Learn Git Basics
- 1. Git www.paradigmcreatives.com @pcreatives
- 2. Before talking about Git lets talk about : What is Version Control?
- 3. About Version Control • Locally if one were to maintain a backup of the working directory, then what we do is maintain copies of our files in properly named folders to track the change. • Now a smarter way is to maintain a database locally to track these changes. • Git just does this for us. Maintains a database of all the local changes and takes it further to create a centralized server that will help in making the code available to others.
- 4. Operations in a VCS • Commit changes • Track file changes in working directory • Compare changes between versions • Ability to checkout any earlier version • Collaborate between many systems through a server accessible to all involved. These are few basic operations that all VCS are able to perform.
- 5. Why Git?
- 6. • Different from subversion and other existing VCS being used. • Very efficient and much more sophisticated. • Snapshots, not differences
- 7. Snapshots and differences • Differences: Most VCS store each file and keep a track of changes that happen in each file at each commit. That is, they keep a track of the differences made in each file and store information as a list of file based changes. • Snapshots: Git doesn’t think of or store its data this way. Instead, Git thinks of its data more like a set of snapshots of a mini filesystem. Every time you commit, or save the state of your project in Git, it basically takes a picture of what all your files look like at that moment and stores a reference to that snapshot. To be efficient, if files have not changed, Git doesn’t store the file again—just a link to the previous identical file it has already stored
- 8. • Nearly every operation is local • It generally adds data • The Three Stages
- 9. The three stages of local operations • Working directory: The working directory is a single checkout of one version of the project. These files are pulled out of the compressed database in the Git directory and placed on disk for you to use or modify. • Staging Area: The staging area is a simple file, generally contained in your Git directory, that stores information about what will go into your next commit. It’s sometimes referred to as the index, but it’s becoming standard to refer to it as the staging area. • Git Directory: The Git directory is where Git stores the metadata and object database for your project. This is the most important part of Git, and it is what is copied when you clone a repository from another computer.
- 10. The basic Git workflow goes something like this: 1. You modify files in your working directory. 2. You stage the files, adding snapshots of them to your staging area. 3. You do a commit, which takes the files as they are in the staging area and stores that snapshot permanently to your Git directory. • If a particular version of a file is in the git directory, it’s considered committed. • If it’s modified but has been added to the staging area, it is staged. • And if it was changed since it was checked out but has not been staged, it is modified.
- 11. First time Git setup • Your identity This is important because Git commit uses these information in all its operations. $ git config --global user.name "John Doe" $ git config --global user.email [email protected] --global is for default value that will be picked. If any specific value is required for any particular project then config can be set for that particular project. • Your diff tool and default editor (Optional) $ git config --global merge.tool vimdiff $ git config --global core.editor emacs
- 12. git init • Initializing git in an existing directory $ git init • Start tracking files in the directory $ git add *.c $ git add README $ git commit -m 'initial project version'
- 13. Recording Changes to Repository
- 14. File Status Lifecycle Each file in working directory can be in one of two states: • Tracked: files that were there in the last snapshot. They can be of 3 types: o Unmodified o Modified o Staged • Untracked: everything else. i.e any files that were not in the last snapshot and are not in the staging area. To track them we have to stage and commit them first. As you edit tracked files, Git sees them as modified, because you’ve changed them since your last commit. You stage these modified files and then commit all your staged changes, and the cycle repeats.
- 16. Checking status of files in Repo git status • No file modifications. $ git status # On branch master nothing to commit (working directory clean) • Status for untracked file $ vim README $ git status # On branch master # Untracked files: # (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) # # README nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
- 17. Tracking new files git add In order to track a new file README the following command will suffice: $ git add README To see that it has been tracked we can check the status now: $ git status # On branch master # Changes to be committed: # (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) # # new file: README #
- 18. Staging Modified Files git add • For a modified unstaged file git status will show something like : $ git status # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # # On branch master # modified: benchmarks.rb #
- 19. git add • After git add $ git add benchmarks.rb $ git status # Changes to be committed: # # (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) # # On branch master # # modified: benchmarks.rb #
- 20. • Modifying a staged file $ git status # Changes to be committed: # (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) # On branch master # # modified: benchmarks.rb # # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # # modified: benchmarks.rb #
- 21. • Now the staged files are snapshots taken during the earlier git add. To stage the new changes git add needs to be called again. $ git add benchmarks.rb $ git status # On branch master # Changes to be committed: # (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) # modified: benchmarks.rb # • Now finally all the modifications are staged! Not committed though. But before that lets see something more that git has to offer at this stage..
- 22. Ignoring files .gitignore The rules for the patterns you can put in the .gitignore file are as follows: • Blank lines or lines starting with # are ignored. • Standard glob patterns work. • You can end patterns with a forward slash (/) to specify a directory. • You can negate a pattern by starting it with an exclamation point (!). • This file can be added to the root directory and/or to any subfolder. • The particular sub folder's .gitignore's conditions will have precedence over the parent folder's .gitignore. • This file should be added to the git repository and it gets tracked like any other file.
