How to Lock Down Apache Kafka and Keep Your Streams Safe
- 1. How to Lock Down Apache Kafka and Keep Your Streams Safe Rajini Sivaram
- 2. About me • Principal Software Engineer at Pivotal UK • Apache Kafka Committer • Project Lead: Reactor Kafka – https://github.com/reactor/reactor-kafka • Previously at IBM – Message Hub developer: Kafka-as-a-Service on Bluemix
- 3. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 4. Kafka Cluster Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerKafka Broker Kafka Cluster Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerZookeeper Server Zookeeper Cluster Kafka Clients Kafka Producer Kafka Consumer Kafka Connect Kafka Streams Kafka Admin Admin/ConfigTools
- 5. External client Internal client Security Protocol security.protocol=SASL_SSL bootstrap.servers=kafka01.a.com:9094 listeners=PLAINTEXT://10.0.0.1:9092, SSL://192.168.1.1:9093, SASL_SSL://192.168.1.1:9094 advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://10.0.0.1:9092, SSL://kafka01.a.com:9093, SASL_SSL://kafka01.a.com:9094 security.inter.broker.protocol=PLAINTEXT External client Internal client Kafka Broker Kafka Broker security.protocol=SSL bootstrap.servers=kafka01.a.com:9093 PLAINTEXT SSL SASL_SSL SASL_PLAINTEXT
- 6. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 7. Authentication • Client authentication – Server verifies the identity (user principal) of the client • Server authentication – Client verifies that connection is to a genuine server • Authentication mechanisms in Kafka – TLS – SASL
- 8. Authentication using TLS or SASL Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerKafka Broker Kafka Cluster Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerZookeeper Server Zookeeper Cluster Kafka Clients Kafka Producer Kafka Consumer Kafka Connect Kafka Streams Kafka Admin TLS/SASL TLS/SASL TLS/SASL TLS/SASL SASL TLS/SASL SASL Admin/ConfigTools SASL TLS/SASL
- 9. TLS Handshake Client ClientHello Server ServerHello Certificate [ServerKeyExchange] [CertificateRequest] ServerHelloDone [Certificate] ClientKeyExchange [CertificateVerify] ChangeCipherSpec Client Finished ChangeCipherSpec Server Finished Server cert Client cert
- 10. Client trust store Server key store Issuer’s certificate TLS authentication ssl.keystore.location=/path/ks.jks ssl.keystore.password=ks-secret ssl.key.password=key-secret ssl.truststore.location=/path/trust.jks ssl.truststore.password=ts-secret ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=https Server’s certificate Distinguished Name(DN) Server hostname (SAN) Valid from: to: Issuer DN Issuer Digital Signature Server Public Key Issuer’s certificate Issuer Public Key Issuer Digital Signature Issuer DN Server Private Key ✔ ✔ ✔
- 11. TLS Security Considerations Threat Mitigation Security vulnerability in older protocols • Use latest TLS version: TLSv1.2 Cryptographic attacks • Only strong cipher suites (e.g. 256-bit encryption key size) • Minimum 2048-bit RSA key size Man-in-the-middle attack • Disable anonymous key exchange using Diffie-Hellman ciphers • Enable hostname verification Private key compromised • Certificate revocation using CRL • Use short-lived keys to reduce exposure Man-in-the-middle attack during renegotiation • Disable insecure renegotiation • Note: TLS renegotiation is disabled in Kafka Tampering with data during transit • Use ciphers with secure message digest to guarantee integrity DDoS attack • Enable quotas and connection rate throttling
- 12. Why TLS? • Authentication – Server – Client • Confidentiality – Guarantees privacy of data in motion • Integrity – Message digest included with many ciphers • Horizontally scalable
- 13. TLS drawbacks • Performance impact – latency and throughput • 20-30% degradation • High CPU cost of encryption – Lose zero-copy transfer • TLS-renegotiation is disabled – Authenticate only once • Vulnerable to DDoS attacks • PKI infrastructure required Throughput Message Size CA VA RA CRL RA VA
