Function : Introduction
- 1. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 1
- 2. What is function? https://www.geogebra.org/m/mzxvxe44 INPUT Num. OUTPUT Num. (INPUT, OUTPUT) (3, 9) 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 2 Click here f(x) = x2 Every input as a unique output
- 3. -3 3 -2 2 -1 1 4 9 4 1 16 A B f A = {-3, - 2, - 1 ,1, 2, 3,4 } f(x) = x2 https://www.geogebra.org/m/mzxvxe44 B = {9, 4 ,1, 16 } Click here INPUT OUTPUT 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 3
- 4. In arrow diagram In ordered pair form f = { (- 3, 9), (- 2, 4), (- 1, 1), (1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 9), (4, 16) } 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 4
- 5. Find out again by looking at the matching diagram below and discussing the answers to the questions asked in the group. 2 3 4 5 6 7 A B R1 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 A B R2 Does each member of set A have a relation with only one member of set B? Is there no reflection of any member of A to B? 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 6 A B Does each member of set A have a relation with only one member of set B? Are there any members in set B without relationship ? R3 -1 1 -2 2 1 4 5 A B R4 Does each member of set A have a relation with only one member of set B 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 5 Does each member of set A have a relation with only one member of set B
- 6. 2 3 4 5 6 7 A B R1 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 A B R2 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 6 A B R3 -1 1 -2 2 1 4 5 A B R4 In R1 , R3and R4 of the above relations, each member of group A has relation with only one member of group B and there is no any member in group B without relation. These relations are functions. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 6
- 7. Let us consider a following example Person A 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 7
- 8. Let A and B are two no-empty sets. A relation from set A to a set B is said to be a function if every elements of set A has one and only one image in set B Conclusion.: 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 8 A function from set A to set B is denoted as f : A → B, g : A → B, h : A → B, etc.
- 9. Domain, Co-domain and range of a function • https://www.geogebra.org/m/mzxvxe44 INPUT Num. OUTPUT Num. (INPUT, OUTPUT) (3, 9), (4, 16) Pre- image image 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 9 Click here f(x) = x2 Every input as a unique output
- 10. -3 3 -2 2 -1 1 4 9 4 1 16 A B f In arrow diagramA = {-3, - 2, - 1 ,1, 2, 3,4 } f(x) = x2 https://www.geogebra.org/m/mzxvxe44 B = {9, 4 ,1, 16 } Click here Pre-image Image 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 10
- 11. -3 3 -2 2 -1 1 4 9 4 1 16 2 A B fIn arrow diagram In ordered pair form f = { (- 3, 9), (- 2, 4), (- 1, 1), (1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 9), (4, 16) } Domain 9 4 1 16 Range Co-domain 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 11 f(- 3) = 9 f( 3) = 9 f(- 2) = 4 f (2) = 4 f( - 1) = 1 f( 1)= 1 f(x) = x2
- 12. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 12 A f Domain Range Co-domain f(- 3) = 9 f( 3) = 9 f(- 2) = 4 f (2) = 4 f( - 1) = 1 f( 1)= 1 f( 4)= 16 f(x) = x2 9 is image of – 3 & 3 4 is image of – 2 & 2 1 is image of – 1 & 1 16 is image of & 4 - 3 & 3 are pre-images of 9 - 2 & 2 are pre images of 4 - 1 & 1 are pre-images of 1 4 is pre-image of 16 Range is subset of co-domain
- 13. • Set of pre-image is domain • Set of image of the function is Range 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 13 A f Domain Range Co-domain • If function f :A→B , then the set A is DOMAIN of f and • set B is CO-DOMAIN of f • Set of elements of B which are the images of elements of A is RANGE
- 14. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 14 A f f(x) A f x Functional value
- 15. 6/23/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 15 Range Domain Function (f) Another function Domain Range https://tasyaluftwascher.blogspot.com/2017/01/newest-for-images- drawing-cute-water.htmlSource
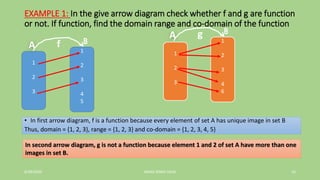
- 16. EXAMPLE 1: In the give arrow diagram check whether f and g are function or not. If function, find the domain range and co-domain of the function • In first arrow diagram, f is a function because every element of set A has unique image in set B Thus, domain = {1, 2, 3}, range = {1, 2, 3} and co-domain = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 16 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 A f 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 6 A g In second arrow diagram, g is not a function because element 1 and 2 of set A have more than one images in set B.
