Ectopic Fat: An Important Feature of Intra-Abdominal Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes
- 1. ECTOPIC FAT: AN IMPORTANT FEATURE OF INTRA- ABDOMINAL OBESITY IN TYPE 2 DIABETES Marja-Riitta Taskinen, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital Helsinki, Finland
- 2. What Is Ectopic Fat Accumulation? and/ Caloric intake or Energy expenditure Positive energy balance Lipid overflow into liver, pancreas, muscle and heart FFA Inflamed adipose tissue Imbalance between loading and export of lipids results in ectopic fat accumulation at organs FFA: free fatty acids Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 3. Why Is the Fatty Liver Dangerous for Cardiovascular Health Risk? Glucose VLDL HDL ALT The fatty liver : overproduction of cardiometabolic Fibrinogen risk factors Obesity CRP Genetic predisposition Fat in the diet? PAI-1 Fructose? FVII ALT: alanine aminotransferase CRP: C-reactive protein FVII: factor VII PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 4. Determination of Liver Fat Content Using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Water peak Liver fat 6% Liver fat 28% Triglyceride peak Reproduced by permission of the American Diabetes Association. Copyright© 2000 American Diabetes Association. From Ryysy L et al. Diabetes 2000;49:749-58 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 5. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in the Liver Free fatty De novo acid flux lipogenesis Fatty acid oxidation Dietary VLDL assembly fatty acids VLDL secretion Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 6. The Atherogenic Lipoprotein Triad Lifestyle Insulin resistance Type 2 diabetes Large FCH subjects Low HDL subjects VLDL Genes Small, dense Increased HDL LDL CAD Risk CAD: coronary artery disease FCH: familial combined hyperlipidemia Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 7. Relationship Between VLDL1 Production Rate and Plasma VLDL1 Triglyceride (TG) Pools VLDL1 TG production 600 (mg/kg/day) r=0.62, p<0.001 400 200 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 VLDL1 TG pool (mg/kg) VLDL1 TG production rate is the predictor for VLDL1 TG pool size Adapted from Adiels M et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005;25:1697-703 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 8. VLDL1 Triglyceride (TG) Production Is Linked With Detrimental Changes of LDL Size and HDL Cholesterol VLDL1 TG production (mg/kg/day) VLDL1 TG production (mg/kg/day) 600 600 r=-0.56, p<0.005 r=-0.64, p<0.001 500 500 400 400 300 300 200 200 100 100 0 0 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.7 LDL size (nm) HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2006;49:755-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
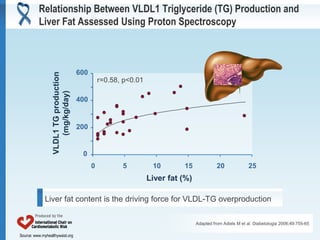
- 9. Relationship Between VLDL1 Triglyceride (TG) Production and Liver Fat Assessed Using Proton Spectroscopy 600 VLDL1 TG production r=0.58, p<0.01 (mg/kg/day) 400 200 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Liver fat (%) Liver fat content is the driving force for VLDL-TG overproduction Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2006;49:755-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
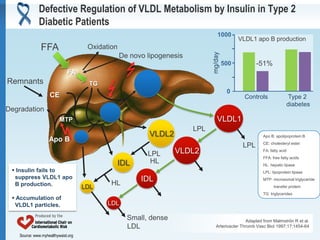
- 10. Defective Regulation of VLDL Metabolism by Insulin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients 1000 VLDL1 apo B production FFA Oxidation mg/day De novo lipogenesis 500 -51% FA Remnants TG 0 CE Controls Type 2 diabetes Degradation MTP VLDL1 LPL VLDL2 Apo B: apolipoprotein B Apo B CE: cholesteryl ester LPL LPL VLDL2 FA: fatty acid FFA: free fatty acids IDL HL HL: hepatic lipase Insulin fails to LPL: lipoprotein lipase suppress VLDL1 apo IDL MTP: microsomal triglyceride B production. LDL HL transfer protein TG: triglycerides Accumulation of VLDL1 particles. LDL Small, dense Adapted from Malmströn R et al. LDL Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997;17:1454-64 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 11. Characteristics of the Subjects Low liver fat High liver fat (n=10) (n=10) Body mass index (kg/m2) 26.0 2.9 28.4 3.6 Subcutaneous