Drupal CDN integration: easier, more flexible and faster!
90% of the page loading time is spent on retrieving CSS, JavaScript and images. There are lots of techniques to reduce this, but using a CDN is the most effective. Currently it's expensive to integrate with a CDN (especially if you want to avoid vendor lock-in) and it's hard to serve file A from a CDN, file B from a static file server and file C from neither. In this session, you'll learn about the push-to-CDN model, which makes all of this trivial. Session Overview This session will explain how a CDN (Content Delivery Network) improves page loading times and how you should analyze the page loading performance while evaluating a CDN. Existing techniques for integrating a CDN with Drupal will be compared and an alternative, comprehensive solution will be presented. Agenda - How pages are loaded by the browser - How a CDN improves page loading times - Evaluating the results - Existing Drupal CDN integration techniques - Push-to-CDN model: pros & cons - CDN integration module: synchronization via Drupal or highly scalable daemon - Alternative uses: create your own CDN, massive back-up tool Goals - You should have a good overview of the different techniques to integrate Drupal with a CDN. - You should have learned how you can evaluate page loading performance to know which files should be served from a CDN.













































































Recommended




























































More Related Content
What's hot (13)


























Similar to Drupal CDN integration: easier, more flexible and faster! (20)








































Recently uploaded (20)






































Editor's Notes
- #16: Popular: d.o usage statistics indicate >125,000 web sites Conclusion: important for: - Drupal project growth - More Happy People
- #17: Popular: d.o usage statistics indicate >125,000 web sites Conclusion: important for: - Drupal project growth - More Happy People
- #18: Popular: d.o usage statistics indicate >125,000 web sites Conclusion: important for: - Drupal project growth - More Happy People
- #24: There are also CDNs out there that can serve content other than static files, but in this talk, only static files are concerned.
- #25: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #26: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #27: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #28: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #29: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #30: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
- #31: - geographical spread: more spread is better, but more expensive - PoP = Point of Presence = connection with >= 1 ISPs - lock-in: * push: supporting all transfer protocols is too hard * pull: not every CDN supports pulling (and unlikely that the same features are supported)
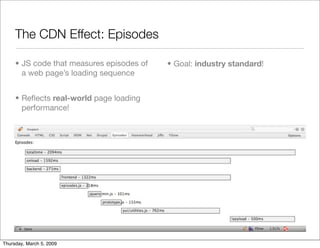
- #36: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #37: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #38: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #39: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #40: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #41: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #42: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #43: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #44: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #45: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders
- #46: - industry standard goal is realistic because the author is Steve Souders