- 23. An example of .gitignore instructions: # a comment - this is ignored *.a # no .a files !lib.a # but do track lib.a, even though you're ignoring .a files above /TODO # only ignore the root TODO file, not subdir/TODO build/ # ignore all files in the build/ directory doc/*.txt # ignore doc/notes.txt, but not doc/server/arch.txt
- 24. Viewing differences • To view all unstaged changes. $ git diff • To view all staged changes with respect to the previous commit $git diff --cached • To view all changes from last commit (staged + unstaged) $git diff HEAD • To compare difference between 2 different branch index(tips) $git diff master..test • To compare difference between 2 different branch index(tips) from their common ancestor $git diff master...test
- 25. Committing changes git commit • This commits all the staged changes to the local commit history. • It launches the default editor to help add the commit message since git never commits with an empty message • We can use a shorthand to provide inline commit message though o -m ex - $ git commit -m "adding inline commit message" • We can also skip the staging step and directly commit all changes o -a ex - $ git commit -a -m "inline commit message"
- 26. Removing files from being tracked git rm • To remove a file from being tracked and also deleting it git rm followed by file name can be used. o $ git rm <file name> • Another good way to not track a file but keep the copy of it in the directory is to use --cached shorthand. o $ git rm --cached <file name> • Simple deleting a file from directory will just be considered as a unstaged modification. git rm needs to be used to commit it.
- 27. Viewing the commit history git log • This will show all the commit logs done in the repository in reverse chronological order. • There are few shorthands that come in handy with git log like: o -p : Will show the diff introduced in the each commit. -p -<n> :will give only n line(s) of the diff in each commit log (the last n diff line(s) of each commit). o --stat : This shorthand will provide abbreviated stats for each commit
- 28. Undoing changes • Changing last commit Suppose one missed staging a particular change needed for the commit, but dont want to create one more commit for this. To tackle these situations we can use git commit --amend: $ git add <forgotten file> $ git commit --amend This will merge the new commit to the existing commit.
- 29. Undoing changes • Unstaging a staged file $ git reset HEAD <file name> This will unstage the file but keep the modifications we made in the file • Unmodifying a modified file $ git checkout -- <file name> This will revert the changes we did in the file to the last commit state.
- 30. Summarized flow of commands git init . add files . git add/rm <file> . modified files. hence have to stage again . git add/rm <file> git commit -m "commit message"
- 31. Recap • Starting a local repository o git init • Staging o git add/rm • Committing o git commit • Comparing o git diff • Undoing staging and committing o git reset/checkout
- 32. Git Branching
- 33. First lets see how git stores data
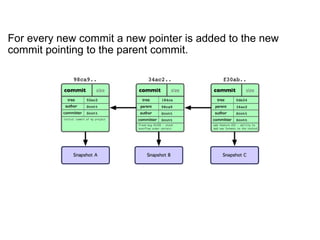
- 34. For every new commit a new pointer is added to the new commit pointing to the parent commit.
- 35. A branch in a git repository is a slightly moveable pointer pointer to one of the various commits in the network
- 36. Creating a new branch $ git branch testing This will create a new pointer pointing to the latest commit of the existing branch
- 37. Now git keeps tag on which branch we are currently working on by a special pointer called HEAD. It always points to the local branch we are presently working on
- 38. To switch between branches $ git checkout testing we can also merge these two steps of creating and switching by adding a shorthand $ git checkout -b <new branch name> This will create as well as switch directly to the new branch. Of course after that we have to use only checkout command for switching between already existent branches.
- 39. Now the network looks like this
- 40. Lets commit a change to this branch and see how the state of the network changes $ git commit -a -m "made some change"
- 41. Now if we decide to go back to master branch and make some changes there. $ git checkout master
- 42. Now lets make some changes ... $ git commit -a -m "made master changes"
- 43. Branch merging Lets say we have, at some point of time, a network similar to..
- 44. Merging the hotflix branch with master. • We have to first switch to the branch we want another branch to be merged to. $ git checkout master $ git merge hotflix
- 45. Deleting a branch Lets delete the hotflix branch. $ git branch -d hotflix The image here shows a later stage where we have made more changes to the iss53 branch after the delete of hotflix branch
- 46. Now it becomes a bit more complex to merge iss53 and master as they both have different parents. But git is smart in this case. It determines the best common ancestor for both the branches and uses it as its merge base. This is different that how other from other version control systems.