fat (cm3) 2150 730 2420 520 Intra-abdominal (visceral) fat (cm3) 1600 880 2480 860* Liver fat (%) 2.1 1.5 11.4 4.5*** M value (mg/kg/min) 6.4 1.8 4.0 2.1* Fasting triglycerides (mmol/l) 1.4 0.5 2.0 0.8 HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) 1.4 0.2 1.1 0.3** LDL size (nm) 26.6 0.8 25.3 1.1** * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 *** p<0.001 Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2007;50:2356-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 12. High Liver Fat: Lack of VLDL1 Suppression in Response to Insulin VLDL1 triglyceride production rate % of total VLDL at baseline 100 61%, p<0.01 Low liver fat <5.5% 75 High liver fat >5.5% 50 25 0 0 200 400 600 Time (minutes) Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2007;50:2356-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 13. Normal Production and Suppression of VLDL1 Particles in Normal Healthy Subjects by Insulin Low liver fat Insulin Apo B: apolipoprotein B MTP: microsomal triglyceride transfer protein TG: triglycerides TG MTP VLDL1 Apo B VLDL2 VLDL2 Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2007;50:2356-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 14. Overproduction and Dysregulation of VLDL1 Particles in Type 2 Diabetes High liver fat Insulin Apo B: apolipoprotein B TG: triglycerides TG VLDL1 Apo B VLDL2 VLDL2 High liver fat is linked with hepatic insulin resistance and overproduction of large VLDL particles Adapted from Adiels M et al. Diabetologia 2007;50:2356-65 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 15. Why People With a Big Waist do not all Have Dyslipidemia? Metabolic syndrome? Elevated VLDL1 concentrations Insulin resistance? Insulin resistance Normal The lipid atherogenic profile Intra-abdominal Intra-abdominal triad (visceral) obesity (visceral) obesity Low HDL Small, dense LDL particles Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 16. Sources of Fatty Acids for Liver and VLDL Triglycerides (TG) FFA 1 POOL STORAGE? FA CM 2 β-ox TG 4 2 LIVER TG DNL Apo B 5 VLDL Apo B: apolipoprotein B 3 TG -ox: -oxidation GLUCOSE CM: chylomicron INSULIN DNL: de novo lipogenesis FA: fatty acids FFA: free fatty acids Adapted from Adiels M et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008;28:1225-36 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 17. Whole-Body Palmitate Rate of Appearance in Obese Subjects Without and With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Palmitate rate of appearence * Normal IHTG NAFLD (µmol/minute) n=14 n=14 Liver fat (%) 3.4 0.4 22.7 2.0 BMI (kg/m2) 35.3 1.3 36.8 1.2 *Significantly different from the normal IHGT group, p<0.05 IHTG: intrahepatic triglycerides The rate of the release of fatty acids from adipose tissue is increased in obese subjects with NAFLD Adapted from Fabbrini E et al. Gastroenterology 2008;134:424-31 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 18. VLDL Triglyceride (TG) Secretion Rate Is Increased in Obese Subjects With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) 30 * Systemic plasma FFA 25 Nonsystemic fatty acids * (µmol/minute) 20 15 10 5 * 0 Normal IHGT NAFLD BMI: body mass index Liver fat (%) 3.4 0.4 22.7 2.0 BMI (kg/m2) 35.3 1.3 36.8 1.2 FFA: free fatty acids IHTG: intrahepatic triglycerides *Significantly different from the normal IHGT group, p<0.05 Fatty acids derived from nonsystemic sources are the major factors responsible for the increase in VLDL TG secretion Adapted from Fabbrini E et al. Gastroenterology 2008;134:424-31 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 19. Sources of Fatty Acids for Liver Fat and VLDL Triglycerides Increased rate of free fatty acid flux from adipose tissue results in increased rate of hepatic free fatty acid uptake. Intrahepatic de novo lipogenesis is enhanced in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The production and secretion of large VLDL particles correlate with liver fat content. Basal hepatic lipid oxidation seems to be unaltered in subjects with NAFLD. Overproduction of VLDL particles is NOT able to adequately compensate for increase of hepatic triglyceride production liver fat accumulation
