Flex Building User Interface Components
- 1. Building User Interface ComponentsFLEX 2.01
- 2. In this presentationComponent lifecycle and optimization tipsGeneralizing components Designing component API
- 3. Why create Components?Ease of development Reusability Maintainability
- 4. What are Components?OwnerEventsEventsEventsUI ComponentsubcomponentsData PropertiesData PropertiesData Properties
- 5. MXML vs. AS Flex Components Some basic guidelines include the following: Simple components, it is simpler and faster to create them in MXML.
- 6. Composite components that contains other components & the Layout of those other components can be set using one of the Flex layout containers, use MXML.
- 7. Complex components, such as to modifying the way a container lays out its children, use ActionScript.
- 8. Visual component forinstance creating a subclass from UIComponent, use ActionScript.
- 9. Nonvisual component, such as a formatter, validator, or effect, use ActionScript. Component LifecycleFrom birth to death, A Component goes through a defined set of steps:ConstructionConfigurationAttachmentInitializationInvalidationValidationInteractionDetachmentGarbage CollectionBuilding your prototype is the process of implementing this lifecycle…
- 10. Component Lifecycle in FLEXImplementing the lifecycle boils down to these methods:Constructor()createChildren()commitProperties()measure()updateDisplayList()Custom events
- 11. ConstructionMXML-able components must have zero arg constructorsCall super()…or the compiler will do it for you.Good place to attach your own event handlersTry to avoid creating children here…for best performance
- 12. ConstructionCONSUMER<local:RandomWalk />orVarinstance:RandomWalk = newRandomWalk();COMPONENTpublic function RandomWalk(){super();this.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK,clickHandler);}
- 13. ConfigurationMXML assigns properties before sub-components are attached and initialized (avoids duplicate code execution).Your properties (get, set functions) need to expect that subcomponents haven’t been created yet.Avoid creating performance bottlenecks: make set functions defer work until validation.
- 15. Configuration (pattern)CONSUMER…instance.dataProvider = xmlDataSet;instance.width = 600;instance.height = 200;instance.labelText = “hello”;...Or via binding… labelText=“{hello}” width=“600” … dataprovider=“{xmlDataSet}”COMPONENTprivate var _labelText:String;private var _labelTextDirty;public function setlabelText(value:String):void{If (_labelText != value){_labelText= value;//BAD _label.text = _labelText;_labelTextDirty = true;invalidateProperties(); //invalidation }}
- 16. AttachmentMost component initialization is deferred until it gets attached to a Parent
- 17. Styles may not be initialized until its ancestors get rooted to the displayList()
- 18. Parent.addChild(At) calls initialize() method to trigger next phase…you can call this explicitly if necessaryParentaddChild (ComponentInstance)Component initialization begins
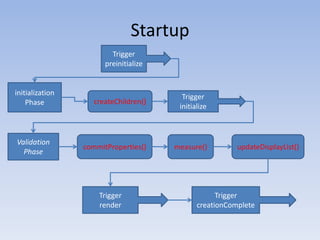
- 19. StartupTrigger preinitializeinitialization PhasecreateChildren()TriggerinitializeValidation PhasecommitProperties()measure()updateDisplayList()TriggercreationCompleteTriggerrender
- 20. StartupStartup happens in multiple sub-phases:1. ‘preinitialize’ event is dispatched2. createChildren method is called, adds sub-components3. ‘initialize’ event is called – component is fully created4. First validation pass occurs5. ‘creationComplete’ event is fired – component is fully commited, measured, and updated.