- 14. SASL • Simple Authentication and Security Layer – Extensible authentication framework for connection-oriented protocols • Standard protocol for different mechanisms – GSSAPI (since 0.9.0) – PLAIN (since 0.10.0) – SCRAM (since 0.10.2) • Can negotiate security layer, but this feature is not used in Kafka – SASL_SSL/SASL_PLAINTEXT
- 15. SASL Handshake Client Kafka SaslHandshake request (mechanism=GSSAPI) Server Establish connection Kafka SaslHandshake response Enabled mechanisms=GSSAPI,PLAIN SASL handshake for selected mechanism Challenge Transport Layer (eg. TLS handshake) Kafka SASL Handshake request SASL authentication using selected mechanism Kafka requests and responses Response Authenticated
- 16. Kafka SASL configuration JAAS configuration listeners=SASL_SSL://host:port1, SASL_PLAINTEXT://host:port2 security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=GSSAPI sasl.enabled.mechanisms=GSSAPI,SCRAM-SHA-256 KafkaServer { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true storeKey=true keyTab="/etc/security/keytabs/kafka_server.keytab“ principal="kafka/[email protected]"; o.a.k.c.s.s.ScramLoginModule required; }; KafkaClient { o.a.k.c.s.s.ScramLoginModule required username="alice” password="alice-secret"; }; http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jgss/tutorials/LoginConfigFile.html Broker config: server.properties security.protocol=SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512 sasl.jaas.config=o.a.k.c.s.s.ScramLoginModule required username="alice" password="alice-secret”; producer/consumer.properties sasl.jaas.config (since 0.10.2) JAAS configuration
- 17. KDC SASL/GSSAPI Key Distribution Centre Kafka BrokerKafka Client Authentication Service Ticket Granting Service KafkaServer { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true storeKey=true keyTab=“/server.keytab" principal="kafka/[email protected]";}; sasl.jaas.config= com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true storeKey=true keyTab=/client.keytab” principal=“[email protected]”; • Kerberos V5 (RFC 475https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4752) • Principal: <primary>[/<instance>]@<REALM> TGT TGT ticket ticket
- 18. SASL/GSSAPI Security Considerations Threat Mitigation Dictionary attack • Enforce strong password policies Keytab file compromised • Restrict access to keytab files and directory • If user compromised, revoke access using ACLs. Restart processes to force reconnections if required. Eavesdropping, tampering with data (after authentication completes) • Kafka does not use Kerberos encryption • SASL_SSL should be used to guarantee confidentiality and integrity if the traffic is not on a secure network Hostname resolution issues • Secure correctly configured DNS KDC failure • Set up multiple slave KDCs alongside a master KDC to avoid single-point-of-failure
- 19. SASL/PLAIN sasl.jaas.config= org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="alice” password="alice-secret"; Kafka Broker Kafka Client alice alice-secret • Simple username/password authentication RFC 4616: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4616 • Basic support in Kafka brokers, replace for production use KafkaServer { o.a.k.c.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required user_alice=“alice-secret”; };
- 20. SASL/PLAIN customization • Integrate with external authentication server • SASL/PLAIN security provider Kafka Broker MyPlainProviderMyPlainLoginModule KafkaServer { com.pivotal.MyPlainLoginModule required authentication.server=“https://my.server"; }; Authentication Server
- 21. SASL/PLAIN Security Considerations Threat Mitigation Dictionary attack • Enforce strong password policies Eavesdropping and replay attack • PLAIN must only be used with TLS • Connection between Kafka and authentication server/database must also be secure User compromised • Revoke all access using ACLs • Restart brokers if required to break connections Password database compromised • Update authentication server • Re-authentication of existing connections is not supported, restart brokers.
