergence Protocol
- 10. PDCP- Features Transfer of Data (C-Plane and U-Plane) between RLC and Higher U-Plane interface Maintenance of PDCP SN(Sequence Number) Transfer of SN Status (for use Upon Handover) ROHC (Robust Header Compression) In-Sequence delivery of Upper Layer PDUs at re-establishment of lower layer Elimination of duplicate of lower layer SDUs at re-establishment of lower layer for RLC AM Ciphering and Deciphering of C-Plane and U-Plane data Integrity Protection and Integrity verification of C-Plane Data Timer based Discard Duplicate Discard
- 11. Where PDCP fits in LTE Radio Protocol stack??
- 12. PDCP sublayer functional view Radio Interface (Uu) UE/E-UTRAN E-UTRAN/UE Transmitting PDCP entity Ciphering Header Compression (u-plane only) Receiving PDCP entity Sequence numbering Integrity Protection (c-plane only) Add PDCP header Header Decompression (u- plane only) Deciphering Remove PDCP Header In order delivery and duplicate detection (u-plane only) Integrity Verification (c-plane only) Packets associated to a PDCP SDU Packets associated to a PDCP SDU Packetsnot associatedtoa PDCPSDU Packetsnot associatedtoa PDCPSDU
- 13. Integrity protection and verification Pure computation function to protect transmitted data against a non-authorised third-party from alteration. Applies on header and data part of SRB1 and SRB2 PDU in CP. Security Control Information Element “IntegrityProtAlgorithm ” of RRC contain 4 bit field: ‘0001’ – SNOW 3G based algorithm (128-EIA1) ‘0010’ – AES based algorithm (128-EIA2) EIAKEY MAC -ISender COUNT DIRECTION MESSAGE BEARER-ID EIA XMAC -I COUNT DIRECTION MESSAGE BEARER-ID KEY Receiver
- 14. Ciphering and Deciphering CP: Ciphers/deciphers data part and MAC-I of PDCP data PDU. UP: Ciphers/deciphers data part of PDCP data PDU. Algorithm common for CP and UP Security Control Information Element “CipheringAlgorithm ”of RRC contain 4 bit field: ‘0000’ – no ciphering (EPS Encryption Algo, EEA0) ‘0001’ – SNOW 3G based algorithm (128-EEA1) ‘0010’ – AES based algorithm (128-EEA2) PLAINTEXT BLOCK EEA COUNT DIRECTION BEARER LENGTH KEY KEYSTREAM BLOCK CIPHERTEXT BLOCK EEA COUNT DIRECTION BEARER LENGTH KEY KEYSTREAM BLOCK PLAINTEXT BLOCK Sender Receiver
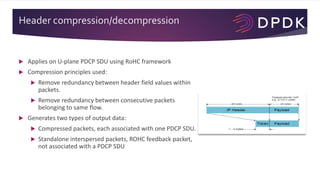
- 15. Header compression/decompression Applies on U-plane PDCP SDU using RoHC framework Compression principles used: Remove redundancy between header field values within packets. Remove redundancy between consecutive packets belonging to same flow. Generates two types of output data: Compressed packets, each associated with one PDCP SDU. Standalone interspersed packets, ROHC feedback packet, not associated with a PDCP SDU
- 16. PDCP sequence number options Depending on the type of packet, different Sequence numbers are chosen. Control plane PDCP Data PDU (5 Bits) User plane PDCP Data PDU with long PDCP SN (12 bits) User plane PDCP Data PDU with short PDCP SN (7 bits) User plane PDCP Data PDU with extended PDCP SN (15 bits)
- 17. PDCP – Basic / Complicated PDCP can do ciphering, integrity, header compression. But it may have certain messages which do not require any ciphering, integrity, header compression. It can be as simple as null – cipher, null – auth, no header compression It can be as complicated as cipher (with ZUC, snow-3g) and auth (with AES-CMAC, ZUC etc) PDCP has evolved from basic Release 8 to complicated Release 13 of 3GPP. Current proposal for rte_security is for supporting cipher and auth operations with PDCP header(lookaside)
- 18. rte_security -revisit Updates for PDCP
- 19. rte_security – Update for PDCP Create PDCP security session using rte_security_session_create() with updated session configuration as follows: struct rte_security_session_conf { enum rte_security_session_action_type action_type; /**< Type of action to be performed on the session */ enum rte_security_session_protocol protocol; /**< Security protocol to be configured */ RTE_STD_C11 union { struct rte_security_ipsec_xform ipsec; /**< IPSec specific configurations */ struct rte_security_macsec_xform macsec; /**< macsec Specific configurations */ struct rte_security_pdcp_xform pdcp; /**< PDCP specific configurations */ }; /**< Configuration parameters for security session */ struct rte_crypto_sym_xform *crypto_xform; /**< Security Session Crypto Transformations */ void *userdata; /**< Application specific userdata to be saved with session */ }; Here protocol should be RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_PDCP.
