Getting Started with DDS in C++, Java and Scala
- 1. Getting Started with DDS [In C++, Java and Scala] OpenSplice DDS Angelo CORSARO, Ph.D. Chief Technology Officer OMG DDS Sig Co-Chair PrismTech [email protected]
- 2. General Information This tutorial will get you started with DDS. At the end of this course Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ you should have a firm grip of DDS concepts and the capacity of designing and writing DDS applications OpenSplice DDS ☐ The tutorial will be highly interactive and provide plenty of examples and live demonstrations ☐ The tutorial will cover the new C++ and Java API ☐ The tutorial will also introduce you into distributed functional programming with Scala and DDS
- 3. Outline ☐ Background Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ DDS Basics ☐ Data Reader/Writer Caches OpenSplice DDS ☐ DDS Quality of Service ☐ Data & State Selectors ☐ Advanced Topics in DDS ☐ Concluding Remarks
- 4. OpenSplice DDS Background
- 5. Data Distribution Service For Real-Time Systems Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Introduced in 2004 to address the Data Distribution Real-Timeliness Scale challenges faced by a wide class of Defense and Aerospace Applications OpenSplice DDS Key requirement for the Parallelism Determinism Throughput, Availability Scalability, Persistence, Security ☐ standard were to deliver very Systemic Signal Data Real-Time Information Near Real-Time Fault- Tolerant Information Complex Information high and predictable Processing Processing Management Processing Processing performance while scaling from embedded to ultra- Parallel Systems Distributed Systems large-scale deployments
- 6. Data Distribution Service For Real-Time Systems Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Recommended by key Real-Timeliness Scale administration worldwide, e.g. DoD, MoD, EUROCAE, etc. OpenSplice DDS Widely adopted across Parallelism Determinism Throughput, Availability Scalability, Persistence, Security ☐ several different domains, Systemic Signal Data Real-Time Information Near Real-Time Fault- Tolerant Information Complex Information e.g., Automated Trading, Processing Processing Management Processing Processing Simulations, SCADA, Telemetry, etc. Parallel Systems Distributed Systems
- 7. DDS Standard Ecosystem Application Application Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. 2012 API 2012 DDS RMI DDS RMI 2012 2010 2010 2012 ANSI C ISO C++ Java-5 Scala OpenSplice DDS 2004 2010 2010 201x Security Security X-Types X-Types DDS 2004 Wire Protocol DDSI-RTPS network DDSI-RTPS 2006 2006
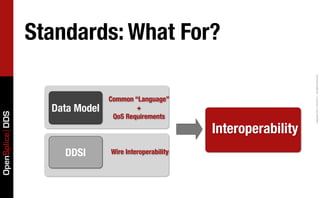
- 8. Standards: What For? Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Common “Language” Data Model + OpenSplice DDS QoS Requirements Interoperability DDSI Wire Interoperability
- 9. OpenSplice DDS DDS Application API Standard Standards: What For? Portability Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved.
- 10. Defense and Aerospace Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. OpenSplice DDS Integrated Modular Vetronics Training & Simulation Systems Naval Combat Systems Air Traffic Control & Management Unmanned Air Vehicles Aerospace Applications
- 11. Commercial Applications Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. OpenSplice DDS Agricultural Vehicle Systems Large Scale SCADA Systems Smart Cities Train Control Systems Complex Medical Devices High Frequency Auto-Trading
- 12. OpenSplice DDS D D BaS ics
- 13. Data Distribution Service For Real-Time Systems DDS provides a Topic-Based Publish/ Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Subscribe abstraction based on: Data Reader Data Writer ☐ Topics: data distribution subject’s OpenSplice DDS Data Reader Data TopicD Writer DataWriters: data producers TopicA ☐ Data TopicB Reader Data Writer ☐ DataReaders: data consumers TopicC ... Data Data Writer Reader DDS Global Data Space
- 14. Data Distribution Service For Real-Time Systems Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ DataWriters and DataReaders are automatically and Data Reader dynamically matched by the Data Writer DDS Dynamic Discovery OpenSplice DDS Data Reader Data TopicD Writer TopicA ☐ A rich set of QoS allows to Data Reader TopicB control existential, temporal, Data Writer TopicC ... and spatial properties of data Data Data Writer Reader DDS Global Data Space
- 15. DDS Topics “Circle”, “Square”, “Triangle”, ... ☐ A Topic defines a class of streams Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ A Topic has associated a unique Name name, a user defined extensible type and a set of QoS policies Topic Typ S OpenSplice DDS DURABILITY, Qo ☐ QoS Policies capture the Topic e DEADLINE, ShapeType non-functional invariants PRIORITY, … ☐ Topics can be discovered or locally defined struct ShapeType { @Key string color; long x; long y; long shapesize; };
- 16. Topic Instances ☐ Each unique key value Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Instances Instances identifies a unique stream of data color =”Green” DDS not only struct ShapeType { ☐ color =”red” @Key string color; Topic OpenSplice DDS long x; long y; demultiplexes “streams” color = “Blue” long shapesize;}; but provides also lifecycle information ☐ A DDS DataWriter can write multiple instances
- 17. Anatomy of a DDS Application Domain (e.g. Domain 123) Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Participant Topic Partition (e.g. “Telemetry”, “Shapes”, ) OpenSplice DDS Publisher Subscriber Topic Instances/Samples DataWrter DataReader
- 18. Anatomy of a DDS Application [Scala API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId) Participant Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS DataWriter DataReader
- 19. Anatomy of a DDS Application [Scala API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId) Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber val pub = Publisher(dp) val sub = Subscriber(dp) DataWriter DataReader
- 20. Anatomy of a DDS Application [Scala API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId) Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber val pub = Publisher(dp) val sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Create a DataWriter/DataWriter val writer = DataWriter[ShapeType](pub, topic) Reader/Writer for val reader = DataReader[ShapeType](sub, topic) application defined Topic Types
- 21. Anatomy of a DDS Application [Scala API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId) Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber val pub = Publisher(dp) val sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Write data val data = new ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 75) writer write data Reader/Writer for // But you can also write like this... application defined writer ! data Topic Types // Read new data and print it on the screen (reader read) foreach (prinln)
- 22. Anatomy of a DDS Application [DDS C++ API 2010] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId); Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS auto topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber auto pub = Publisher(dp) auto sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Create a DataWriter/DataWriter auto writer = DataWriter<ShapeType>(pub, topic); Reader/Writer for auto reader = DataReader<ShapeType>(sub, topic); application defined Topic Types
- 23. Anatomy of a DDS Application [DDS C++ API 2010] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId); Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS auto topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber auto pub = Publisher(dp) auto sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Write data writer.write(ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89)); Reader/Writer for // But you can also write like this... writer << ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89); application defined Topic Types // Read new data (loaned) auto data = reader.read();
- 24. Anatomy of a DDS Application [DDS Java 5 API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId); Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS val topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber val pub = Publisher(dp) val sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Create a DataWriter/DataWriter auto writer = DataWriter<ShapeType>(pub, topic); Reader/Writer for auto reader = DataReader<ShapeType>(sub, topic); application defined Topic Types
- 25. Anatomy of a DDS Application [DDS Java 5 API] Domain Domain Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Do dp = DomainParticipant(domainId); Participant Session // Create a Topic Publisher Topic Subscriber OpenSplice DDS val topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”) // Create a Publisher / Subscriber val pub = Publisher(dp) val sub = Subscriber(dp) Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter DataReader // Write data writer.write(ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89)); Reader/Writer for // But you can also write like this... writer << ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89); application defined Topic Types // Read new data (loaned) auto data = reader.read();
- 27. DDS Model Topic Instances DataWriter DataReader DataReader Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... OpenSplice DDS DataWriter Cache DataReader Cache DataReader Cache Writer History Reader History network
- 28. DDS Model DataWriter DataReader DataReader Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... OpenSplice DDS DataWriter Cache DataReader Cache DataReader Cache QoS Policies ‣ History ‣ Destination Order ‣ Presentation network ‣ Partition ‣ Time Based Filter QoS Policies ‣ Ownership ‣ Reliability ‣ Durability ‣ History ‣ Transport Priority ‣ Latency Budget ‣ Time Based Filter
