How to use MetaMapp and ChemRICH software for metabolomics ?
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes1,018 views
Tutorial slides on using the MetaMapp and ChemRICH tool for #metabolomics. Contact me at [email protected] for any questions. metamapp.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu & chemrich.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu
1 of 59
Downloaded 21 times


























































Ad
Recommended
Metabolic Network Mapping Exericse



Metabolic Network Mapping ExericseDinesh Barupal This document provides instructions for visualizing metabolic networks using the MetaMapp R package and Cytoscape software. It describes how to:
1) Prepare input files for MetaMapp and address common errors, 2) Obtain network and node attribute files from MetaMapp, 3) Import these files into Cytoscape and visualize the network using various layouts, 4) Map node attributes such as color, size, and label to experimental metadata, and 5) Manipulate the network view through filtering, clustering, and exporting for publication. The goal is to create clear, focused visualizations of metabolic subnetworks from omics data.
Metabolic network mapping for metabolomics



Metabolic network mapping for metabolomicsDinesh Barupal We present a novel approach to integrate biochemical pathway and chemical relationships to map all detected metabolites in network graphs (MetaMapp) using KEGG reactant pair database, Tanimoto chemical and NIST mass spectral similarity scores. In fetal and maternal lungs, and in maternal blood plasma from pregnant rats exposed to environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), 459 unique metabolites comprising 179 structurally identified compounds were detected by gas chromatography time of flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOF MS) and BinBase data processing. MetaMapp graphs in Cytoscape showed much clearer metabolic modularity and complete content visualization compared to conventional biochemical mapping approaches. Cytoscape visualization of differential statistics results using these graphs showed that overall, fetal lung metabolism was more impaired than lungs and blood metabolism in dams. Fetuses from ETS-exposed dams expressed lower lipid and nucleotide levels and higher amounts of energy metabolism intermediates than control animals, indicating lower biosynthetic rates of metabolites for cell division, structural proteins and lipids that are critical for in lung development.
MetaMapp graphs efficiently visualizes mass spectrometry based metabolomics datasets as network graphs in Cytoscape, and highlights metabolic alterations that can be associated with higher rate of pulmonary diseases and infections in children prenatally exposed to ETS. The MetaMapp scripts can be accessed at http://metamapp.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu.
Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis (ChemRICH)



Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis (ChemRICH)Dinesh Barupal This document describes the ChemRICH method for metabolite set enrichment analysis of metabolomics data. ChemRICH uses chemical similarity clustering to group metabolites into non-overlapping sets, addressing limitations of pathway-based enrichment methods. It employs the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for enrichment statistics without relying on background databases. The method was developed as open source software and has been applied to analyze a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease metabolomics study.
(Manual spss)



(Manual spss)Enas Ahmed The document provides instructions for launching and using the statistical software SPSS. It discusses finding the SPSS icon on the computer and launching the program. Once SPSS is open, the user can start a new data file or open an existing one. Basic steps for using SPSS are outlined, including entering data, defining variables, testing for normality, statistical analysis, and interpreting results. Specific functions and menus in SPSS are demonstrated for descriptive statistics, normality testing, and t-tests.
Microsoft excel



Microsoft excelPremnath R This document provides an introduction and overview of Microsoft Excel. It covers opening and navigating Excel, understanding the basic interface and features like tabs, menus and cells. It then explains how to perform common tasks like formatting cells, typing data, inserting and deleting rows/columns, sorting data, using AutoSum and basic equations, and creating charts and graphs. It also briefly covers more advanced functions like copying/pasting data, filling data across cells, saving files, printing, and finding help resources before closing Excel. The document is intended to teach beginning computer users the essential basics of using the spreadsheet program Microsoft Excel.
Install Addin Excel - Data Analysis Tool Pak - Thiyagu



Install Addin Excel - Data Analysis Tool Pak - ThiyaguThiyagu K The Analysis ToolPak is an Excel add-in program
that provides data analysis tools for
financial, statistical and engineering data analysis. We can do statistical analysis in very easily with the use of Data Analysis Tool Pak of Excel Addin. This presentation describes the steps of installing the Addin Software - Data Analysis ToolPak in Excel.
SPSS an intro...



SPSS an intro...Jithin Zcs This document provides an introduction to using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) for data analysis. It discusses the four main windows in SPSS - the data editor, output viewer, syntax editor, and script window. It also covers the basics of managing data files, including opening SPSS, defining variables, and sorting data. Several basic analysis techniques are introduced, such as frequencies, descriptives, and linear regression. Examples are provided for how to conduct these analyses and interpret the outputs.
Advanced Cascading Style Sheets



Advanced Cascading Style Sheetsfantasticdigitaltools Advanced CSS
by: Alexandra Vlachakis
Sandy Creek High School, Fayette County Schools
Slide Show correlates Georgia Deparment of Edcuation Career and Technology PATHWAY: Interactive Media
COURSE: Advanced Web Design
UNIT 6: BCS-AWD-6 Advanced CSS
Data Visualization in Health



Data Visualization in HealthRamon Martinez My talk in the technical meeting "Global Burden of Diseases and Scientific Computation in Health". 25-26 September 2015. FIOCRUZ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Step by-step creation of a bapi in detailed steps with scr…



Step by-step creation of a bapi in detailed steps with scr…sapsarath612 This document provides a step-by-step guide to creating a custom BAPI in SAP. It involves creating a structure, function module, and BAPI using transactions SE11, SE37, and SWO1. The BAPI is then tested by passing input parameters and verifying the output matches expectations. Key steps include defining import/export parameters, setting the object and method release statuses, generating the BAPI, and executing it to ensure it works as intended.
Spss



Spsssalemhusin SPSS is a statistical software package used for data management and analysis. It allows users to enter and manage large amounts of data, perform a wide range of statistical analyses, and output results in tables and graphs. The main SPSS windows are the Data Editor, used to enter and view data, and the Viewer, which displays output of statistical analyses. Common analysis techniques demonstrated in the document include independent and paired t-tests to compare group means. The document provides guidance on using SPSS for questionnaire design and statistical analysis to efficiently analyze social science and business data.
SPSS How to use Spss software



SPSS How to use Spss softwareDebashis Baidya This document provides an overview of using SPSS to analyze data. It discusses opening data files in SPSS, viewing the data, entering new data values, setting up variable properties like name, type, and label. It also covers running frequency analyses and descriptive statistics, computing new variables, and concludes that SPSS is a powerful tool for statistical analysis.
Data visualization



