GE8151 Problem Solving and Python Programming
- 1. GE8151 - Problem Solving and Python Programming Important University Questions and Answers Prepared By B.Muthukrishna Vinayagam, Assistant Professor/CSE
- 4. The print Statement >>> print ('hello‘) hello >>> print ( 'hello', 'there‘ ) hello there >>>a=15 >>>print(“The value of a is %d.” %(a) ) •Elements separated by commas print with a space between them •A comma at the end of the statement (print ‘hello’,) will not print a newline character Interactive Mode Script Mode - filename.py print (‘hello’) Run: python filename.py Output: hello
- 5. Variables • Are not declared, just assigned • The variable is created the first time you assign it a value • Are references to objects • Type information is with the object, not the reference • Everything in Python is an object
- 8. Beginners' Python 8 Built-in Object Types (Data Types) Type Ordered Mutable Examples Numbers N/A No 3.14, 123, 99L, 1-2j, 071, 0x0a Strings Yes No 'A string', "A double ed string" Lists Yes Yes [1, [2, 'three'], [5E-1, 10e3], -8L] Dictionaries No Yes {‘key':‘value', ‘b':'ball'} Tuples Yes No (1, 'two', -3j, 04, 0x55, 6L) Can be changed in place? Can be indexed/sliced?
- 9. Operator
- 10. Functions, Procedures A function is a group of statements that together perform a task. def name(arg1, arg2, ...): """documentation""" # optional doc string statements return # from procedure return expression # from function
- 11. Function Basics def max(x,y) : if x < y : return x else : return y >>> import functionbasics >>> max(3,5) 5 >>> max('hello', 'there') 'there' >>> max(3, 'hello') 'hello' functionbasics.py
- 12. Anonymous Functions • A lambda expression returns a function object • The body can only be a simple expression, not complex statements >>> f = lambda x,y : x + y >>> f(2,3) 5 >>> lst = ['one', lambda x : x * x, 3] >>> lst[1](4) 16
- 13. Duck Typing • Function Overloading: achieved polymorphism #function definition def add(x,y,z): return x+y+z #function calling Output add(10,20,30) #60 add('muthu',"krishna","vinayagam") #muthukrishnavinayagam add(5.5,4.5,15.5) #25.5
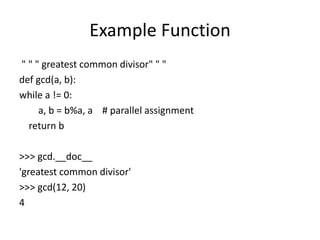
- 14. Example Function " " " greatest common divisor" " " def gcd(a, b): while a != 0: a, b = b%a, a # parallel assignment return b >>> gcd.__doc__ 'greatest common divisor' >>> gcd(12, 20) 4
- 15. Required argument def fun(a,b): #statement fun(10) #throws error Keyword argument def fun(a,b): #statement fun(b=10, a=”Python”) Default argument with value def fun(a, b=20): #statement fun(10) Variable length argument def fun(*var): #statement fun(10,20,30)
- 16. def foo(x, y): global a a = 42 x,y = y,x b = 33 b = 17 c = 100 print(a,b,x,y) a, b, x, y = 1, 15, 3,4 foo(17, 4) print(a, b, x, y) Global and Local Variable The output looks like this: 42 17 4 17 42 15 3 4
- 17. Strings & its operation It is collection of characters enclosed by single/double/triple quotes Example: 'single quotes' """triple quotes""" r"raw strings" • "hello"+"world" "helloworld" # concatenation • "hello"*3 "hellohellohello" # repetition • "hello"[0] "h" # indexing • "hello"[-1] "o" # (from end) • "hello"[1:4] "ell" # slicing • len("hello") 5 # size • "hello" < "jello" 1 # comparison • "e" in "hello" True # search • "hello“[::-1] “olleh” #reverse • "escapes: n etc, 033 etc, tif etc“ #display escape sequence
- 18. capitalize() Converts first character to Capital Letter center() Pads string with specified character count() returns occurrences of substring in string endswith() Checks if String Ends with the Specified Suffix encode() returns encoded string of given string find() Returns the Highest Index of Substring format() formats string into nicer output index() Returns Index of Substring isalnum() Checks Alphanumeric Character isalpha() Checks if All Characters are Alphabets