- 29. Dynamic View of a Stream Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. OpenSplice DDS ... Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 30. Dynamic View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) WriterHistory = KeepLast (m) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Writer History OpenSplice DDS ... Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 31. Dynamic View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) WriterHistory = KeepLast (m) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Samples ‘on Writer History the wire’ OpenSplice DDS ... Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 32. Dynamic View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) WriterHistory = KeepLast (m) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Samples ‘on Writer History the wire’ Reader History OpenSplice DDS ... Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 33. Dynamic View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) WriterHistory = KeepLast (m) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Samples ‘on Writer History the wire’ Reader History ‘Past’ Samples OpenSplice DDS ... Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
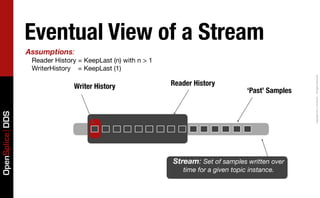
- 34. Eventual View of a Stream Assumptions (Default Settings): Reader History = KeepLast (1) WriterHistory = KeepLast (1) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Writer History Reader History ‘Past’ Samples OpenSplice DDS Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 35. Eventual View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) with n > 1 WriterHistory = KeepLast (1) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Writer History Reader History ‘Past’ Samples OpenSplice DDS Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 36. Eventual View of a Stream Assumptions: Reader History = KeepLast (n) with n > 1 WriterHistory = KeepLast (m) with n > m > 1 Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Writer History Reader History ‘Past’ Samples OpenSplice DDS Stream: Set of samples written over time for a given topic instance.
- 37. Reading Data Samples ☐ Samples can be read from the Data Reader History Cache Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The action of reading a sample is non-destructive. Samples are not removed from the cache OpenSplice DDS DataReader DataReader ... read ... DataReader Cache DataReader Cache
- 38. Taking Data Samples ☐ Samples can be taken from the Data Reader History Cache Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The action of taking a sample is destructive. Samples are removed from the cache OpenSplice DDS DataReader DataReader ... ... take DataReader Cache DataReader Cache
- 39. Read vs. Take Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The read operation should always be access the latest know value for topics that represent distributed state OpenSplice DDS ☐ The take operation should be used to get the last notification from a topic that represent an event
- 40. Eventual Consistency DDS caches provide eventual consistency semantics Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ ☐ This means that a read will see the effect of a preceding write eventually OpenSplice DDS ☐ Furthermore, given a data-writer that is currently matching N readers, we can think of DDS as providing eventual consistency with W=0 and R=1 ☐ W: the number of Acks expected in order to return from a write ☐ R: the number of sources from which a read access data
- 41. OpenSplice DDS QoS
- 42. QoS Model ☐ QoS-Policies control local and end-to-end properties of DDS Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Type Matching entities QoS matching QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS ☐ Local properties controlled by Topic Name QoS are related resource usage Publisher Subscriber ... DataWriter writes Type reads DataReader ... OpenSplice DDS ... ☐ End-to-end properties DomainParticipant DataWriter writes Type reads DataReader DomainParticipant controlled by QoS are related Topic Name to temporal and spatial aspects QoS QoS QoS of data distribution ☐ Some QoS-Policies are matched based on a Request vs. Offered Model thus QoS-enforcement
- 43. QoS Policies [T: Topic] [DR: DataReader] [DW: DataWriter] [P: Publisher] [S: Subscriber] [DP: Domain Participant] QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. USER_DATA DP, DR, DW N Y TOPIC_DATA T N Y Configuration GROUP_DATA P, S N Y DURABILITY T, DR, DW Y N OpenSplice DDS DURABILITY T, DW N N SERVICE Data Availability HISTORY T, DR, DW N N PRESENTATION P, S Y N RELIABILITY T, DR, DW Y N PARTITION P, S N Y Data Delivery DESTINATION T, DR, DW Y N ORDER LIFESPAN T, DW N Y
- 44. QoS Policies [T: Topic] [DR: DataReader] [DW: DataWriter] [P: Publisher] [S: Subscriber] [DP: Domain Participant] QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. DEADLINE T, DR, DW Y Y LATENCY T, DR, DW Y Y BUDGET Temporal/ TRANSPORT T, DW N Y Importance PRIORITY Characteristics OpenSplice DDS TIME BASED DR N Y FILTER OWNERSHIP T, DR, DW Y N OWNERSHIP DW N Y Replication STRENGTH LIVELINESS T, DR, DW Y N Fault-Detection
- 45. OpenSplice DDS Partition Data Delivery Reliability Presentation Data Delivery Order Destination Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved.
- 46. Reliability QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable RELIABILITY T, DR, DW Y N Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. The Reliability Policy controls the level of guarantee offered by the DDS in delivering data to subscribers ☐ Reliable. In steady-state, and no data writer crashes, the OpenSplice DDS middleware guarantees that all samples in the DataWriter history will eventually be delivered to all the DataReader ☐ Best Effort. Indicates that it is acceptable to not retry propagation of any samples
- 47. Partition QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable ☐ The Partition QoS Policy can PARTITION P, S N Y Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. be used as subjects for organizing the flows of data ☐ The Partition QoS Policy is Subscriber used to connect Publishers/ Publisher "tracks.kfo" "tracks.ufo" OpenSplice DDS Subscribers to a Partitions’ List which might also contain wildcards, e.g. Subscriber Publisher tracks.* ☐ Topics instances are published and subscribed Publisher Subscriber across one or more Partition Partitions
- 48. Data Availability History Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Data OpenSplice DDS Lifespan Durability Availability Ownership Ownership Strength
- 49. Durability QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable DURABILITY T, DR, DW Y N Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. The DURABILITY QoS controls the data availability w.r.t. late joiners, specifically the DDS provides the following variants: ☐ Volatile. No need to keep data instances for late joining data readers OpenSplice DDS ☐ Transient Local. Data instance availability for late joining data reader is tied to the data writer availability ☐ Transient. Data instance availability outlives the data writer ☐ Persistent. Data instance availability outlives system restarts
- 50. History QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable HISTORY T, DR, DW N N Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. For DataWriters, the HISTORY QoS policy controls the amount of data that can be made available to late joining DataReaders under TRANSIENT_LOCAL Durability OpenSplice DDS For DataReader, the HISTORY QoS policy controls how many samples will be kept on the reader cache ☐ Keep Last. DDS will keep the most recent “depth” samples of each instance of data identified by its key ☐ Keep All. The DDS keep all the samples of each instance of data identified by its key -- up to reaching some configurable resource limits
- 51. Ownership QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable OWNERSHIP T, DR, DW Y N STRENGTH DW N Y Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Availability of data producers can be controlled via two QoS Policies ☐ OWNERSHIP (SHARED vs. EXCLUSIVE) OpenSplice DDS ☐ OWNERSHIP STRENGTH ☐ Instances of exclusively owned Topics can be modified (are owned) by the higher strength writer ☐ Writer strength is used to coordinate replicated writers
- 52. Temporal Properties Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. TimeBasedFilter Deadline [Inbound] OpenSplice DDS Throughput LatencyBudget Latency [Outbound] TransportPriority
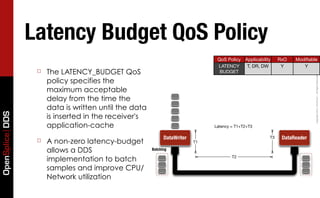
- 53. Latency Budget QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable LATENCY T, DR, DW Y Y ☐ The LATENCY_BUDGET QoS BUDGET Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. policy specifies the maximum acceptable delay from the time the data is written until the data OpenSplice DDS is inserted in the receiver's application-cache Latency = T1+T2+T3 DataWriter T3 DataReader ☐ A non-zero latency-budget T1 allows a DDS Batching implementation to batch T2 samples and improve CPU/ Network utilization
- 54. Deadline QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable DEADLINE T, DR, DW Y Y Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The DEADLINE QoS policy allows to define the maximum inter-arrival time between data samples ☐ DataWriter indicates that the application commits to write a new OpenSplice DDS value at least once every deadline period ☐ DataReaders are notified by the DDS when the DEADLINE QoS contract is violated DataWriter Deadline Deadline Deadline Deadline Deadline DataReader Deadline Violation
- 55. Transport Priority QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable TRANSPORT T, DW N Y PRIORITY Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The TRANSPORT_PRIORITY QoS policy is a hint to the infrastructure as OpenSplice DDS to how to set the priority of the underlying transport used to send the data.
