Ad
MySQL: From Single Instance to Big Data
- 2. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | From Single Instance to Big Data Popular LAMP Architectures Morgan Tocker MySQL Community Manager August, 2014
- 3. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 3
- 4. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Welcome .. and thank you for coming! • Today talk is: • Experience-‐Level: Beginner • We will be discussing topologies and common MySQL setups to respond to various needs • There are no stupid questions • Please raise your hand and interrupt! 4
- 5. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 5 Program Agenda Common Architectures Sharding and Functional Partitioning Caching The Cloud Hadoop 1 2 3 4 5
- 6. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted In the beginning… • Single server for all usage • MySQL and Web Server run side-‐by-‐side 6 www + mysql
- 7. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Web and Database Tiers • Web Server Tier speaking to Database Server via local network • Network latency not normally the issue • Retrofits well 7 www MySQL www www
- 8. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Network Latency How important is it to merge queries together? • Simple queries to MySQL: • 0.1ms • Typical network latency: • 0.1ms to 1ms • It can matter in some poorly designed applications that repeat similar queries within a loop (often called N+1). 8 http://www.tocker.ca/2013/11/18/how-‐important-‐is-‐it-‐to-‐merge-‐queries-‐together.html
- 9. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Web and Database (Alternative) • Common practice for shared hosting environments • Provides increased “noisy neighbour” protection. • Less common otherwise. 9 www + mysql www + mysql www + mysql
- 10. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted High Availability Options Built-‐in MySQL Replication Asynchronous and Semi-‐ Synchronous Good support for remote replicas. SAN/Shared Storage Requires use of ACID Storage Engine. Use with cluster tools to failover. DRBD Linux kernel module to provide network-‐level RAID. Usage is similar to SAN/ Shared Storage MySQL Cluster Storage Engine with built in Replication. Suitability situationally dependent. 10 MySQL MySQLMySQL MySQL MySQLSAN MySQL MySQLDRBD MySQL MySQLNDB
- 11. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted How HA Failover Works In combination with a management framework • A Virtual IP Address pointing to active master • A proxy address (routing to active master) • A modified MySQL connector 11 ^ typically
- 12. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | MySQL Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Most Common HA Starting Point • Primary MySQL Server • Passive slaves using MySQL Replication • Replication is logical • Very useful to support version upgrades (and some other changes) 12 www (multiple) MySQL
- 13. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Circular ring 13 • Not a common topology • No conflict resolution or shared locking infrastructure. • Bad things can happen. MySQL MySQL MySQL MySQL
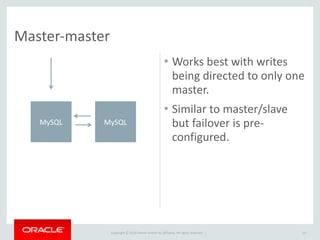
- 14. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Master-‐master 14 • Works best with writes being directed to only one master. • Similar to master/slave but failover is pre-‐ configured. MySQLMySQL
- 15. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Making Use of the Slave • Reporting queries are an immediate candidate for slaves • Ensures good QoS for primary MySQL Server 15 www (multiple) MySQL MySQLMySQL
- 16. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Read-‐Write Split • Application-‐awareness to send writes to master and reads to slaves • Historically very common with MySQL 16 www (multiple) MySQL MySQLMySQL
- 17. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Read-‐Write Split Limitations • Read-‐after-‐write can return stale data • All slaves must accept all writes • Relies on read volume being much higher than write volume (true for many applications) 17
- 18. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Multi-‐Source Fan-‐In 18 • MySQL 5.7 announced feature • Currently a slave can only have one master MySQL MySQL MySQL MySQL
- 19. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | 1 Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 19 Program Agenda Common Architectures Sharding and Functional Partitioning Caching The Cloud Hadoop 2 3 4 5
- 20. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Write Scaling • Replication Provides Read-‐Scaling • By default all nodes accept all writes • Filtering by table or database possible, but reduces failover ability 20
- 21. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Functional Partitioning • Find a set of unrelated tables and move them to their own MySQL Server • The application must manage which MySQL server to connect to 21
- 22. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Sharding • Split an Individual table across multiple Servers • Sharding is performed based on a key 22
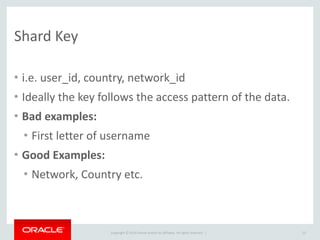
- 23. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Shard Key • i.e. user_id, country, network_id • Ideally the key follows the access pattern of the data. • Bad examples: • First letter of username • Good Examples: • Network, Country etc. 23
- 24. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Shard Balancing • Harder than it sounds. • In many applications one user can consume far more resources than the average. 24
- 25. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Cross shard queries? • Cross Shard queries usually* pushed down to the application to perform • Ideally the shard key follows the access pattern of the data so this is not required. 25 * Third party middleware does exist.
