Geert Driessen & Frederik Smit (2005) ERNAPE Integration participation and education Pres.ppt
- 1. Integration, participation, and education: effects of minority parents’ societal participation on their children’s cognitive and non-cognitive competencies Dr. Geert Driessen Dr. Frederik Smit ITS, Radboud University Nijmegen Contact: www.geertdriessen.nl Paper ERNAPE conference 14–16 September 2005, Oviedo (ES)
- 2. Three categories: • former colonies (e.g., Surinamese: 325,000, Antillean: 131,000) • labor immigrants (e.g., Turkish: 352,000; Moroccan: 306,000) • refugees/asylum seekers (e.g., Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, Yugoslavia) Characteristics: • differences with respect to language, culture, religion (Islam) • many illiterate, little education, no job, on social welfare; overrepresentation in crime statistics 1. Ethnic minorities in the Netherlands Non-Western immigrants 10% of the Dutch population of 16.5 million
- 3. Since 1980s: ‘integration with maintenance of own culture’ Since 2001: increased negative view on immigration Shift towards assimilation: compulsory integration; accent on one’s own responsibility Goal: shared citizenship immigrants and native inhabitants Willingness to actively contribute to society and participate in all facets of society: education (diploma); labor market (job); social (membership in associations); political (voting); cultural; societal (volunteer work); sports 2. Integration policy in the NL
- 4. Integration pertains to immigrants themselves and also to their children. Better integrated immigrant parents → more favorable educational and societal opportunities for their children. Integration policy emphasizes the responsibility of immigrant parents. Expectations derived from notions of social and cultural capital (Bourdieu, Coleman). More parental participation → greater social and cultural capital → positively influences child-rearing situation, educational and societal opportunities of their children. 3. Participation, capital, and educational opportunity
- 5. Study of immigrant background, participation, and educational results in conjunction with each other. “What relations exist between parental participation and the cognitive and non- cognitive educational outcomes of their children?” Answer → empirical support for the position held by the Dutch government with respect to ‘participation as capital’? 4. Research question
- 6. Cohort study Primary Education (‘PRIMA’). 583 or 9% of all Dutch primary schools. 10,680 children in kindergarten (6 years of age) and their parents. Data sources: parents, pupils, teachers, schools 5. Data and variables
- 7. 6. Model Family structural parental ethnicity parental education parental length of residence Aspects of participation labor religious political societal social cultural Cognitive outcome measures language skill math skill Non-cognitive outcome measures social position self-confidence well-being
- 8. 7. Ethnicity, participation, and effect measures bivariately Ethnicity Dutch Sur/Ant Tur/Mor Other eta Participation Labor % paid work 87 54 49 52 .38 Religious % (practically) never 58 36 15 45 .31 % few times a year 24 44 17 25 .11 % 1-3 times a month 9 13 20 13 .12 % 1 times a week 9 7 48 16 .39 Political % no times 21 45 43 58 .28 % one time 12 17 26 17 .14 % two times 67 38 30 25 .33 Societal % volunteer work 28 12 12 14 .16 Social % 0 48 63 48 65 .10 % 1 47 32 42 30 .11 % 2 5 5 9 5 .06 Cultural % never 14 15 73 24 .49 % <1 a year 42 60 18 47 .20 % 1 a year 30 16 8 21 .19 % 2 a year 13 9 1 9 .14 Effect measures Language 987 967 952 969 .36 Math 57 50 47 52 .28 Social position 3.8 3.7 3.7 3.7 .12 Self-confidence 3.6 3.6 3.6 3.6 .02 Well-being 4.1 4.0 4.0 4.0 .05
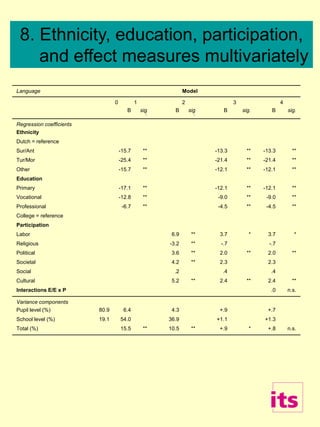
- 9. Language Model 0 1 2 3 4 B sig . B sig . B sig. B sig. Regression coefficients Ethnicity Dutch = reference Sur/Ant -15.7 ** -13.3 ** -13.3 ** Tur/Mor -25.4 ** -21.4 ** -21.4 ** Other -15.7 ** -12.1 ** -12.1 ** Education Primary -17.1 ** -12.1 ** -12.1 ** Vocational -12.8 ** -9.0 ** -9.0 ** Professional -6.7 ** -4.5 ** -4.5 ** College = reference Participation Labor 6.9 ** 3.7 * 3.7 * Religious -3.2 ** -.7 -.7 Political 3.6 ** 2.0 ** 2.0 ** Societal 4.2 ** 2.3 2.3 Social .2 .4 .4 Cultural 5.2 ** 2.4 ** 2.4 ** Interactions E/E x P .0 n.s. Variance components Pupil level (%) 80.9 6.4 4.3 +.9 +.7 School level (%) 19.1 54.0 36.9 +1.1 +1.3 Total (%) 15.5 ** 10.5 ** +.9 * +.8 n.s. 8. Ethnicity, education, participation, and effect measures multivariately
- 10. 9. Conclusions and discussion Hypothesis: participation indication of integration; greater parental integration promotes a more favorable educational position for their children. Only a consistent effect of cultural participation on language and math skills. ‘High brow’ cultural participation: regular attendance of concerts, films, and museums. Confirmation of cultural capital thesis. Assumption with regard to chances of immigrant children receive only partial confirmation. Expectations have been stretched too high and greater realism is called for.