- 56. Time-Based Filter QoS Policy QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable TIME BASED DR N Y FILTER Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. mit mit ☐ The Time Based Filter allows to control the throughput at which Latency = T1+T2+T3 data is received by a data reader OpenSplice DDS DataWriter T3 DataReader ☐ Samples produced more often T2 than the minimum inter-arrival time are not delivered to the data reader mit mit mit = minimum inter-arrival time produced sample delivered sample discarded sample
- 57. Setting QoS Policies Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Setting Partition QoS-Policy on Publisher C++ qos::PublisherQos pubQos; pubQos << policy::Partition("Partition"); Publisher pub(dp, pubQoS); OpenSplice DDS // Setting various QoS-Policy on a Topic qos::TopicQos tqos; tqos << policy::Reliability::Reliable() << policy::Durability::Transient() << policy::History::KeepLast(5); Topic<VehicleDynamics> topic(dp,"Partition", tqos);
- 59. Read Styles Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. The new API supports two read styles ☐ User-Provided Buffers read OpenSplice DDS ☐ Loaned Buffers read
- 60. User-Provided Buffers Read Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ! // --- Forward Iterators: --- // !! template <typename SamplesFWIterator, typename InfoFWIterator> !! uint32_t !! read(SamplesFWIterator sfit, !! ! ! InfoFWIterator ifit, !! ! ! size_t max_samples); OpenSplice DDS !! // --- Back-Inserting Iterators: --- // !! template <typename SamplesBIIterator, typename InfoBIIterator> !! uint32_t !! read(SamplesBIIterator sbit, !! ! ! InfoBIIterator ibit);
- 61. Example Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. uint32_t max_size = 10; std::vector<ShapeType> data(max_size); std::vector<DDS::SampleInfo> info(max_size); uint32_t len = dr.read(data.begin(), info.begin(), max_size); OpenSplice DDS for (uint32_t i = 0; i < len; ++i) ! std::cout << data[i] << std::endl;
- 62. Loaned Buffers read template <typename T, template <typename Q> class DELEGATE> class dds::sub::LoanedSamples : Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. public dds::core::Value< DELEGATE<T> > { public: typedef T DataType; typedef Sample<DataType> SampleType; dds::sub::LoanedSamples<T> read(); public: OpenSplice DDS /* Snipped... */ }; public: const Iterator begin() const; const Iterator end() const; public: // explicitly return loan void return_loan(); };
- 63. Cherry Picking in DDS Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ DDS provides some very flexible mechanisms for selecting the data to be read: OpenSplice DDS ☐ Data Content ☐ Data Status ☐ These mechanisms are composable
- 65. Filters and Queries Application ☐ DDS Filters allow to control what gets into a DataReader cache Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Query ☐ DDS Queries allow to control what gets out of a DataReader cache DataReader OpenSplice DDS ☐ Filters are defined by means of ... ContentFilteredTopics ... ... ... ☐ Queries operate in conjunction with DataReader Cache read operations Filter ☐ Filters and Queries are expressed as SQL where clauses
- 66. struct ShapeType { Filters @Key string color; long x; long y; [Scala API] }; long shapesize; /** Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. * NOTE: The Scala API if not provided with DP/Sub/Pub assumes * default domains and default partition. **/ // Create a Topic val topic = Topic[ShapeType](“Circle”) // Define filter expression and parameters OpenSplice DDS val query = Query(“x < %0 AND y < %1”, List(“200”, “300”)) // Define content filtered topic val cftopic = ContentFilteredTopic[ShapeType](“Circle”, topic, query) // Create a DataReader for the content-filtered Topic val reader = DataReader[ShapeType](cftopic)
- 67. struct ShapeType { QueryAPI 2010] @Key string color; long x; long y; [DDS C++ }; long shapesize; Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Define the query and the parameters std::vector<std::string> p; p.push_back("100"); p.push_back("100"); OpenSplice DDS dds::core::Query q("x < %0 AND y < %1", p.begin(), p.end()); auto data = reader .selector() .filter_content(q) .read();
- 68. Instances ☐ DDS provides a very efficient way of reading data belonging to a Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. specific Topic Instance ☐ Obviously, one could use queries to match the key’s value, but this is not as efficient as the special purpose instance selector OpenSplice DDS // C++ auto data = reader .selector() .instance(handle) .read(); // Scala val data = reader read(handle)
- 70. Sample, Instance, and View State ☐ The samples included in the DataReader cache have associated Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. some meta-information which, among other things, describes the status of the sample and its associated stream/instance ☐ The Sample State (READ, NOT_READ) allows to distinguish between OpenSplice DDS new samples and samples that have already been read ☐ The View State (NEW, NOT_NEW) allows to distinguish a new instance from an existing one ☐ The Intance State (ALIVE, NOT_ALIVE_DISPOSED, NOT_ALIVE_NO_WRITERS) allows to track the life-cycle transitions of the instance to which a sample belongs
- 71. State Selector in Action Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Read only new samples auto data = reader C++ Scala .selector() // Read only new samples .filter_state(status::DataState::new_data()) val data = reader read .read() // Read any samples from live instances OpenSplice DDS // Read any samples from live instances val data = reader read(SampleSelector.AnyData) auto data = reader .selector() .filter_state(status::DataState::any_data()) .read()
- 72. Putting all Together Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Selectors can be composed in a flexible and expressive manner OpenSplice DDS auto data = reader C++ ! .selector() .instance(handle) ! ! .filter_state(status::DataState::new_data()) ! ! .filter_content(q) .read();
- 73. OpenSplice DDS Communication Statuses Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved.
- 74. OpenSplice DDS Liveliness Changed Status Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved.
