Ad
I2 c from phillips[1]
- 1. AN10216-01 I2C Manual INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATION NOTE AN10216-01 I2C MANUAL Abstract – The I2C Manual provides a broad overview of the various serial buses, why the I2C bus should be considered, technical detail of the I2C bus and how it works, previous limitations/solutions, comparison to the SMBus, Intelligent Platform Management Interface implementations, review of the different I2C devices that are available and patent/royalty information. The I2C Manual was presented during the 3 hour TecForum at DesignCon 2003 in San Jose, CA on 27 January 2003. Jean-Marc Irazabal – I2C Technical Marketing Manager Steve Blozis – I2C International Product Manager Specialty Logic Product Line Logic Product Group Philips Semiconductors March 24, 2003 1
- 2. AN10216-01 I2C Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS ...................................................................................................................................................2 OVERVIEW .......................................................................................................................................................................4 DESCRIPTION .....................................................................................................................................................................4 SERIAL BUS OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................................................4 UART OVERVIEW.............................................................................................................................................................6 SPI OVERVIEW..................................................................................................................................................................6 CAN OVERVIEW ...............................................................................................................................................................7 USB OVERVIEW................................................................................................................................................................9 1394 OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................................................10 I2C OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................11 SERIAL BUS COMPARISON SUMMARY .............................................................................................................................12 I2C THEORY OF OPERATION ....................................................................................................................................13 I2C BUS TERMINOLOGY...................................................................................................................................................13 START AND STOP CONDITIONS ....................................................................................................................................14 HARDWARE CONFIGURATION ...............................................................................................................................14 BUS COMMUNICATION.............................................................................................................................................14 TERMINOLOGY FOR BUS TRANSFER ................................................................................................................................15 I2C DESIGNER BENEFITS .................................................................................................................................................17 I2C MANUFACTURERS BENEFITS .....................................................................................................................................17 OVERCOMING PREVIOUS LIMITATIONS .............................................................................................................18 ADDRESS CONFLICTS ......................................................................................................................................................18 CAPACITIVE LOADING > 400 PF (ISOLATION) .................................................................................................................19 VOLTAGE LEVEL TRANSLATION .....................................................................................................................................20 INCREASE I2C BUS RELIABILITY (SLAVE DEVICES).........................................................................................................21 INCREASING I2C BUS RELIABILITY (MASTER DEVICES)..................................................................................................22 CAPACITIVE LOADING > 400 PF (BUFFER)......................................................................................................................22 LIVE INSERTION INTO THE I2C BUS .................................................................................................................................24 LONG I2C BUS LENGTHS .................................................................................................................................................25 PARALLEL TO I2C BUS CONTROLLER ..............................................................................................................................25 DEVELOPMENT TOOLS AND EVALUATION BOARD OVERVIEW..................................................................26 PURPOSE OF THE DEVELOPMENT TOOL AND I2C EVALUATION BOARD ...........................................................................26 WIN-I2CNT SCREEN EXAMPLES.....................................................................................................................................28 HOW TO ORDER THE I2C 2002-1A EVALUATION KIT .....................................................................................................31 COMPARISON OF I2C WITH SMBUS ........................................................................................................................31 I2C/SMBUS COMPLIANCY ...............................................................................................................................................31 DIFFERENCES SMBUS 1.0 AND SMBUS 2.0 ....................................................................................................................32 INTELLIGENT PLATFORM MANAGEMENT INTERFACE (IPMI) ....................................................................32 INTEL SERVER MANAGEMENT.........................................................................................................................................33 PICMG ...........................................................................................................................................................................33 VMEBUS .........................................................................................................................................................................34 I2C DEVICE OVERVIEW ..............................................................................................................................................35 TV RECEPTION................................................................................................................................................................36 RADIO RECEPTION ..........................................................................................................................................................36 2
- 3. AN10216-01 I2C Manual AUDIO PROCESSING ........................................................................................................................................................37 DUAL TONE MULTI-FREQUENCY (DTMF)......................................................................................................................37 LCD DISPLAY DRIVER ....................................................................................................................................................37 LIGHT SENSOR ................................................................................................................................................................38 REAL TIME CLOCK/CALENDAR .......................................................................................................................................38 GENERAL PURPOSE I/O EXPANDERS ...............................................................................................................................38 LED DIMMERS AND BLINKERS .......................................................................................................................................40 DIP SWITCH ....................................................................................................................................................................42 MULTIPLEXERS AND SWITCHES.......................................................................................................................................43 VOLTAGE LEVEL TRANSLATORS .....................................................................................................................................45 BUS REPEATERS AND HUBS ............................................................................................................................................45 HOT SWAP BUS BUFFERS ................................................................................................................................................45 BUS EXTENDERS .............................................................................................................................................................46 ELECTRO-OPTICAL ISOLATION ........................................................................................................................................47 RISE TIME ACCELERATORS .............................................................................................................................................47 PARALLEL BUS TO I2C BUS CONTROLLER ......................................................................................................................48 DIGITAL POTENTIOMETERS .............................................................................................................................................48 ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS ................................................................................................................................48 SERIAL RAM/EEPROM .................................................................................................................................................49 HARDWARE MONITORS/TEMP & VOLTAGE SENSORS .....................................................................................................49 MICROCONTROLLERS ......................................................................................................................................................49 I2C PATENT AND LEGAL INFORMATION ..............................................................................................................50 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ...................................................................................................................................50 APPLICATION NOTES..................................................................................................................................................50 3