Data visualizationChristian Stade-Schuldt This document discusses principles of effective data visualization. It outlines different types of visualizations like bar charts, line charts, and scatter plots that effectively convey relationships in data. It emphasizes designing visualizations that maximize the data-ink ratio to clearly present information while minimizing non-essential elements. Guidelines are provided for proper use of different chart types and ensuring visualizations are designed accessibly and avoid distortion or deception.
SAP BW - Info object (characteristics)



SAP BW - Info object (characteristics)Yasmin Ashraf This document discusses characteristic info objects in SAP BW, which are used to analyze facts. It describes the types of info objects and provides steps to create a characteristic info object in BW. These include giving the info object a name and description, selecting attributes and settings for general properties, master data, hierarchies, and compounding. Characteristic info objects structure the master data needed for analysis in BW.
Charts in excel



Charts in excelJithin Krishnan Area charts display changes in magnitude over time using colored areas below lines. They can be 2D or 3D, stacked to show contribution, or 100% stacked to show percentage contribution over time. Scatter charts show relationships between numeric variables and are used for scientific data. Bubble charts are like scatter charts but show three variables where the third determines bubble size. Stock charts illustrate price fluctuations over time using high, low, close values or including open and volume values.
Genome-Scale Metabolic Models and Systems Medicine of Metabolic Syndrome



Genome-Scale Metabolic Models and Systems Medicine of Metabolic SyndromeNatal van Riel workshop on 'The interplay of fat and carbohydrate metabolism with application in Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes', December 12 and 13, 2013, Eindhoven University of Technology
Introduction to Network Analysis in Gephi



Introduction to Network Analysis in GephiVictor Blaer This document provides an introduction to network analysis and visualization using Gephi software. It begins with some mindset tips, such as expecting troubleshooting challenges and iterative work. The document then outlines Gephi's interface, including the Overview panel for interactive exploration, Data Laboratory for raw data, and Preview panel for final visualization export. Basic network concepts like nodes, edges, and layout algorithms are defined. The rest of the document demonstrates how to import node and edge data from CSV files, visualize the resulting network, run statistics and filtering, and tweak the layout for clearer presentation. Examples using real-world Twitter data are also briefly mentioned.
Basic guide to SPSS



Basic guide to SPSSpaul_gorman This is a very basic guide to SPSS. It is aimed at total novices wishing to understand the basic layout of the package and how to generate some simple tables and graphs
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) help



Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) helpcasestudyhelp CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
Styles define how to display HTML elements
External Style Sheets can save a lot of work
Styles are normally saved in external .css files. External style sheets enable you to change the appearance and layout of all the pages in a Web site, just by editing one single file!
InDesign intro



InDesign introDanielle Oser, APR 1. Adobe InDesign allows users to work with documents, objects, frames, and pages. It provides different viewing modes and ways to navigate multi-page documents.
2. The software enables formatting of text using features like character styles, paragraph styles, glyphs, and find and replace. It also offers tools for working with objects and creating lists.
3. InDesign supports adding graphics, color, lines, and arranging page elements using guides and rulers. Users can hide or lock objects and group multiple objects together.
5 Secrets to Better Presentation Charts and Graphs



5 Secrets to Better Presentation Charts and GraphsMetamorph Training Pvt Ltd Presenting data-driven charts? Here are 5 secrets to delivering Presentation Charts and Graphs powerfully. Visit presentation-process.com for more such insights.
SAP BPC 10.1 NW Master Data loading 



SAP BPC 10.1 NW Master Data loading Manoj Kumar This document provides instructions for loading master data (texts and attributes) from a flat file into SAP BPC. It involves creating a flat file source system and two data sources to extract the attribute and text data from the flat file. Transformations are created to load the data into the characteristic, and infoPackages and data transfer processes are used to move the data from the persistent storage area to the characteristic. The process loads the attribute data successfully but the text data is not loaded yet and additional steps are needed to create a new data source for the text data.
excel charts and graphs.ppt



excel charts and graphs.pptChemOyasan1 This document discusses charts and graphs in Excel. It defines a chart as a graphical representation of worksheet data that makes the data easier to understand visually. There are different chart types for different data, including column charts, line charts, and pie charts. The document outlines how to create charts by selecting data, choosing a chart type, and determining the chart location. It also covers troubleshooting tips, making separate chart sheets, designing charts by selecting and arranging elements, and choosing chart layouts and styles.
Draw A Chemical Structure Using Chemsketch



Draw A Chemical Structure Using ChemsketchArvind306 The document provides 7 steps to draw the chemical structure of azobenzene using ChemSketch software:
1) Open ChemSketch and start drawing.
2) Add the first benzene ring.
3) Add the second benzene ring.
4) Add the first NH2 group and attach it to the first benzene ring.
5) Add another NH2 group and attach it to the first.
6) Attach the second benzene ring to the second NH2 group with a single bond.
7) Change the single bond between the two NH groups to a double bond.
Chart Components



Chart Componentswmassie The document discusses charts and graphs used in business, including their components and purposes. It explains that charts visually represent spreadsheet data in a way that highlights trends and relationships. Charts contain elements like data series, titles, axes, labels, legends and more. Examples of using charts include representing sales trends, expenses, and stock prices. The document identifies key chart components and their functions.
135. Graphic Presentation



135. Graphic PresentationLAKSHMANAN S The document discusses various types of statistical diagrams and graphs that can be used to represent numerical data in a visual format. It describes line diagrams, bar diagrams, component bar diagrams, percentage bar diagrams, pie charts, pictograms, frequency graphs including histograms, frequency polygons, frequency curves and ogives. It also covers scatter diagrams, dot plots, stem-and-leaf plots, box-and-whisker plots and their uses in visually representing data distributions.
Lsmw (Legacy System Migration Workbench)



Lsmw (Legacy System Migration Workbench)Leila Morteza This document provides instructions for using SAP's Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW) tool to migrate legacy vendor master data into SAP. It outlines the 15 steps to create an LSMW project and upload vendor records, including recording transactions, mapping fields, uploading a data file, reading and converting the data, and running a batch input session to complete the migration. The instructions are accompanied by screenshots to illustrate each step in the process.
ARCHIVED: new version available - METASPACE Step by Step guide



ARCHIVED: new version available - METASPACE Step by Step guideMETASPACE These slides provide a guide to using the METASPACE platform for annotating metabolites in high resolving power imaging mass spectrometry datasets. It describes
* the science behind molecular annotation
* how to use our web application to upload, browse, interpret and export annotations from the platform.
社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start Guide



社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start GuideCheer Chain Enterprise Co., Ltd. 社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start Guide
This guide provides a quick introduction to UCINET. It assumes that the software has been installedwith the data in the folder C:\Program Files\Analytic Technologies\Ucinet 6\DataFiles and this hasbeen left as the default directory.
Source : https://sites.google.com/site/ucinetsoftware/home
Practice discovering biological knowledge using networks approach.