- 77. Advanced Topics Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Depending on time and attendees interest, I’ll be covering a set of advanced topics such as: OpenSplice DDS ☐ Distributed State and Events ☐ Advanced Distributed Algorithms with DDS, such as Leader Election, Mutual Exclusion, etc.
- 78. Distributed Events vs. OpenSplice DDS Distributed State
- 79. OpenSplice DDS Foundations
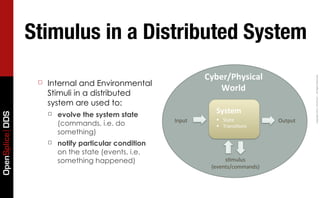
- 80. Defining a System Cyber/Physical. Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. World. ☐ A set of interacting or System. OpenSplice DDS interdependent parts Input& ! State& Output& forming an integrated ! Transi"ons& whole s"mulus& (events/commands)&&
- 81. Defining a Distributed System Cyber/Physical. Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. World. Distributed. ☐ A Distributed System is a System. System whose parts can Input& ! State& Output& OpenSplice DDS ! Transi"ons& only interact by communicating over a network s"mulus& (events/commands)&&
- 82. State in a Distributed System ☐ The State of a distributed system Cyber/Physical. Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. is the collection of the states of its parts plus the stimulus currently World. propagating through the system System. OpenSplice DDS ☐ As Distributed Systems don’t Input& ! State& Output& share memory, one problem to ! Transi"ons& address is how to access arbitrary subsets of its state (or of its parts) ☐ The other problem is the s"mulus& consistency of this state... (events/commands)&&
- 83. Stimulus in a Distributed System Cyber/Physical. Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Internal and Environmental World. Stimuli in a distributed system are used to: evolve the system state System. OpenSplice DDS ☐ Input& ! State& Output& (commands, i.e. do ! Transi"ons& something) ☐ notify particular condition on the state (events, i.e. something happened) s"mulus& (events/commands)&&
- 84. State vs Stimulus Temp State% Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The state of a system is always defined to have a value time OpenSplice DDS ☐ A Stimulus only exists at a OverheatAlarm S&mulus% particular point in time time
- 85. State and Events in DDS OpenSplice DDS
- 86. OpenSplice DDS State in DDS
- 87. Distributed State with DDS Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The “public” state of the elements making the distributed system can easily be captured via topic definitions ☐ Representing state with topics is more a matter of discipline w.r.t. to OpenSplice DDS the QoS being used and the way in which it is accessed
- 88. State’s DDS QoS Topics representing state should have the following QoS Settings Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ RELIABILITY = RELIABLE ☐ HISTORY = KEEP_LAST(1) OpenSplice DDS ☐ DURABILITY = (TRANSIENT |PERSISTENT) ☐ OWNERSHIP = EXCLUSIVE ☐ DESTINATION_ORDER = SOURCE_TIMESTAMP
- 89. Soft-State’s DDS QoS Topics representing soft-state, meaning state that is periodically Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. updated, should have the following QoS Settings ☐ RELIABILITY = BEST_EFFORT OpenSplice DDS ☐ HISTORY = KEEP_LAST(1) ☐ DURABILITY = VOLATILE ☐ OWNERSHIP = EXCLUSIVE ☐ DESTINATION_ORDER = SOURCE_TIMESTAMP
- 90. Accessing State in DDS ☐ The DataReader.read operation should be used to access topics Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. representing state ☐ This ensures that the last value for the state will be kept in DDS and will be readable again and again OpenSplice DDS ☐ The DataReader data should be accessed with the following flags: ☐ ANY_SAMPLE_STATE ☐ ALIVE_INSTANCE_STATE ☐ ANY_VIEW_STATE
- 91. Example [1/3] A Robot Position in 2D is an example of state Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ ☐ Let’s assume that the Robot only update position when it moves ☐ Topic Type: OpenSplice DDS struct RobotPosition { @key long rid; long x; long y; };
- 92. Example [2/3] ☐ The Topic and DataReader would be constructed as follows Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Create Topic Qos val tQos = OpenSplice DDS TopicQos() <= KeepLastHistory(1) <= Reliable() <= TransientDurability() <= ExclusiveOwnership() <= SourceTimestamp(); // Create Topic val rpt = Topic[RobotPosition](“RobotPosition”,topicQos) // Create DataReader val rpdr = DataReader[RobotPosition](rpt, DataReaderQos(tqos))
- 93. Example [3/3] ☐ Data can be read as follows Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Read data val data = rpdr.read(ReadState.AllData) OpenSplice DDS // Or specific to Escalier val data = rpdr.history
- 94. OpenSplice DDS Events in DDS
- 95. Distributed Events with DDS ☐ Events raised by a distributed system can be easily captured via Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. topic definitions ☐ Representing events with topics is more a matter of discipline w.r.t. to the QoS being used and the way in which it is accessed OpenSplice DDS ☐ Event topics are often keyless
- 96. Events’ DDS QoS Events should have the following QoS Settings Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ RELIABILITY = RELIABLE ☐ HISTORY = KEEP_ALL OpenSplice DDS ☐ DURABILITY = VOLATILE ☐ OWNERSHIP = SHARED ☐ DESTINATION_ORDER = SOURCE_TIMESTAMP
- 97. Events’ DDS QoS Events should have the following QoS Settings Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ RELIABILITY = RELIABLE ☐ HISTORY = KEEP_ALL OpenSplice DDS ☐ DURABILITY = VOLATILE ☐ OWNERSHIP = SHARED ☐ DESTINATION_ORDER = SOURCE_TIMESTAMP
- 98. Accessing Events in DDS Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The DataReader.take operation should be used to access topics representing events ☐ This ensures that the DDS cache is always freed by available events OpenSplice DDS ☐ The DataReader data should be accessed with the following flags: ☐ NEW_SAMPLE_STATE ☐ ALIVE_INSTANCE_STATE ☐ ANY_VIEW_STATE
- 99. Example [1/3] Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ A CollisionEvent could be raised by a Robot when it is colliding (or about to collide) with something ☐ Topic Type: OpenSplice DDS struct CollisionEvent { long detectingRobotId; long collidingRobotId; long xe; long ye; };
- 100. Example [2/3] ☐ The Topic and DataReader would be constructed as follows Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Create Topic Qos val tQos = TopicQos() <= KeepAll() OpenSplice DDS <= Reliable() <= VolatileDurability() <= SharedOwnership() <= SourceTimestamp(); // Create Topic val cet = Topic[CollisionEvent](“CollisionEvent”,topicQos) // Create DataReader val cedr = DataReader[CollisionEvent](cet, DataReaderQos(tqos))
- 101. OpenSplice DDS ☐ Example // Take data [3/3] val data = cedr.take() Data can be read as follows Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved.