- 19. Conditional Statements if condition: #stm elif condition: #stm else: #stm if condition: #stm No Switch Statement: print({1:”one”,2:”Two”,3:”Three”}.get(1,”Invalid”)) if condition: #stm else: #stm
- 20. While loop Syntax while condition: #stms Example: i=1 While i<=5: print(i) i=i+1 Output: 1 2 3 4 5
- 21. For Loops • Similar to perl for loops, iterating through a list of values ~: python forloop1.py 1 7 13 2 for x in [1,7,13,2] : print xforloop1.py ~: python forloop2.py 0 1 2 3 4 for x in range(5) : print xforloop2.py range(N) generates a list of numbers [0,1, …, n-1]
- 22. Loop Control Statements break Jumps out of the closest enclosing loop continue Jumps to the top of the closest enclosing loop pass Does nothing, empty statement placeholder
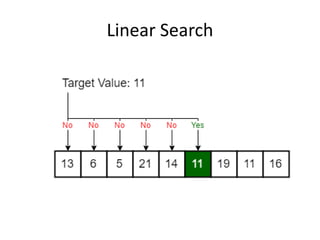
- 23. Linear Search
- 25. List Operations & its methods >>> a=[1,5,10] # List creation >>> a = range(5) # [0,1,2,3,4] >>> a.append(5) # [0,1,2,3,4,5] >>> a.pop() # [0,1,2,3,4] 5 >>> a.insert(0, 42) # [42,0,1,2,3,4] >>> a.pop(0) # [0,1,2,3,4] 42 >>> a.reverse() # [4,3,2,1,0] >>> a.sort() # [0,1,2,3,4] >>>print(len(a)) #5
- 26. Methods Functions append() to add element to the end of the list extend() to extend all elements of a list to the another list insert() to insert an element at the another index remove() to remove an element from the list pop() to remove elements return element at the given index clear() to remove all elements from the list index() to return the index of the first matched element count() to count of number of elements passed as an argument sort() to sort the elements in ascending order by default reverse() to reverse order element in a list copy() to return a copy of elements in a list
- 28. Tuples • key = (lastname, firstname) • point = x, y, z # parentheses optional • x, y, z = point # unpack • lastname = key[0] • singleton = (1,) # trailing comma!!! • empty = () # parentheses!
- 29. Python Expression Results Operation len((1, 2, 3)) 3 Length (1, 2, 3) + (4, 5, 6) (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) Concatenation ('Hi!',) * 4 ('Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!') Repetition 3 in (1, 2, 3) True Membership for x in (1, 2, 3): print x, 1 2 3 Iteration Tuple and its Operations tuple=(10,20,20,40) len(tuple) -> Gives the total length of the tuple. max(tuple) -> Returns item from the tuple with max value. min(tuple) -> Returns item from the tuple with min value. tuple(seq) -> Converts a list into tuple. tuple1=(10,20,20,40) tuple2=(20,20,20,40) cmp(tuple1, tuple2) -> Compares elements of both tuples.
- 30. Dictionaries • Hash tables, "associative arrays" • d = {"duck": "eend", "water": "water"} • Lookup: • d["duck"] #eend • d["back"] # raises KeyError exception • Delete, insert, overwrite: • d["back"] = "rug" # {"duck": "eend", "water": "water“,"back": "rug"} • del d["water"] # {"duck": "eend", "back": "rug"} • d["duck"] = "duik" # {"duck": "duik", "back": "rug"} •Keys, values, items: d.keys() -> ["duck", "back"] d.values() -> ["duik", "rug"] d.items() -> [("duck","duik"), ("back","rug")]