Practice discovering biological knowledge using networks approach.Elena Sügis This practice session gives an overview how to analyze biological data using networks approach. It covers netwokrs topology, data integration, differential expression, network visualization, functional enrichment analysis and retrieving data from external sources. Primarily Cytoscape software is used for this practice session.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (19)
Data Visualization in Health



Data Visualization in HealthRamon Martinez My talk in the technical meeting "Global Burden of Diseases and Scientific Computation in Health". 25-26 September 2015. FIOCRUZ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Step by-step creation of a bapi in detailed steps with scr…



Step by-step creation of a bapi in detailed steps with scr…sapsarath612 This document provides a step-by-step guide to creating a custom BAPI in SAP. It involves creating a structure, function module, and BAPI using transactions SE11, SE37, and SWO1. The BAPI is then tested by passing input parameters and verifying the output matches expectations. Key steps include defining import/export parameters, setting the object and method release statuses, generating the BAPI, and executing it to ensure it works as intended.
Spss



Spsssalemhusin SPSS is a statistical software package used for data management and analysis. It allows users to enter and manage large amounts of data, perform a wide range of statistical analyses, and output results in tables and graphs. The main SPSS windows are the Data Editor, used to enter and view data, and the Viewer, which displays output of statistical analyses. Common analysis techniques demonstrated in the document include independent and paired t-tests to compare group means. The document provides guidance on using SPSS for questionnaire design and statistical analysis to efficiently analyze social science and business data.
SPSS How to use Spss software



SPSS How to use Spss softwareDebashis Baidya This document provides an overview of using SPSS to analyze data. It discusses opening data files in SPSS, viewing the data, entering new data values, setting up variable properties like name, type, and label. It also covers running frequency analyses and descriptive statistics, computing new variables, and concludes that SPSS is a powerful tool for statistical analysis.
Data visualization



Data visualizationChristian Stade-Schuldt This document discusses principles of effective data visualization. It outlines different types of visualizations like bar charts, line charts, and scatter plots that effectively convey relationships in data. It emphasizes designing visualizations that maximize the data-ink ratio to clearly present information while minimizing non-essential elements. Guidelines are provided for proper use of different chart types and ensuring visualizations are designed accessibly and avoid distortion or deception.
SAP BW - Info object (characteristics)



SAP BW - Info object (characteristics)Yasmin Ashraf This document discusses characteristic info objects in SAP BW, which are used to analyze facts. It describes the types of info objects and provides steps to create a characteristic info object in BW. These include giving the info object a name and description, selecting attributes and settings for general properties, master data, hierarchies, and compounding. Characteristic info objects structure the master data needed for analysis in BW.
Charts in excel



Charts in excelJithin Krishnan Area charts display changes in magnitude over time using colored areas below lines. They can be 2D or 3D, stacked to show contribution, or 100% stacked to show percentage contribution over time. Scatter charts show relationships between numeric variables and are used for scientific data. Bubble charts are like scatter charts but show three variables where the third determines bubble size. Stock charts illustrate price fluctuations over time using high, low, close values or including open and volume values.
Genome-Scale Metabolic Models and Systems Medicine of Metabolic Syndrome



Genome-Scale Metabolic Models and Systems Medicine of Metabolic SyndromeNatal van Riel workshop on 'The interplay of fat and carbohydrate metabolism with application in Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes', December 12 and 13, 2013, Eindhoven University of Technology
Introduction to Network Analysis in Gephi



Introduction to Network Analysis in GephiVictor Blaer This document provides an introduction to network analysis and visualization using Gephi software. It begins with some mindset tips, such as expecting troubleshooting challenges and iterative work. The document then outlines Gephi's interface, including the Overview panel for interactive exploration, Data Laboratory for raw data, and Preview panel for final visualization export. Basic network concepts like nodes, edges, and layout algorithms are defined. The rest of the document demonstrates how to import node and edge data from CSV files, visualize the resulting network, run statistics and filtering, and tweak the layout for clearer presentation. Examples using real-world Twitter data are also briefly mentioned.
Basic guide to SPSS



Basic guide to SPSSpaul_gorman This is a very basic guide to SPSS. It is aimed at total novices wishing to understand the basic layout of the package and how to generate some simple tables and graphs
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) help



Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) helpcasestudyhelp CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
Styles define how to display HTML elements
External Style Sheets can save a lot of work
Styles are normally saved in external .css files. External style sheets enable you to change the appearance and layout of all the pages in a Web site, just by editing one single file!
InDesign intro



InDesign introDanielle Oser, APR 1. Adobe InDesign allows users to work with documents, objects, frames, and pages. It provides different viewing modes and ways to navigate multi-page documents.
2. The software enables formatting of text using features like character styles, paragraph styles, glyphs, and find and replace. It also offers tools for working with objects and creating lists.
3. InDesign supports adding graphics, color, lines, and arranging page elements using guides and rulers. Users can hide or lock objects and group multiple objects together.
5 Secrets to Better Presentation Charts and Graphs



5 Secrets to Better Presentation Charts and GraphsMetamorph Training Pvt Ltd Presenting data-driven charts? Here are 5 secrets to delivering Presentation Charts and Graphs powerfully. Visit presentation-process.com for more such insights.
SAP BPC 10.1 NW Master Data loading 



SAP BPC 10.1 NW Master Data loading Manoj Kumar This document provides instructions for loading master data (texts and attributes) from a flat file into SAP BPC. It involves creating a flat file source system and two data sources to extract the attribute and text data from the flat file. Transformations are created to load the data into the characteristic, and infoPackages and data transfer processes are used to move the data from the persistent storage area to the characteristic. The process loads the attribute data successfully but the text data is not loaded yet and additional steps are needed to create a new data source for the text data.
excel charts and graphs.ppt



excel charts and graphs.pptChemOyasan1 This document discusses charts and graphs in Excel. It defines a chart as a graphical representation of worksheet data that makes the data easier to understand visually. There are different chart types for different data, including column charts, line charts, and pie charts. The document outlines how to create charts by selecting data, choosing a chart type, and determining the chart location. It also covers troubleshooting tips, making separate chart sheets, designing charts by selecting and arranging elements, and choosing chart layouts and styles.
Draw A Chemical Structure Using Chemsketch



Draw A Chemical Structure Using ChemsketchArvind306 The document provides 7 steps to draw the chemical structure of azobenzene using ChemSketch software:
1) Open ChemSketch and start drawing.
2) Add the first benzene ring.
3) Add the second benzene ring.
4) Add the first NH2 group and attach it to the first benzene ring.
5) Add another NH2 group and attach it to the first.
6) Attach the second benzene ring to the second NH2 group with a single bond.
7) Change the single bond between the two NH groups to a double bond.
Chart Components