- 47. The final state
- 48. Basic merge conflicts • Auto merging after git merge stops when a conflict arises. • In such a case we have to manually resolve the conflict and stage the changes. • Without staging the conflict cannot be resolved and the merge cannot be completed. • An example how a file having a merge conflict looks like <<<<<<< HEAD:index.html <div id="footer">contact : [email protected]</div> ======= <div id="footer"> please contact us at [email protected] </div> >>>>>>> iss53:index.html Here HEAD means the current branch code segment and the rest after "=======" is the code in the branch that is being merged into current branch
- 49. Working with remote server
- 50. Remote • By remote we mean the server through which we collaborate • It has all the integrated union of the commit network of each and every system involved in the project • This brings us to GitHub
- 51. GitHub • It is a social code sharing network. • Share your code • Clone/download code from repository • Fork code from a readonly repository to own repository • Browse available public repositories • Control visibility of your repository • Offers nice interface to view code, branch network and commit history, and much more • Very well maintained
- 52. Showing remote servers git clone $ git clone <remote git server url/ SSH url> This will create a new local repository which is a clone of the server repository. Along with all its branches. By default it will add the server url as a remote name origin and all the branches in the server will be represented by origin/<branch name>. The origin/master local repo by default starts tracking the master branch of the server repo
- 53. Add remote repositories • To check existent remote repositories added to the our local repository: $ git remote We can also use the shorthand -v to show us the remote url too • If we want to add more remote repositories to our local repository: $ git remote add [short name] [url]
- 54. Fork a repository • This feature of GitHub allows us to make a mutable copy of a read only public repository into our own GitHub repository and work with it. • This feature also allows us to stay in sync with the original repository by simple git pull/ git fetch commands. • But for the above to happen we have to add the remote address of the original server using $ git remote add [short name] [url]
- 55. Fetching and Pulling from remote git fetch $ git fetch [remote name] This will fetch all the code from the remote keep a copy of it. It won't merge the files in the working directory but we have to manually merge it. But if we have a branch in server which is being tracked by our local working branch then its easier to call git pull which will fetch and automatically merge the files. $ git pull [remote name]
- 56. Pushing to remote git push This command pushes the latest committed files of the working branch of the local repository to the remote server. $ git push [remote server name] [branch name] This will push the code without error if the remote server's latest commit in this branch is a part of out commit history. Else it will ask us to pull the server code first and then we can push out code.
- 57. Inspecting a remote If we want to see information about a remote server we have reference to in the local repository, we can do so with the help of: $ git remote show [remote name] There are other methods like: • renaming remote $ git remote rename [existing remote name] [new remote name] • removing remote $ git remote rm [remote name]
- 58. Remote branches List of branches present in our clone $ git branch -a This will list all the branches present in the local repository along with all the branches that have been cloned from the server ([remote name]/[branch name]). Switching to a particular branch in the clone which our local repository doesn't have we need to create a new branch by merging the remote branch $ git checkout -b [local branch name] [[remote name]/[remote branch name]]
- 59. • Tracking Remote branches By default a cloned repository's master branch tracks the remote server's [remote name]/master branch. But we can change which branch to track and our local repo will start tracking this branch in the remote server. $ git checkout --track [remote name]/[branch name] • Pushing a particular branch to server $ git push [remote name] [local brach name]:[remote branch name] • Deleting remote branch $ git push [remote name] :[remote branch name]
- 60. Thank you • Prepared by Robin Srivastava , Soumya Behera – [email protected] – [email protected]




















































![Add remote repositories
• To check existent remote repositories added to the our local
repository:
$ git remote
We can also use the shorthand -v to show us the remote url too
• If we want to add more remote repositories to our local
repository:
$ git remote add [short name] [url]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-53-320.jpg)
![Fork a repository
• This feature of GitHub allows us to make a mutable copy of
a read only public repository into our own GitHub repository
and work with it.
• This feature also allows us to stay in sync with the original
repository by simple git pull/ git fetch commands.
• But for the above to happen we have to add the remote
address of the original server using
$ git remote add [short name] [url]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-54-320.jpg)
![Fetching and Pulling from remote
git fetch
$ git fetch [remote name]
This will fetch all the code from the remote keep a copy of it. It
won't merge the files in the working directory but we have to
manually merge it.
But if we have a branch in server which is being tracked by our
local working branch then its easier to call git pull which will
fetch and automatically merge the files.
$ git pull [remote name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-55-320.jpg)
![Pushing to remote
git push
This command pushes the latest committed files of the working
branch of the local repository to the remote server.
$ git push [remote server name] [branch name]
This will push the code without error if the remote server's
latest commit in this branch is a part of out commit history. Else
it will ask us to pull the server code first and then we can push
out code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-56-320.jpg)
![Inspecting a remote
If we want to see information about a remote server we have
reference to in the local repository, we can do so with the help
of:
$ git remote show [remote name]
There are other methods like:
• renaming remote
$ git remote rename [existing remote name] [new remote
name]
• removing remote
$ git remote rm [remote name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-57-320.jpg)
![Remote branches
List of branches present in our clone
$ git branch -a
This will list all the branches present in the local repository
along with all the branches that have been cloned from the
server ([remote name]/[branch name]).
Switching to a particular branch in the clone which our local
repository doesn't have we need to create a new branch by
merging the remote branch
$ git checkout -b [local branch name] [[remote name]/[remote
branch name]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-58-320.jpg)
![• Tracking Remote branches
By default a cloned repository's master branch tracks the
remote server's [remote name]/master branch.
But we can change which branch to track and our local repo will
start tracking this branch in the remote server.
$ git checkout --track [remote name]/[branch name]
• Pushing a particular branch to server
$ git push [remote name] [local brach name]:[remote branch
name]
• Deleting remote branch
$ git push [remote name] :[remote branch name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitpresentation-121106030824-phpapp02/85/Learn-Git-Basics-59-320.jpg)
