ESD Presenation.pptx All about embeded system
- 1. Total Slide 34 1 Presentation of Industrial Training on Embedded System Design Presented by: Vinit Roll No = 220151520029
- 2. Total Slide 34 2 Topics to be Discussed Company Profile. What is an Embedded System Comparison : Microcontroller vs Microprocessor. Embedded C. Prior Requirements and Setup. AVR Microcontrollers Basic devices to be attached with Microcontroller. Importance of Ram Managements in Embedded C. Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller . GJU Parking System using Interrupt Handling.
- 3. Total Slide 34 3 Company Profile NSDC, MSDE, ESSCI, IASC, HSSC Affiliated & ISO 9001:2015 Certified: Skill development and training company with industry affiliations and government recognition. Vast Industry Experience: Over three decades of expertise in providing turnkey solutions for diverse sectors like power, cement, oil & gas and more. Practical, Industry-Focused Training: Emphasizes hands-on training in labs and on-site exposure, bridging the gap between industry and academia to ensure employability. Strong Placement Network: Dedicated placement team across 8+ cities.
- 4. Total Slide 34 4 What is an Embedded System? Definition: An embedded system is a specialized computing system designed to perform dedicated functions or tasks within a larger system. Components: Typically consists of a microcontroller or microprocessor, memory, and input/output interfaces. Real-time Operation: Often operates in real-time, meaning it processes data and reacts to inputs within a strict timeframe.
- 5. Total Slide 34 5 What is an Embedded System? Specific Purpose: Unlike general-purpose computers, embedded systems are optimized for specific applications, such as controlling machinery, managing sensors, or processing signals. Examples: Found in everyday devices like smartphones, washing machines, cars, medical devices, and industrial machines.
- 6. Total Slide 34 6 What is an Embedded System?
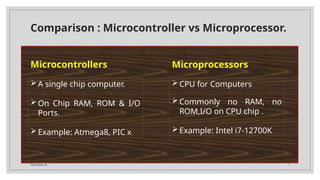
- 7. Total Slide 34 7 Comparison : Microcontroller vs Microprocessor. Microcontrollers Microprocessors CPU for Computers Commonly no RAM, no ROM,I/O on CPU chip . Example: Intel i7-12700K A single chip computer. On Chip RAM, ROM & I/O Ports. Example: Atmega8, PIC x
- 8. Total Slide 34 8 Comparison : Microcontroller vs Microprocessor. Microcontrollers Microprocessors
- 9. Total Slide 34 9 Embedded C Definition: Embedded C is a set of language extensions for the C programming language to support embedded processors and microcontrollers. Purpose: Used to program microcontrollers and develop firmware for embedded systems. Key Features: • Direct hardware access (registers and memory). • Efficient use of resources (memory and CPU). • Real-time operations and responsiveness.
- 10. Total Slide 34 10 Embedded C Characteristics: Portability: Can be used across different microcontrollers with minimal changes. Low-Level Operations: Supports bit manipulation and direct control of hardware. Optimized Code: Generates compact and fast-executing code suitable for resource- constrained devices.
- 11. Total Slide 34 11 Basic Commands in Embedded C to Initialize a Microcontroller Include Header Files: Define microcontroller-specific settings and registers. #include <avr/io.h> // For AVR microcontrollers Configure Ports: Set data direction for input or output. DDRB = 0xFF; // Configure Port B as output Set Initial Values: Initialize output ports to a known state. PORTB = 0x00; // Set all pins on Port B to low Enable Global Interrupts: Activate interrupts if needed. sei(); // Enable global interrupts For more Information: https://shorturl.at/dHt1W
- 12. Total Slide 34 12 Prior Requirements and Setup. ◦ MPLAB X IDE ◦ Proteus Design Suite
- 13. 13 MPLAB X IDE Key Features: Cross-Platform: Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. Multiple Language Support: Supports programming in C, C++, and assembly. Integrated Tools: Offers a built-in editor, compiler, debugger, and simulator for comprehensive development. Project Management: Facilitates easy management of multiple projects with version control integration. Programming Area Output Status Projects List Programming Area Total Slide 34
- 14. 14 Proteus Design Suite Key Features: Circuit Simulation: Allows for real-time simulation of both analog and digital circuits, including microcontroller-based designs. Schematic Capture: Provides tools for drawing and organizing circuit schematics with extensive component libraries. Microcontroller Simulation: Enables simulation of popular microcontrollers with their firmware, allowing users to test code in a virtual environment before hardware implementation. Working Area Simulation Controls Component List Page Zoom Setup Total Slide 34
- 15. Total Slide 34 15 AVR Microcontrollers Definition: AVR microcontrollers are a family of microcontrollers developed by Atmel (now part of Microchip Technology) based on the modified Harvard architecture. Key Features: 8-bit RISC Architecture: Provides high performance with low power consumption. Flash Memory: In-system programmable flash memory, allowing easy firmware updates. Wide Range of Models: Available in different series (e.g., ATmega, ATtiny) for various applications and requirements. Integrated Peripherals: Includes built-in peripherals like timers, ADCs, PWM, UART, SPI, and I2C for diverse functionalities.