Chart Componentswmassie The document discusses charts and graphs used in business, including their components and purposes. It explains that charts visually represent spreadsheet data in a way that highlights trends and relationships. Charts contain elements like data series, titles, axes, labels, legends and more. Examples of using charts include representing sales trends, expenses, and stock prices. The document identifies key chart components and their functions.
135. Graphic Presentation



135. Graphic PresentationLAKSHMANAN S The document discusses various types of statistical diagrams and graphs that can be used to represent numerical data in a visual format. It describes line diagrams, bar diagrams, component bar diagrams, percentage bar diagrams, pie charts, pictograms, frequency graphs including histograms, frequency polygons, frequency curves and ogives. It also covers scatter diagrams, dot plots, stem-and-leaf plots, box-and-whisker plots and their uses in visually representing data distributions.
Lsmw (Legacy System Migration Workbench)



Lsmw (Legacy System Migration Workbench)Leila Morteza This document provides instructions for using SAP's Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW) tool to migrate legacy vendor master data into SAP. It outlines the 15 steps to create an LSMW project and upload vendor records, including recording transactions, mapping fields, uploading a data file, reading and converting the data, and running a batch input session to complete the migration. The instructions are accompanied by screenshots to illustrate each step in the process.
Similar to How to use MetaMapp and ChemRICH software for metabolomics ? (20)
ARCHIVED: new version available - METASPACE Step by Step guide



ARCHIVED: new version available - METASPACE Step by Step guideMETASPACE These slides provide a guide to using the METASPACE platform for annotating metabolites in high resolving power imaging mass spectrometry datasets. It describes
* the science behind molecular annotation
* how to use our web application to upload, browse, interpret and export annotations from the platform.
社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start Guide



社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start GuideCheer Chain Enterprise Co., Ltd. 社會網絡分析UCINET Quick Start Guide
This guide provides a quick introduction to UCINET. It assumes that the software has been installedwith the data in the folder C:\Program Files\Analytic Technologies\Ucinet 6\DataFiles and this hasbeen left as the default directory.
Source : https://sites.google.com/site/ucinetsoftware/home
Practice discovering biological knowledge using networks approach.



Practice discovering biological knowledge using networks approach.Elena Sügis This practice session gives an overview how to analyze biological data using networks approach. It covers netwokrs topology, data integration, differential expression, network visualization, functional enrichment analysis and retrieving data from external sources. Primarily Cytoscape software is used for this practice session.
LamiaFinal data ( results).docx1- label all lanes, label ma.docx



LamiaFinal data ( results).docx1- label all lanes, label ma.docxDIPESH30 Lamia/Final data ( results).docx
1- label all lanes, label marker sizes, and indicate which three lanes, containing at least one BSA sample and one E. coli sample, you are writing about.
2- lanes 2, 5, 6, 9, and 11 are BSA, lanes 14 and 15 are empty, and lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 12, and 13 are E. coli.
Lamia/Graphing page.pdf
Lamia/Guidelines.doc
Biology 105 Laboratory Fall 2013
Instructor: Ayça Akal-Strader
Guidelines for Lab Report
Lab 2: Quantification of Protein (Bradford Assay)
Your report for Lab 2: Quantification of Protein (Bradford Assay) is due the week of October 7/8/9/10. Please include the following information in your report:
Hypothesis: as usual
Introduction:
• Background/theory of Bradford Assay
• Purpose of the experiment
Results:
In addition to the specific data discussed below, your Results section should always include one or more paragraphs of text that provide:
• A brief description of the procedure
• Explanations of any charts, graphs, figures, or calculations that are included
• Statements about the most interesting/noteworthy data
Data:
1. Table of measured absorbances (like Table 2 on p. 31).
2. Table showing protein concentrations of unknowns (like Table 3 on p. 31). Say which unknowns—1, 2, or both—you used.
**Please re-make the tables for your report. DO NOT simply tear out p. 31 from your lab manual and staple it to your report.
3. Standard Curve:
• Label with title and caption
• Label axes: x-axis = Concentration (μg/ml); y-axis = Absorbance at 595 nm. Be sure to include units on Concentration. Remember that absorbance (optical density; OD) has no units.
• Plot points, leaving room to plug in your unknown absorbances to find their concentrations
• Connect the dots
(Note: Do NOT draw a straight line—unless your data really looks like a straight line. The samples we measured did not fall into the “linear range” of the spectrophotometer, and everyone’s data that I saw flattened out a lot at the high concentration end of the range. Connect your data points with a curve.)
• Indicate by drawing horizontal and vertical lines how you found the concentration of your unknowns.
Discussion:
• Did your results match your expectations? If not, why not?
• Did you have any difficulty finding the concentration of any of your unknowns?
• Do you think your measurement of protein concentration was accurate? Did your duplicates agree well? For your standards, did your absorbances increase as your protein concentrations increased?
Conclusion: as usual
Lab Report Rewrites
You may rewrite TWO of your first FIVE lab reports in an effort to improve your grade.
You do not need to rewrite the entire report; just fix the problems that caused you to lose points the first time around.
You MUST hand in the original version of your report along with your corrected version. If you do not have the original attached, we will not accept your rewrite.
Your final grade on the rewritten report will be ...
Reduce Your Gene Editing Data Analysis from Days to Minutes with Magpie



Reduce Your Gene Editing Data Analysis from Days to Minutes with MagpieCourtney Davies Engineered nucleases and gene therapy vectors show promise for treating human diseases but require high efficiency and specificity. Researchers can use whole genome sequencing and deep sequencing to evaluate off-target effects and ensure safety. However, data analysis for gene editing experiments is challenging and slow. Catalytic has developed Magpie, an automated computational pipeline, to quickly analyze gene editing experiments and generate reports to meet regulatory standards. Magpie integrates with existing data systems and can process large amounts of data faster than conventional methods.
Mapping SNP Genotype and CNV Data Patterns to Pharmacogenomic Allele Nomencla...