- 17. EXAMPLE 2 :Identify whether {(1, 2), (3, 6), (- 2, - 4)} is a function or not ? • Since, every element of set A has only one image in set B. • Hence it is a function 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 17 Representing in arrow diagram 1 3 -2 2 6 - 4 A
- 18. Representation of the function a) A table b) A set of ordered pair form c) An arrow diagram d) A graph e) A formula ( or an equation) 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 18
- 19. EXAMPLE 3: Let A = {2, 3, 4} and B= {4, 6, 8} such that f(2 ) = 4, f(3) = 6 and f(4) = 8. Represent the function f by all methods 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 19 • Here, A ={2, 3, 4} and B= {4, 6, 8} a) In a tabular form f(2)= 4 i.e. when x = 2, then y = 4 f(3)= 6 i.e. when x = 3 then y = 6 f(4) = 8 i.e. when x = 4 then y = 8 X Y 3 6 2 4 4 8 (b) A set of ordered pair form: ∴ f = {(2, 4), (3, 6), (4, 8)}
- 20. (c) In an arrow diagram: f(2 ) = 4, f(3) = 6 and f(4) = 8. 2 corresponds with f(2) = 4 3 corresponds with f(3) = 6 4 corresponds with f(4) = 8 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 20 2 3 4 4 6 8 A B
- 21. e) In an equation: When x= 2, then y = f(2) = 4 = 2 x 2 when x = 3, then y = f(3) = 6 = 2 x 3 when x = 4, then y = f(4) = 8 = 2 x 4 Hence, the function f can be expressed as y = 2x or, f(x) = 2x 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 21 d) In a graph : The points with ordered pairs: (2, 4), (3, 6), (4, 8)
- 22. EXAMPLE 4: What will be the functional value of 4 in the function f(x) = x2 ? Here, f(x) = x2 f(4) = ? f(4) = (4)2 = 16 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 22 Functional value means we need to simply put the value of x in the given function
- 23. EXAMPLE 5:If f(x) = {(x, y): y = 2x + 3} and x 𝜖 {2, 4, 6}, find the range and represent the function in arrow diagram. Here, f(x) = 3x – 2 and image of f(x) = 10 So, f(x) = 10 or, 3x – 2 = 10 or, 3x = 10 + 2 or, 3x = 12 or, 3𝑥 3 = 12 3 or, x = 4 Hence, the element in domain is 4 has image 10 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 23
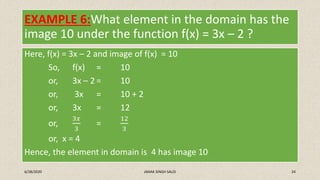
- 24. EXAMPLE 6:What element in the domain has the image 10 under the function f(x) = 3x – 2 ? Here, f(x) = 3x – 2 and image of f(x) = 10 So, f(x) = 10 or, 3x – 2 = 10 or, 3x = 10 + 2 or, 3x = 12 or, 3𝑥 3 = 12 3 or, x = 4 Hence, the element in domain is 4 has image 10 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 24
- 25. EXAMPLE 7:If the range of the function f(x) = 3x – 4 is {- 1, 5}, find its domain. Also represent the function in arrow diagram. Here, f(x) = 3x – 4 and Range = {- 1, 5} So, y = f(x) = 3x - 4 When, y = - 1 or, 3x – 4 = - 1 or, 3x = - 1 + 4 or, 3x = 3 or x = 1 Again when , y = 5 or, 3x – 4 = 5 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 25 or, 3x = 5 + 4 or, 3x = 9 or, x = 3 Hence, Domain = {1, 3} Representing the function f in arrow diagram - 1 - 5 1 - 3 A B f
- 26. PRACTICE QUESTIONS 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 26
- 27. 1. Which of the following are the function of not? Give reason. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 27
- 28. 2. Represent the following relations in arrow diagram. Identify whether they are function of not .Find the domain, range and co-domain of the functions 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 28
- 29. 3. Find the image of the functions a) Find the image of 2 in the function f(x) = 5x b) Find the image of - 2 in the function f(x) = - 6x c) Find the image of 10 in the function f(x) = 𝑥+2 3 d) Find the image of 3 in the function g(x) = 4x - 5 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 29
- 30. 4. Find range: a) f(x) = 2x2- 3; Domain = {- 1, 0 , 1, 2}. Find its range and represent the function in graph. b) f(x) = 2x – 3; Domain= {4, 5, 6}. Find its range and represent the function c) If f(x) = 4x + 5 and domain D = {1, 2, 3}, find the range and list the set of ordered pairs of f. d) If f(x) = {(x, y): y = 2x + 3} and x 𝜖 {2, 4, 6}, find the range and represent the function in arrow diagram. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 30
- 31. 4 (d). If f(x) = {(x, y): y = 2x + 3} and x 𝜖 {2, 4, 6}, find the range and represent the function in arrow diagram. • f(x) = {(x, y) y = 2x + 3, domain = {2, 4, 6} When x = 2, y = 2x2 + 3 = 7 When x = 4, then y = 2x 4 + 3 = 11 When, x = 6, y = 2. 6 + 3 = 15 Hence, range = {7, 11, 15} or, y ∈ {7, 11, 15} Now, representing the function f in arrow diagram. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 31 2 4 6 7 11 15 A B f
- 32. 5. Find the pre-image: a) Find the pre-image of 16 of the function f(x) = 4x b) Find the pre image of 5 in the function g(x) = 5x . c) Find the pre- image of 8 in the function f(x) = 2x + 6. d) What will be the pre- image of 4 in the function f(x) = 𝑥 ? e) What element in the domain has image 7 under the function f(x) = 2𝑥 − 3 5 ? f) What will be the pre image of 8 in f(x) = 3 𝑥? 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 32
- 33. 6. Find the domain: a) If the range of the function f(x) = 4x – 5 is {- 1, 7}, find its domain. Also represent the function in arrow diagram. b) If range of a function f:x→ 3x + 5 is {2, 8}, find its domain . Also represent in the graph . c) If range R = {1, 7, 11}, find the domain in the function f :x → 4x – 5 d) Find the domain of the function f(x) = 4x + 2, if range R = {2, 6}. Also represent the function in table. 6/28/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 33
- 34. https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGxSYD_UZLzXfmAzxaRyYhw?vie w_as=subscriber https://bit.ly/38mTXOK : You tube https://www.facebook.com/janaksinghsaud https://www.slideshare.net/janaksinghsaud [email protected] 6/23/2020 JANAK SINGH SAUD 34