Ad
Function in C++, Methods in C++ coding programming
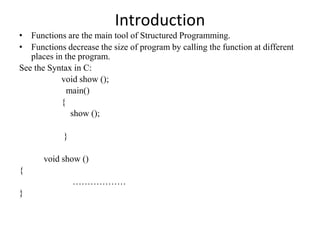
- 2. Introduction • Functions are the main tool of Structured Programming. • Functions decrease the size of program by calling the function at different places in the program. See the Syntax in C: void show (); main() { show (); } void show () { ……………… }
- 3. • Basically Functions in C and C++ have the same importance and the applications. • Also in C++ functions and the operators can be Overloaded. MAIN Function: • No return type for main() in C. • In C++ main() always returns an integer value to the operating system. • That is why we always have a return() statement at the end of the main(). • Operating system checks the return value as the function has been successfully executed or not.
- 4. Function Prototyping • Function Prototype is a kind of template that is used by compiler to ensure that proper arguments are passed and return value is treated correctly. • Earlier C did not has the prototyping, It was firstly introduced in C++ then it was adopted in ANSI C. However it is optional in C but compulsory in C++. returntype function name (argument list) • The names of the arguments are optional in declaration but must in the function definition.
- 5. Call by Reference • When the values are passed to the functions they are using the copies of the original variables. It will create a problem when we have to change the original variables. • But in case of Call be Reference we pass the addresses of the variables hence all the operations are performed on the original variables. • Example: Swapping void swap(int a, int b) { int t; t=a; a=b; b=t; } swap(m,n); void swap(int *a, int *b) { int t=*a; *a=*b; *b=t; } Swap(&x, &y);
- 6. Return by Reference int & max(int x, int y) { if (x>y) return x; else return y; } This function will return the address of either x or y.
- 7. Inline Functions • When a function is called substantial time is wasted the shifting of the control. It adds more overheads when the size of the function is very small. • One alternative to it is Macros, but their errors are not checked during the compilation. • In C++ we have inline functions. Here the compiler replaces the function call with the corresponding function code. inline function-header { function body } inline float cube(float a) { return(a*a*a); } Calling: c=cube(3.0); d=cube(2.5+1.5);
- 8. Inline Functions contd.. • The Inline functions are advantageous only when the size of the function is too small, if we use the same technique for the bigger functions the benefits of the Inline functions will be lost. • In case of Inline function the control doesn't go any where. • The Inline Keyword is just a request to the compiler not the command, the compiler may ignore the request if the size of the function is too large, Then it will be treated as normal functions. • The Inline will not work in the following cases; 1. Functions having the loop, switch or goto statement. 2. Functions not returning any values if a return statement exists. 3. If functions have static variables. 4. If functions are recursive. Using the Inline functions every time the function is invoked new memory is allocated so trade-off becomes necessary.
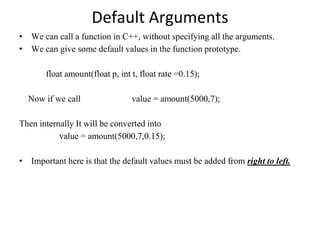
- 9. Default Arguments • We can call a function in C++, without specifying all the arguments. • We can give some default values in the function prototype. float amount(float p, int t, float rate =0.15); Now if we call value = amount(5000,7); Then internally It will be converted into value = amount(5000,7,0.15); • Important here is that the default values must be added from right to left.
- 10. Const Arguments • This tells the compiler that the function should not modify the argument. int strlen (const char *p); int length (const string &s); Specially it is used when we pass arguments as reference of as pointers.
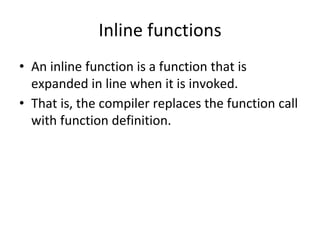
- 11. Inline functions • An inline function is a function that is expanded in line when it is invoked. • That is, the compiler replaces the function call with function definition.
- 12. Why do we use inline functions • Every time a function is called it takes a lot of extra time in executing series of instructions for tasks such as jumping to function, saving registers, returning to calling function. • When function is small, huge execution time is spent in such overheads • To eliminate the cost of calling small functions, INLINE functions are used.
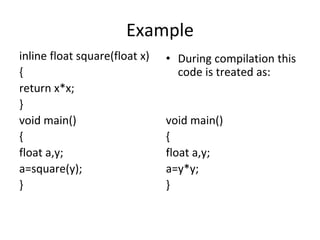
- 14. Example inline float square(float x) { return x*x; } void main() { float a,y; a=square(y); } • During compilation this code is treated as: void main() { float a,y; a=y*y; }
- 15. • While making inline functions all we need to do is to prefix the keyword inline to function definition. • All inline functions must be defined before they are called. • Usually, the functions are made inline when they are small enough to be defined in 1 or 2 lines.
- 16. Situations where inline expansion may not work: • For functions returning values, if a loop, a switch or a goto exists. • For functions not returning value, if a return statement exists. • If function contains static variables • If inline functions are recursive.
- 17. Illustration • #include<iostream.h> • #include<conio.h> • inline int mult(int x,int y) • { • return(x*y); • } • inline int sum(int a,int b) • { • return(a+b); • } • int main() • { • int p,q; • cout<<mult(p,q); • cout<<sum(p,q); • return 0; • }
- 18. Default arguments • To call a function without specifying its arguments. • In such cases, function assigns a default value to the parameter which does not have a matching arguments in the function call. • Default values are specified when function is declared.
- 19. Example of function declaration with default values float amount(float principal,int time,int rate=2); // default value of 2 is assigned to rate Amount(5000,5); // this function call passes value of 5000 to principal and 5 to time and function uses default value of 2 for rate. Amount(5000,5,1); //no missing argument,it passes an explicit value of 1 to rate
- 20. • NOTE: only trailing arguments can have default values. • We must add default values from right to left. We can not provide default value to an argument in the middle of argument list. int sum(int i, int j=5, int k=9); //Right int sum(int i=5, int j); //wrong int sum(int i=0, int j; int k=5); //wrong
- 21. Advantages • We can use default arguments to add new parameters to existing functions. • Default arguments can be used to combine similar functions into one.
- 22. Function Overloading • Overloading; Using the same thing for different purposes. When a same function name performs a variety of tasks is also called function polymorphism in OOP. • The operation to be performed by the function will depend upon the type and the no. of arguments passed to the function. It is done like this : 1. The compiler will try to find the exact match, actual type and no. of arguments. 2. If not the compiler uses integral promotions char to int float to double 3 Then built in conversions are done, and if there is no match then compiler will generate an error message. Precautions: 1. Unrelated functions should not be overloaded. 2. Default arguments can be used sometimes at place of overloading.
- 23. Function Overloading • #include<iostream.h> int volume (int); double volume (double, int); long volume (long, int, int); int main() { cout<<Volume(10)<<“n”; cout<<Volume(2.5,8)<<“n”; cout<<Volume(100L,75,15)<<“n”; return 0; } Int volume(int s) { return(s*s*s); } Int volume(double r, int h) { return(3.14519*r*r*h); } Int volume(long I, int b, int h) { return(l*b*h); } Output 1000 157.26 112500