Mapping SNP Genotype and CNV Data Patterns to Pharmacogenomic Allele Nomencla...Thermo Fisher Scientific Pharmacogenomic (PGx) studies require genetic testing of individuals for multiple variants in drug metabolism enzyme and transporter genes. For phenotype interpretation purposes, genotyping results must be translated to star (*) allele nomenclature. Star alleles are gene level haplotype patterns that are associated with protein activity levels. Genetic variants within a haplotype can include single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), Insertion/Deletions (InDels), and copy number variants (CNVs). Knowing the combination of variants within a given haplotype, and the diploid content in an individual, is of key importance for studying drug metabolism, drug response and adverse drug reactions. To facilitate the translation of results for individuals genotyped in studies using TaqMan® SNP and Drug Metabolism Genotyping Assays and TaqMan® Copy Number Assays, we developed a web-based flexible software tool called AlleleTyper™. This software uses genetic pattern information in user-defined translation tables to map sample genotyping data to star allele or other nomenclature
Introduction to spss 2



Introduction to spss 2Michael Taiwo At the end of this Lesson (Part 1) the students should be able to know the following
Descriptive statistics
Saving an SPSS for Windows
Backing up your data
Retrieving your Data Files
Affect of Metabolic Obesity and Body Mass Index in Coronary Artery Diseases



Affect of Metabolic Obesity and Body Mass Index in Coronary Artery DiseasesNikhil Gupta The project aims to:
1) Train a model capable of predicting the GENSINI score which determines the severity of CAD in the following groups-
-Metabolically Healthy Normal Weight (MHNW)
-Metabolically Obese Normal Weight (MONW)
-Metabolically Healthy Obese (MHO)
-Metabolically Abnormal Obese (MAO)
2) Find the group showing a good association to severity of CAD that is which category is more prone to CAD, metabolically obese or phenotypically obese.
3) Find the prognostic markers for CAD among factors like HBA1C, FI, HOMA IR , TC, TG, HDL, LDL and hsCRP and which group shows more association?
The data was collected by Kasturba Medical College, Manipal.
The results obtained were presented at Hackabout 2016, a data analysis challenge, organized by Philips in Manipal University. We were among the best 5 teams.
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT



MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENTSyed Lokman The document describes multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and different tools that can be used for MSA. There are two major classes of MSA - global alignments and local alignments. Choosing the appropriate tool depends on the type and size of the alignment. The document compares the outputs of several MSA tools, including Clustal Omega, MUSCLE, T-Coffee, Kalign, and MAFFT, when run on the same nucleotide sequences. It also demonstrates how the MAFFT alignment changes when parameters like strategy, gap penalties, and inclusion of homologs are modified.
2017 - METASPACE training guide



2017 - METASPACE training guideMETASPACE The document provides an overview of a METASPACE training guide on metabolite annotation in high-resolution imaging mass spectrometry data. It covers three parts: introduction to the METASPACE platform and annotation process, a tutorial on using the annotation engine and knowledgebase, and exporting data to the required imzML format from different mass spectrometers. The tutorial teaches participants how to prepare and submit data, browse results, and interpret annotations from the METASPACE bioinformatics tools in order to annotate metabolites in imaging MS data.
Genome-wide Association Study (GWAS) Analysis Guide in TASSEL Software (GUI).pdf



Genome-wide Association Study (GWAS) Analysis Guide in TASSEL Software (GUI).pdfRezaDystaSatria This document provides instructions for performing SNP quality control, data filtering, imputation of missing values, general linear model (GLM) analysis, mixed linear model (MLM) analysis using principal components (PCA) and kinship, and plotting GWAS results in R Studio using data from the TASSEL software. The key steps include using HapMap as a reference for SNP quality control, imputing missing values using LD KNNI imputation, filtering the dataset, intersecting files for GLM and MLM analysis, and generating Manhattan and QQ plots of results in R Studio.
Day 4



Day 4HuyPhmNht2 This document discusses techniques for improving deep learning models and reducing overfitting, including regularization, batch normalization, and transfer learning. It provides explanations and examples of common regularization techniques like weight decay, dropout, and early stopping. It also explains batch normalization and how it helps speed up training and reduce internal covariate shift. Finally, it introduces transfer learning as a way to utilize pre-trained models on new tasks by freezing earlier layers and fine-tuning later layers.
Predictive Modeling with Enterprise Miner



Predictive Modeling with Enterprise MinerJeffrey Strickland, Ph.D., CMSP This document provides an overview of using SAS Enterprise Miner software to conduct predictive modeling using regression analysis. It discusses how to import data from Excel, create a project and data source in Enterprise Miner, run linear and logistic regression models to predict outcomes, and interpret the results, including measures of model fit and variable effects. Examples are provided demonstrating linear regression of kilowatt usage on temperature, multiple regression of food expenditures on income and family size, and logistic regression of exam passing on study hours.
Predictive Modeling with Enterprise Miner



Predictive Modeling with Enterprise MinerJeffrey Strickland, Ph.D., CMSP This document provides an overview of using SAS Enterprise Miner software to conduct predictive modeling using regression analysis. It discusses how to import data from Excel, create a project and data source in Enterprise Miner, run linear and logistic regression models to predict outcomes, and interpret the results, including measures of model fit and variable effects. Examples are provided on using linear regression to predict kilowatts from temperature, multiple regression to predict food expenditures from income and family size, and logistic regression to predict exam passing from study hours.
IRSAE aquatic ecology 28 June 2018 metabolomics



IRSAE aquatic ecology 28 June 2018 metabolomicsPanagiotis Arapitsas Metabolomics, basic theory and tools.
IRSAE, Integrating 'Omics' Technologies into Aquatic Ecology,
Metabolic pathway mapping against KEGG, Reactome, HMDB and CPDB



Metabolic pathway mapping against KEGG, Reactome, HMDB and CPDBDinesh Barupal This document describes various approaches for mapping detected metabolites to metabolic pathways using online databases and tools. It discusses obtaining KEGG identifiers for metabolites, using KEGG, Reactome, MetaboAnalyst and ConsensusPathDB to map identifiers to pathways and visualize pathways with overlays of mapped metabolites. It notes some metabolites may not have identifiers or map to pathways and emphasizes mapping identified more compounds than shown on pathway maps through enrichment analysis.
ECHOES_ConSPIC_2014_Write-Up_Korak_Datta



ECHOES_ConSPIC_2014_Write-Up_Korak_DattaKorak Datta The document discusses three approaches - vertical, horizontal, and hybrid - for creating ADaM datasets to report counts of patients meeting criteria for drug-induced liver toxicity using Hy's Law and laboratory data. The vertical approach uses many flags and variables, but has simpler reporting. The horizontal approach adds many new records but keeps the original data. The hybrid approach uses fewer new variables but has a more complicated dataset program. In conclusion, when implementing ADaM, it is important to have an open mind and be willing to experiment with different solutions to find the most optimal approach.
When & Why\'s of Denormalization



When & Why\'s of DenormalizationAliya Saldanha The document discusses denormalization in database design. It begins with an introduction to normalization and outlines the normal forms from 1NF to BCNF. It then describes the denormalization process and different denormalization strategies like pre-joined tables, report tables, mirror tables, and split tables. The document discusses the pros and cons of denormalization and emphasizes the need to weigh performance needs against data integrity. It concludes by stating that selective denormalization is often required to achieve efficient performance.
Drug properties (ADMET) prediction using AI



Drug properties (ADMET) prediction using AIIndrajeetKumar124 ADMET properties prediction using AI will accelerate the process of drug discovery.
This slide mostly focuses on using graph-based deep learning techniques to predict drug properties.
Need and benefits for structure standardization to facilitate integration and...