- 22. SASL/SCRAM • Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism – RFC 5802: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5802 – Secure username/password authentication • SCRAM-SHA-256 and SCRAM-SHA-512 • Default implementation in Kafka stores salted keys in Zookeeper bin/kafka-configs.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 –alter --add-config 'SCRAM-SHA-256=[iterations=8192,password=alice-secret] --entity-type users --entity-name alice Create user:
- 23. SASL/SCRAM protocol sasl.jaas.config= org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="alice” password="alice-secret”; Kafka Broker Kafka Client Zookeeper • Client proves to the broker that client possesses the password for user • Broker proves to the client that broker once possessed the password for user alice, c-nonce /config/users/alice salt,iterations, salted keys c-s-nonce, salt, iterations c-s-nonce, client-proof c-s-nonce, server-proof ✔ ✔ KafkaServer { o.a.k.c.s.scram.ScramLoginModule required; }; Cache
- 24. SASL/SCRAM Security Considerations Threat Mitigation Dictionary attack • Enforce strong password policies Offline brute force attack • Use high iteration count, strong hash function User compromised • Revoke all access for user • Restart broker to disconnect if required Zookeeper compromised • SCRAM is safe against replay attack • Use with TLS to avoid interception of messages for use in dictionary/brute force attacks • Use strong hash function like SHA-256 or SHA-512 • Use high iteration count Insecure Zookeeper installation • Use alternative secure password store for SCRAM
- 25. Custom SASL mechanisms • Integrate with existing authentication servers – e.g sasl.mechanism=EXTERNAL Kafka Broker MyServerProvider MyServerLoginModule KafkaServer { MyServerLoginModule required authentication.server=“https://my.server"; }; Authentication Server KafkaClient { MyClientLoginModule required identity=“alice“; }; Kafka Client MyClientProvider MyClientLoginModule
- 26. Choosing an authentication protocol Authentication protocol Use if: TLS • On insecure network and require encryption • Server authentication and hostname verification required • Already have PKI infrastructure for client auth SASL/GSSAPI • Already have Kerberos infrastructure • Insecure ZooKeeper installation, don’t want to integrate with custom password database for SCRAM SASL/PLAIN • Integrating with existing password server/database SASL/SCRAM • Require username/password authentication without external server • Secure ZooKeeper installation Custom SASL mechanism • Integrating with existing authentication server
- 27. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 28. Authorization • User Principal – ANONYMOUS for unauthenticated clients – Configurable PrincipalBuilder for TLS – Mechanism-specific user name for SASL • Access Control Lists (ACL) • Pluggable Authorizer – Default out-of-the-box authorizer: SimpleAclAuthorizer bin/kafka-acls.sh --authorizer-properties zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181 --add --allow-principal User:alice --allow-host 198.51.100.0 --operation Read --operation Write --topic test-topic ✗
- 29. Access Control alice Allow Read Topic Host Deny Cluster Operation Resource From hostPermissionUser Principal Consumer Group Create Delete Alter Describe Write ClusterAction bob ✔ ✗ Super user
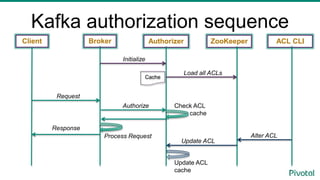
- 30. Kafka authorization sequence Client Request Broker Authorizer ZooKeeper Initialize Load all ACLs Authorize Check ACL cache ACL CLI Update ACL Alter ACL Update ACL cache Response Process Request Cache
- 31. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 32. Quotas • Quota types – Replication quota – Bandwidth quota (Produce/Fetch) – Request quotas (from 0.11.0) • Per-broker quotas – If usage exceeds quota, response is delayed – Throttle time returned to clients, exposed as metrics • Quota configuration in ZooKeeper – Can be dynamically updated bin/kafka-configs.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config 'producer_byte_rate=1024,consumer_byte_rate=2048' --entity-name alice --entity-type users Kafka Broker Client
- 33. Quota Configuration • Multi-level quotas: <client-id>, <user> or <user, client-id> levels • The most specific quota configuration is applied to any connection <user> <client-id> users clients <default> <default> <client-id> <client-id> clients <default>clients <default> config
- 34. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 35. Encryption • TLS – Encrypt data during transit to prevent eavesdropping • Disk encryption – Encrypt data at rest to protect sensitive data • End-to-end encryption – Clients send encrypted data (eg. serialize/deserialize) – Different keys to encrypt data to different topics – Combine with TLS/SASL for authentication, TLS to avoid man-in-the-middle