- 4. AN10216-01 I2C Manual OVERVIEW Description Philips Semiconductors developed the I2C bus over 20 years ago and has an extensive collection of specific use and general purpose devices. This application note was developed from the 3 hour long I2C Overview TecForum presentation at DesignCon 2003 in San Jose, CA on 27 January 2003 and provides a broad overview of how the I2C bus compares to other serial buses, how the I2C bus works, ways to overcome previous limitations, new uses of I2C such as in the Intelligent Platform Management Interface, overview of the various different categories of I2C devices and patent/royalty information. Full size Slides are posted as a PDF file on the Philips Logic I2C collateral web site as DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview PDF file. Place holder and title slides have been removed from this application note and some slides with all text have been incorporated into the application note speaker notes. three shared signal lines, for bit timing, data, and R/W. Serial Bus Overview The selection of communicating partners is made with one separate wire for each chip. As the number of chips Co m m grows, so do the selection wires. The next stage is to un use multiplexing of the selection wires and call them an ic at io n er address bus. s sum Con If there are 8 address wires we can select any one of tive IEEE1394 256 devices by using a ‘one of 256’ decoder IC. In a mo Auto parallel bus system there could be 8 or 16 (or more) SERIAL BUSES data wires. Taken to the next step, we can share the function of the wires between addresses and data but it UART starts to take quite a bit of hardware and worst is, we In du s still have lots of wires. We can take a different tri SPI a l approach and try to eliminate all except the data wiring BUS itself. Then we need to multiplex the data, the selection DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 5 (address), and the direction info - read/write. We need to develop relatively complex rules for that, but we save Slide 5 on those wires. This presentation covers buses that use only one or two data lines so that they are still attractive for sending data over reasonable distances - at least a General concept for Serial communications few meters, but perhaps even km. SCL SDA Typical Signaling Characteristics Parallel to Serial select 3 Shift Register select 2 select 1 READ or enable Shift Reg# enable Shift Reg# enable Shift Reg# WRITE? // to Ser. // to Ser. // to Ser. R/W R/W R/W “MASTER” SLAVE 1 SLAVE 2 SLAVE 3 DATA LVTTL • A point to point communication does not require a Select control signal RS422/485 I2C • An asynchronous communication does not have a Clock signal I2C SMBus • Data, Select and R/W signals can share the same line, depending on the protocol I2C PECL 1394 • Notice that Slave 1 cannot communicate with Slave 2 or 3 (except via the ‘master’) LVPECL LVDS GTL+ Only the ‘master’ can start communicating. Slaves can ‘only speak when spoken to’ DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 6 CML LVT 5V 3.3 V 2.5 V GTL GTLP Slide 6 LVC DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 7 Buses come in two forms, serial and parallel. The data and/or addresses can be sent over 1 wire, bit after bit, or Slide 7 over 8 or 32 wires at once. Always there has to be some way to share the common wiring, some rules, and some Devices can communicate differentially or single ended synchronization. Slide 6 shows a serial data bus with with various signal characteristics as shown in Slide 7. 4
- 5. AN10216-01 I2C Manual also because it may be used within the PC software as a general data path that USB drivers can use. Transmission Standards Terminology for USB: The use of older terms such as 2500 the spec version 1.1 and 2.0 is now discouraged. There is just “USB” (meaning the original 12 Mbits/sec and Data Transfer Rate (Mbps) CML 655 400 1.5 Mbits/sec speeds of USB version 1.1) and Hi-Speed GTLP BTL ETL 35 1394.a LVD ECL S =RS-6 /PEC 4 USB meaning the faster 480 Mbits/sec option included L/LV 4 10 PEC L in spec version 2.0. Parts conforming to or capable of General RS-422 the 480 Mbits/sec are certified as Hi-Speed USB and Purpose 1 Logic RS-485 will then feature the logo with the red stripe “Hi-Speed” 0.1 I2C fitted above the standard USB logo. The reason to avoid RS-232 RS-423 use of the new spec version 2.0 as a generic name is 0.5 0 10 100 1000 that this version includes all the older versions and Backplane Length (meters) Cable Length (meters) speeds as well as the new Hi-Speed specs. So USB 2.0 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 8 compliance does NOT imply Hi-Speed (480 Mbits/sec). ICs can be compliant with USB 2.0 specifications yet Slide 8 only be capable of the older ‘full speed’ or 12 Mbits/sec. The various data transmission rates vs length or cable or backplane length of the different transmission standards are shown in Slide 8. Bus characteristics compared Data rat e Len gth No d es Node number Bu s (bits / sec) ( meter s) Length limiting f actor Typ.number limiting f actor Speed of various connectivity methods (bits/sec) I2 C I2C w ith buf fer 400k 400k 2 100 w iring capacitance propagation delays 20 an y 400pF max no limit I2 C high speed 3.4M 0.5 w iring capacitance 5 100pF max CAN 1 w ire 33k 100 total capacitance 32 load resistance and CAN (1 Wire) 33 kHz (typ) 5k 10km transceiver cur r ent CA N diff erential propagation delays 100 I2C (‘Industrial’, and SMBus) 125k 500 100 kHz 1M 40 drive SPI 110 kHz (original speed) USB (low - speed, 1.1) 1.5M 3 cable specs 2 bus specs CAN (fault tolerant) 125 kHz USB ( full - speed, 1.1) 1.5/12M 25 5 cables linking 6 nodes 127 bus and hub specs I2C 400 kHz Hi- Spe ed USB (2.0) 480M ( 5m cable node to node) IEEE-1394 100 to 400M+ 72 16 hops, 4.5M each 63 6-bit address CAN (high speed) 1 MHz I2C ‘High Speed mode’ 3.4 MHz USB (1.1) 1.5 MHz or 12 MHz SCSI (parallel bus) 40 MHz Fast SCSI 8-80 MHz Ultra SCSI-3 18-160 MHz Firewire / IEEE1394 400 MHz DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 10 Hi-Speed USB (2.0) 480 MHz Slide 10 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 9 In Slide 10 we look at three important characteristics: Slide 9 • Speed, or data rate • Number of devices allowed to be connected (to Increasing fast serial transmission specifications are share the bus wires) shown in Slide 9. Proper treatment of the 480 MHz • Total length of the wiring version of USB - trying to beat the emerging 400 MHz 1394a spec - that is looking to an improved ‘b’ spec - - Numbers are supposed to be realistic estimates but are etc is beyond the scope of this presentation. Philips is based on meeting bus specifications. But rules are made developing leading-edge components to support both to be broken! When buffered, I2C can be limited by USB and 1394 buses. wiring propagation delays but it is still possible to run much longer distances by using slower clock rates and Today the path forward in USB is built on “OTG” (On maybe also compromising the bus rise and fall-time The Go) applications but the costs and complexity of specifications on the buffered bus because it is not this are probably beyond the limits of many customers. bound to conform to I2C specifications. If designers are identified as designing for large international markets then please contact the USB The figure in Slide 10 limiting I2C range by group for additional support, particularly of Host and propagation delays is conservative and allows for OTG solutions. Apologies for inclusion of the parallel published response delays in chips like older E2 SCSI bus. It is intended for comparison purposes and memories. Measured chip responses are typically < 700 ns and that allows for long cable delays and/or 5
- 6. AN10216-01 I2C Manual operation well above 100 kHz with the P82B96. The all the bits and rebuilds the (parallel) byte and puts it in theoretical round-trip delay on 100 m of cable is only a buffer. approx 1 µs and the maximum allowed delay, assuming zero delays in ICs, is about 3 µs at 100 kHz. The Along with converting between serial and parallel, the figures for CAN are not quite as conservative; they are UART does some other things as a byproduct (side the ‘often quoted values’. The round trip delay in 10 effect) of its primary task. The voltage used to represent km cable is about 0.1 ms while 5 kbps implies 0.2 ms bits is also converted (changed). Extra bits (called start nominal bit time, and a need to sample during the and stop bits) are added to each byte before it is second half of the bit time. That is under the user’s transmitted. Also, while the flow rate (in bytes/s) on the control, but needs attention. parallel bus speed inside the computer is very high, the flow rate out the UART on the serial port side of it is USB 2 and IEEE-1394 are still ‘emerging standards’. much lower. The UART has a fixed set of rates Figures quoted may not be practical; they are just based (speeds) that it can use at its serial port interface. on the specification restrictions. UART - Applications UART Overview Server Public / Private LAN application Server Client Client Processor Digital Telephone / Internet What is UART? Processor Network Serial Interface Parallel Interface Processor Processor t t tt tt (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) Datacom t Datacom r rModem Analog or Digital Modem rr Modem Datacom rr Datacom controller r Modem controller controller x x x xx xx controller • Communication standard implemented in the 60’s. WAN application Serial Interface • Simple, universal, well understood and well supported. Appliance Terminals • Slow speed communication standard: up to 1 Mbits/s • Entertainment • Asynchronous means that the data clock is not included in • Home Security the data: Sender and Receiver must agree on timing Cash parameters in advance. register • Robotics Display • “Start” and “Stop” bits indicates the data to be sent Address • Automotive Micro Memory Interface to Micro Data • Parity information can also be sent contr. contr. UART Memory Server • Cellular DUART DUART SC28L92 SC28L92 • Medical Bar code 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Printer reader DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 12 Start bit 8 Bit Data Stop bit Parity Information DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 11 Slide 12 Slide 11 SPI Overview UARTs (Universal Asynchronous Receiver What is SPI? Transmitter) are serial chips on your PC motherboard • Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a 4-wire full-duplex (or on an internal modem card). The UART function synchronous serial data link: may also be done on a chip that does other things as – SCLK: Serial Clock – MOSI: Master Out Slave In - Data from Master to Slave well. On older computers like many 486's, the chips – MISO: Master In Slave Out - Data from Slave to Master were on the disk IO controller card. Still older – SS: Slave Select computers have dedicated serial boards. • Originally developed by Motorola • Used for connecting peripherals to each other and to microprocessors The UARTs purpose is to convert bytes from the PC's • Shift register that serially transmits data to other SPI devices parallel bus to a serial bit-stream. The cable going out • Actually a “3 + n” wire interface with n = number of devices of the serial port is serial and has only one wire for each • Only one master active at a time direction of flow. The serial port sends out a stream of • Various Speed transfers (function of the system clock) bits, one bit at a time. Conversely, the bit stream that DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview enters the serial port via the external cable is converted 13 to parallel bytes that the computer can understand. UARTs deal with data in byte-sized pieces, which is Slide 13 conveniently also the size of ASCII characters. The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) circuit is a Say you have a terminal hooked up to your PC. When synchronous serial data link that is standard across you type a character, the terminal gives that character to many Motorola microprocessors and other peripheral its transmitter (also a UART). The transmitter sends chips. It provides support for a high bandwidth (1 mega that byte out onto the serial line, one bit at a time, at a baud) network connection amongst CPUs and other specific rate. On the PC end, the receiving UART takes devices supporting the SPI. 6