Need and benefits for structure standardization to facilitate integration and...Valery Tkachenko There are a large number of US government databases housing diverse collections of chemical data including bioassay data (PubChem), toxicity data (CompTox Chemistry Dashboard) and environmental data (a large collection of EPA databases), to name just a few. In many cases integration between the databases, at the chemical structure level, is via alphanumeric text identifiers such as CAS Numbers, or via InChI (International Chemical Identifiers). Structure-based integration is hyper-dependent on the initial inputs providing the chemical structures to the InChI generation algorithm. To ensure optimal integration between various databases, community standards and agreement regarding standardization of chemical structures would be beneficial, not only to integration of US government databases and resources but also to the international scientific community and hosts of online databases. This presentation will discuss our progress to deliver a fully Open Source chemical standardization platform as an exemplar for the community to build on and enhance. The system utilizes the CDK (Chemistry Development Kit), RD Kit and other open source components. The resource expands on our previous work regarding the Chemical Validation and Standardization Platform and has been tested using the open data collection provided by the EPA Comptox Chemistry Dashboard.
Mapping SNP Genotype and CNV Data Patterns to Pharmacogenomic Allele Nomencla...



Mapping SNP Genotype and CNV Data Patterns to Pharmacogenomic Allele Nomencla...Thermo Fisher Scientific
Ad
More from Dinesh Barupal (6)
Dinesh Barupal @ California Biomonitoring SGP Meeting July 2020



Dinesh Barupal @ California Biomonitoring SGP Meeting July 2020Dinesh Barupal This document discusses opportunities and challenges in non-targeted analysis (NTA) for exposomics and metabolomics studies. It addresses issues like prioritizing chemicals for hazard assessments, developing a basic data science environment for NTA studies, and improving annotation of unknown signals. Key points discussed are avoiding signal prevalence thresholds to identify rare high-risk exposures, better utilizing chemical databases, and developing approaches to link chemicals to relevant publications to aid prioritization and interpretation of NTA data. Overall challenges of NTA like interpretational biases are acknowledged, and the need for planned analytical and computational strategies is emphasized to realize the potential of NTA for exposome research.
Metabolomics in the 21st century - perspective



Metabolomics in the 21st century - perspectiveDinesh Barupal This document discusses metabolomics as a service (MaaS) and the role of metabolomics core facilities in providing metabolomics data generation and analysis services. It outlines the key aspects of metabolomics including measuring small molecule chemicals in biological samples, the role of metabolism in health and disease, and approaches for blood metabolomics. The document advocates that metabolomics core facilities can provide cost-effective, high-quality metabolomics services including standardized assays, large-scale data generation, robust data analysis, and developing metabolite libraries. This would support metabolic epidemiology and clinical research projects.
ChemRICH - metabolite enrichment analysis



ChemRICH - metabolite enrichment analysisDinesh Barupal This document provides instructions for performing a ChemRICH analysis using an example metabolomics dataset. It describes preparing the data by obtaining identifiers and SMILES codes from PubChem, and notes common input file errors. It then explains how to paste the data into the ChemRICH website to perform the analysis and view interactive results, including a powerpoint slide for explanation. Cluster names and statistical values are listed.
Metabolic network visualization - concepts



Metabolic network visualization - conceptsDinesh Barupal This document discusses biochemical network mapping and visualization. It begins by describing the process of creating a metabolic network graph with nodes representing metabolites and edges representing reactions. While metabolic databases can provide information on known reactions, not all detected metabolites may be present. The document then introduces MetaMapp as an approach to map all detected metabolites into a network graph by combining information on known biochemical reactions with chemical similarity. Cytoscape software allows visualization and analysis of these network graphs. In conclusion, MetaMapp can be used to incorporate all identified metabolites into biochemical modules to aid in interpretation of omics data.
Metabolic Set Enrichment Analysis - chemrich - 2019



Metabolic Set Enrichment Analysis - chemrich - 2019Dinesh Barupal ChemRICH is a method for metabolite set enrichment analysis that uses chemical similarity clustering rather than biochemical pathways. It groups metabolites into non-overlapping sets based on chemical similarity rather than pathway membership. It then uses the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test rather than the hypergeometric test to identify which sets are significantly different between study groups. This overcomes limitations of pathway-based analysis, such as metabolites not being annotated to pathways or pathways having unclear boundaries. The online ChemRICH app allows interactive analysis and downloading of results.
Mapping metabolites against pathway databases 



Mapping metabolites against pathway databases Dinesh Barupal Mapping of metabolites onto pathway databases. I covered KEGG, Reactome, HMDB and ConsensusPathDB in this lecture.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Gender Bias and Empathy in Robots: Insights into Robotic Service Failures



Gender Bias and Empathy in Robots: Insights into Robotic Service FailuresSelcen Ozturkcan Ozturkcan, S., & Merdin-Uygur, E. (2025). Gender Bias and Empathy in Robots: Insights into Robotic Service Failures. Consumers + Technology Dialogue (CTD) Conference, 24-25 Apr 2025, ESADE Business School, Barcelona, Spain.
Effect of nutrition in Entomophagous Insectson



Effect of nutrition in Entomophagous InsectsonJabaskumarKshetri Effect of nutrition in Entomophagous Insects
Explains about insect nutrition and their effects.
Introduction to Mobile Forensics Part 1.pptx



Introduction to Mobile Forensics Part 1.pptxNivya George Introduction to Mobile Forensics, Sim card crimes
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- Father of Microbiology



Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- Father of MicrobiologyAnoja Kurian Antonie van Leeuwenhoek- Father of Microbiology
2025 Insilicogen Company English Brochure



2025 Insilicogen Company English BrochureInsilico Gen Insilicogen is a company, specializes in Bioinformatics. Our company provides a platform to share and communicate various biological data analysis effectively.
Skin function_protective_absorptive_Presentatation.pptx



Skin function_protective_absorptive_Presentatation.pptxmuralinath2 Protective function of skin, protection from mechanical blow, UV rays, regulation of water and electrolyte balance, absorptive activity, secretory activity, excretory activity, storage activity, synthetic activity, sensory activity, role of sweat glands regarding heat loss, cutaneous receptors and stratum corneum
Direct Evidence for r-process Nucleosynthesis in Delayed MeV Emission from th...