- 103. Lamport’s Distributed Mutex ☐ A relatively simple Distributed Mutex Algorithm was proposed by Leslie Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Lamport as an example application of Lamport’s Logical Clocks ☐ The basic protocol (with Agrawala optimization) works as follows (sketched): OpenSplice DDS ☐ When a process needs to enter a critical section sends a MUTEX request by tagging it with its current logical clock ☐ The process obtains the Mutex only when he has received ACKs from all the other process in the group ☐ When process receives a Mutex requests he sends an ACK only if he has not an outstanding Mutex request timestamped with a smaller logical clock
- 104. Mutex Abstraction ☐ A base class defines the Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. Mutex Protocol abstract class Mutex { def acquire() ☐ The Mutex companion def release() uses dependency injection } OpenSplice DDS to decide which concrete mutex implementation to use
- 105. Foundation Abstractions Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The mutual exclusion algorithm requires essentially: ☐ FIFO communication channels between group members ☐ Logical Clocks OpenSplice DDS ☐ MutexRequest and MutexAck Messages These needs, have now to be translated in terms of topic types, topics, readers/writers and QoS Settings
- 106. Topic Types Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ For implementing the Mutual Exclusion Algorithm it is sufficient to define the following topic types: OpenSplice DDS struct TLogicalClock { long ts; long mid; }; #pragma keylist LogicalClock mid struct TAck { long amid; // acknowledged member-id LogicalClock ts; }; #pragma keylist TAck ts.mid
- 107. Topics We need essentially two topics: Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ One topic for representing the Mutex Requests, and ☐ Another topic for representing Acks OpenSplice DDS This leads us to: ☐ Topic(name = MutexRequest, type = TLogicalClock, QoS = {Reliability.Reliable, History.KeepAll}) ☐ Topic(name = MutexAck, type = TAck, QoS = {Reliability.Reliable, History.KeepAll})
- 108. Distinguishing Groups ☐ To distinguish between members belonging to different groups we Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. introduce a group-id gid that is used to uniquely identify a group ☐ At a DDS-level, the gid is used to name the partition in which all the group related traffic will take place OpenSplice DDS Partition associated to the group with gid=2 “2” “1” “3” DDS Domain
- 109. Show me the Code! Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ All the algorithms presented were implemented using DDS and Scala OpenSplice DDS ☐ Specifically we’ve used the OpenSplice Escalier language mapping for Scala ☐ The resulting library has been baptized “dada” (DDS Advanced Distributed Algorithms) and is available under LGPL-v3
- 110. LCMutex ☐ The LCMutex is one of the possible Mutex protocol, implementing the Agrawala variation of the classical Lamport’s Algorithm Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. class LCMutex(val mid: Int, val gid: Int, val n: Int)(implicit val logger: Logger) extends Mutex { private var group = Group(gid) private var ts = LogicalClock(0, mid) OpenSplice DDS private var receivedAcks = new AtomicLong(0) private var pendingRequests = new SynchronizedPriorityQueue[LogicalClock]() private var myRequest = LogicalClock.Infinite private val reqDW = DataWriter[TLogicalClock](LCMutex.groupPublisher(gid), LCMutex.mutexRequestTopic, LCMutex.dwQos) private val reqDR = DataReader[TLogicalClock](LCMutex.groupSubscriber(gid), LCMutex.mutexRequestTopic, LCMutex.drQos) private val ackDW = DataWriter[TAck](LCMutex.groupPublisher(gid), LCMutex.mutexAckTopic, LCMutex.dwQos) private val ackDR = DataReader[TAck](LCMutex.groupSubscriber(gid), LCMutex.mutexAckTopic, LCMutex.drQos) private val ackSemaphore = new Semaphore(0)
- 111. LCMutex.acquire Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. def acquire() { ts = ts.inc() myRequest = ts Notice that as the LCMutex reqDW ! myRequest is single-threaded we can’t ackSemaphore.acquire() issue concurrent acquire. OpenSplice DDS }
- 112. LCMutex.release Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. def release() { myRequest = LogicalClock.Infinite Notice that as the LCMutex (pendingRequests dequeueAll) foreach { req => is single-threaded we can’t ts = ts inc() issue a new request before ackDW ! new TAck(req.id, ts) } we release. OpenSplice DDS
- 113. LCMutex.onACK ackDR.reactions += { case DataAvailable(dr) => { Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. // Count only the ACK for us val acks = ((ackDR take) filter (_.amid == mid)) val k = acks.length // Set the local clock to the max (tsi, tsj) + 1 synchronized { val maxTs = math.max(ts.ts, (acks map (_.ts.ts)).max) + 1 ts = LogicalClock(maxTs, ts.id) OpenSplice DDS } val ra = receivedAcks.addAndGet(k) val groupSize = group.size // If received sufficient many ACKs we can enter our Mutex! if (ra == groupSize - 1) { receivedAcks.set(0) ackSemaphore.release() } } }
- 114. LCMutex.onReq reqDR.reactions += { case DataAvailable(dr) => { val requests = (reqDR take) filter (_.mid != mid) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. synchronized { val maxTs = math.max((requests map (_.ts)).max, ts.ts) + 1 ts = LogicalClock(maxTs, ts.id) } requests foreach (r => { if (r < myRequest) { ts = ts inc() OpenSplice DDS val ack = new TAck(r.mid, ts) ackDW ! ack } else { (pendingRequests find (_ == r)).getOrElse( { pendingRequests.enqueue(r) r }) } }) } }
- 115. Dealing with Faults... OpenSplice DDS
- 116. How to deal with Faults? ☐ The algorithm presented here intentionally ignores failures to keep the presentation simple Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The failure of a single group member would violate progress ☐ It is not hard to extend the algorithm to deal with failures, OpenSplice DDS especially under the assumption of eventual synchrony ☐ If you want to learn more attend the following RTWS-2012 presentation this Thursday: Classical Distributed Algorithms with DDS Sara Tucci-Piergiovanni, Research Engineer, CEA LIST Angelo Corsaro, Chief Technology Officer, PrismTech
- 118. Concluding Remarks ☐ The DDS provides a powerful and feature- rich topic-based publish/subscribe Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. abstraction ☐ This technology is widely used in mission and business critical systems and it being OpenSplice DDS swiftly adopted in data-centric/big-data systems ☐ Differently from what some people think, DDS is very simple to get-started with ☐ Very good Open Source implementation are available... Good Hacking!