- 21. Startup1.Parent-> preinitializeParent-> createChildren Child-> preinitialize Child-> createChildrengrandChild-> preinitializegrandChild-> createChildrengrandChild-> initialize Child-> initialize Child2-> preinitialize Child2-> createChildren Child2-> initializeParent-> initialize2.Parent-> commitProperties Child-> commitPropertiesgrandChild-> commitPropertiesgrandChild-> measure Child-> measureParent-> measure3. Parent-> updateDisplayList Child-> updateDisplayListgrandChild-> updateDisplayList4. Parent-> render Child-> rendergrandChild-> rendergrandChild-> creationComplete Child-> creationCompleteParent-> creationComplete
- 22. Initialization : createChildren()Creating children here streamlines startup performanceFollow the same pattern MXML uses: create, configure, attach.Flex components give subclasses first-crack at defining subcomponents.Don’t forget to call super.createChildren();Defer creating dynamic and data-driven components to commitProperties();
- 23. Initialization : createChildren//exampleprotected varcommitButton:UIComponent;override protected function createChildren():void{if (commitButton == null) //only create once—why ?{commitButton = new Button(); Button(commitButton).label = “OK”;}addChild(commitButton);commitButton.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK, commitHandler);super.createChildren();}
- 24. Invalidation Flex imposes a deferred validation modelAggregate changes, defer work until the last possible momentavoid creating performance traps for your consumersThree main invalidation functions:invalidateProperties()invalidateSize()invalidateDisplayList()
- 25. Invalidation Rules of Thumb:1. Change values immediately2. Dispatch events immediately3. Defer Side-effects and calculations to commitProperties()4. Defer rendering to updateDisplayList()5. Be suspicious of rules of Thumb
- 26. Validation : commitPropertiesInvoked by the framework immediately before measurement and layoutUse it to calculate and commit the effects of changes to properties and underlying dataAvoid extra work: Use flags to filter what work needs to be doneProper place to destroy and create dynamic subcomponents based on changes to properties or underlying data.
- 27. Validation : commitProperties//exampleoverride protected function commitProperties():void{if (_cme_datachanged) { _ cme_datachanged = false; //reset flag //data change effects applied here }super.commitProperties(); }
- 28. Validation : measureInvoked by the framework when a component’s invalidateSize() is calledComponents calculate their ‘natural’ size based on content and layout rules.Implicitly invoked when component children change size.Don’t count on it: Framework optimizes away unnecessary calls to measure.Quick Tip: start by explicitly sizing your component, and implement this later.
- 29. Validation : updateDisplayListInvoked by the framework when a component’s invalidateDisplayList() is calledThe ‘right’ place to do all of your drawing and layout
- 30. InteractionProperties: Talk to your componentEvents: Listen to your componentPublic methods: Only in very specific cases where you can not use properties or events to fulfill the need
- 31. Interaction: EventsEvents consist of:Name: A unique (per target) name identifying the type of eventTarget: the object that dispatched the eventEvent: An Object containing additional information relevant to the eventHandler: the function invoked when the event occurs.
- 32. Interaction: Events1. Handling Events Registering, removing, capture, bubble2. Dispatching Events Flex’s event system is extensible – you can define the events you need to make your component useful. – more on this laterRemember that events will bubble up from your sub-components. If you don’t want that to happen, you need to explicitly stop them from propagating.
- 33. How the Flash Player Works?
- 34. Other topicsGeneralizing ComponentsDesigning Components
- 35. Generalizing ComponentsThree important concepts for generalizing your componentSKINNING!STYLING!TEMPLATING!
- 36. Generalizing ComponentsThree important concepts for generalizing your componentUse Properties to generalize the behavior and dataUse Skinning and Styling to generalize the lookUse Templating to generalize the content.
- 37. Generalizing Component : TemplatingInstance propertiesProperties typed as UIComponent can be set in MXML like any other property.Reparenting allows you to embed passed values into your own display tree.Allows you to define complex components with configurable partspublic function set thumbnailView(value:UIComponent){ _thumbnailView = value;addChild(thumbnailView);}
- 38. Generalizing Component : Templating2. Item Renderers (Factories)Factories are used to generate multiple child componentsData driven components use them to generate renderers for the dataAllows you to separate management of the data from displaying the data.Quick Tips:Type your item renderers as IFactoryUse the IDataRenderer interface to pass your data to the instancesIf you have additional data to pass, define a custom interface and test to see if it is supported first.
- 39. Generalizing Component : BindingDatabinding is there to eliminate boilerplate data routing code<mx:Button enabled=“{randomWalk.selectedItem != null}” />Any property can be the destination of a binding, but the source needs special SupportGood rule of thumb: If you think someone might want to bind to it…make it bindable.