- 7. AN10216-01 I2C Manual synchronized by the serial clock (SCLK). One bit of SPI - How are the connected devices recognized? data is transferred for each clock cycle. Four clock SCLK SCLK SLAVE 1 modes are defined for the SPI bus by the value of the MOSI MOSI MISO MISO clock polarity and the clock phase bits. The clock SS 1 SS 2 SS polarity determines the level of the clock idle state and SS 3 SCLK MOSI SLAVE 2 the clock phase determines which clock edge places MASTER MISO SS new data on the bus. Any hardware device capable of SLAVE 3 operation in more than one mode will have some SCLK MOSI method of selecting the value of these bits. MISO SS • Simple transfer scheme, 8 or 16 bits CAN Overview • Allows many devices to use SPI through the addition of a shift register • Full duplex communications What is CAN ? (Controller Area Network) • Number of wires proportional to the number of devices in the bus DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 14 • Proposed by Bosch with automotive applications in mind (and promoted by CIA - of Germany - for industrial applications) Slide 14 • Relatively complex coding of the messages • Relatively accurate and (usually) fixed timing The SPI is essentially a “three-wire plus slave selects” • All modules participate in every communication serial bus for eight or sixteen bit data transfer • Content-oriented (message) addressing scheme applications. The three wires carry information between devices connected to the bus. Each device on the bus acts simultaneously as a transmitter and receiver. Two of the three lines transfer data (one line for each Filter Frame Filter direction) and the third is a serial clock. Some devices may be only transmitters while others only receivers. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 15 Generally, a device that transmits usually possesses the capability to receive data also. An SPI display is an Slide 15 example of a receive-only device while EEPROM is a receiver and transmit device. CAN objective is to achieve reliable communications in The devices connected to the SPI bus may be classified relatively critical control system applications e.g. as Master or Slave devices. A master device initiates an engine management or anti-lock brakes. There are information transfer on the bus and generates clock and several aspects to reliability - availability of the bus control signals. A slave device is controlled by the when important data needs to be sent, the possibility of master through a slave select (chip enable) line and is bits in a message being corrupted by noise etc., and active only when selected. Generally, a dedicated select electrical/mechanical failure modes in the wiring. line is required for each slave device. The same device At least a ceramic resonator and possibly a quartz can possess the functionality of a master and a slave but crystal are needed to generate the accurate timing at any point of time, only one master can control the needed. The clock and data are combined and 6 ‘high’ bus in a multi-master mode configuration. Any slave bits in succession is interpreted as a bus error. So the device that is not selected must release (make it high clock and bit timings are important. All connected impedance) the slave output line. modules must use the same timings. All modules are The SPI bus employs a simple shift register data looking for any error in the data at any point on the transfer scheme: Data is clocked out of and into the wiring and will report that error so the message can be active devices in a first-in, first-out fashion. It is in this re-sent etc. manner that SPI devices transmit and receive in full duplex mode. All lines on the SPI bus are unidirectional: The signal on the clock line (SCLK) is generated by the master and is primarily used to synchronize data transfer. The master-out, slave-in (MOSI) line carries data from the master to the slave and the master-in, slave-out (MISO) line carries data from the slave to the master. Each slave device is selected by the master via individual select lines. Information on the SPI bus can be transferred at a rate of near zero bits per second to 1 Mbits per second. Data transfer is usually performed in eight/sixteen bit blocks. All data transfer is 7
- 8. AN10216-01 I2C Manual CAN protocol CAN Bus Advantages Start Of Frame Identifier • Accepted standard for Automotive and industrial applications Remote Transmission Request – interfacing between various vendors easier to implement Identifier Extension Data Length Code • Freedom to select suitable hardware Data – differential or 1 wire bus Cyclic Redundancy Check • Secure communications, high Level of error detection Acknowledge End Of Frame – 15 bit CRC messages (Cyclic Redundancy Check) Intermission Frame – Reporting / logging Space – Faulty devices can disconnect themselves – Low latency time – Configuration flexibility • High degree of EMC immunity (when using Si-On-Insulator • Very intelligent controller requested to generate such protocol technology) DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 16 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 17 Slide 16 Slide 17 Like I2C, the CAN bus wires are pulled by resistors to I2C products from many manufacturers are all their resting state called a ‘recessive’ state. When a compatible but CAN hardware will be selected and transceiver drives the bus it forces a voltage called the dedicated for each particular system design. Some CAN ‘dominant’ state. The identifier indicates the meaning transceivers will be compatible with others, but that is of the data, not the intended recipient. So all nodes more likely to be the exception than the rule. CAN receive and ‘filter’ this identifier and can decide designs are usually individual systems that are not whether to act on the data or not. So the bus is using intended to be modified. Philips parts greatly enhance ‘multicast’ - many modules can act on the message, and the feature of reliability by their ability to use part- all modules are checking the message for transmission broken bus wiring and disconnect themselves if they are errors. Arbitration is ‘bit wise’ like I2C - the module recording too many bus errors. forcing a ‘1’ beats a module trying for a ‘0’ and the loser withdraws to try again later. There are several aspects to reliability - availability of the bus when important data needs to be sent, the - DLC: data length code possibility of bits in a message being corrupted by noise - CRC: cyclic redundancy check (remainder of a etc., and the consequences of electrical/mechanical division calculation). All devices that pass the CRC failure modes in the wiring. All these aspects are treated will acknowledge or will generate an error flag seriously by the CAN specifications and the suppliers after the data frame finishes. of the interface ICs - for example Philips believes - ACK: acknowledge. conventional high voltage IC processes are not good - Error frame: (at least) 6 consecutive dominant bits enough and uses Silicon-on-insulator technology to then 7 recessive bits. increase ruggedness and avoid the alternative of using common-mode chokes for protection. To give an A message ‘filter’ can be programmed to test the 11-bit example of immunity, a transceiver on 5 V must be able identifier and one or two bytes of the data (In general to cope with jump-start and load-dump voltages on its up to 32 bits) to decide whether to accept the message supply or bus wires. That is 40 V on the supply and +/- and issue an interrupt. It could also look at all of the 40 V on the bus lines, plus transients of –150 V/+100 V 29-bit identifier. capacitively coupled from a pulse generator in a test circuit! 8
- 9. AN10216-01 I2C Manual USB Overview USB Bus Advantages What is USB ? (Universal Serial Bus) • Hot pluggable, no need to open cabinets • Originally a standard for connecting PCs to peripherals • Automatic configuration • Defined by Intel, Microsoft, … • Up to 127 devices can be connected together • Intended to replace the large number of legacy ports in the PC • Push for USB to become THE standard on PCs • Single master (= Host) system with up to 127 peripherals – standard for iMac, supported by Windows, now on > 99%of PCs • Simple plug and play; no need to open the PC • Interfaces (bridges) to other communication channels exist • Standardized plugs, ports, cables – USB to serial port (serial port vanishing from laptops) • Has over 99% penetration on all new PCs – USB to IrDA or to Ethernet • Adapting to new requirements for flexibility of Host function • Extreme volumes force down IC and hardware prices – New Hardware/Software allows dynamic exchanging of Host/Slave • Protocol is evolving fast roles – PC is no longer the only system Host. Can be a camera or a printer. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 20 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 18 Slide 20 Slide 18 USB aims at mass-market products and design-ins may USB is the most complex of the buses presented here. be less convenient for small users. The serial port is While its hardware and transceivers are relatively vanishing from the laptop and gone from iMac. There simple, its software is complex and is able to efficiently are hardware bridges available from USB to other service many different applications with very different communication channels but there can be higher power data rates and requirements. It has a 12 Mbps rate (with consumption to go this way. Philips is innovating its 200 Mbps planned) over a twisted pair with a 4-pin USB products to minimize power and offer maximum connector (2 wires are power supply). It also is limited flexibility in system design. to short distances of at most 5 meters (depends on configuration). Linux supports the bus, although not all devices that can plug into the bus are supported. It is Versions of USB specification synchronous and transmits in special packets like a • USB 1.1 network. Just like a network, it can have several devices – Established, large PC peripheral markets – Well controlled hardware, special 4-pin plugs/sockets attached to it. Each device on it gets a time-slice of – 12MBits/sec (normal) or 1.5Mbits/sec (low speed) data rate exclusive use for a short time. A device can also be • USB 2.0 guaranteed the use of the bus at fixed intervals. One – Challenging IEEE1394/Firewire for video possibilities – 480 MHz clock for Hi-Speed means it’s real “UHF” transmission device can monopolize it if no other device wants to use – Hi-Speed option needs more complex chip hardware and software – Hi-Speed component prices about x 2 compared to full speed it. • USB “OTG” (On The Go) Supplement USB Topology (original concept, USB1.1, USB2.0) – New hardware - smaller 5-pin plugs/sockets – Lower power (reduced or no bus-powering) Host Monitor DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 21 − One PC host per system − Provides power to peripherals Host 5m Hub Hub − Provides ports for connecting more PC 5m Slide 21 peripheral devices. 5m 5m 5m − Provides power, terminations − External supply or Bus Powered For USB 1.1 and 2.0 the hardware is well established. Device, Interfaces and Endpoints The shape of the plug/socket at Host end is different − Device is a collection of data interface(s) Device from the shape at the peripheral end. USB is always a − Interface is a collection of single point-to-point link over the cable. To allow endpoints (data channels) − Endpoint associated with FIFO(s) - connection of multiple peripherals a HUB is introduced. for data I/O interfacing The Hub functions to multiplex the data from the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 19 ‘downstream’ peripherals into one ‘upstream’ data linkage to the Host. In Hi-Speed systems it is necessary Slide 19 for the system to start communicating as a normal USB 1.1 system and then additional hardware (faster Slide 19 shows a typical USB configuration. transceivers etc) is activated to allow a higher speed. The Hi-Speed system is much more complex (hardware/software) than normal USB (1.1). For USB 9