- 119. References ¥ DDS-based Advanced Distributed Algorithms Toolkit ¥ Open Source ¥ github.com/kydos/dada Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. OpenSplice | DDS Escalier ¥ #1 OMG DDS Implementation ¥ Fastest growing JVM Language ¥ Scala API for OpenSplice DDS ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ www.opensplice.org ¥ www.scala-lang.org ¥ github.com/kydos/escalier OpenSplice DDS [C++] [Java] DDS-PSM-Cxx 2010 ¥ Simple C++ API for DDS ¥ DDS-PSM-Java for OpenSplice DDS ¥ DDS-PSM-Cxx API Standard ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ code.google.com/p/simd-cxx ¥ github.com/kydos/simd-java ¥ github.com/kydos/dds-psm-cxx
- 120. :: Connect with Us :: ¥opensplice.com ¥forums.opensplice.org ¥@acorsaro ¥opensplice.org ¥[email protected] ¥@prismtech OpenSplice DDS ¥ [email protected] ¥[email protected] ¥youtube.com/opensplicetube ¥slideshare.net/angelo.corsaro
- 121. OpenSplice DDS
- 122. OpenSplice DDS Appendix
- 123. Stepping into Scala OpenSplice DDS Angelo CORSARO, Ph.D. Chief Technology Officer OMG DDS Sig Co-Chair PrismTech [email protected]
- 124. What is Scala Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Scala (pronounced Skah-lah) stands for “Scalable language” ☐ It is a language that carefully and creatively blends Object Oriented and Functional constructs into a statically typed OpenSplice DDS language with sophisticated type inference ☐ Scala targets the JVM and .NET runtime and is 100% compatible with Java
- 125. Why Should You Care? Scala is simple to write, extremely compact and easy to Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ understand ☐ Scala is strongly typed with a structural type system OpenSplice DDS ☐ Scala is an extensible language (many construct are build in the standard library) ☐ Scala makes it easy to design Domain Specific Language
- 126. Case Study: Complex Numbers OpenSplice DDS
- 127. Complex Numbers Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ To explore some of the nice features of Scala, let’s see how we might design a Complex number class ☐ What we expect to be able to do is all mathematical operations OpenSplice DDS between complex numbers as well as scalar multiplications and division ☐ [(1+i2)+2*(3-i5)*(i4)]/(1+i3) ☐ ~(1+i2) [conjugate] ☐ !(3+i4) [Modulo]
- 128. Constructor ☐ Scala allows to implicitly create constructors and attributes starting from Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. a simple argument list associated with the class declaration OpenSplice DDS class Complex(val re: Float, val im: Float)
- 129. In Java public class Complex { Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ! private final float re; ! private final float im; ! public Complex(float re, float im) { ! ! this.re = re; OpenSplice DDS ! ! this.im = im; ! } ! public Complex(float f) { ! ! this.re = f; ! ! this.im = 0; ! } ! public float re() { return re;} ! public float im() { return im;}
- 130. Methods ☐ Everything in Scala is a method even operators Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Methods name can be symbols such as *, !, +, etc. OpenSplice DDS def + (c: Complex) : Complex = Complex(re + c.re, im + c.im) or, taking advantage of type inference.... def + (c: Complex) = Complex(re + c.re, im + c.im)
- 131. In Java... Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. public Complex add(Complex that) { return new Complex(this.re() + that.re(), OpenSplice DDS this.im() + that.im()); }
- 132. As a result... val result = Complex(1,2) + Complex(2,3) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. OpenSplice DDS Complex c1 = new Complex(1, 2); Complex c2 = new Complex (3,4); Complex c3 = c1.add(c2); or... Complex c3 = (new Complex(1, 2).add(new Complex (3,4));
- 133. Companion Object ☐ Scala does not have the concept of static methods/attributes ☐ On the other hand it provides built-in support for Singletons, Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. which are specified with the “object” keyword as opposed to the “class” keyword OpenSplice DDS object Complex { The companion object, is def apply(real: Float, img: Float) = new Complex(real, img) the object associated with def apply(real: Float) = new Complex(real, 0) a class, which shares the same name and provides implicit def floatToReComplex (f: Float) = new ReComplex(f) typically helper methods implicit def intToReComplex(i : Int) = new ReComplex(i) }
- 134. “apply” Magic ☐ When an instance of a class is followed by parentheses with a list of zero Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. or more parameters, the compiler invokes the apply method for that instance ☐ This is true for an object with a defined apply method (such as a companion object), as well as an instance of a class that defines an OpenSplice DDS apply method val result = Complex(1,2) is the same as.... val result = Complex.apply(1,2)
- 135. Negation and Scalar Multiplication Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ In order to design a Complex class that is well integrated in our type system we should be able to support the following cases: ☐ -(a+ib) ☐ c*(a+ib) OpenSplice DDS ☐ (a+ib)*c ☐ How can we supporting something like -(a+ib) and c*(a+ib)?
- 136. Scala Unary Operators ☐ Scala allows to define unary operators for the following method Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. identifiers +, -, !, ~ def unary_-() = Complex(-re, -im) OpenSplice DDS ! def unary_!() = Math.sqrt(re*re + im*im) ! def unary_~() = Complex(re, -im) as a result we can write: val result = -Complex(1,2) + ~Complex(2,3)
- 137. Scala Implicit Conversions Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The expression: val c3 = 3*Complex(5, 7) ☐ Is equivalent to: OpenSplice DDS val c3 = 3.*(Complex(5, 7)) ☐ Yet, the method to multiply a Integer to a Complex is not present in the Scala Int class ☐ What can we do to make the trick?
- 138. Scala Implicit Conversions Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Scala does not support Open Classes, thus allowing to add new methods to existing classes ☐ Yet Scala supports implicit conversions that can be used to achieve the same result OpenSplice DDS ☐ Lets see how...
- 139. Scala Implicit Conversion object Complex { Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. implicit def floatToReComplex (f: Float) = new ReComplex(f) implicit def intToReComplex(i : Int) = new ReComplex(i) } OpenSplice DDS class ReComplex(re: Float) { def * (that: Complex) = Complex(re*that.re,re*that.im) }
- 140. The Result is... val c3 = 3*Complex(5, 7) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. is converted automatically into: val c3 = ReComplex(3).*(Complex(5, 7)) OpenSplice DDS
- 141. Putting it all together case class Complex(val re: Float, val im: Float) { // Unary Operators Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. def unary_-() = Complex(-re, -im) // Binary Operators def unary_!() = Math.sqrt(re*re + im*im) def + (c: Complex) = Complex(re + c.re, im + c.im) def unary_~() = Complex(re, -im) def - (c: Complex) = Complex(re - c.re, im - c.im) // Formatting def * (f: Float) = Complex(f*re, f*im) override def toString() : String = { OpenSplice DDS def * (c: Complex) = Complex((re*c.re) - (im*c.im), if (im > 0) re + "+i" + im ((re*c.im) + (im*c.re))) else if (im < 0) re + "-i" + (-im) else re.toString def / (c: Complex) = { val d = c.re*c.re + c.im*c.im } Complex(((re*c.re) + (im + c.im))/d, } ((im*c.re) - (re*c.im))/d ) }
- 142. Functions, Closures and Currying OpenSplice DDS
- 143. Functions Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Scala has first-class functions ☐ Functions can be defined and called, but equally functions can be defined as unnamed literals and passed as values OpenSplice DDS def inc(x: Int) = x + 1 val vinc = (x: Int) => x+1 inc(5) vinc(5) Notice once again the uniform access principle
- 144. Playing with Functions val list = List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. val g5 = list.filter((x: Int) => x > 5) g5: List[Int] = List(6, 7, 8, 9) OpenSplice DDS Or with placeholder syntax val list = List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) val g5 = list.filter(_ > 5) g5: List[Int] = List(6, 7, 8, 9)
- 145. Closures Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Scala allows you to define functions which include free variables meaning variables whose value is not bound to the parameter list ☐ Free variable are resolved at runtime considering the closure of visible variable OpenSplice DDS ☐ Example: def mean(e : Array[Float]) : Float = { def mean(e : Array[Float]) : Float = { var sum = 0.0F var sum = 0.0F e.foreach((x: Int) => sum += x) e.foreach(sum += _) return sum/e.length return sum/e.length } }
- 146. Currying ☐ Scala provides support for curried functions which are applied to Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. multiple argument lists, instead of just one ☐ Currying is the mechanism Scala provides for introducing new control abstraction OpenSplice DDS def curriedSum(x: Int)(y: Int) = x + y curriedSum(1) { 3 +5 }
- 147. OpenSplice DDS Traits
- 148. Traits ☐ Scala supports single inheritance from classes but can mix-in multiple Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. traits ☐ A trait is the unit of code reuse for Scala. It encapsulate methods and field definitions Traits usually expect a class to implement an abstract method, which OpenSplice DDS ☐ constitutes the “narrow” interface that allows to implement a rich behaviour ☐ Traits are also very useful for dependency injection
- 149. Ordered Complex Numbers Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Our complex numbers are not comparable ☐ Let’s assume that we wanted to make them comparable, and lets supposed that we define the total order as based on the module of the complex number OpenSplice DDS ☐ How can we implement this behavior?