Direct Evidence for r-process Nucleosynthesis in Delayed MeV Emission from th...Sérgio Sacani The origin of heavy elements synthesized through the rapid neutron capture process (r-process) has been an enduring mystery for over half a century. J. Cehula et al. recently showed that magnetar giant flares, among the brightest transients ever observed, can shock heat and eject neutron star crustal material at high velocity, achieving the requisite conditions for an r-process.A. Patel et al. confirmed an r-process in these ejecta using detailed nucleosynthesis calculations. Radioactive decay of the freshly synthesized nuclei releases a forest of gamma-ray lines, Doppler broadened by the high ejecta velocities v 0.1c into a quasi-continuous spectrum peaking around 1 MeV. Here, we show that the predicted emission properties (light curve, fluence, and spectrum) match a previously unexplained hard gamma-ray signal seen in the aftermath of the famous 2004 December giant flare from the magnetar SGR 1806–20. This MeV emission component, rising to peak around 10 minutes after the initial spike before decaying away over the next few hours, is direct observational evidence for the synthesis of ∼10−6 Me of r-process elements. The discovery of magnetar giant flares as confirmed r-process sites, contributing at least ∼1%–10% of the total Galactic abundances, has implications for the Galactic chemical evolution, especially at the earliest epochs probed by low-metallicity stars. It also implicates magnetars as potentially dominant sources of heavy cosmic rays. Characterization of the r-process emission from giant flares by resolving decay line features offers a compelling science case for NASA’s forthcomingCOSI nuclear spectrometer, as well as next-generation MeV telescope missions.
VERMICOMPOSTING A STEP TOWARDS SUSTAINABILITY.pptx



VERMICOMPOSTING A STEP TOWARDS SUSTAINABILITY.pptxhipachi8 Vermicomposting: A sustainable practice converting organic waste into nutrient-rich fertilizer using worms, promoting eco-friendly agriculture, reducing waste, and supporting environmentally conscious gardening and farming practices naturally.
SuperconductingMagneticEnergyStorage.pptx



SuperconductingMagneticEnergyStorage.pptxBurkanAlpKale Ultra-fast, ultra-efficient grid storage
Presented by:
Burkan Alp Kale 20050711038
Numan Akbudak 21050711021
Nebil weddady 21050741003
Osama Alfares 21050741013
when is CT scan need in breast cancer patient.pptx



when is CT scan need in breast cancer patient.pptxRukhnuddin Al-daudar when is CT scan need in breast cancer patient
whole ANATOMY OF EYE with eye ball .pptx



whole ANATOMY OF EYE with eye ball .pptxsimranjangra13 The human eye is a complex organ responsible for vision, composed of various structures working together to capture and process light into images. The key components include the sclera, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve, and various fluids like aqueous and vitreous humor. The eye is divided into three main layers: the fibrous layer (sclera and cornea), the vascular layer (uvea, including the choroid, ciliary body, and iris), and the neural layer (retina).
Here's a more detailed look at the eye's anatomy:
1. Outer Layer (Fibrous Layer):
Sclera:
The tough, white outer layer that provides shape and protection to the eye.
Cornea:
The transparent, clear front part of the eye that helps focus light entering the eye.
2. Middle Layer (Vascular Layer/Uvea):
Choroid:
A layer of blood vessels located between the retina and the sclera, providing oxygen and nourishment to the outer retina.
Ciliary Body:
A ring of tissue behind the iris that produces aqueous humor and controls the shape of the lens for focusing.
Iris:
The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil, regulating the amount of light entering the eye.
Pupil:
The black opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
3. Inner Layer (Neural Layer):
Retina:
The light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
Optic Nerve:
A bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual signals from the retina to the brain.
4. Other Important Structures:
Lens:
A transparent, flexible structure behind the iris that focuses light onto the retina.
Aqueous Humor:
A clear, watery fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the lens, providing nourishment and maintaining eye shape.
Vitreous Humor:
A clear, gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina, helping maintain eye shape.
Macula:
A small area in the center of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision.
Fovea:
The central part of the macula with the highest concentration of cone cells, providing the sharpest vision.
These structures work together to allow us to see, with the light entering the eye being focused by the cornea and lens onto the retina, where it is converted into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain for interpretation.
he eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit. Six extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye. These muscles move the eye up and down, side to side, and rotate the eye.
The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera. This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball.he layers of the tear film keep the front of the eye lubricated.
Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. These three layers together are called the tear film. The mucous layer is made by the conjunctiva. The watery part of the tears is made by the lacrimal gland
RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST (RDT) overviewppt.pptx



RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST (RDT) overviewppt.pptxnietakam This a overview on rapid diagnostic test which is also known as rapid test focusing primarily on its principle which is lateral flow assay
Application of Microbiology- Industrial, agricultural, medical



Application of Microbiology- Industrial, agricultural, medicalAnoja Kurian Application of microbiology, medical microbiology, agricultural microbiology, industrial microbiology
Water analysis practical for ph, tds, hardness, acidity, conductivity, and ba...



Water analysis practical for ph, tds, hardness, acidity, conductivity, and ba...ss0077014 water analysis
Turkey Diseases and Disorders Volume 2 Infectious and Nutritional Diseases, D...