- 10. AN10216-01 I2C Manual and Hi-Speed the development of ‘stand-alone’ Host specified to well over 1A at 8-30 volts (approx) - ICs such as ISP1161 and ISP1561 allowed the Host leading to some unkind references to a ‘fire’ wire! function to be embedded in products such as Digital Still Cameras or printers so that more direct transfer of 1394 software or message format consists of timeslots data was possible without using the path Camera → PC within which the data is sent in blocks or ‘channels’. → Printer under control of the PC as the host. That two For real-time data transfer it is possible to guarantee the step transfer involves connecting the camera to the PC availability of one or more channels to guarantee a (one USB cable) and also the PC to the printer (second certain data rate. This is important for video because USB cable). The goal is to do without the PC. it’s no good sending a packet of corrected data after a blank has appeared on the screen! The next step involved the shrinking of the USB connector hardware, to make it more compatible with Microsoft says, “IEEE 1394 defines a single small products like digital cameras, and making interconnection bus that serves many purposes and user provision (extra pin) for dynamic exchanging of Host scenarios. In addition to its adoption by the consumer and slave device functions without removing the USB electronics industry, PC vendors—including Compaq, cable for reversing the master/slave connectors. The Dell, IBM, Fujitsu, Toshiba, Sony, NEC, and new hardware and USB specification version is called Gateway—are now shipping Windows-based PCs with “On The Go” (OTG). The OTG specification no longer 1394 buses. requires the Host to provide the 1/2 A power supply to peripherals and indeed allows arbitration to determine The IEEE 1394 bus complements the Universal Serial whether Host or peripheral (or neither) will provide the Bus (USB) and is particularly optimized for connecting system power. digital media devices and high-speed storage devices to a PC. It is a peer-to-peer bus. Devices have more built- 1394 Overview in intelligence than USB devices, and they run independently of the processor, resulting in better performance. What is IEEE1394 ? • A bus standard devised to handle the high data throughput The 100-, 200-, and 400-Mbps transfer rates currently requirements of MPEG-2 and DVD specified in the IEEE 1394a standard and the proposed – Video requires constant transfer rates with guaranteed bandwidth enhancements in 1394b are well suited to meeting the – Data rates 100, 200, 400 Mbits/sec and looking to 3.2 Gb/s • Also known as “Firewire” bus (registered trademark of Apple) throughput requirements of multiple streaming • Automatically re-configures itself as each device is added input/output devices connected to a single PC. The – True plug & play licensing fee for use of patented IEEE 1394 technology – Hot-plugging of devices allowed has been established at US $0.25 per system. • Up to 63 devices, 4.5 m cable ‘hops’, with max. 16 hops • Bandwidth guaranteed With connectivity for storage, scanners, printers, and other types of consumer A/V devices, IEEE 1394 gives users all the benefits of a great legacy-free connector— DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 22 a true Plug and Play experience and hassle-free PC connectivity.” Slide 22 1394 Topology 1394 may claim to be more proven or established than USB but both are ‘emerging’ specifications that are trying to out-do each other! Philips strongly supports BOTH. 1394 was chosen by Philips as the bus to link set-top boxes, DVD, and digital TVs. 1394 has an ’a’ version taking it to 400 Mb/sec and more recently a ‘b’ version for higher speed and to allow longer cable runs, • Physical layer – Analog interface to the cable perhaps 100 meter hops! – Simple repeater – Performs bus arbitration 1394 sends information over a PAIR of twisted pairs. • Link layer – Assembles and dis-assembles bus packets One for data, the other is the clocking strobe. The clock – Handles response and acknowledgment functions is simply recovered by an Ex-Or of the data and strobe • Host controller line signals. No PLL is needed. There is provision for – Implements higher levels of the protocol DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 23 lots of remote device powering via the cable if the 6-pin plug connection version is used. The power wires are Slide 23 10
- 11. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Overview • Each device connected to the bus is software addressable by a unique address and simple What is I2C ? (Inter-IC) master/slave relationships exist at all times; masters can operate as master-transmitters or as • Originally, bus defined by Philips providing a simple way to master-receivers. talk between IC’s by using a minimum number of pins • It’s a true multi-master bus including collision • A set of specifications to build a simple universal bus detection and arbitration to prevent data corruption guaranteeing compatibility of parts (ICs) from different manufacturers: if two or more masters simultaneously initiate data – Simple Hardware standards transfer. – Simple Software protocol standard • Serial, 8-bit oriented, bi-directional data transfers • No specific wiring or connectors - most often it’s just PCB can be made at up to 100 kbit/s in the Standard- tracks mode, up to 400 kbit/s in the Fast-mode, or up to • Has become a recognised standard throughout our industry 3.4 Mbit/s in the High-speed mode. and is used now by ALL major IC manufacturers • On-chip filtering (50 ns) rejects spikes on the bus data line to preserve data integrity. • DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview The number of ICs that can be connected to the 24 same bus segment is limited only by the maximum Slide 24 bus capacitive loading of 400 pF. Originally, the I2C bus was designed to link a small number of devices on a single card, such as to manage the tuning of a car radio or TV. The maximum I2C Bus - Software allowable capacitance was set at 400 pF to allow proper • Simple procedures that allow communication to start, to rise and fall times for optimum clock and data signal achieve data transfer, and to stop – Described in the Philips protocol (rules) integrity with a top speed of 100 kbps. In 1992 the – Message serial data format is very simple standard bus speed was increased to 400 kbps, to keep – Often generated by simple software in general purpose micro – Dedicated peripheral devices contain a complete interface up with the ever-increasing performance requirements – Multi-master capable with arbitration feature of new ICs. The 1998 I2C specification, increased top speed to 3.4 Mbits/sec. All I2C devices are designed to • Each IC on the bus is identified by its own address code – Address has to be unique be able to communicate together on the same two-wire bus and system functional architecture is limited only • The master IC that initiates communication provides the clock signal (SCL) by the imagination of the designer. – There is a maximum clock frequency but NO MINIMUM SPEED But while its application to bus lengths within the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 25 confines of consumer products such as PCs, cellular phones, car radios or TV sets grew quickly, only a few Slide 25 system integrators were using it to span a room or a building. The I2C bus is now being increasingly used in I2C Communication Procedure multiple card systems, such as a blade servers, where One IC that wants to talk to another must: the I2C bus to each card needs to be isolatable to allow 1) Wait until it sees no activity on the I2C bus. SDA for card insertion and removal while the rest of the and SCL are both high. The bus is 'free'. system is in operation, or in systems where many more 2) Put a message on the bus that says 'its mine' - I devices need to be located onto the same card, where have STARTED to use the bus. All other ICs then the total device and trace capacitance would have LISTEN to the bus data to see whether they might exceeded 400 pF. be the one who will be called up (addressed). 3) Provide on the CLOCK (SCL) wire a clock signal. New bus extension & control devices help expand the It will be used by all the ICs as the reference time I2C bus beyond the 400 pF limit of about 20 devices at which each bit of DATA on the data (SDA) wire and allow control of more devices, even those with the will be correct (valid) and can be used. The data on same address. These new devices are popular with the data wire (SDA) must be valid at the time the designers as they continue to expand and increase the clock wire (SCL) switches from 'low' to 'high' range of use of I2C devices in maintenance and control voltage. applications. 4) Put out in serial form the unique binary 'address' (name) of the IC that it wants to communicate I2C Features with. • Only two bus lines are required: a serial data line 5) Put a message (one bit) on the bus telling whether (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL). it wants to SEND or RECEIVE data from the other chip. (The read/write wire is gone!) 11
- 12. AN10216-01 I2C Manual 6) Ask the other IC to ACKNOWLEDGE (using one But several Masters could control one Slave, at bit) that it recognized its address and is ready to different times. Any ‘smart’ communications must be communicate. via the transferred DATA, perhaps used as address info. 7) After the other IC acknowledges all is OK, data The I2C bus protocol does not allow for very complex can be transferred. systems. It’s a ‘keep it simple’ bus. But of course 8) The first IC sends or receives as many 8-bit words system designers are free to innovate to provide the of data as it wants. After every 8-bit data word the complex systems - based on the simple bus. sending IC expects the receiving IC to acknowledge the transfer is going OK. Serial Bus Comparison Summary 9) When all the data is finished the first chip must free up the bus and it does that by a special Pros and Cons of the different buses message called 'STOP'. It is just one bit of CAN USB SPI UART I2 C information transferred by a special 'wiggling' of • Well Known • Secure • Fast • Fast • Simple the SDA/SCL wires of the bus. • Cost effective • Fast • Plug&Play HW • Universally • Well known accepted • Simple • Simple • Universally The bus rules say that when data or addresses are being • Low cost • Low cost accepted • Plug&Play • Large Portfolio sent, the DATA wire is only allowed to be changed in • Large portfolio voltage (so, '1', '0') when the voltage on the clock line is • Cost effective LOW. The 'start' and 'stop' special messages BREAK • Limited • Complex • Powerful master • No Plug&Play required • Limited speed functionality HW that rule, and that is how they are recognized as special. • Point to Point • Automotive oriented • No Plug&Play • No “fixed” SW - Specific standard • Limited drivers required portfolio • Expensive How are the connected devices firmware recognized? DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 27 • Master device ‘polls’ used a specific unique identification or Slide 27 “addresses” that the designer has included in the system • Devices with Master capability can identify themselves to Most Philips CAN devices are not plug & play. That is other specific Master devices and advise their own specific address and functionality because for MOST chips the system needs to be fixed – Allows designers to build ‘plug and play’ systems and nothing can be added later. That is because an – Bus speed can be different for each device, only a maximum limit added chip is EXPECTED to take part in EVERY data • Only two devices exchange data during one ‘conversation’ conversation but will not know the clock speed and cannot synchronize. That means it falsely reports a bus timing error on every message and crashes the system. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview Philips has special transceivers that allow them listen to 26 the bus without taking part in the conversations. This Slide 26 special feature allows them to synchronize their clocks and THEN actively join in the conversations. So, from Any device with the ability to initiate messages is Philips, it becomes POSSIBLE to do some minor called a ‘master’. It might know exactly what other plug/play on a CAN system. chips are connected, in which case it simply addresses the one it wants, or there might be optional chips and it USB/SPI/MicroWire and mostly UARTS are all just then checks what’s there by sending each address and 'one point to one point' data transfer bus systems. USB seeing whether it gets any response (acknowledge). then uses multiplexing of the data path and forwarding of messages to service multiple devices. An example might be a telephone with a micro in it. In some models, there could be EEPROM to guarantee Only CAN and I2C use SOFTWARE addressing to memory data, in some models there might be an LCD determine the participants in a transfer of data between display using an I2C driver. There can be software two (I2C) or more (CAN) chips all connected to the written to cover all possibilities. If the micro finds a same bus wires. I2C is the best bus for low speed display then it drives it, otherwise the program is maintenance and control applications where devices arranged to skip that software code. I2C is the simplest may have to be added or removed from the system. of the buses in this presentation. Only two chips are involved in any one communication - the Master that initiates the signals and the one Slave that responded when addressed. 12
