git2.ppt
- 1. Git A distributed version control system Powerpoint credited to University of PA And modified by Pepper 5-Apr-23
- 2. Version control systems Version control (or revision control, or source control) is all about managing multiple versions of documents, programs, web sites, etc. Almost all “real” projects use some kind of version control Essential for team projects, but also very useful for individual projects Some well-known version control systems are CVS, Subversion, Mercurial, and Git CVS and Subversion use a “central” repository; users “check out” files, work on them, and “check them in” Mercurial and Git treat all repositories as equal Distributed systems like Mercurial and Git are newer and are gradually replacing centralized systems like CVS and Subversion 2
- 3. Why version control? For working by yourself: Gives you a “time machine” for going back to earlier versions Gives you great support for different versions (standalone, web app, etc.) of the same basic project For working with others: Greatly simplifies concurrent work, merging changes For getting an internship or job: Any company with a clue uses some kind of version control Companies without a clue are bad places to work 3
- 4. Download and install Git Tutorials Standard one: http://git-scm.com/downloads Here’s one from StackExchange: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/315911/git-for-beginners-the- definitive-practical-guide#323764 Install Git on your machine from http://git-scm.com/downloads Accept context menu items Git access: Right click from windows explorer gitBash to enter commands Current local directory is folder you launched from Good idea - one folder for your git local access 4
- 5. Introduce yourself to Git Start git / gitBash See your options: git config -l Enter these lines (with appropriate changes): git config --global user.name "John Smith" git config --global user.email [email protected] You only need to do this once If you want to use a different name/email address for a particular project, you can change it for just that project cd to the project directory Use the above commands, but leave out the --global 5
- 6. Setting options When you “commit,” git will require you to type in a commit message For longer commit messages, you will use an editor To change the default editor: git config --global core.editor /usr/bin/vim You may also want to turn on colors: git config --global color.ui auto See your options: git config -l 6
- 7. Clone repositories on panther Our repositories http://home.adelphi.edu/~pe16132/csc440/repositories.html Get the files from your repository before starting Make a local respository as a clone of master Make a new folder Right click the folder and choose git bash Type: git clone ssh://[email protected]/opt/git/csc480ASpring15.git Enter your ecampus password See all the contents of the folder Windows Explorer: Change folder and search options to show hidden files, folders and drives Git Bash (unix) : ls -a to see the .git folder. 7
- 8. Using Gui to Clone repository 8 • Open git Gui • Choose Clone Existing Repository • Source: ssh://[email protected]/opt/git/csc480ASpring15.git • Target: New folder on your system • Enter password 3 times
- 9. GitBash Changing your repositories Make changes See what changed git diff Stage changes git add –all (or particular files) note 2 dashes! git diff –cached (:q! to exit) Still only in your repository Put changes back up into repository Commit your staged changes in your repository git commit -m "the reason for the change" Update the respository: git push origin 9
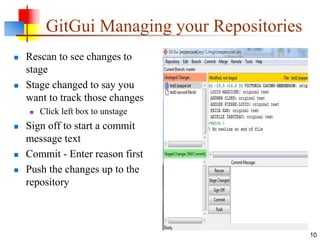
- 10. GitGui Managing your Repositories Rescan to see changes to stage Stage changed to say you want to track those changes Click left box to unstage Sign off to start a commit message text Commit - Enter reason first Push the changes up to the repository 10
- 11. Viewing and Resetting repository See what is on the repository git remote ls to see files cd & cd .. to move around folders cat to see file contents vi to edit file contents and end with <esc> :wq Get what is on repository git pull If it says to resolve manually, just vi that file and see the head which is yours 11
- 12. Failed Push When you don't have the latest copy it will fail: 12
- 13. Recover from failed push Copy your repository elsewhere first just in case Use git bash Git pull to pull down the changes Files needing merging will have both sets of text : <<<<<<< HEAD change once not pushed ======= change once pushed >>>>>>> d43e1181ce3d7d0ca45fe0d2ce1a6120def02c37 Head is your local copy version Add --all ; commit and push again 13
- 14. Typical workflow git pull remote_repository Get changes from a remote repository and merge them into your own repository git status See what Git thinks is going on Use this frequently! Work on your files git add –-all (or just changes) git commit –m “What I did” git push 14
- 15. Helpful gitBash commands Show staged differences: git diff -- cached Show status : git status Show branches: git branch See history: git log Checkout a branch: git checkout branch Fetch so you can look but maybe not take: git fetch Pull will fetch and merge with what you have: git merge 15
- 16. Git log commands git log --pretty=oneline --max-count=2 git log --pretty=oneline --since='5 minutes ago' git log --pretty=oneline --until='5 minutes ago' git log --pretty=oneline --author=<your name> git log --pretty=oneline –all 16
- 17. Git log pretty git log --pretty=format:"%h %ad | %s%d [%an]" --graph -- date=short --pretty="..." defines the output format. %h is the abbreviated hash of the commit %d commit decorations (e.g. branch heads or tags) %ad is the commit date %s is the comment %an is the name of the author --graph tells git to display the commit tree in the form of an ASCII graph layout --date=short keeps the date format short and nice 17
- 18. Good aliases alias gs='git status ' alias ga='git add ' alias gb='git branch ' alias gc='git commit' alias gd='git diff' alias go='git checkout ' alias gk='gitk --all&' alias gx='gitx --all' alias got='git ' alias get='git ' 18















![Git log pretty
git log --pretty=format:"%h %ad | %s%d [%an]" --graph --
date=short
--pretty="..." defines the output format.
%h is the abbreviated hash of the commit
%d commit decorations (e.g. branch heads or tags)
%ad is the commit date
%s is the comment
%an is the name of the author
--graph tells git to display the commit tree in the form of
an ASCII graph layout
--date=short keeps the date format short and nice
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/git2-230405081937-66e39a1f/85/git2-ppt-17-320.jpg)