- 26. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL Fabric MySQL Farm Management • We now how an official tool to support sharding! • MySQL Fabric released May 2014 26
- 27. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL Fabric MySQL Farm Management 27 http://dev.mysql.com/tech-‐resources/articles/mysql-‐fabric-‐ga.html
- 28. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 28 Program Agenda Common Architectures Sharding and Functional Partitioning Caching The Cloud Hadoop 2 3 4 5 1 3
- 29. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Caching With memcached or a similar technology • Common to include a look aside cache in combination with MySQL: 29 value = get_from_memcache(key); if (value === null) { value = get_value_from_database(key); set_memcache(key, value) }
- 30. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Caching Benefits • Increases capacity by eliminating high expense items • Sits on top of another application very easily 30
- 31. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Caching Downsides • Need to ensure that non-‐cached performance is still acceptable. • Cache invalidation is hard :) 31 http://www.tocker.ca/2013/11/25/query-‐optimization-‐versus-‐caching.html
- 32. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Not-‐Caching MySQL Memcached Interface • MySQL 5.6 now speaks the memcached protocol! • An alternative high performance interface to MySQL 32
- 33. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL Memcached 5.6 Performance Benchmark 33
- 34. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL Memcached 5.7 Performance Benchmark 34 48 Core Machine / Read Only Memcached http://dimitrik.free.fr/blog/archives/2013/11/mysql-performance-over-1m-qps-with-innodb-memcached-plugin-in-mysql-57.html http://mysqlserverteam.com/mysql-5-7-3-deep-dive-into-1mil-qps-with-innodb-memcached/
- 35. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 35 Program Agenda Common Architectures Sharding and Functional Partitioning Caching The Cloud Hadoop 2 3 4 5 1 4
- 36. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Cloud + MySQL Not much changes! • Typically no VIPs for HA failover • Typical for smaller hardware to be used as building blocks 36
- 37. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Is it better to scale vertical or horizontal? • Ideally some level of both. • Too small: can not balance out sudden blips. • Too big: no natural isolation from very large bursts. 37 http://www.tocker.ca/2014/04/22/five-‐reasons-‐why-‐vertical-‐scalability-‐matters.html
- 38. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | More RAM is often better • Twice as much RAM != Twice as Fast • In some scenarios it will be >10x 38 http://www.tocker.ca/2013/05/10/twice-‐as-‐much-‐ram-‐does-‐not-‐equal-‐twice-‐as-‐fast.html
- 39. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 39 Program Agenda Common Architectures Sharding and Functional Partitioning Caching The Cloud Hadoop 2 3 4 5 1 5
- 40. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL Usage By Query Type 40 Easy :) Great GoodDataVolume Query Complexity *Hadoop Applier
- 41. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted The Edge Case MySQL Hadoop Applier • Common to use the tools together • Run queries in parallel with Hive 41
- 42. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted Hive SQL Queries for Hadoop • Think of it like a large freight train • Queries may take minutes • Does not specifically require indexes 42
- 43. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted MySQL+Hive • Incredibly common to see both in use • Real-‐time data stored in MySQL • Log-‐like historical data stored in Hive • Reporting queries sent to Hive 43
- 44. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Hive (cont.) 44 CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE page_view_stg(viewTime INT, userid BIGINT, page_url STRING, referrer_url STRING, ip STRING COMMENT 'IP Address of the User', country STRING COMMENT 'country of origination') COMMENT 'This is the staging page view table' ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '44' LINES TERMINATED BY '12' STORED AS TEXTFILE LOCATION '/user/data/staging/page_view'; hadoop dfs -put /tmp/pv_2008-06-08.txt /user/data/staging/page_view FROM page_view_stg pvs INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE page_view PARTITION(dt='2008-06-08', country='US') SELECT pvs.viewTime, pvs.userid, pvs.page_url, pvs.referrer_url, null, null, pvs.ip WHERE pvs.country = 'US';
- 45. Copyright © 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | Oracle Confidential – Internal/Restricted/Highly Restricted 45

















































































































![Get & Download Wondershare Filmora Crack Latest [2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/revolutionizingresidentialwi-fi-250422112639-60fb726f-250429170801-59e1b240-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)










![Pixologic ZBrush Crack Plus Activation Key [Latest 2025] New Version](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/fashionevolution2-250322112409-f76abaa7-250428124909-b51264ff-250504160528-fc2bb1c5-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