- 13. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Theory Of Operation • Compatible with a number of processors with integrated I2C ports (micro 8,16,32 bits) in 8048, I2C Introduction 80C51 or 6800 and 68xxx architectures • I2 C bus = Inter-IC bus • Easily emulated in software by any microcontroller • Bus developed by Philips in the 80’s • Available from an important number of component • Simple bi-directional 2-wire bus: manufacturers – serial data (SDA) – serial clock (SCL) • Has become a worldwide industry standard and used by all major IC manufacturers I2C Hardware architecture • Multi-master capable bus with arbitration feature • Master-Slave communication; Two-device only communication Pull-up resistors Typical value 2 kΩ to 10 kΩ • Each IC on the bus is identified by its own address code • The slave can be a: – receiver-only device – transmitter with the capability to both receive and send data DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 29 SCL Open Drain structure (or Open Collector) for both SCL and SDA Slide 29 10 pF Max The I2C bus is a very easy bus to understand and use. Slides 29 and 30 give a good explanation of bus specifics and the different speeds. Many people have DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 31 asked where rise time is measured and the specification stipulates it’s between 30% and 70% of VDD. This Slide 31 becomes important when buffers ‘distort’ the rising edges on the bus. By keeping any waveform distortions I2C Bus Terminology below 30% of VDD, that portion of the rising edge will • Transmitter - the device that sends data to the bus. not be counted as part of the formal rise time. A transmitter can either be a device that puts data on the bus of its own accord (a ‘master- I2C by the numbers transmitter’), or in response to a request from data Standard-Mode Fast-Mode High-Speed- Mode from another devices (a ‘slave-transmitter’). Bit Rate 0 to 100 0 to 400 0 to 0 to • Receiver - the device that receives data from the (kbits/s) 1700 3400 Max Cap Load 400 400 400 100 bus. (pF) Rise time • Master - the component that initializes a transfer, 1000 300 160 80 (ns) Spike Filtered generates the clock signal, and terminates the N/A 50 10 (ns) transfer. A master can be either a transmitter or a Address Bits 7 and 10 7 and 10 7 and 10 Rise Time receiver. VDD • Slave - the device addressed by the master. A slave VIH 0.7xVDD can be either receiver or transmitter. • Multi-master - the ability for more than one VIL 0.3xVDD master to co-exist on the bus at the same time VOL 0.4 V @ 3 mA Sink Current GND without collision or data loss. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 30 • Arbitration - the prearranged procedure that authorizes only one master at a time to take control Slide 30 of the bus. • Synchronization - the prearranged procedure that 2 I C is a low to medium speed serial bus with an synchronizes the clock signals provided by two or impressive list of features: more masters. • Resistant to glitches and noise • SDA - data signal line (Serial DAta) • Supported by a large and diverse range of • SCL - clock signal line (Serial CLock) peripheral devices • A well-known robust protocol • A long track record in the field • A respectable communication distance which can be extended to longer distances with bus extenders 13
- 14. AN10216-01 I2C Manual START/STOP conditions I2C Address, Basics µcon- µcon- • Data on SDA must be stable when SCL is High troller I/O A/D D/A LCD RTC troller II SCL SDA A0 1010 0 1 1 A1 EEPROM A2 1010A2A1A0R/W New devices or functions can be Fixed Hardware easily ‘clipped on to • Exceptions are the START and STOP conditions Selectable an existing bus! • Each device is addressed individually by software • Unique address per device: fully fixed or with a programmable part through hardware pin(s). S P • Programmable pins mean that several same devices can share the same bus • Address allocation coordinated by the I2C-bus committee • 112 different types of devices max with the 7-bit format (others reserved) DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 32 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 33 Slide 32 Slide 33 START and STOP Conditions HARDWARE CONFIGURATION Within the procedure of the I2C bus, unique situations Slide 33 shows the hardware configuration of the I2C arise which are defined as START (S) and STOP (P) bus. The ‘bus’ wires are named SDA (serial data) and conditions. SCL (serial clock). These two bus wires have the same configuration. They are pulled-up to the logic ‘high’ START: A HIGH to LOW transition on the SDA line level by resistors connected to a single positive supply, while SCL is HIGH usually +3.3 V or +5 V but designers are now moving to +2.5 V and towards 1.8 V in the near future. STOP: A LOW to HIGH transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH All the connected devices have open-collector (open- drain for CMOS - both terms mean only the lower The master always generates START and STOP transistor is included) driver stages that can transmit conditions. The bus is considered to be busy after the data by pulling the bus low, and high impedance sense START condition. The bus is considered to be free amplifiers that monitor the bus voltage to receive data. again a certain time after the STOP condition. The bus Unless devices are communicating by turning on the stays busy if a repeated START (Sr) is generated lower transistor to pull the bus low, both bus lines instead of a STOP condition. In this respect, the remain ‘high’. To initiate communication a chip pulls START (S) and repeated START (Sr) conditions are the SDA line low. It then has the responsibility to drive functionally identical. The S symbol will be used as a the SCL line with clock pulses, until it has finished, and generic term to represent both the START and repeated is called the bus ‘master’. START conditions, unless Sr is particularly relevant. BUS COMMUNICATION Detection of START and STOP conditions by devices Communication is established and 8-bit bytes are connected to the bus is easy if they incorporate the exchanged, each one being acknowledged using a 9th necessary interfacing hardware. However, data bit generated by the receiving party, until the data microcontrollers with no such interface have to sample transfer is complete. The bus is made free for use by the SDA line at least twice per clock period to sense the other ICs when the ‘master’ releases the SDA line transition. during a time when SCL is high. Apart from the two special exceptions of start and stop, no device is allowed to change the state of the SDA bus line unless the SCL line is low. If two masters try to start a communication at the same time, arbitration is performed to determine a “winner” (the master that keeps control of the bus and continue the transmission) and a “loser” (the master that must abort its transmission). The two masters can even generate a few cycles of the clock and data that ‘match’, but eventually one will output a ‘low’ when the other tries for a ‘high’. The ‘low’ wins, so the 14
- 15. AN10216-01 I2C Manual ‘loser’ device withdraws and waits until the bus is freed master releases SDA line to accomplish the again. Acknowledge phase. If the other device is connected to the bus, and has decoded and recognized its ‘address’, it There is no minimum clock speed; in fact any device will acknowledge by pulling the SDA line low. The that has problems to ‘keep up the pace’ is allowed to responding chip is called the bus ‘slave’. ‘complain’ by holding the clock line low. Because the device generating the clock is also monitoring the voltage on the SCL bus, it immediately ‘knows’ there is I2C Read and Write Operations (1) a problem and has to wait until the device releases the • Write to a Slave device SCL line. < n data bytes > Master SCL Slave S slave address W W A data S slave address A data A data dataP A A transmitter receiver A P SDA For full details of the bus capabilities refer to Philips “0” = Write Each byte is acknowledged by the slave device Semiconductors Specification document ‘The I2C bus The master is a “MASTER - TRANSMITTER”: –it transmits both Clock and Data during the all communication specification’ or ‘The I2C bus from theory to practice’ • Read from a Slave device book by Paret and Fenger published by John Wiley & < n data bytes > SCL receiver Sons. transmitter S slave address R A data A data A P SDA “1” = Read Each byte is acknowledged by the master device (except the last one, just before the STOP condition) The I2C specification and other useful application The master is a “MASTER TRANSMITTER then MASTER - RECEIVER”: information can be found on Philips Semiconductors – it transmits Clock all the time – it sends slave address data and then becomes a receiver web site at DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/i2c/ 35 Slide 35 I2C Address, 7-bit and 10-bit formats • The 1st byte after START determines the Slave to be addressed Terminology for Bus Transfer • Some exceptions to the rule: • F (FREE) - the bus is free; the data line SDA and – “General Call” address: all devices are addressed : 0000 000 + R/W = 0 – 10-bit slave addressing : 1111 0XX + R/W = X the SCL clock are both in the high state. •7-bit addressing • S (START) or SR (Repeated START) - data transfer begins with a start condition (not a start S X X X X X X X R/W A DATA bit). The level of the SDA data line changes from The 7 bits Only one device will acknowledge high to low, while the SCL clock line remains high. • 10-bit addressing When this occurs, the bus is ‘busy’. S 1 1 1 1 0 X X R/W A1 X X X X X X X X A2 DATA • C (CHANGE) - while the SCL clock line is low, XX = the 2 MSBs The 8 remaining the data bit to be transferred can be applied to the More than one device can bits Only one device will SDA data line by a transmitter. During this time, acknowledge acknowledge DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 34 SDA may change its state, as along as the SCL line remains low. • D (DATA) - a high or low bit of information on the Slide 34 SDA data line is valid during the high level of the SCL clock line. This level must be maintained Slide 34 shows the I2C address scheme. Any I2C device stable during the entire time that the clock remains can be attached to the common I2C bus and they talk high to avoid misinterpretation as a Start or Stop with each other, passing information back and forth. condition. Each device has a unique 7-bit or 10-bit I2C address. For 7-bit devices, typically the first four bits are fixed, • P (STOP) - data transfer is terminated by a stop the next three bits are set by hardware address pins (A0, condition, (not a stop bit). This occurs when the A1, and A2) that allow the user to modify the I2C level on the SDA data line passes from the low address allowing up to eight of the same devices to state to the high state, while the SCL clock line operate on the I2C bus. These pins are held high to VCC, remains high. When the data transfer has been sometimes through a resistor, or held low to GND. terminated, the bus is free once again. The last bit of the initial byte indicates if the master is going to send (write) or receive (read) data from the slave. Each transmission sequence must begin with the start condition and end with the stop condition. On the 8th clock pulse, SDA is set ‘high’ if data is going to be read from the other device, or ‘low’ if data is going to be sent (write). During its 9th clock, the 15
- 16. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Read and Write Operations (2) Slide 38 shows how multiple masters can synchronize • Combined Write and Read their clocks, for example during arbitration. When bus < n data bytes > < m data bytes > capacitance affects the bus rise or fall times the master S slave address W W S slave address A P A A data data A data dataSr slave address R A A Sr A data A data A P will also adjust its timing in a similar way. “0” = Write Each byte is “1” = Read Each byte is acknowledged acknowledged by the slave device by the master device (except the last one, just before the STOP I2C Protocol - Arbitration • Combined Read and Write condition) < n data bytes > < m data bytes > • Two or more masters may generate a START condition at the same time S slave address R A data A data A S slave address W WA Adata A P slave address Sr data data data P A A • Arbitration is done on SDA while SCL is HIGH - Slaves are not involved A P “1” = Read Each byte is “0” = Write Each byte is acknowledged acknowledged Master 1 loses arbitration DATA1 ≠SDA by the master device by the slave device (except the last one, just before the Re-START condition) DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 36 Slide 36 Slide 36 shows a combined read and write operation. Start command “1” “0” “0” “1” “0” “1” DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 39 Acknowledge; Clock Stretching • Acknowledge Slide 39 Done on the 9th clock pulse and is mandatory Transmitter releases the SDA line Receiver pulls down the SDA line (SCL must be HIGH) If there are two masters on the same bus, there are Transfer is aborted if no acknowledge arbitration procedures applied if both try to take control No acknowledge of the bus at the same time. When two chips try to start Acknowledge communication at the same time they may even generate a few cycles of the clock and data that ‘match’, but eventually one will output a ‘low’ when the other tries for a ‘high’. The ‘low’ wins, so the • Clock Stretching ‘loser’ device withdraws and waits until the bus is freed - Slave device can hold the CLOCK line LOW when performing other functions again. Once a master (e.g., microcontroller) has control, - Master can slow down the clock to accommodate slow slaves no other master can take control until the first master DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 37 sends a stop condition and places the bus in an idle state. Slide 37 Slide 37 shows how the Acknowledge phase is done What do I need to drive the I2C bus? and how slave devices can stretch the clock signal. Most Philips slave devices do not control the clock line. Slave 1 Slave 2 Slave 3 Slave 4 Master I2C BUS I2C Protocol - Clock Synchronization There are 3 basic ways to drive the I2C bus: Vdd 1) With a Microcontroller with on-chip I2C Interface Master 1 Master 2 Bit oriented - CPU is interrupted after every bit transmission (Example: 87LPC76x) Byte oriented - CPU can be interrupted after every byte transmission CLK 1 CLK 2 (Example: 87C552) SCL 2) With ANY microcontroller: 'Bit Banging’ The I2C protocol can be emulated bit by bit via any bi-directional open drain port 3) With a microcontroller in conjunction with bus controller like the PCF8584 or PCA9564 parallel to I2C bus interface IC 1 4 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 40 2 3 Slide 40 • LOW period determined by the longest clock LOW period • HIGH period determined by shortest clock HIGH period Slide 40 shows there are multiple ways to control I2C DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 38 slaves. Slide 38 16