- 31. Dictionaries & its Operation & Methods: len(dict) -> Gives the total length of the dictionary. This would be equal to the number of items in the dictionary. str(dict) -> Produces a printable string representation of a dictionary type(variable) -> Returns the type of the passed variable. If passed variable is dictionary, then it would return a dictionary type. cmp(dict1, dict2) -> Compares elements of both dict. Accessing Values in Dictionary dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}; print (dict['Name']) Updating Dictionary dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}; dict['Age'] = 8 # update existing entry dict['School'] = "DPS School" # Add new entry print (dict['School']) Delete Dictionary Elements dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}; del dict['Name']; # remove entry with key 'Name' dict.clear(); # remove all entries in dict del dict ; # delete entire dictionary Five methods are used to delete the elements from the dictionary: pop(), popitem(), clear(), del(), update(d)
- 32. Selection sort
- 33. Insertion sort
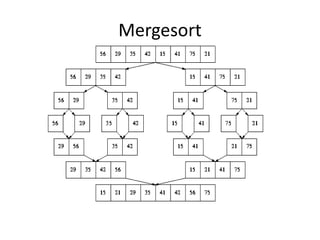
- 34. Mergesort
- 35. File operation: Step1: Open a file object in read or write or append mode Step2: Read or write the file contents using read() or write() methods or Read or write entire line of file using readline() or writelines() methods Step3: Close file object close() method Example f=open("sample.txt","r") print(f.read()) f.close()
- 36. File operation fobj.read(7); # read only 5th bytes fobj.tell(); #tell the current position fobj.seek(5); #move to the 5th byte location import os os.rename(“old.txt”, “new.txt”) os.remove(“file.txt”)
- 37. File Copy 1) from shutil import copyfile copyfile('test.py', 'abc.py') 2) f1=open(“t.txt","r") f2=open(“d.txt",“w") c=f1.read() f2.write(c) f1.close() f2.close()
- 38. An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of the program's instructions. Need of Exception Handling: • An exception is an error that happens during execution of a program. When that error occurs, Python generate an exception that can be handled, which avoids your program to crash. • Need graceful exit that is save all works and close it. Syntax: try: # Suspected Code except: # Remedial Action
- 39. Exception: To handle Abnormal program termination, gracefully exit while True: try: n = int(input("Please enter an integer: ")) break except ValueError: print("No valid integer! Please try again ...") finally: print("Great, you successfully entered an integer!")
- 40. def divide(x, y): try: result = x / y except ZeroDivisionError: print("division by zero!") else: print("result is", result) finally: print("executing finally clause") Note: if try block doesn’t raise the exception then else block is executed. Finally block is always executed or clean up process
- 41. User Exception class MyException(Exception): #pass Code snippet while True: try: n = int(input("Please enter an integer: ")) raise MyException("An exception doesn't always prove the rule!") except ValueError: print("No valid integer! Please try again ...") finally: print("Great, you successfully entered an integer!")
- 42. Module: Python has a way to put definitions in a file and use them in a script or in an interactive instance of the interpreter. Such a file is called a module; definitions from a module can be imported into other modules or into the main module fibo.py def fib1(n): # write Fibonacci series up to n a, b = 0, 1 while b < n: print(b, end=' ') a, b = b, a+b print() def fib2(n): # return Fibonacci series up to n result = [] a, b = 0, 1 while b < n: result.append(b) a, b = b, a+b return result >>>import fibo or >>>from fibo import fib2 >>>fibo.fib1(5) # 1 1 2 3 5
- 43. Package New directory: demopack • First.py • Second.py • __init__.py Use Package Test.py from demopack import First from demopack import Second First.display() Second.show()