- 16. Total Slide 34 16 AVR Microcontrollers Characteristics: High Efficiency: Executes most instructions in a single clock cycle, leading to faster processing. Low Power Consumption: Optimized for low power operation, ideal for battery-operated devices. Easy to Program: Supported by robust development tools like AVR Studio, MPLAB X, and compatible with languages like C and assembly. Cost-Effective: Affordable solution for a wide range of applications. Wikipedia: https://shorturl.at/RMNm1
- 17. Total Slide 34 17 AVR Microcontrollers Atmega8 is an AVR Microcontroller which is an example of the one of the most commonly used AVR Microcontroller. I have used Atmega8 for all my Projects during training period. Wikipedia: https://shorturl.at/RMNm1
- 18. 18 Atmega 8 Key Features: 8-bit AVR RISC Architecture: Executes most instructions in a single clock cycle, providing fast efficient performance. Memory: • 8 KB Flash Memory • 1 KB SRAM • 512 Bytes EEPROM Operating Voltage: Can operate from 2.7V to 5.5V Clock Speed: Operates at a clock frequency of 16 MHz Datasheet: https://shorturl.at/lY6QX Total Slide 34
- 19. Total Slide 34 19 Basic devices to be attached with Microcontroller 16x2 LCD Push Button L293d IC LED DC Motor Potentiometer BreadBoard
- 20. Total Slide 34 20 Basic devices to be attached with Microcontroller 16x2 LCD Sr. No. Hex Code Command to LCD instruction Register 1 01 Clear display screen 2 02 Return home 3 04 Decrement cursor (shift cursor to left) 4 06 Increment cursor (shift cursor to right) 5 05 Shift display right 6 07 Shift display left 12 10 Shift cursor position to left 13 14 Shift cursor position to right 16 80 Force cursor to beginning ( 1st line) 17 C0 Force cursor to beginning ( 2nd line) A 16x2 LCD display is a type of alphanumeric liquid crystal display that can show up to 32 characters at a time, arranged in 2 rows with 16 characters per row.
- 21. Total Slide 34 21 Basic devices to be attached with Microcontroller 16x2 LCD Interfacing Command void LCD_initialization(void) { DDRD = 0xff; DDRC = 0x07; LCD_CMD(0x01); /* Clear display */ LCD_CMD(0x02); /* Return home */ LCD_CMD(0x06); /* Entry mode set */ LCD_CMD(0x38); /* Function set: 8-bit mode, 2 lines, 5x8 dots */ LCD_CMD(0x0c); /* Display on, cursor off */ } void LCD_DATA(char data) { PORTD = data; PORTC |= 0x01; // RS = 1 PORTC &= ~0x02; // RW = 0 PORTC |= 0x04; // Enable = 1 _delay_ms(2); PORTC &= ~0x04; // Enable = 0 _delay_ms(2); } void LCD_CMD(char cmd) { PORTD = cmd; PORTC &= ~0x01; // RS = 0 PORTC &= ~0x02; // RW = 0 PORTC |= 0x04; // Enable = 1 _delay_ms(2); PORTC &= ~0x04; // Enable = 0 _delay_ms(2); }
- 22. Total Slide 34 22 Basic devices to be attached with Microcontroller L293D Motor Driver IC Definition: The L293D is a dual H-bridge motor driver IC that allows for controlling the direction and speed of two DC motors independently. It can also drive stepper motors and relays. Key Features: Dual H-Bridge Bidirectional Control Motor Voltage Range Output Current Logic Compatibility Datasheet: https://shorturl.at/BGuOX
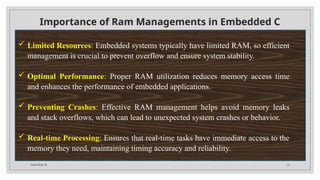
- 23. Total Slide 34 23 Importance of Ram Managements in Embedded C Limited Resources: Embedded systems typically have limited RAM, so efficient management is crucial to prevent overflow and ensure system stability. Optimal Performance: Proper RAM utilization reduces memory access time and enhances the performance of embedded applications. Preventing Crashes: Effective RAM management helps avoid memory leaks and stack overflows, which can lead to unexpected system crashes or behavior. Real-time Processing: Ensures that real-time tasks have immediate access to the memory they need, maintaining timing accuracy and reliability.
