Hpc, grid and cloud computing - the past, present, and future challenge
- 1. HPC, Grid and Cloud Computing - The Past, Present and Future Jason Shih Academia Sinica Grid computing FBI 極簡主義, Nov 3rd, 2010
- 2. Outline Trend in HPC Grid: eScience Research @ PetaScale Cloud Hype and Observation Future Exploration Path of Computing Summary
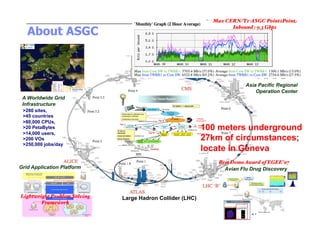
- 3. Max CERN/T1-ASGC Point2Point About ASGC Inbound : 9.3 Gbps! 1. Most Reliable T1: 98.83%! 2. Very Highly Performing and most Stable Site in CCRC08! Asia Pacific Regional Operation Center A Worldwide Grid Infrastructure >280 sites, >45 countries >80,000 CPUs, >20 PetaBytes 100 meters underground >14,000 users, >200 VOs 27km of circumstances; >250,000 jobs/day locate in Geneva Best Demo Award of EGEE’07! Grid Application Platform Avian Flu Drug Discovery Lightweight Problem Solving Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Framework! 21
- 4. Emerging Trend and Technologies: 2009 -2010
- 5. Hype Cycle for Storage Technologies - 2010
- 6. Trend in High Performance Computing
- 7. Ugly? Performance of HPC Cluster 272 (52%) of world fastest clusters have efficiency lower than 80% (Rmax/Rpeak) Only 115 (18%) could drive over 90% of theoretical peak Sampling from Top500 HPC cluster Trend of Cluster Efficiency 2005-2009
- 8. Performance and Efficiency 20% of Top-performed clusters contribute 60% of Total Computing Power (27.98PF) 5 Clusters Eff. < 30
- 9. Impact Factor: Interconnectivity - Capacity and Cluster Efficiency Over 52% of Cluster base on GbE With efficiency around 50% only InfiniBand adopt by ~36% HPC Clusters
- 10. HPC Cluster - Interconnect Using IB SDR, DDR and QDR in Top500 Promising efficiency >= 80% Majority of IB ready cluster adopt DDR (87%) (2009 Nov) Contribute 44% of total computing power ~28 Pflops Avg efficiency ~78%
- 11. Trend in HPC Interconnects: Infiniband Roadmap
- 12. Common semantics Programmer productivity Easy of deployment HPC filesystem are more mature, wider feature set: High concurrent read and write In the comfort zone of programmers (vs cloudFS) Wide support, adoption, acceptance possible pNFS working to be equivalent Reuse standard data management tools Backup, disaster recovery and tiering
- 14. Trend in HPC
- 15. Some Observations & Looking for Future (I) Computing Paradigm (Almost) Free FLOPS (Almost) Logic Operation Data Access (Memory) Is A Major Bottleneck Synchronization Is the Most Expensive Data Communication Is A Big Factor in Performance I/O Still A Major Programming Consideration MPI Coding Is the Motherhood of Large Scale Computing Computing in Conjunction of Massive Data Management Finding Parallelism Is Not A Whole Issue In Programming Data Layout Data Movement Data Reuse Frequency of Interconnected Data Communication
- 16. Some Observations & Looking for Future (II) Emerging New Possibility Massive “Small” Computing Elements with On Board Memory Computing Node Can Be Caonfigured Dynamically (including Failure recovery) Network Switch (within on site complex) Will Nearly Match Memory Performance Parallel I/O Support for Massive Parallel System Asynchronous Computing/Communication Operation Sophisticate Data Pre-fetch Scheme (Hardware/Algorithm) Automate Dynamic Load Balance Method Very High Order Difference Scheme (also Implicit Method) Full Coupling of Formerly Split Operators Fine Numerical Computational Grid (grid number > 10,000) Full Simulation of Protein Full Coupling of Computational Model Grid Computing for All
- 17. Some Observations & Looking for Future (3) System will get more complicate & Computing Tool will get more sophisticated: Vendor Support & User Readiness?