- 17. AN10216-01 I2C Manual • The I2C bus is a de facto world standard that is Pull-up Resistor calculation implemented in over 1000 different ICs (Philips DC Approach - Static Load has > 400) and licensed to more than 70 companies Worst Case scenario: maximum current load that the output transistor can handle 3 mA . This gives us the minimum pull-up resistor value Vdd min - 0.4 V R= With Vdd = 5V (min 4.5 V), Rmin = 1.3 kΩ I2C Bus recovery 3 mA • Typical case is when masters fails when doing a read operation in a slave AC Approach - Dynamic load • SDA line is then non usable anymore because of the “Slave-Transmitter” • maximum value of the rise time: mode. – 1µs for Standard-mode (100 kHz) • Methods to recover the SDA line are: – 0.3 µs for Fast-mode (400 kHz) – Reset the slave device (assuming the device has a Reset pin) • Dynamic load is defined by: – Use a bus recovery sequence to leave the “Slave-Transmitter” mode – device output capacitances V(t) = VDD (1-e -t /RC ) • Bus recovery sequence is done as following: (number of devices) Rising time defined between 30% and 70% 1 - Send 9 clock pulses on SCL line – trace, wiring 2 - Ask the master to keep SDA High until the “Slave-Transmitter” releases Trise = 0.847.RC the SDA line to perform the ACK operation DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 41 3 - Keeping SDA High during the ACK means that the “Master-Receiver” does not acknowledge the previous byte receive Slide 41 4 - The “Slave-Transmitter” then goes in an idle state 5 - The master then sends a STOP command initializing completely the bus Slide 41 shows the typical resistor values needed for DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 42 proper operation. C is the total capacitance on either SDA or SCL bus wire, with R as its pull-up resistor. Slide 42 I2C Designer Benefits Slide 42 shows how a hung bus could be recovered. • Functional blocks on the block diagram correspond The bus can become hung for several reasons, e.g.…. with the actual ICs; designs proceed rapidly from 1. Incorrect power-up and/or reset procedure for block diagram to final schematic. ICs • No need to design bus interfaces because the I2C 2. Power to a chip is interrupted – brown-outs etc bus interface is already integrated on-chip. 3. Noise on the wiring causes false clock or data • Integrated addressing and data-transfer protocol signals allow systems to be completely software-defined. • The same IC types can often be used in many different applications. I2C Protocol Summary • Design-time reduces as designers quickly become START STOP HIGH to LOW transition on SDA while SCL is HIGH LOW to HIGH transition on SDA while SCL is HIGH familiar with the frequently used functional blocks DATA 8-bit word, MSB first (Address, Control, Data) - must be stable when SCL is HIGH represented by I2C bus compatible ICs. - can change only when SCL is LOW - number of bytes transmitted is unrestricted • ICs can be added to or removed from a system ACKNOWLEDGE - done on each 9th clock pulse during the HIGH period - the transmitter releases the bus - SDA HIGH without affecting any other circuits on the bus. - the receiver pulls DOWN the bus line - SDA LOW • Fault diagnosis and debugging are simple; CLOCK - Generated by the master(s) - Maxim um speed specified but NO minimum speed malfunctions can be immediately traced. - A receiver can hold SCL LOW when performing another function (transmitter in a Wait state) • Assembling a library of reusable software modules ARBITRATION - A master can slow down the clock for slow devices - Master can start a transfer only if the bus is free can reduce software development time. - Several masters can start a transfer at the same time - Arbitration is done on SDA line - Master that lost the arbitration must stop sending data I2C Manufacturers Benefits • The simple 2-wire serial I2C bus minimizes DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 43 interconnections so ICs have fewer pins and there are not so many PCB tracks; result - smaller and Slide 43 less expensive PCBs • The completely integrated I2C bus protocol Slide 43 provides a summary of the I2C protocol. eliminates the need for address decoders and other ‘glue logic’ • The multi-master capability of the I2C bus allows rapid testing/alignment of end-user equipment via external connections to an assembly-line • Increases system design flexibility by allowing simple construction of equipment variants and easy upgrading to keep design up-to-date 17
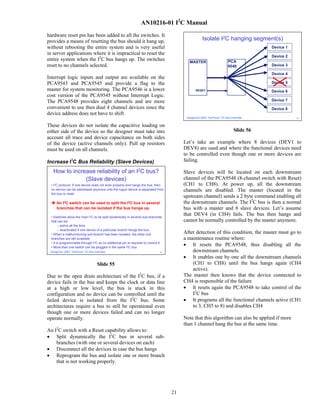
- 18. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Summary - Advantages For example, in an application where 4 identical I2C EEPROMs are used (EE1, EE2, EE3 and EE4), a four • Simple Hardware standard channel PCA9546 can be used. The master is plugged • Simple protocol standard • Easy to add / remove functions or devices (hardware and software) to the main upstream bus while the 4 EEPROMs are • Easy to upgrade applications plugged to the 4 downstream channels (CH1, CH2, • Simpler PCB: Only 2 traces required to communicate between devices CH3 and CH4). If the master needs to perform an • Very convenient for monitoring applications operation on EE3, it will have to: • Fast enough for all “Human Interfaces” applications - Connect the upstream channel to CH3 – Displays, Switches, Keyboards - Simply communicate with EE3. – Control, Alarm systems • Large number of different I2C devices in the semiconductors business EE1, EE2 and EE4 are electrically removed from the • Well known and robust bus main I2C bus as long as CH3 is selected. Some of the I2C multiplexers offer an Interrupt feature, allowing DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 44 collection of the different downstream Interrupts (generated by the downstream devices). An Interrupt Slide 44 output provides the information (transition from High to Low) to the master every time one or more Interrupt Slide 44 summarizes the advantages of the I2C bus. is generated (transition from High to Low) by any of the downstream devices. Overcoming Previous Limitations Address Conflicts I2C Multiplexers: Address Deconflict How to solve I2C address conflicts? I2C EEPROM 1 I2C EEPROM 2 • I2C protocol limitation: when a device does not have its I2C address programmable (fixed), only one same device can be plugged in the same MASTER bus Same I2C devices with same address An I2 C multiplexer can be used to get rid of this limitation I2C EEPROM I2C EEPROM • It allows to split dynamically the main I2C in several sub-branches in order to 1 2 talk to one device at a time • It is programmable through I2C so no additional pins are required for control I2C MULTIPLEXER • More than one multiplexer can be plugged in the same I2C bus MASTER The multiplexer allows to address 1 device • Products then the other one # of Channels Standard w/Interrupt Logic DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 48 2 PCA9540 PCA9542/43 4 PCA9546 PCA9544/45 8 PCA9548 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 47 Slide 48 Slide 47 The SCL/SDA upstream channel fans out to multiple SCx/SDx channels that are selected by the A 7 or 10-bit address that is unique to each device programmable control register. The I²C command is identifies an I2C device. sent via the main I²C bus and is used to select or This address can be: deselect the downstream channels. • Partly fixed, part programmable (allowing to have more than one of the same device on the same bus) The Multiplexers can select none or only one SCx/SDx channels at a time since they were designed primarily • Fully fixed allowing to have only one single same for address conflict resolution such as when multiple device on the device. devices with the same I2C address need to be attached to the same I2C bus and you can only talk to one of the If more than one same “non programmable” device devices at a time. (fully fixed address) is required in a specific application, it is then necessary to temporarily remove These devices are used in video projectors and server the non-addressed device(s) from the bus when talking applications. Other applications include: with the targeted device. I2C multiplexers allow to dynamically split the main I2C bus into 2, 4 or 8 sub- • Address conflict resolution (e.g., SPD EEPROMs I2C buses. Each sub-bus (downstream channel) can be on DIMMs). connected to the main bus (upstream channel) by a • I2C sub-branch isolation simple 2-byte I2C command. 18
- 19. AN10216-01 I2C Manual • I2C bus level shifting (e.g., each individual Multiplexers allow dynamic splitting of the overloaded SCx/SDx channel can be operated at 1.8 V, 2.5 V, I2C bus into several sub-branches with a total capacitive 3.3 V or 5.0 V if the device is powered at 2.5 V). load smaller than the specified 400 pF. Note that this method does not allow the master to access all the buses Interrupt logic inputs for each channel and a combined at the same time. Only part of the bus will be accessible output are included on every multiplexer and provide a at a time. flag to the master for system monitoring. These devices do not isolate the capacitive loading on either side of Multiplexers allow bus splitting but do not have a the device so the designer must take into account all buffering capability. Buffers and repeaters allow trace and device capacitance on both sides of the device increasing the total capacitive load beyond the 400 pF and on any active channels. Pull up resistors must be without splitting the bus in several branches. If a used on all channels PCA9515 is used, the bus can be loaded up to 800 pF with 400 pF on each side of the device. Capacitive Loading > 400 pF (isolation) How to go beyond I2C max cap load? Practical case: Multi-card application • I2C protocol limitation: the maximum capacitive load in a bus is 400 pF. If the load is higher AC parameters will be violated. • The following example shows how to build an application where: An I2C multiplexer can be used to get rid of this limitation – Four identical control cards are used (same devices, same I2Caddress) – Devices in each card are controlled through I2C • It allows to split dynamically the main I2C in several sub-branches in order to – Each card monitors and controls some digital information divide the bus capacitive load – Digital information is: • It is programmable through I2C so no additional pins are required for control 1) Interrupt signals (Alarm monitoring) • More than one multiplexer can be plugged in the same I2C bus 2) Reset signals (device initialization, Alarm Reset) • LIMITATION: All the sub-branches cannot be addressed at the same time – Each card generates an Interrupt when one (or more) device generates an Interrupt (Alarm condition detected) • Products: – The master can handle only one Interrupt signal for all the application # of Channels Standard w/Interrupt Logic 2 PCA9540 PCA9542/43 4 PCA9546 PCA9544/45 8 PCA9548 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 51 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 49 Slide 49 Slide 51 The I2C specification limits the maximum capacitive In this application, 4 identical cards are used. Identical load in the bus to 400 pF. In applications where a means that the same devices are used, and that the I2C higher capacitive load is required, 2 types of devices devices on each card have the same address. Each card can be used: monitors and controls some specific signal and those • I2C multiplexers and switches signals are controlled/monitored through the I2C bus by • I2C buffers and repeaters using a PCA9554 type device. In this application, each card monitors some alarm I2C Multiplexers: Capacitive load split system’s sub system and controls some LEDs for visual status. Each alarm, when triggered, generates an 500 pF Interrupt that is sent to the master for processing. MASTER PCA9554 collects the Interrupt signals and sends a I2C bus “Card General Interrupt” to the master. When the master processes the alarm, it sends a Reset signal to 200 pF I2C bus 2 200 pF the corresponding alarm to clear it. Master receives I2C bus 3 only an Interrupt signal, which is a combination of all 300 pF I2C MULTIPLEXER 300 pF the Interrupt signals in the cards. Since the cards are MASTER identical, it is then necessary to deconflict the different I2C bus 1 100 pF addresses and isolate the cards that are not accessed. The multiplexer splits the bus in two downstream 200 pF busses + 100 pF upstream PCA9544 in this application has 2 functions: DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 50 • Deconflict the I2C addresses by creating 4 sub I2C busses that can be isolated Slide 50 • Collect the Interrupt from each card and propagate a “General Interrupt” to the master 19