![Beginners' Python 8
Built-in Object Types (Data Types)
Type Ordered Mutable Examples
Numbers N/A No 3.14, 123, 99L, 1-2j, 071, 0x0a
Strings Yes No 'A string', "A double ed string"
Lists Yes Yes [1, [2, 'three'], [5E-1, 10e3], -8L]
Dictionaries No Yes {‘key':‘value', ‘b':'ball'}
Tuples Yes No (1, 'two', -3j, 04, 0x55, 6L)
Can be changed in place?
Can be indexed/sliced?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-8-320.jpg)



![Anonymous Functions
• A lambda
expression returns a
function object
• The body can only
be a simple
expression, not
complex statements
>>> f = lambda x,y : x + y
>>> f(2,3)
5
>>> lst = ['one', lambda x : x * x, 3]
>>> lst[1](4)
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-12-320.jpg)



![Strings & its operation
It is collection of characters enclosed by
single/double/triple quotes
Example: 'single quotes' """triple quotes""" r"raw strings"
• "hello"+"world" "helloworld" # concatenation
• "hello"*3 "hellohellohello" # repetition
• "hello"[0] "h" # indexing
• "hello"[-1] "o" # (from end)
• "hello"[1:4] "ell" # slicing
• len("hello") 5 # size
• "hello" < "jello" 1 # comparison
• "e" in "hello" True # search
• "hello“[::-1] “olleh” #reverse
• "escapes: n etc, 033 etc, tif etc“ #display escape sequence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-17-320.jpg)



![For Loops
• Similar to perl for loops, iterating through a list of values
~: python forloop1.py
1
7
13
2
for x in [1,7,13,2] :
print xforloop1.py
~: python forloop2.py
0
1
2
3
4
for x in range(5) :
print xforloop2.py
range(N) generates a list of numbers [0,1, …, n-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-21-320.jpg)


![List Operations & its methods
>>> a=[1,5,10] # List creation
>>> a = range(5) # [0,1,2,3,4]
>>> a.append(5) # [0,1,2,3,4,5]
>>> a.pop() # [0,1,2,3,4]
5
>>> a.insert(0, 42) # [42,0,1,2,3,4]
>>> a.pop(0) # [0,1,2,3,4]
42
>>> a.reverse() # [4,3,2,1,0]
>>> a.sort() # [0,1,2,3,4]
>>>print(len(a)) #5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-25-320.jpg)


![Tuples
• key = (lastname, firstname)
• point = x, y, z # parentheses optional
• x, y, z = point # unpack
• lastname = key[0]
• singleton = (1,) # trailing comma!!!
• empty = () # parentheses!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-28-320.jpg)

![Dictionaries
• Hash tables, "associative arrays"
• d = {"duck": "eend", "water": "water"}
• Lookup:
• d["duck"] #eend
• d["back"] # raises KeyError exception
• Delete, insert, overwrite:
• d["back"] = "rug" # {"duck": "eend", "water": "water“,"back": "rug"}
• del d["water"] # {"duck": "eend", "back": "rug"}
• d["duck"] = "duik" # {"duck": "duik", "back": "rug"}
•Keys, values, items:
d.keys() -> ["duck", "back"]
d.values() -> ["duik", "rug"]
d.items() -> [("duck","duik"), ("back","rug")]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-30-320.jpg)
![Dictionaries & its Operation & Methods:
len(dict) -> Gives the total length of the dictionary. This would be equal to the number of
items in the dictionary.
str(dict) -> Produces a printable string representation of a dictionary
type(variable) -> Returns the type of the passed variable. If passed variable is dictionary,
then it would return a dictionary type.
cmp(dict1, dict2) -> Compares elements of both dict.
Accessing Values in Dictionary
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'};
print (dict['Name'])
Updating Dictionary
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'};
dict['Age'] = 8 # update existing entry
dict['School'] = "DPS School" # Add new entry
print (dict['School'])
Delete Dictionary Elements
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'};
del dict['Name']; # remove entry with key 'Name'
dict.clear(); # remove all entries in dict
del dict ; # delete entire dictionary
Five methods are used to delete the elements from the dictionary:
pop(), popitem(), clear(), del(), update(d)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-31-320.jpg)









![Module: Python has a way to put definitions in a file and use them in a
script or in an interactive instance of the interpreter. Such a file is
called a module; definitions from a module can be imported into other
modules or into the main module
fibo.py
def fib1(n): # write Fibonacci series up to n
a, b = 0, 1
while b < n:
print(b, end=' ')
a, b = b, a+b
print()
def fib2(n): # return Fibonacci series up to n
result = []
a, b = 0, 1
while b < n:
result.append(b)
a, b = b, a+b
return result
>>>import fibo or >>>from fibo import fib2
>>>fibo.fib1(5) # 1 1 2 3 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-191207061933/85/GE8151-Problem-Solving-and-Python-Programming-42-320.jpg)