- 18. Grid: eScience Research @ PetaScale
- 19. WLCG Computing Model - The Tier Structure Tier-0 (CERN) Data recording Initial data reconstruction Data distribution Tier-1 (11 countries) Permanent storage Re-processing Analysis Tier-2 (~130 countries) Simulation End-user analysis
- 20. Enabling Grids for E-sciencE Archeology Astronomy Astrophysics Civil Protection Comp. Chemistry Earth Sciences Finance Fusion Geophysics High Energy Physics Life Sciences Multimedia Material Sciences … EGEE-II INFSO-RI-031688 EGEE07, Budapest, 1-5 October 2007 4
- 21. Objectives Building sustainable research and collaboration infrastructure Support research by e-Science, on data intensive sciences and applications require cross disciplinary distributed collaboration
- 22. ASGC Milestone Operational from the deployment of LCG0 since 2002 ASGC CA establish on 2005 (IGTF in same year) Tier-1 Center responsibility start from 2005 Federated Taiwan Tier-2 center (Taiwan Analysis Facility, TAF) is also collocated in ASGC Rep. of EGEE e-Science Asia Federation while joining EGEE from 2004 Providing Asia Pacific Regional Operation Center (APROC) services to regional-wide WLCG/EGEE production infrastructure from 2005 Initiate Avian Flu Drug Discovery Project and collaborate with EGEE in 2006 Start of EUAsiaGrid Project from April 2008
- 23. LHC First Beam – Computing at the Petascale General Purpose, pp, heavy ions LHCb: B-physics, CP Violation ALICE: Heavy ions, pp CMS: General Purpose, pp, heavy ions ATLAS: General Purpose, pp, heavy ions
- 24. Size of LHC Detector ATLAS Bld. 40 7,000 Tons ATLAS Detector CMS 25 Meters in Height 45 Meters in Length
- 25. Standard Cosmology Good model from 0.01 sec after Big Bang Energy, Density, Temperature Supported by considerable observational evidence Time Elementary Particle Physics From the Standard Model into the unknown: towards energies of 1 TeV and beyond: the Terascale Towards Quantum Gravity From the unknown into the unknown... http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/gr/public/bb_history.html UNESCO Information 25 Preservation debate, April 2007 - [email protected]
- 26. WLCG Timeline First Beam on LHC, Sep. 10, 2008 Severe Incident after 3w operation (3.5TeV)
- 27. Petabyte Scale Data Challenges Why Petabyte? Experiment Computing Model Comparing with conventional data management Challenges Performance: LAN and WAN activities Sufficient B/W between CPU Farm Eliminate Uplink Bottleneck (Switch Tires) Fast responding of Critical Events Fabric Infrastructure & Service Level Agreement Scalability and Manageability Robust DB engine (Oracle RAC) KB and Adequate Administration (Training)
- 28. Tier Model and Data Management Components
- 29. Disk Pool Configuration - T1 MSS (CASTOR)
- 30. Distribution of Free Capacity - Per Disk Servers vs. per Pool
- 31. Storage Server Generation - Drive vs. Net Capacity (Raid6) TB TB 21TB/DS 31TB/DS TB TB 40TB/DS 15TB/DS
- 32. IDC Collocation Facility install complete at Mar 27th Tape system delay after Apr 9th Realignment RMA for faulty parts
- 33. Storage Farm ~ 110 raid subsystem deployed since 2003. Supporting both Tier1 and 2 storage fabric DAS connection to front-end blade server Flexible switching front end server upon performance requirement 4-8G fiber channel connectivity
- 35. Throughput of WLCG Experiments Throughput defined as Job Eff. x # Jobs running Characteristic of 4 LHC Exp. depicting in-efficiency is due to poor coding.
- 36. Reliability From Different View Perspective
- 37. Storage Fabric Management – The Challenges: Events Management
- 38. Open Cloud Consortium Cloud Hype and Observation
- 40. Cloud Hype Metacomputing (~1987, L. Smarr) Grid Computing (~1997, I. Foster, K. Kesselman) Cloud Computing (~2007, E. Schmidt?)
- 41. Type of Infrastructure roprietary solutions by public providers P Turnkey solutions developed internally as they own the software and hardware solution/tech. loud specific support C Developers of specific hardware and/or software solutions that are utilized by service providers or used internally when building private cloud raditional providers T Leverage or tweak their existing
- 42. Grid and Cloud: Comparison Cost & Performance Scale & Usability Service Mapping Interoperability Application Scenarios
- 43. Cloud Computing: “X” as a Service ype of Cloud T ayered Service Model L eference Model R
- 44. Virtualization is not Cloud computing Performance Overhead FV vs. PV Disk I/O and network throughput (VM scalability) Ref: Linux-based virtualization for HPC clusters.
- 45. Cloud Infrastructure Best practical & Real world performance tart Up: 60 ~ 44s S estart : 30 ~ 27s R eletion: 60 ~ <5s D igrate M 30 VM ~ 26.8s 60 VM ~ 40s 20 VM ~ 89s 1 top S 30VM ~ 27.4s 60VM ~ 26s 20VM ~ 57s 1
- 46. Cloud Infrastructure Best practical Real World Performance tart Up: 60 ~ 44s S estart : 30 ~ 27s R eletion: 60 ~ <5s D igrate M 30 VM ~ 26.8s 60 VM ~ 40s 20 VM ~ 89s 1 top S 30VM ~ 27.4s 60VM ~ 26s 20VM ~ 57s 1
- 47. Virtualization: HEP Best Practical
- 49. Grid over Cloud or Cloud over Grid?
- 51. Conclusion: My Opinion Future of Computing: Technology-Push & Demand- Pull Emerging of new science paradigm Virtualization: Promising Technology but being overemphasized Green: Cloud Service Transparency & Common Platform More Computing Power ~ Power Consumption Challenge Private Clouds Will be predominant way Commercial Cloud (Public) expect not evolving fast
- 52. Acknowledgment Thanks valuable discussion/inputs from TCloud (Cloud OS: Elaster) Professional Technical Support from Silvershine Tech. at beginning of the collaboration. The interesting thing about Cloud Computing is that we’ve defined Cloud Computing to include everything that we already do….. I don’t understand what we would do differently in the light of Cloud Computing other than change the wording of some of our ads. Larry Ellison, quote in the Wall Street Journal, Sep 26, 2008
- 53. Issues Scalability? Infrastructure operation vs. performance Assessment Application aware – Cloud service Cost analysis Data center power usage – PUE Cloud Myth Top 10 Cloud Computing Trend http://www.focus.com/articles/hosting-bandwidth/ top-10-cloud-computing-trends/ Use Cases & Best Practical
- 54. Issues (II) Volunteer computing (boinc)? Total capacity & performance successful stories & research Despines What’s hindering cloud adoption? Try human. http://gigaom.com/cloud/whats-hindering-cloud- adoption-how-about-humans/ Future projection? service readiness? Service level? Technical barriers?