Gender Equality (1Vey imp presentation by mr unknown 69pptx
- 2. Gender Equality The view that both men and women should receive equal treatment and not be discriminated against based on their gender. Also known as sex equality , gender equalitarianism, sexual equality or equality of the genders. The process of being fair to women and men. Requires equal enjoyment by women and men of socially valued- goods, opportunities, resources and rewards. It doesn’t mean men and women being the same.
- 3. Gender Inequality in India
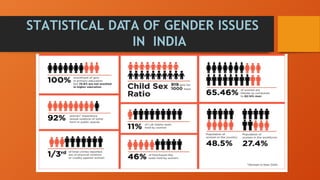
- 5. Factors responsible for gender inequality Illiteracy Illiteracy is one of the factors responsible for gender inequality. According to 2011 census of India., the literacy level in India is 74.04% in which the male literacy level is 82.14% and female literacy level is only 65.46%. Child Marriage Children specially the girls are married at a very young age. This proves fatal for their overall development and have a negative impact on their health, too. Social evils Social evils like dowry system, sati system, are also responsible for the low status of women. Discrimination against the girl child The girl child is not treated properly in the family. People still prefer the birth of a boy rather than a girl. The girl child is basically trained for household work only. Even today, female infanticide is a common social evil.
- 6. Lack of employment equality The current global labor force participation rate for women is close to 49%. For men, it’s 75%. That’s a difference of 26 percentage points, with some regions facing a gap of more than 50 percentage points. Job segregation One of the causes for gender inequality within employment is the division of jobs. In most societies, there’s an inherent belief that men are simply better equipped to handle certain jobs. Most of the time, those are the jobs that pay the best. This discrimination results in lower income for women. Lack of legal protections In many countries, there’s also a lack of legal protections against harassment in the workplace, at school, and in public. These places become unsafe and without protection, women frequently have to make decisions that compromise and limit their goals. Factors responsible for gender inequality
- 7. Lack of bodily autonomy According to the WHO, over 200 million women who don’t want to get pregnant are not using contraception. There are various reasons for this such as a lack of options, limited access, and cultural/religious opposition. On a global scale, about 40% of pregnancies are not planned and while 50% of them do end in abortion, 38% result in births. These mothers often become financially dependent on another person or the state, losing their freedom. Poor medical care women receive lower-quality medical care than men. This is linked to other gender inequality reasons such as a lack of education and job opportunities, which results in more women being in poverty. They are less likely to be able to afford good healthcare. Factors responsible for gender inequality
- 8. Types of Gender Inequality There are many kinds of gender inequality or gender disparity which are as follows: Inequality in Family Natality inequality Professional or Employment inequality Ownership inequality Household inequality
- 9. Inequality in Family ▶ The divorce proceedings have been equal for men and women since 1976. Divorce by mutual consent is legal but in reality, any woman who initiates a divorce is condemned by the public opinion. For that reason, divorces are very rare.
- 10. Natality inequality In this type of inequality a preference is given for boys over girls that many male- dominated societies have, gender inequality can manifest itself in the form of the parents wanting the newborn to be a boy rather than a girl. There was a time when this could be no more than a wish (a daydream or a nightmare, depending on one's perspective), but with the availability of modern techniques to determine the gender of the fetus, sex-selective abortion has become common in many countries. It is particularly prevalent in East Asia, in China and South Korea in particular, but also in Singapore and Taiwan, and it is beginning to emerge as a statistically significant phenomenon in India and South Asia as well.
- 11. Professional or Employment inequality In terms of employment as well as promotion in work and occupation, women often face greater handicap than men. A country like Japan and India may be quite egalitarian in matters of demography or basic facilities, and even, to a great extent, in higher education, and yet progress to elevated levels employment and occupation seems to of be much more problematic for women than for men. The example includes unequal pay at work, unpaid care work.
- 12. Ownership inequality In many societies the ownership of property can also be very unequal. Even basic assets such as homes and land may be very asymmetrically shared. The absence of claims to property can not only reduce the voice of women, but also make it harder for women to enter and flourish in commercial, economic and even some social activities. This type of inequality has existed in most parts of the world, though there are also local variations.
- 13. Household Inequality It is, quite common in many societies to take it for granted that while men will naturally work outside the home, women could do it if and only if they could combine it with various inescapable and unequally shared household duties. This is sometimes called "division of labor," though women could be forgiven for seeing it as "accumulation of labor.“ The reach of this inequality includes not only unequal relations within the family, but also derivative inequalities in employment and recognition in the outside world. Also, the established fixity of this type of "division" or "accumulation" of labor can also have far-reaching effects on the knowledge and understanding of different types of work in professional circles.