- 40. Generalizing Component: BindingAdd [Bindable] to your class:[Bindable] public class RandomWalk extends UIComponent { …Makes all public varsbindableConvenience feature for value objects.Add [Bindable] to your property[Bindable] public varselectedItem:Object;[Bindable] public function get selectedItem():Object { …Wraps the variable or property in an autogenerated get/setGood for simple properties.Roll your own event based bindings:[Bindable(event=“selectedItemChange”)] public function get selectedItem():Object { …dispatchEvent(new Event(“selectedItemChange”));Works well for read only and derived properties
- 41. Designing you API: base Class?What Base Class should you extend?UIComponent:Base class for all component and containersGateway to key flex functionality: styles, Containers, invalidation, etc.Best choice for most componentsContainer (and derivatives):Only use if your customers will think of your component as a containerAllows developers to specify children in MXML (but there are other ways)Scrolling, clipping, and chrome management for freeOther ‘Leaf’ ComponentsGood for minor enhancements and guaranteeing type compatibilityMajor Functionality changes run the risk of ‘dangling properties’Consider using aggregation instead
- 42. Designing your API: MXML schemaRemember, Your API defines your MXML schemaSpecifically:ClassName -> XML Tags NamePackage -> XML NamespaceProperties -> XML AttributesComplex Properties -> Child Tags
- 43. Designing your API: ExamplesA Few Examples:Choose Properties over MethodsProperties can be set from MXML Avoid write-once propertiesAnything that can be set in MXML can be bound to.Use value objects for complex and multi-valued propertiesMXML makes object graphs simple<DataGrid><columns><DataGridColumncolumnName=“revenue” width=“30” dataField=“revYr” /><DataGridColumncolumnName=“profit” width=“30” dataField=“profYr” /></columns></DataGrid>Use different names for styles, events, and properties.
Editor's Notes
- #4: A common coding practice is to divide an application into functional units, or modules, where each module performs a discrete task. Dividing your application into modules provides you with many benefits, including the following:Ease of development Different developers or development groups can develop and debug modules independently of each other. Reusability You can reuse modules in different applications so that you do not have to duplicate your work.Maintainability By developing your application in discrete modules, you can isolate and debug errors faster than you could if you developed your application in a single file.
- #5: Ideally components are placed inside another component or container or document. They fire events and have properties for configuration. As we said earlier components may contain other subcomponents. A point I’m going to stress now and always. Its never recommended to have public methods for components you should always try to introduce events for listening to your component and modify data properties to configure your components. using events and properties allow you to integrate smoothly with the UI model of flex and not create performance issues.
- #6: Simple Components: are components that standardize the look and feel for another component by extending it.Composite Components: are components that group one or more components together to control their layout using on of flexlayout container(vBox,hBox,canvas,panel)Complex Components: are “complex” , they modify a container, control behaviour and the way it lays its data Nonvisual Components: such as formatters, validator,
- #8: Constructor is called when you instantiate your component.CreateChildren is for instantiating your subcomponents Commitproperties for reading all assign properties … this may be called more than once Measure doing all measurmentsUpdateDisplaylist layout and drawing
- #9: Keep in mind , overriding methods is always little bit better than handling events inside a component because IF used correctly they reduce the number rendering cycles
- #11: Binding calls the setter of the property
- #13: Recommnedations Check if the value actually changed Create a flag to notify the component that the property changed Invalidate the component so it reapplies the property.
- #17: 2. Differentiate events from internal methods3. Constructor stuff -> preinitialize createChildren stuff -> initializecommitproperties, measure, updateDisplayList ->render, creationComplete (causing rerendering )
- #18: Dynamic data driven properties components like those that you don’t need if certain properties are set. Flex calls it when the call to the addChild() ….. That is why it might be called more than once check next slide
- #19: Recommendation Check if a subcomponent is already instantiated because createChildren might be called more than when
- #20: invalidateProperties() for deferred calculation, child managementinvalidateSize() for changes to the measured size of a componentinvalidateDisplayList() for changes to the appearance of a component