- 20. AN10216-01 I2C Manual high level voltage value, determined by the voltage I2C Multiplexers: Multi-card Application applied to the pull up resistors. In applications where - Cards are identical several voltage levels are required (e.g. accommodate - One card is selected / controlled Card 0 Card 1 legacy architecture at 5.0 V with newer devices at a time - PCA9544 collects Interrupt Card 2 working at 3.3 V only), I2C switches allow creating a Card 3 0 Reset bus with different high level voltage values at a I2C bus 0 1 Reset Alarm 1 minimum cost. I2C bus 1 PCA I2C bus 2 Alarm 1 9544 MASTER I2C bus 3 1 PCA 0 Int Int In this example, we have an existing 5.0 V I2C bus and INT INT0 95540 Reset we want to add some new features with devices “non INT1 Sub System 5.0 V tolerant”. An I2C bus can be used. The master INT2 INT3 INT 1 Int controlling the existing and new devices will be located in the upstream channel and the 2 downstream channels Interrupt signals are collected into one signal will be used with pull up resistors at 5.0 V in one and to DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 52 3.3 V in the other one. Software changes will include the drivers for the new 3.3 V devices and a simple 2- Slide 52 byte command allows to program the I2C switch with the 2 downstream channels active all the time. The When one card in the application triggers an alarm master then sees an I2C bus with new devices and does condition, the PCA9554 collects it through one of its not have to take care of the high level voltage required inputs and generates an Interrupt (at the card level). to make them work correctly. It does not have to care PCA9544 collects the Interrupts (from each card) and either about the location of the device it needs to talk to sends a “General Interrupt” to the master. (downstream channel 0 or channel 1) since both are 1. Master then interrogates the PCA9544 Interrupt active at the same time. status register in order to determine which card is in cause 2. Master then connects the corresponding sub I2C I2C Switches: Voltage Level Shifting channel in order to interrogate the PCA9554 by I2C device I2C device I2C device I2C device I2C device 1 2 3 4 5 reading its Input register. 3. Once 1) and 2) are done, Master knows which Devices supplied by 5V Devices supplied by 3.3V and not 5.0 V tolerant • Products alarm has been triggered and can process it MASTER I2C bus # Channels 1 GTL2002 Int When this is done, Master can then clear the 2 PCA9540 corresponding alarm by accessing the corresponding I2C device I2C device I2C device 1 2 3 PCA9542/43 PCA9546 X card and programming the PCA9554 (write in the 4 PCA9544/45 X output register) 5 8 GTL2010 PCA9548 5V bus I2C I2C device I2C device MASTER SWITCH 11 GTL2000 4 5 Voltage Level Translation 3.3V bus How to accommodate different I2C logic levels in the same bus? DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 54 • I2C protocol: Due to the open drain structure of the bus, voltage level in the bus is fixed by the voltage connected to the pull-up resistor. If different voltage levels are required (e.g., master core at 1.8 V, legacy I2C bus at 5 V Slide 54 and new devices at 3.3 V), voltage level translators need to be used The SCL/SDA upstream channel fans out to multiple An I2C switch can be used to accommodate those SCx/SDx channels that are selected by the different voltage levels. programmable control register. The Switches can select • It allows to split dynamically the main I2C in several sub-branches and allow individual SCx/SDx channels one at a time, all at once different supply voltages to be connected to the pull up resistors • PCA devices are programmable through I2C bus so no additional pin is or in any combination through I2C commands and very required to control which channel is active primary designed for sub-branch isolation and level • More than one channel can be active at the same time so the master does shifting but also work fine for address conflict not have to remember which branch it has to address (broadcast) • More than one switch can be plugged in the same I2C bus resolution. Just make sure you do not select two DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 53 channels at the same time. Slide 53 Applications are the same as for the multiplexers but since multiple channels can be selected at the same time Due to the open drain architecture of the I2C bus, pull the switches are really great for I2C bus level shifting up resistors to a specific voltage is required. Once this (e.g., individual SCx/SDx channels at 1.8 V, 2.5 V, 3.3 is done, all the devices in the bus will have the same V or 5.0 V if the device is powered at 2.5 V). A 20
- 21. AN10216-01 I2C Manual hardware reset pin has been added to all the switches. It provides a means of resetting the bus should it hang up, Isolate I2C hanging segment(s) without rebooting the entire system and is very useful Device 1 in server applications where it is impractical to reset the Device 2 entire system when the I2C bus hangs up. The switches MASTER PCA reset to no channels selected. 9548 Device 3 Device 4 Interrupt logic inputs and output are available on the PCA9543 and PCA9545 and provide a flag to the Device 5 master for system monitoring. The PCA9546 is a lower RESET Device 6 cost version of the PCA9545 without Interrupt Logic. The PCA9548 provides eight channels and are more Device 7 convenient to use then dual 4 channel devices since the Device 8 device address does not have to shift. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 56 These devices do not isolate the capacitive loading on either side of the device so the designer must take into Slide 56 account all trace and device capacitance on both sides of the device (active channels only). Pull up resistors Let’s take an example where 8 devices (DEV1 to must be used on all channels. DEV8) are used and where the functional devices need to be controlled even though one or more devices are Increase I2C Bus Reliability (Slave Devices) failing. How to increase reliability of an I2C bus? Slave devices will be located on each downstream (Slave devices) channel of the PCA9548 (8-channel switch with Reset) • I2C protocol: If one device does not work properly and hangs the bus, then (CH1 to CH8). At power up, all the downstream no device can be addressed anymore until the rogue device is separated from channels are disabled. The master (located in the the bus or reset. upstream channel) sends a 2 byte command enabling all An I2C switch can be used to split the I2C bus in several the downstream channels. The I2C bus is then a normal branches that can be isolated if the bus hangs up. bus with a master and 8 slave devices. Let’s assume • Switches allow the main I2C to be split dynamically in several sub-branches that DEV4 (in CH4) fails. The bus then hangs and that can be: cannot be normally controlled by the master anymore. – active all the time – deactivated if one device of a particular branch hangs the bus • When a malfunctioning sub-branch has been isolated, the other sub After detection of this condition, the master must go to branches are still available a maintenance routine where: • It is programmable through I2C so no additional pin is required to control it • More than one switch can be plugged in the same I2C bus • It resets the PCA9548, thus disabling all the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 55 downstream channels. • It enables one by one all the downstream channels Slide 55 (CH1 to CH8) until the bus hangs again (CH4 active). Due to the open drain architecture of the I2C bus, if a The master then knows that the device connected to device fails in the bus and keeps the clock or data line CH4 is responsible of the failure at a high or low level, the bus is stuck in this • It resets again the PCA9548 to take control of the configuration and no device can be controlled until the I2C bus failed device is isolated from the I2C bus. Some • It programs all the functional channels active (CH1 architectures require a bus to still be operational even to 3, CH5 to 8) and disables CH4 though one or more devices failed and can no longer operate normally. Note that this algorithm can also be applied if more than 1 channel hang the bus at the same time. An I2C switch with a Reset capability allows to: • Split dynamically the I2C bus in several sub- branches (with one or several devices on each) • Disconnect all the devices in case the bus hangs • Reprogram the bus and isolate one or more branch that is not working properly. 21
- 22. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Isolate hanging segments Isolate failing master Discrete stand alone solution MAIN Slave P82 SEGMENT 1 MASTER SDA Main I2C 2 B96 Demux SCL I2 C BACKUP bus P82 SEGMENT 2 MASTER B96 MASTER Slave P82 • Main Master control the I2 C bus SEGMENT 3 B96 • When it fails, backup master asks to take control of the bus • Previous master is then isolated by the multiplexer • A bus buffer isolates the branch (capacitive isolation) • Downstream bus is initialized (all devices waiting for START condition) • Its power supply is controlled by a bus sensor • Switch to the new master is done • SDA and SCL are sensed and the sensor generates a timeout when the bus stays low • Products Device # of upstream channels • Bus buffer is Hi-Z when power supply is off. PCA9541 2 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 57 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 59 Slide 57 Slide 59 Slide 57 shows one discrete solution with option to set The 2:1 master selector allows switching between one timing, by discrete capacitors, to isolate a bus segment. master and its backup (and vice versa if the main master comes back on line). Before switching from one Increasing I2C Bus Reliability (Master Devices) upstream channel to the other one, the device makes sure that the previous device is not on the bus anymore How to increase reliability of an I2C bus? (fully isolated) (Master devices) • I2C protocol: If the master does not work properly , reliability of the systems The switching is done after making sure that the will decrease since monitoring or control of critical parameters are not downstream bus is in a “clean” configuration. All the possible anymore (voltage, temperature, cooling system) downstream devices have been initialized again An I2C demultiplexer can be used to switch from one (essential when the previous master failed in the middle failing master to its backup. of a transaction and thus the bus is not well initialized) and the bus is in an idle configuration. This is done by • It allows to have 2 independent masters to control the bus without any fault or system corruption converting the 2:1 master selector into a temporary – failed master completely isolated from the bus master (just after isolating the failing master) allowing – I2C bus is initialized by the demultiplexer before switching from one it to send the necessary I2C sequence (9 clock pulses on master to the other one • It is programmable through I2C so no additional pin is required to control it SCL while SDA is maintained high then a STOP • More than one demultiplexer can be plugged in the same I2C bus command). While the sequence is done, the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 58 downstream I2C bus is well initialized and the switch to the new master can be performed automatically by the Slide 58 PCA9541. If the I2C master fails or does not work properly, Capacitive Loading > 400 pF (Buffer) reliability of applications will decrease since monitoring and control of essential parameters cannot How to go beyond I2C max cap load? be controlled anymore (e.g. temperature monitoring, • I2C protocol limitation: the maximum capacitive load in a bus is 400 pF. If the voltage monitoring, cooling control). It is then often load is higher AC parameters will be violated. essential to have a backup I2C master to replace a mal An I2C bus repeater or an I2C hub can be used to get rid functioning main I2C master. The I2C 2:1 master of this limitation selector is then an essential device allowing switching between 2 masters. • It allows to double the I2C max capacitive load (repeater) or to make it 5 times higher (hub = 5 repeaters) • Multi-master capable, voltage level translation It can be used in: • All channels can be active at the same time • Limitation: Repeater/hub cannot be used in series • A point to point application - master and backup master control one card • Products: • A multi point application - master and backup Device PCA9515 # of repea te rs 1 # of ENABLE pins 1 master control several cards. PC9516 5 4 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 60 Slide 60 22