- 14. Gender Discrimination In Indian Society In India, discriminatory attitude towards men and women have existed for generations and effect the lives of both genders. Although the constitution of India has granted men and women equal rights, gender disparity still remains. Gender discrimination violates human rights. These are mostly seen in family land sharing among sisters and brothers. Everyday, women and girls around the world face violence and discrimination. 1 in 3 women experience physical or sexual violence in their lifetime, regardless of age, background or country, and every country in the world has laws that treat women and girls as second-class citizens. Sexual exploitation, violence, harmful cultural practices and systemic inequalities violate their human rights and prevent them from reaching their potential
- 15. Discrimination Where ? In the workplace Deciding not to hire or promote someone, treating employees differently, or paying them less based on their gender are all examples of workplace discrimination. In schools Preventing or discouraging girls and young women from participating in traditionally male-dominated fields, such as science, math, and sports, is an example of gender discrimination. Schools may also enforce gendered dress codes, punish those who do not conform to gender norms, or fail to punish bad behavior on the basis that “Boys will be boys.”
- 16. In public Sexual harassment and catcalling are unwanted, and they are forms of discrimination. These behaviors can make people feel unsafe, and they can restrict how people use public spaces. This limits a person’s freedom. In institutions Organizations, governments, and legal and healthcare systems can enact policies that discriminate against certain genders, either intentionally or unintentionally. In relationships People who prevent their partners from doing things on the basis of their gender are also acting in a discriminatory way. This might include stopping women from working, managing their money, and driving. Discrimination Where ?
- 17. Effect of Gender Discrimination Depression Anxiety PTSD Eating Disorder Illness Low self stream Poor Health Injury and death Suicide Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Women are also 1.5 times more likely to attempt suicide than men. Effect of Gender Discrimination
- 18. Gender Issues Gender Issues Unequal education Child sex Ratio Unequal Pay Sexual harassment Racism Less Promotion Health Nutrition Violence Gender issues include all aspects and concerns related to women’s and men’s lives and situation in society, to the way they interrelate, their differences in access to and use of resources, their activities, and how they react to changes, interventions and policies.
- 19. Unequal Education India’s education landscape is extremely unequal. These inequalities manifest themselves in the form of differences based on caste, class and in some case of gender. Achievement, earnings, health status, and political participation also contribute to educational inequality within the United States and other countries. Child sex Ratio The Child Sex Ratio is defined as the number of females per 1000 males in the age group 0–6 years. As per Census 2011, the Gender ratio of India is 943 females per 1000 males. There are 949 females to 1000 men in rural areas, while in an urban area, there are 929 females to 1000 males.
- 20. Unequal pay Gender pay gap in India refers to the difference in earnings between women and men in the paid employment and labor market. The Indian Constitution recognized the principle of 'Equal Pay for Equal Work' for both men and women, and 'Right to Work' through Article 39(d) and 41. Racism Races are the physical qualities that one inherits biologically and serves as a way of self- identification from the other groups. Racism is a theory that one race is superior that the other based on the physical attributes, caste, creed, ethnicity or origin. ARTICLE 15(1) says that there should be no discrimination on the grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth
- 21. Sexual Harassment Sexual harassment involves inappropriate promises, rewards in exchange for sexual favors or unwelcome sexual behavior that is offensive, humiliating, or intimidating, or use of explicit or implicit sexual overtones, etc. A woman is sexually harassed every twelve minutes. Harmonizing our Indian law, sexual harassment violates the fundamental right of gender equality and life with dignity under Article 14 and Article 21 of the Indian Constitution respectively. Less Promoted 85% of Indian women say they have missed out on a raise, promotion or work offer because of their gender. This is markedly higher than the region’s average of 60%.
- 22. Health Indian women have high mortality rates, particularly during childhood and in their productive years. The health of Indian women is intrinsically linked to their status in society. The women in India belong to various socio-economic backgrounds and are sometimes marginalized or neglected when it comes to basic healthcare. Nutrition In India and in South Asia, gender discrimination is one of the most significant underlying factors for poor nutrition. Poverty that itself underlies conditions like limited ability to access nutritious food, limited time and control over time and access to sanitation are important determinants. Violence Violence occurs in about 35 per cent of women globally in their lifetime. on about 10000 women, 26 per cent reported having experienced physical violence from spouses during their lifetime. The prevalence could be as high as 45 per cent as indicated by data from Uttar Pradesh.
- 23. STATISTICAL DATA OF GENDER ISSUES IN INDIA
- 24. Contemporary Challenges of Gender equality, Discrimination, Issues Poverty Gender based Violence Family Violence Lack of Girls Friendly school environment Child Marriage & Early Pregnancy Body Shaming killing girl in fetus Psychological violence Physical violence Verbal violence Unequal seats (Only 33% seats reserve for women in politics)