- 36. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 37. Rolling upgrade to enable security Kafka Client Kafka Broker Kafka Broker listeners=PLAINTEXT://host:9092 security.inter.broker.protocol=PLAINTEXT listeners=PLAINTEXT://host:9092,SSL://host:9093 security.inter.broker.protocol=PLAINTEXT listeners=PLAINTEXT://host:9092,SSL://host:9093 security.inter.broker.protocol=SSL listeners=SSL://host:9093 security.inter.broker.protocol=SSL Dynamic configs • ACL • Quotas
- 38. Zookeeper Server Securing ZooKeeper • ZooKeeper stores critical metadata for Kafka • Lock down updates to Zookeeper – SASL • GSSAPI (Kerberos) • Digest-MD5 – Set zookeeper.set.acl=true on Kafka brokers • TLS is currently not supported for ZooKeeper – Use network segmentation to limit access SASL
- 39. Secure Kafka Cluster Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerKafka Broker Kafka Cluster Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerZookeeper Server Zookeeper Cluster Kafka Clients Kafka Producer Kafka Consumer Kafka Connect Kafka Streams Kafka Admin Admin/ConfigTools
- 40. Secure Kafka on the Cloud Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerKafka Broker Private Network Kafka BrokerKafka BrokerZookeeper Server Kafka Producer Kafka Consumer Kafka Connect Kafka Streams Kafka Admin Public Network TLS ProxyTLS ProxyTLS Proxy Kafka Clients Admin/ConfigTools
- 41. Outline • Kafka Cluster Overview • Securing Kafka Clusters – Authentication – Authorization – Quotas – Encryption • Lock Down Kafka and ZooKeeper • New security features
- 42. New features in 0.10.2 • Broker – Multiple endpoints with the same security protocol • Client – Dynamic JAAS configuration without a file – Multiple credentials within a JVM • SASL mechanisms – SCRAM-SHA-256, SCRAM-SHA-512 Kafka Broker Kafka Broker
- 43. Future work • KIP-48: Delegation tokens • KIP-124: CPU utilization quota for requests • KIP-117: Add a public AdminClient API for Kafka • KIP-86: Configurable SASL callbacks • KIP-111: Improve custom PrincipalBuilder/Authorizer integration
- 44. Summary • Authentication – TLS – SASL: GSSAPI, PLAIN, SCRAM • Authorization – User principal – IP address • Quotas – <client-id>, <user>, <user, client-id> • Encryption – TLS – End-to-end encryption
- 45. Want to find out more? • References – https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/ – https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#security – https://www.confluent.io/blog/apache-kafka-security-authorization-authentication- encryption/ – http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/r3.4.9/zookeeperProgrammers.html#sc_ZooKeeperA ccessControl – https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Kafka+Improvement+Proposals • Mailing lists – [email protected], [email protected] • Report security issues – [email protected]
- 46. Thank you for listening. Questions? Stay connected. [email protected]









![TLS Handshake
Client
ClientHello
Server
ServerHello
Certificate
[ServerKeyExchange]
[CertificateRequest]
ServerHelloDone
[Certificate]
ClientKeyExchange
[CertificateVerify]
ChangeCipherSpec
Client Finished
ChangeCipherSpec
Server Finished
Server
cert
Client
cert](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtolockdownkafka1-170524221033/85/How-to-Lock-Down-Apache-Kafka-and-Keep-Your-Streams-Safe-9-320.jpg)







![KDC
SASL/GSSAPI
Key Distribution Centre
Kafka BrokerKafka
Client
Authentication
Service
Ticket
Granting
Service
KafkaServer {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useKeyTab=true storeKey=true keyTab=“/server.keytab"
principal="kafka/kafka1.a.com@EXAMPLE.COM";};
sasl.jaas.config=
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useKeyTab=true storeKey=true keyTab=/client.keytab”
principal=“kafka-client-1@EXAMPLE.COM”;
• Kerberos V5 (RFC 475https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4752)
• Principal: <primary>[/<instance>]@<REALM>
TGT
TGT
ticket
ticket](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtolockdownkafka1-170524221033/85/How-to-Lock-Down-Apache-Kafka-and-Keep-Your-Streams-Safe-17-320.jpg)




![SASL/SCRAM
• Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism
– RFC 5802: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5802
– Secure username/password authentication
• SCRAM-SHA-256 and SCRAM-SHA-512
• Default implementation in Kafka stores salted keys in Zookeeper
bin/kafka-configs.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 –alter
--add-config 'SCRAM-SHA-256=[iterations=8192,password=alice-secret]
--entity-type users --entity-name alice
Create user:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtolockdownkafka1-170524221033/85/How-to-Lock-Down-Apache-Kafka-and-Keep-Your-Streams-Safe-22-320.jpg)