- 20. Regulation of DNL by SREBP1-C, ChREBP and LXRs in Liver ACC: acetyl-CoA carboxylase ChREBP: carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein DGAT: diacylglycerol acyltransferase DNL: de novo lipogenesis ELOVL6: long-chain elongase FAS: fatty acid synthase GK: glucokinase GPAT: mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase L-PK: liver-pyruvate kinase LXR: liver X receptors SCD1: stearoyl-CoA desaturase SREBP-1: sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 TG: triglycerides Adapted from Postic C and Girard J. J Clin Invest 2008;118:829-38 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 21. Mechanisms Leading to Insulin Resistance in the Liver Akt: protein kinase B DAG: diacylglycerol FA: fatty acids Acylcarnitine LPA: lysophosphatidic acid mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin FA TG NFkB: nuclear factor-kappa B Fatty acyl-CoA PA: phosphatidic acid β-oxidation PKC: protein kinase C Acetyl-CoA TG: triglycerides FA CO2 Fatty acyl-CoA Ketones Ceramide Acylcarnitines G-3-P LPA Akt Fatty acyl-CoA NFĸB PKC ? PA mTOR DAG Insulin resistance Fatty TG acyl-CoA Adapted from Fabbrini E et al. Hepatology 2010;51:679-89 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 22. Consequences of Ectopic Fat Accumulation: Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia, NAFLD and Left Ventricular Dysfunction FFA Glucose production Glucose Subcutaneous fat Oxidation ChREBP SREBP-1c Intra-abdominal FFA DNL (visceral) fat TG FFA TG Insulin Atherogenic VLDL dyslipidemia CAD: coronary artery disease LV dysfunction ChREBP-1c: carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein-1c CAD risk factor? Glucose uptake DNL: de novo lipogenesis FFA: free fatty acids NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease SREBP-1: sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 TG: triglycerides Adapted from Fabbrini E et al. Hepatology 2010;51:679-89 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 23. Fat in Cardiomyocyte Low myocardial High myocardial TG content TG content CH2 H2O H2O CH3 • Adapted from McGavock JM et al. Circulation 2007; 116: 1170-5 x 50 CH2 + CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ppm ppm TG: triglycerides Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 24. Cardiac Steatosis – a Component of Ectopic Fat Lean Obese Impaired glucose tolerance Type 2 diabetes 1.2 * Myocardial triglycerides * 1.0 (fat/water ) 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Intra-abdominal 54 ± 39 120 ± 53* 132 ± 36* 160 ± 65* (visceral) fat (cm2) Hepatic fat (fat/water) 1.1 ± 0.9 4.3 ± 5.2 8.3 ± 11.1* 8.9 ± 8.8* *p<0.05 vs. lean Adapted from McGavock JM et al. Circulation 2007;116:1170-5 Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 25. Myocardial Fat and Coronary Heart Disease Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy is technically challenging but a powerful research tool. Is accumulation of myocardial triglycerides related to diastolic dysfunction? - More rigorous characterization of diastolic function needed. No data available on the relationship between myocardial fat and coronary heart disease. Determinants of myocardial triglyceride accumulation are largely unknown. Data on responses of myocardial triglycerides to pharmacological interventions are non-existing.
- 26. Why Is Ectopic Fat Accumulation a Health Hazard? and/ Caloric intake or Energy expenditure Positive energy balance Lipid overflow into liver, pancreas, muscle and epicardium FFA Inflamed adipose tissue Ectopic fat accumulation results in lipotoxicity at organ levels with deleterious consequences at cardiovascular disease health. FFA: free fatty acids Source: www.myhealthywaist.org
- 27. My Warmest Thanks to my Collaborators "Current players" Gothenburg Anne Hiukka Martin Adiels Eeva Leinonen Jan Boren Sakari Mänttäri Sven-Olof Olofsson Aino Soro-Paavonen Sanni Söderlund Glasgow Jukka Westerbacka Muriel Caslake Hannele Yki-Järvinen Chris J. Packard Philip Steward "The ladies of the lab" Imaging team Hannele Hilden Nina Lundbom Virve Naatti Jesper Lundbom Helinä Perttunen-Nio Antti Hakkarainen