- 20. PDCP Configuration /** * PDCP security association configuration data. * * This structure contains data required to create a PDCP security session. */ struct rte_security_pdcp_xform { int8_t bearer; /**< PDCP bearer ID */ enum rte_security_pdcp_domain domain; /** < PDCP mode of operation: Control or data */ enum rte_security_pdcp_direction pkt_dir; /**< PDCP Frame Direction 0:UL 1:DL */ enum rte_security_pdcp_sn_size sn_size; /**< Sequence number size, 5/7/12/15 */ int8_t hfn_ovd; /**< Overwrite HFN per operation 0:disable,1:enable */ uint32_t hfn; /**< Hyper Frame Number */ uint32_t hfn_threshold; /**< HFN Threshold for key renegotiation */ };
- 21. PDCP Capabilities Example { /* PDCP Lookaside Protocol offload Data Plane */ .action = RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_LOOKASIDE_PROTOCOL, .protocol = RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_PDCP, .pdcp = { .domain = RTE_SECURITY_PDCP_MODE_DATA, }, .crypto_capabilities = pdcp_capabilities }, { /* PDCP Lookaside Protocol offload Control Plane */ .action = RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_LOOKASIDE_PROTOCOL, .protocol = RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_PDCP, .pdcp = { .domain = RTE_SECURITY_PDCP_MODE_CONTROL, }, .crypto_capabilities = pdcp_capabilities }, static const struct rte_cryptodev_capabilities pdcp_capabilities[] = { { /* SNOW 3G (UIA2) */ .op = RTE_CRYPTO_OP_TYPE_SYMMETRIC, {.sym = { .xform_type = RTE_CRYPTO_SYM_XFORM_AUTH, {.auth = { .algo = RTE_CRYPTO_AUTH_SNOW3G_UIA2, .block_size = 16, .key_size = { .min = 16, .max = 16, .increment = 0 }, .digest_size = { .min = 4, .max = 4, .increment = 0 }, .iv_size = { .min = 16, .max = 16, .increment = 0 } }, } }, } }, }
- 22. API Sequence Security Instance NET/CRYPTO PMD user ìnstance->ops->session_create() allocate SA entry sec_sess rte_security_session_create() set parameters in security_session_conf program SA to hw HW
- 23. rte_security – Error handling Handling for protocol errors Anti-replay errors, Sequence number overflow errors For inline protocol – rte_eth_events can be used to pass error information to the application For look-aside – Crypto errors can be extended for security errors in rte_crypto_op_status
- 24. Summary Rte_security can be used as a framework to support various security protocols. PDCP protocol is briefly discussed in this presentation Basic API sequence and data flow shall remain same for every protocol. Updates for PDCP are floated on the mailing list. Please have a look. PMD owners supporting PDCP shall come up and send updates for there drivers.
- 25. FutureWork Header Compression/Decompression(RoHC) support for PDCP Inline crypto/protocol implementation for PDCP Multi process support Enable Event based security sessions Test application for PDCP Software equivalent enablement It could be possible to offer software equivalent processing under this API, may or may not be desirable depending on protocol and it’s processing overhead.
- 26. Questions? <Akhil Goyal, Hemant Agrawal> <[email protected], [email protected]>
Editor's Notes
- #9: Session reuse



















![PDCP Capabilities Example
{ /* PDCP Lookaside Protocol offload Data Plane */
.action = RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_LOOKASIDE_PROTOCOL,
.protocol = RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_PDCP,
.pdcp = {
.domain = RTE_SECURITY_PDCP_MODE_DATA,
},
.crypto_capabilities = pdcp_capabilities
},
{ /* PDCP Lookaside Protocol offload Control Plane */
.action = RTE_SECURITY_ACTION_TYPE_LOOKASIDE_PROTOCOL,
.protocol = RTE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_PDCP,
.pdcp = {
.domain = RTE_SECURITY_PDCP_MODE_CONTROL,
},
.crypto_capabilities = pdcp_capabilities
},
static const struct rte_cryptodev_capabilities pdcp_capabilities[] =
{
{ /* SNOW 3G (UIA2) */
.op = RTE_CRYPTO_OP_TYPE_SYMMETRIC,
{.sym = {
.xform_type = RTE_CRYPTO_SYM_XFORM_AUTH,
{.auth = {
.algo = RTE_CRYPTO_AUTH_SNOW3G_UIA2,
.block_size = 16,
.key_size = {
.min = 16,
.max = 16,
.increment = 0
},
.digest_size = {
.min = 4,
.max = 4,
.increment = 0
},
.iv_size = {
.min = 16,
.max = 16,
.increment = 0
}
}, }
}, }
},
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpdk-dublin-2018-pdcp-190514120356/85/Dpdk-rte_security-An-update-and-introducing-PDCP-21-320.jpg)