- 150. Ordered Trait Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ The Ordered[T] traits encapsulates the set of methods that allow to define a total ordering over a type ☐ All the behaviour is defined in terms of an abstract method, namely “compare” OpenSplice DDS ☐ Classes that mix-in this trait have to implement the “compare” method class Complex(val re: Float, val im: Float) extends Ordering[Complex] { def compare(x: Complex, y: Complex) = { if (x == y) 0 else if (!x > !y) 1 else -1 }
- 151. Case Classes & OpenSplice DDS Pattern Matching
- 152. Case Classes and Pattern Matching ☐ Case Classes and Pattern Matching are twin constructs that are pretty Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. useful when dealing with tree-like recursive data structures ☐ These constructs allow to match patterns in an expression and reconstruct the object graph that makes it up OpenSplice DDS ☐ Lets see an example...
- 153. Case Classes and Pattern abstract class Expr case class Var(name: String) extends Expr Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. case class Number(num: Float) extends Expr case class UnOp(operator: String, arg: Expr) extends Expr case class BinOp(operator: String, left: Expr, right: Expr) OpenSplice DDS def simplifyExpr(expr: Expr) : Expr = expr match { case UnOp("-", UnOp("-", e)) => e case BinOp("+", e, Number("0")) => e case BinOp("*", e, Number("1")) => e case _ => expr }
- 155. Type Parametrization Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ Scala provides support for type parametrization and makes it available for both classes as well as traits trait Queue[T] { def head: T OpenSplice DDS def tail: Queue[T] def append(x: T) : Queue[T] } ☐ Scala allows to annotate the parametrized type to control the resulting type variance
- 156. Type Variance ☐ If S <: T is Queue[S] <: Queue[T]? Copyright 2011, PrismTech – All Rights Reserved. ☐ By default Scala makes generic types nonvariant. This behaviour can be changed using the following annotations: ☐ Queue[+T] indicates that the the sub-typing is covariant in the parameter T OpenSplice DDS ☐ Queue[-T] indicates that the the sub-typing is contravariant in the parameter T

![Getting Started with DDS
[In C++, Java and Scala]
OpenSplice DDS
Angelo CORSARO, Ph.D.
Chief Technology Officer
OMG DDS Sig Co-Chair
PrismTech
angelo.corsaro@prismtech.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-1-320.jpg)















![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[Scala API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId)
Participant
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
DataWriter
DataReader](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-18-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[Scala API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId)
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
val pub = Publisher(dp)
val sub = Subscriber(dp)
DataWriter
DataReader](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-19-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[Scala API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId)
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
val pub = Publisher(dp)
val sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Create a DataWriter/DataWriter
val writer = DataWriter[ShapeType](pub, topic) Reader/Writer for
val reader = DataReader[ShapeType](sub, topic) application defined
Topic Types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-20-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[Scala API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
val dp = DomainParticipant(domainId)
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
val topic = Topic[ShapeType](dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
val pub = Publisher(dp)
val sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Write data
val data = new ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 75)
writer write data
Reader/Writer for
// But you can also write like this... application defined
writer ! data Topic Types
// Read new data and print it on the screen
(reader read) foreach (prinln)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-21-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[DDS C++ API 2010]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId);
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
auto topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
auto pub = Publisher(dp)
auto sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Create a DataWriter/DataWriter
auto writer = DataWriter<ShapeType>(pub, topic); Reader/Writer for
auto reader = DataReader<ShapeType>(sub, topic);
application defined
Topic Types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-22-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[DDS C++ API 2010]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId);
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
auto topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
auto pub = Publisher(dp)
auto sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Write data
writer.write(ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89)); Reader/Writer for
// But you can also write like this...
writer << ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89);
application defined
Topic Types
// Read new data (loaned)
auto data = reader.read();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-23-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[DDS Java 5 API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
auto dp = DomainParticipant(domainId);
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
val topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
val pub = Publisher(dp)
val sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Create a DataWriter/DataWriter
auto writer = DataWriter<ShapeType>(pub, topic); Reader/Writer for
auto reader = DataReader<ShapeType>(sub, topic);
application defined
Topic Types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-24-320.jpg)
![Anatomy of a DDS Application
[DDS Java 5 API]
Domain
Domain
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
Do dp = DomainParticipant(domainId);
Participant
Session
// Create a Topic
Publisher
Topic
Subscriber
OpenSplice DDS
val topic = Topic<ShapeType>(dp, “Circle”)
// Create a Publisher / Subscriber
val pub = Publisher(dp)
val sub = Subscriber(dp)
Reader/Writers for User Defined for Types DataWriter
DataReader
// Write data
writer.write(ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89)); Reader/Writer for
// But you can also write like this...
writer << ShapeType(“RED”, 131, 107, 89);
application defined
Topic Types
// Read new data (loaned)
auto data = reader.read();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-25-320.jpg)
















![QoS Policies
[T: Topic] [DR: DataReader] [DW: DataWriter] [P: Publisher] [S: Subscriber] [DP: Domain Participant]
QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
USER_DATA DP, DR, DW N Y
TOPIC_DATA T N Y Configuration
GROUP_DATA P, S N Y
DURABILITY T, DR, DW Y N
OpenSplice DDS
DURABILITY T, DW N N
SERVICE Data Availability
HISTORY T, DR, DW N N
PRESENTATION P, S Y N
RELIABILITY T, DR, DW Y N
PARTITION P, S N Y
Data Delivery
DESTINATION T, DR, DW Y N
ORDER
LIFESPAN T, DW N Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-43-320.jpg)
![QoS Policies
[T: Topic] [DR: DataReader] [DW: DataWriter] [P: Publisher] [S: Subscriber] [DP: Domain Participant]
QoS Policy Applicability RxO Modifiable
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
DEADLINE T, DR, DW Y Y
LATENCY T, DR, DW Y Y
BUDGET Temporal/
TRANSPORT T, DW N Y Importance
PRIORITY Characteristics
OpenSplice DDS
TIME BASED DR N Y
FILTER
OWNERSHIP T, DR, DW Y N
OWNERSHIP DW N Y Replication
STRENGTH
LIVELINESS T, DR, DW Y N Fault-Detection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-44-320.jpg)







![Temporal Properties
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
TimeBasedFilter Deadline
[Inbound]
OpenSplice DDS
Throughput LatencyBudget Latency
[Outbound]
TransportPriority](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-52-320.jpg)







![Example
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
uint32_t max_size = 10;
std::vector<ShapeType> data(max_size);
std::vector<DDS::SampleInfo> info(max_size);
uint32_t len =
dr.read(data.begin(), info.begin(), max_size);
OpenSplice DDS
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < len; ++i)
! std::cout << data[i] << std::endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-61-320.jpg)




![struct ShapeType {
Filters
@Key
string color;
long x;
long y;
[Scala API] };
long shapesize;
/**
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
* NOTE: The Scala API if not provided with DP/Sub/Pub assumes
* default domains and default partition.
