Firewall Design and Implementation
- 1. Outline Introduction Firewall design principles Firewall characteristics What firewalls do? What firewalls cannot do? Types of firewalls references
- 2. Firewall
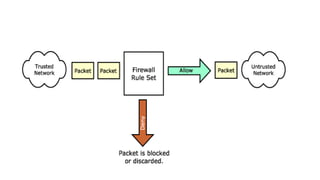
- 3. Introduction • A firewall : Acts as a security gateway between two networks-Usually between trusted and untrusted networks (such as between a corporate network and the Internet) • Tracks and controls network communications Decides whether to pass, reject, encrypt, or log communications (Access Control) • Is hardware, software, or a combination of both. • used to prevent unauthorized programs or Internet users from accessing a private network and/or a single computer. • A firewall sits at the junction point or gateway between the two networks, usually a private network and a public network such as the Internet.
- 5. Hardware vs. Software Firewalls • Hardware Firewalls • Protect an entire network • Implemented on the router level • Usually more expensive, harder to configure • Software Firewalls • Protect a single computer • Usually less expensive, easier to configure
- 6. Firewall Design Principles • The firewall is inserted between the premises network and the Internet • Aims: • Establish a controlled link • Protect the premises network from Internet-based attacks • Provide a single choke point
- 7. Firewall Characteristics • Design goals: • All traffic from inside to outside must pass through the firewall . • Only authorized traffic (defined by the local security police) will be allowed to pass • The firewall itself is immune to penetration (use of trusted system with a secure operating system)
- 8. Firewall Characteristics • Four general techniques: 1. Service control • Determines the types of Internet services that can be accessed, inbound or outbound 2. Direction control • Determines the direction in which particular service requests are allowed to flow 3. User control • Controls access to a service according to which user is attempting to access it 4. Behavior control • Controls how particular services are used (e.g. filter e-mail)
- 9. What Firewalls Do • Positive Effects • Negative Effects
- 10. Positive Effects • User authentication. Firewalls can be configured to require user authentication. This allows network administrators to control ,track specific user activity. • Auditing and logging. By configuring a firewall to log and audit activity, information may be kept and analyzed at a later date.
- 11. • Anti-Spoofing - Detecting when the source of the network traffic is being "spoofed", i.e., when an individual attempting to access a blocked service alters the source address in the message so that the traffic is allowed. • Network Address Translation (NAT) - Changing the network addresses of devices on any side of the firewall to hide their true addresses from devices on other sides. There are two ways NAT is performed: • One-to-One - where each true address is translated to a unique translated address. • Many-to-One - where all true addresses are translated to a single address, usually that of the firewall.
- 12. • Negative Effects Although firewall solutions provide many benefits, negative effects may also be experienced. • Traffic bottlenecks. By forcing all network traffic to pass through the firewall, there is a greater chance that the network will become congested. • Single point of failure. In most configurations where firewalls are the only link between networks, if they are not configured correctly or are unavailable, no traffic will be allowed through. • Increased management responsibilities. A firewall often adds to network management responsibilities and makes network troubleshooting more complex.
- 13. What Firewalls Cannot Do • Do Firewalls Prevent Viruses and Trojans? NO!! A firewall can only prevent a virus or Trojan from accessing the internet while on your machine • 95% of all viruses and Trojans are received via e-mail, through file sharing or through direct download of a malicious program • Firewalls can't prevent this -- only a good anti-virus software program can however , once installed on your PC, many viruses and Trojans "call home" using the internet to the hacker that designed it • This lets the hacker activate the Trojan and he/she can now use your PC for his/her own purposes • A firewall can block the call home and can alert you if there is suspicious behavior taking place on your system
- 14. Types of Firewalls • Three common types of Firewalls: • Packet-filtering routers • Circuit-level gateways • Application-level gateways • Basic TCP/IP Flow review
- 15. Packet Filtering Firewall • Applies a set of rules to each incoming IP packet and then forwards or discards the packet • Filter packets going in both directions • The packet filter is typically set up as a list of rules based on matches to fields in the IP or TCP header • Two default policies (discard or forward)
- 17. • A packet filtering firewall is often called a network layer firewall because the filtering is primarily done at the network layer (layer three) or the transport layer (layer four) of the OSI reference model.
- 18. Packet filtering rules or filters can be configured to allow or deny traffic based on one or more of the following variables: • Source IP address • Destination IP address • Protocol type (TCP/UDP) • Source port • Destination port
- 19. advantages: • Packet filtering is typically faster than other packet screening methods. Because packet filtering is done at the lower levels of the OSI model, the time it takes to process a packet is much quicker. • Packet filtering firewalls can be implemented transparently. They typically require no additional configuration for clients. • Packet filtering firewalls are typically less expensive. Many hardware devices and software packages have packet filtering features included as part of their standard package. • Disadvantages: • Difficulty of setting up packet filter rules • Lack of Authentication
- 20. Circuit-level Gateway • Unlike a packet filtering firewall, a circuit-level gateway does not examine individual packets. Instead, circuit-level gateways monitor TCP or UDP sessions. • The main difference between packet filtering and this is that it validates TCP and UDP sessions before opening a connection through the firewall. Once a session has been established, it leaves the port open to allow all other packets belonging to that session to pass. The port is closed when the session is terminated. circuit-level gateways operate at the transport layer (layer 4) and session layer of the OSI model.
- 22. • The firewall maintains a virtual circuit table, which stores the connection details of the successful connections. Advantages- • More secure than packet filter firewalls. • Faster than application level firewalls. Disadvantages- • Only detect one transport layer protocol-TCP. • Cannot perform security checks on higher level protocols.
- 23. Application-level Gateway • Also called proxy server • Gateway sits between user on inside and server on outside. Instead of talking directly, user and server talk through proxy. • This type of firewall operates at the application level of the OSI model. For source and destination endpoints to be able to communicate with each other, a proxy service must be implemented for each application protocol.
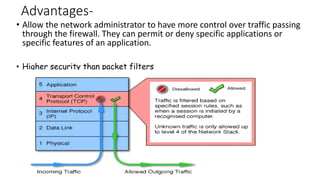
- 24. Advantages- • Allow the network administrator to have more control over traffic passing through the firewall. They can permit or deny specific applications or specific features of an application. • Higher security than packet filters
- 25. Disadvantages- Additional processing overhead on each connection (gateway as splice point) 1. Not all services have proxied versions. 2. May need different proxy server for each service.
- 26. References- • Behrouz A. Forouzan, “Cryptography and Network Security”, McGraw- Hill publication. • William Stallings , “Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Standards”, Prentice Hall India.
- 27. Thank you