- 24. Total Slide 34 24 Importance of Ram Managements in Embedded C Energy Efficiency: Minimizing RAM usage can reduce power consumption, extending battery life in portable and low-power devices. Code Optimization: Encourages writing efficient, streamlined code, which is critical for maintaining system responsiveness and reliability. Scalability: Good RAM management practices allow the system to handle increased complexity or additional features without requiring significant hardware upgrades.
- 25. Total Slide 34 25 Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller An interrupt is a signal generated by hardware or software and it suspend normal flow of execution. Whenever an interrupt occurs, the controller completes the execution of ongoing instruction, pause it and starts the execution of interrupt service routine ( ISR ) or interrupt handler. After handling interrupt, microcontroller again resumes the normal flow of instructions. ISR contains a set of instructions that should be executed by controller when an interrupt is triggered. Usually different interrupts have their own ISR. For every interrupt there is a fixed location in program memory that holds the address of its ISR and this is known as interrupt vector
- 26. Total Slide 34 26 Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller
- 27. Total Slide 34 27 Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller Sources of Interrupt • The AVE 8-bits microcontroller provides both Internal and External interrupt sources. • The Internal Interrupts are associated with the microcontroller’s Timers/Counters, ADC, USART etc. • The external interrupts are triggered via external pins. • The figure shows the pins, on which the external interrupts can be triggered.
- 28. Total Slide 34 28 Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller General Interrupt Control Register – GICR Purpose: GICR is used to enable or disable external interrupts in the ATmega8 microcontroller. It controls the activation of external interrupts like INT0 and INT1. Structure: GICR is an 8-bit register with multiple control bits. INT1 (Bit 7): Enables external interrupt 1. INT0 (Bit 6): Enables external interrupt 0. IVSEL (Bit 1): Interrupt vector select. IVCE (Bit 0): Interrupt vector change enable.
- 29. Total Slide 34 29 Concept of interrupts in Atmega8 Microcontroller General Interrupt Control Register – GICR Usage: To enable an external interrupt, set the corresponding bit (INT1 or INT0) to 1. Example: GICR |= (1 << INT0); enables external interrupt 0. Clearing these bits disables the respective interrupts.
- 30. Total Slide 34 30 GJU Parking System using Interrupt Handling Download the Project: https://tinyurl.com/leloproject
- 31. Total Slide 34 31 GJU Parking System using Interrupt Handling Download the Project: https://tinyurl.com/leloproject
- 32. Total Slide 34 32 GJU Parking System using Interrupt Handling ISR(INT0_vect) { car_in_count++; PORTD ^= 0x02; // Toggle PD1 LCD_initialization(); char a[ ] = "Car In"; LCD_print(a, 0); // Print on first line char b[16]; snprintf(b, 16, "Total Car: %d" , car_in_count); // Prepare second line LCD_print(b, 1); // Print on second line } Download the Project: https://tinyurl.com/leloproject
- 33. Total Slide 34 33 GJU Parking System using Interrupt Handling int main() { DDRD |=(1<<PD0) | (1<<PD1) | (1<<PD7); MCUCR=(1<<ISC01); GICR |=(1<<INT0); GICR |=(1<<INT1); sei(); while(1) { PORTD^=(1<<PD0); _delay_ms(100); } } Download the Project: https://tinyurl.com/leloproject
- 34. Total Slide 34 34 Thank You Question and Answers




























![Total Slide 34 32
GJU Parking System using Interrupt
Handling
ISR(INT0_vect)
{
car_in_count++;
PORTD ^= 0x02; // Toggle PD1
LCD_initialization();
char a[ ] = "Car In";
LCD_print(a, 0); // Print on first line
char b[16];
snprintf(b, 16, "Total Car: %d" , car_in_count); // Prepare second line
LCD_print(b, 1); // Print on second line
}
Download the Project: https://tinyurl.com/leloproject](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esdpresenation-241122074517-46e5e6a4/85/ESD-Presenation-pptx-All-about-embeded-system-32-320.jpg)