**/
// Create a Topic
val topic = Topic[ShapeType](“Circle”)
// Define filter expression and parameters
OpenSplice DDS
val query = Query(“x < %0 AND y < %1”, List(“200”, “300”))
// Define content filtered topic
val cftopic =
ContentFilteredTopic[ShapeType](“Circle”, topic, query)
// Create a DataReader for the content-filtered Topic
val reader =
DataReader[ShapeType](cftopic)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-66-320.jpg)
![struct ShapeType {
QueryAPI 2010]
@Key
string color;
long x;
long y;
[DDS C++ };
long shapesize;
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
// Define the query and the parameters
std::vector<std::string> p;
p.push_back("100");
p.push_back("100");
OpenSplice DDS
dds::core::Query q("x < %0 AND y < %1", p.begin(), p.end());
auto data = reader
.selector()
.filter_content(q)
.read();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-67-320.jpg)






















![Example [1/3]
A Robot Position in 2D is an example of state
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐
☐ Let’s assume that the Robot only update position when it moves
☐ Topic Type:
OpenSplice DDS
struct RobotPosition {
@key
long rid;
long x;
long y;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-91-320.jpg)
![Example [2/3]
☐ The Topic and DataReader would be constructed as follows
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
// Create Topic Qos
val tQos =
OpenSplice DDS
TopicQos() <= KeepLastHistory(1)
<= Reliable()
<= TransientDurability()
<= ExclusiveOwnership()
<= SourceTimestamp();
// Create Topic
val rpt = Topic[RobotPosition](“RobotPosition”,topicQos)
// Create DataReader
val rpdr = DataReader[RobotPosition](rpt, DataReaderQos(tqos))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-92-320.jpg)
![Example [3/3]
☐ Data can be read as follows
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
// Read data
val data = rpdr.read(ReadState.AllData)
OpenSplice DDS
// Or specific to Escalier
val data = rpdr.history](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-93-320.jpg)





![Example [1/3]
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ A CollisionEvent could be raised by a Robot when it is colliding (or
about to collide) with something
☐ Topic Type:
OpenSplice DDS
struct CollisionEvent {
long detectingRobotId;
long collidingRobotId;
long xe;
long ye;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-99-320.jpg)
![Example [2/3]
☐ The Topic and DataReader would be constructed as follows
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
// Create Topic Qos
val tQos =
TopicQos() <= KeepAll()
OpenSplice DDS
<= Reliable()
<= VolatileDurability()
<= SharedOwnership()
<= SourceTimestamp();
// Create Topic
val cet = Topic[CollisionEvent](“CollisionEvent”,topicQos)
// Create DataReader
val cedr = DataReader[CollisionEvent](cet, DataReaderQos(tqos))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-100-320.jpg)
![OpenSplice DDS
☐
Example
// Take data
[3/3]
val data = cedr.take()
Data can be read as follows
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-101-320.jpg)








![LCMutex
☐ The LCMutex is one of the possible Mutex protocol, implementing
the Agrawala variation of the classical Lamport’s Algorithm
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
class LCMutex(val mid: Int, val gid: Int, val n: Int)(implicit val logger: Logger) extends Mutex {
private var group = Group(gid)
private var ts = LogicalClock(0, mid)
OpenSplice DDS
private var receivedAcks = new AtomicLong(0)
private var pendingRequests = new SynchronizedPriorityQueue[LogicalClock]()
private var myRequest = LogicalClock.Infinite
private val reqDW =
DataWriter[TLogicalClock](LCMutex.groupPublisher(gid), LCMutex.mutexRequestTopic, LCMutex.dwQos)
private val reqDR =
DataReader[TLogicalClock](LCMutex.groupSubscriber(gid), LCMutex.mutexRequestTopic, LCMutex.drQos)
private val ackDW =
DataWriter[TAck](LCMutex.groupPublisher(gid), LCMutex.mutexAckTopic, LCMutex.dwQos)
private val ackDR =
DataReader[TAck](LCMutex.groupSubscriber(gid), LCMutex.mutexAckTopic, LCMutex.drQos)
private val ackSemaphore = new Semaphore(0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-110-320.jpg)








![References ¥ DDS-based Advanced Distributed
Algorithms Toolkit
¥ Open Source
¥ github.com/kydos/dada
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
OpenSplice | DDS Escalier
¥ #1 OMG DDS Implementation ¥ Fastest growing JVM Language ¥ Scala API for OpenSplice DDS
¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source
¥ www.opensplice.org ¥ www.scala-lang.org ¥ github.com/kydos/escalier
OpenSplice DDS
[C++] [Java] DDS-PSM-Cxx 2010
¥ Simple C++ API for DDS ¥ DDS-PSM-Java for OpenSplice DDS ¥ DDS-PSM-Cxx API Standard
¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source ¥ Open Source
¥ code.google.com/p/simd-cxx ¥ github.com/kydos/simd-java ¥ github.com/kydos/dds-psm-cxx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-119-320.jpg)







![Complex Numbers
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ To explore some of the nice features of Scala, let’s see how we
might design a Complex number class
☐ What we expect to be able to do is all mathematical operations
OpenSplice DDS
between complex numbers as well as scalar multiplications and
division
☐ [(1+i2)+2*(3-i5)*(i4)]/(1+i3)
☐ ~(1+i2) [conjugate]
☐ !(3+i4) [Modulo]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-127-320.jpg)
















![Playing with Functions
val list = List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
val g5 = list.filter((x: Int) => x > 5)
g5: List[Int] = List(6, 7, 8, 9)
OpenSplice DDS
Or with placeholder syntax
val list = List(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
val g5 = list.filter(_ > 5)
g5: List[Int] = List(6, 7, 8, 9)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-144-320.jpg)
![Closures
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ Scala allows you to define functions which include free variables
meaning variables whose value is not bound to the parameter list
☐ Free variable are resolved at runtime considering the closure of visible
variable
OpenSplice DDS
☐ Example:
def mean(e : Array[Float]) : Float = { def mean(e : Array[Float]) : Float = {
var sum = 0.0F var sum = 0.0F
e.foreach((x: Int) => sum += x) e.foreach(sum += _)
return sum/e.length return sum/e.length
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-145-320.jpg)




![Ordered Trait
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ The Ordered[T] traits encapsulates the set of methods that allow to
define a total ordering over a type
☐ All the behaviour is defined in terms of an abstract method, namely
“compare”
OpenSplice DDS
☐ Classes that mix-in this trait have to implement the “compare” method
class Complex(val re: Float, val im: Float) extends
Ordering[Complex] {
def compare(x: Complex, y: Complex) = {
if (x == y) 0
else if (!x > !y) 1
else -1
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-150-320.jpg)




![Type Parametrization
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ Scala provides support for type parametrization and makes it
available for both classes as well as traits
trait Queue[T] {
def head: T
OpenSplice DDS
def tail: Queue[T]
def append(x: T) : Queue[T]
}
☐ Scala allows to annotate the parametrized type to control the
resulting type variance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-155-320.jpg)
![Type Variance
☐ If S <: T is Queue[S] <: Queue[T]?
Copyright
2011,
PrismTech
–
All
Rights
Reserved.
☐ By default Scala makes generic types nonvariant. This behaviour can be
changed using the following annotations:
☐ Queue[+T] indicates that the the sub-typing is covariant in the
parameter T
OpenSplice DDS
☐ Queue[-T] indicates that the the sub-typing is contravariant in the
parameter T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-16-dds-tutorial-v1-1-120417081311-phpapp01/85/Getting-Started-with-DDS-in-C-Java-and-Scala-156-320.jpg)