Turkey Diseases and Disorders Volume 2 Infectious and Nutritional Diseases, D...Ali Raei Turkey Diseases and Disorders
How to use MetaMapp and ChemRICH software for metabolomics ?
- 1. Unit 2.5 MetaMapp and ChemRICH exercise Dinesh Barupal [email protected]
- 3. Input file : MetaMapp R- Package (openCPU version) Network file Node attribute file How to use MetaMapp ?
- 4. How to get SMILES codes ?
- 5. How to use MetaMapp ? Prepare the input file. • This is the minimum input • No duplicate CIDs are allowed Example : spring_2018_metabolomics_course_metamapp_ example.xlsx
- 6. About the example dataset • Comparison of the plasma metabolome in Non alcoholic fatty liver disease subjects and the controls. • HILIC + CSH assays • ~ 650 identified metabolites. • Unpublished (you can write a paper out of it).
- 7. MetaMapp input file errors - • Duplicate PubChem CIDs • Duplicate names • Missing SMILES codes • Missing p-value or fold-change • Headers mismatch • > 1000 compounds
- 8. How to use MetaMapp ? Obtaining the MetaMapp files. • Go to http://metamapp.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu Copy and paste your data in this box Click here Now, click on these two buttons chemsim_krp_07.sif node_attributes_chemsim_krp_07.tsv Both files are provided in the example folder for the case study.
- 9. chemsim_krp_07.sif node_attributes_chemsim_krp_07.tsv Structure of the created files. Both files will be imported in the Cytoscape software for visualization KRP – KEGG Reaction Pairs – biochemical relationships TMSIM – Tanimoto similarity – chemical relationships
- 10. What is Cytoscape ? The most used network visualization and analysis tool. http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1001843http://www.cytoscape.org/ Backed by strong institutions
- 11. Visualize a range of experimental data on a network graph Useful graph layout algorithms Graph theory calculations Easy organization of multiple networks for comparisons. Faster navigation of large networks Filter and query the network Contributed plugins Works on PC, Max and Linux system USB drive contains a copy of Cytoscape software Cytoscape basic features
- 12. Click here Start Cytoscape software Locate the chemsim_krp_07.sif file and click import. The file shall be in your download folder or you can use the file in the example folder. How to use Cytoscape?
- 13. Import a new network If you want to import a new network file in already running Cytoscape Select the .sif file
- 14. Visualization panel Table panel highlights the data related to selected node (yellow). Cytoscape windwos
- 15. Show graphics details Tip: if you don’t see the labels/edges/shapes/colors in graph, click on “Show graphics details”.
- 16. Visualize using the yFiles (organic layout). You can try other layout methods, but this one is recommended. Layout a network graph
- 17. Network graph after organic layout
- 18. Now import your Node Attributes file
- 19. Import your Node Attributes file
- 20. Import your Node Attributes file “Key” symbol should be PubChem_ID
- 21. Import your Node Attributes file Table panel after importing the node attributes.
- 22. Data visualization All visual properties can be accessed in the style tab. Node color Node size Node label Node label position Node Label font size Edge color Edge width Network background color
- 23. Change network background color 1 2 3 Select black background color or any color you like.
- 24. Double click here click here Node coloring : “Node Fill color”
- 25. Red = higher Blue = lower Yellow = no change Node coloring : “Node Fill color”
- 26. Change node label You can choose any label from the node attribute file. You need to zoom in to see the labels Use the scroll button to zoom in and out.
- 27. If you don’t see the labels
- 28. Intermediate network graph crowded, overlapping labels and unpublishable.
- 29. Change label font size Showing labels for only the significant compounds. It is bit clearer.
- 30. Change node size Select the values by press the left click on mouse. Then right click. Node size rules FC 1.0 – size = 20 FC >1 & <2 --size = 60 FC >2 & < 3 -- size = 100 FC >3 & < 5 --size = 150 FC > 5-- size = 200
- 31. Intermediate network graph Bit clearer, has experimental results. Highlighting the clusters that are changed. Not yet publication ready
- 32. Node moving Press “control” key and click left mouse button and select the area Now you can move these nodes
- 33. Intermediate network graph Not yet publication ready
- 34. Change edge colors This box must be checked. The visual property is under the subtab – “edge”
- 35. Intermediate network graph KEGG reactions Chemical similarity Lipids Amino acids and amines
- 36. Observations • Several fatty acids and DAGs are increased in NAFLD plasma. • Metformin was higher in NAFLD subjects along with increased in MTA and Hypoxanthine. • PE, CER, PC and CEs were decreased in the NAFLD subjects. • Stachydrine- orange juice related compound was 5- fold lower in the NFALD subjects. • One carbon and lipid metabolism were altered in the NAFLD subjects.
- 37. Cluster detection Check this box Large network can be divided into smaller modules for better visualization and interpretation
- 38. Useful buttons in the menu-bar Zoom in Zoom out Zoom-all Zoom in selected You will use these often.
- 40. Create a sub-network Select a cluster by pressing “Ctrl” and then left click and make a square box. Once selected the nodes, Prese Ctrl+N to make a new network Show graphics details
- 41. Node label position Click on the label position It will make label position property available in the style tab.
- 42. Select right side nodes Click on this box to change the property for selected node. Drag the object box to the left and click ok Node label position
- 43. Increase the scaling factor to remove the overlaps of labels. Scaling Focused view of the fatty acids and DG cluster.
- 44. Network navigation Click on a network you want to visualize Create subnetworks for – • Sphingolipids • Cholesteroyl esters • TGs • Phopspholipids • One carbon metabolism
- 45. Sphingolipid cluster Cholestroyl esters PC cluster + acetyl carnitines Focused visualization of clusters Clearer, readable, less crowded. This can go in a paper.
- 46. One carbon metabolism and FAFLD
- 47. The commonly used anti-diabetic agent metformin targets mitochondrial complex I and thus decreases the NAD+/NADH ratio. Metformin also inhibits cancer cell growth, in part through inhibition of biosynthetic metabolism (Griss et al., 2015). Metformin-induced growth inhibition can be partially rescued by supplementation with hypoxanthine and thymidine, products of 1C metabolism (Corominas-Faja et al., 2012). It remains unclear, however, if the impact of metformin on 1C metabolism is clinically significant at normal therapeutic doses. One carbon metabolism and FAFLD Increased homocysteine also occurs in liver disease, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (Dai et al., 2016). In animals fed high-fat diets to induce NAFLD, liver 1C metabolism is dysregulated, as evidenced by intrahepatic increases in SAH and free homocysteine and decreases in methionine and the GNMT enzyme (Pacana et al., 2015). At the same time, deletions of 1C enzymes lead to development of liver disease.
- 48. Save the session for future
- 49. Export the network as a pdf file
- 51. ChemRICH : Data preparation Example dataset available in the chemrich example folder spring_2018_metabolomics_course_chemrich_example Use PubChem Identified Exchange Service to obtain identifiers, InchiKeys and SMILES for compound names.
- 52. ChemRICH input file errors - • Duplicate PubChem CIDs • Duplicate names • Missing SMILES codes • Missing p-value or fold-change • Headers mismatch • > 1000 compounds
- 53. Perform ChemRICH analysis www.ChemRICH.us Paste your data in this box
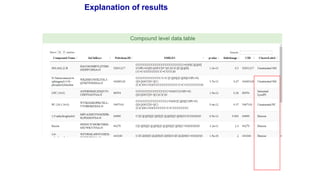
- 54. Explanation of results Editable power-point slide
- 56. Download/interact with results Imino Acids Saturated_Lysophosphatidylcholines Lysophospholipids Unsaturated_Lysophosphatidylcholines NewCluster_32 Cholestenes Phosphatidylethanolamines NewCluster_14 Unsaturated_Phosphatidylcholines Sphingomyelins Diglycerides Plasmalogens Unsaturated_Ceramides Galactosylceramides Cholesterol Esters 0 10 20 30 0 5 10 15 20 median XlogP of clusters -log(pvalue)