- 23. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C bus repeaters and hubs allow increasing the Using the PCA9516 in this application, the sub masters maximum capacitive load on the bus without degrading can only talk with sub masters on the same hub or the the AC performances (rising and falling times) of the main master since a low signal can not be sent through data and clock signals. They are multi-master capable. two hubs. Sub masters will not be able to arbitrate for bus control if located on different hubs. That is not ideal and limits the designers’ ability to expand their I2C Bus repeater (PCA9515) and Hub (PCA9516) I2C bus. The PCA9515 and the PCA9516 can only be used one device (either the PCA9515 or PCA9516) per system since low levels will not be transmitted through PCA the second device. Master 9515 Hub 1 Hub 1 To overcome this limitation, the PCA9518 was released. Similar to the PCA9516 but with four extra open drain signal pins that allow the internal device Hub 2 logic to be interconnected into an unlimited number of PCA Hub 3 Hub 3 9516 segments with only one repeater delay between any two Hub 4 segments. Hub 5 Hub 5 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 61 PCA9518 Applications Hub 4 Hub 8 Slide 61 PCA PCA Hub 3 Hub 7 9518 9518 Hub 2 Hub 6 • Repeaters allow doubling the capacitive load, 400 Hub 1 Hub 5 pF on each side of the device • Hubs allow multiplying the load by 5 with 400 pF Master Master I2 C on each hub channel Inter Device I2C bus Hub 12 Non used Hub In Slide 61, the possible communication paths are Hub 11 PCA PCA Hub 15 9518 9518 shown in green. No communication is possible over the Hub 10 Hub 14 red paths, no hub can communicate with any other hub. Hub 9 Hub 9 Hub 13 When communication between all hubs and the master is required then a multi-drop bus approach with P82B96 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 63 should be used. Slide 63 How to scale the I2C bus by adding The PCA9518, like the PCA9515/16, is transparent to 400 pF segments? bus arbitration and contention protocols in a multi- • Some applications require architecture enhancements where one or several isolated I2C hubs need to be added with the capability of hub to hub master environment and any master can talk to any communication other master on any segment. The enable pins can be used to isolate four of the five segments per device. An expandable I2C hub can be used to easily upgrade Place a pull up resistor on the un-isolatable segment this type of application and leave it unused if there is a requirement to enable or • It allows to expand the numbers of hubs without any limit disable the segment. • Multi-master capable, voltage level translation • All channels can be active at the same time (4 channels per expandable hub can be individually disabled) Using the PCA9518 in this 15 hub application, any sub master can talk to any other sub master on any of the • Products: Device # of repeate rs # of ENABLE pins cards and the main master can talk with any sub master PCA9518 5 4 with only one repeater delay. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 62 Slide 62 There are some applications where more than 5 channels are required. Sub Masters on Server Blades Application - Main Master is able to isolate any blade with the hardware enable pin via I2C & GPIO 23
- 24. AN10216-01 I2C Manual • One main master with the ability of choosing How to accommodate 100 kHz and 400 kHz between 100 kHz and 400 kHz depending on the devices in the same I2C bus? devices it needs to talk to. • I2C protocol limitation: in an application where 100 kHz and 400 kHz devices (masters and/or slaves) are present in the same bus, the lowest frequency • Two masters, one working at 100 kHz only (can be must be used to guarantee a safe behavior. part of the system legacy) and another one working at 400 kHz. An I2C bus repeater can be used to isolate 100 kHz from 400 kHz devices when a 400 kHz communication is required In the 1st case, the master located in the “400 kHz only” side has the capability to control the PCA9515’s • It allows to easily upgrade applications where legacy 100 kHz I2C devices ENABLE pin in order to disable the device when a 400 share bus access with newer 400 kHz I2C devices • Each side of the repeater can work with different logic voltage levels kHz communication is initiated (the “100 kHz only” side will then not see the communication). During a 100 • Products: Device # of repeaters # of ENABLE pins kHz communication, the PCA9515 is enabled to allow PCA9515 1 1 communication with the other side. In the 2nd case, both DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview masters are located in each side of the PCA9515 and 64 the control is basically the same as above for the 400 Slide 64 kHz devices. Due to the different I2C specification available (100 kHz, 400 kHz and now 3.4 MHz), devices designed for Live Insertion into the I2C Bus the 100 kHz specification are not suitable to work properly at 400 kHz, while the opposite is true. In How to live insert? applications where upgrades have been performed by •I2C protocol limitation: in an application where the I2C bus is active, it was using newer 400 kHz devices while keeping the 100 not designed for insertion of new devices. kHz legacy devices, it may become necessary to separate the 400 kHz devices from the 100 kHz devices An I2C hot swap bus buffer can be used to detect bus idle when a 400 kHz I2C transfer is performed. condition isolate capacitance, and prevent glitching SDA & SCL when inserting new cards into an active backplane. • Repeaters work with the same logic level on each side except the PCA9512 which works with 3.3 V and 5 V logic voltage levels at the same time PCA9515 - Application Example • Products: 3.3 V 5.0 V Device # of repeaters # of ENABLE pins 400 kHz slave 100 kHz slave PCA9511 1 1 devices devices PCA9512 1 0 SCL0 SCL1 PCA9513 1 1 PCA9514 1 1 SDA0 SDA1 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 66 ENABLE MASTER 1 MASTER 2 400 kHz 100 kHz OPTIONAL Slide 66 • Master 1 works at 400 kHz and can access 100 & 400 kHz slaves at their maximum speed (100 kHz only for 100 kHz devices) The I2C bus was never designed to be used in live • Master 2 works at only 100 kHz insertion applications, but newer applications in for • PCA9515 is disabled (ENABLE = 0) when Master 1 sends commands at 400 kHz telecom cards that require 24/7 operation require the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 65 ability to be removed and inserted into an active system for maintenance and control applications. Slide 65 The PCA9515 can be used for this purpose. One side of the device will have all the devices running at 400 kHz while the other side will have all the devices running to 100 kHz. Note that each side of the PCA9515 can work at different logic voltage levels. For example, the “older” 100 kHz devices can run at 5.0 V while the “newer” 400 kHz devices can work at 3.3 V. There could also be more than one master in the bus: 24
- 25. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Parallel to I2C Bus Controller I2C Hot Swap Bus Buffer PLUG How to use a micro-controller without I2C bus or SCL0 SCL1 how to develop a dual master application with a single micro-controller? SDA0 SDA1 READY • Some micro-controllers integrates an I2C port, others don’t An I2C bus controller can be used to interface with the micro-controller’s parallel port • Card is plugged on the system - Buffer is on Hi-Z state • It generates the I2C commands with the instructions from the micro • Bus buffer checks the activity on the main I2C bus controller’s parallel port (8-bits) • When the bus is idle, upstream and downstream buses are connected • It receives the I2C data from the bus and send them to the micro-controller • It converts by software any device with a parallel port to an I2C device • Ready signal informs that both buses are connected together DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 67 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 69 Slide 67 Slide 69 The PCA9511/12/13/14 are designed for these types of live insertion applications. There are many applications where there is a need to convert 8 bits of parallel data into an I2C bus port. The Long I2C Bus Lengths PCF8584 and PCA9564 allow building a single I2C master system using the parallel port of a 8051 type How to send I2C commands through long cables? microcontroller that does not have an I2C interface. It • I2C limitation: due to the bus 400 pF maximum capacitive load limit, sending commands over wire (80 pF/m) long distances is hard to achieve also allows building a double master system with using the built-in I2C interface and the parallel port of the An I2C bus extender can be used same micro-controller. • It has high drive outputs • Possible distances range from 50 meters at 85 kHz to 1km at 31 kHz over twisted-pair phone cables. Up to 400 kHz over short distances. • Others applications: Parallel Bus to I2C Bus Controller – Multi-point applications: link applications, factory applications • Master without I2C interface – I2C opto-electrical isolation – Infra-red or radio links Master PCA SDA 9564 SCL • Products: Device P82B715 • Multi-Master capability or 2 isolated I2C bus with the same device P82B96 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 68 PCA SDA1 Master 9564 SCL1 SDA2 Slide 68 SCL2 • Products Voltage range Max I2C freq Clock source Parallel interface The P82B715 and P82B96 are designed for long PCF8584 4.5 - 5.5V 90 kHz External Slow distance transmission of the I2C bus. PCA9564 2.3 - 3.6V w/5V tolerance 360 kHz Internal Fast DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 70 Slide 70 Philips offers two devices, the PCF8584 and PCA9564. The PCA9564 is similar to the PCF8584 but operates at 2.3 to 3.6 V VCC and up to 360 kHz with various enhancements added that were requested by engineers. The PCA9564 serves as an interface between most standard parallel-bus microcontrollers/ microprocessors and the serial I2C bus and allows the parallel bus system to communicate bi-directionally with the I2C bus. This commonly is referred as the bus master. Communication with the I2C bus is carried out on a byte-wise basis using interrupt or polled handshake. It 25
- 26. AN10216-01 I2C Manual controls all the I2C bus specific sequences, protocol, WIN-I2CNTDLL: 32-bit Win-I2CNT kit including arbitration and timing. The internal oscillator in the DLL driver and docs - Developer Kit for 32-bit PCA9564 is regulated to within +/- 10%. embedded I2C applications PCA9564 PCF8584 Comments WIN-I2CNT: 32-bit I2C Software/Adapter kit for Win 1. Voltage range 2.3-3.6V 4.5-5.5V PCA9564 is 5V tolerant 2. Max I2C freq. 360 kHz 90 kHz Faster I2C 95/98/ME/2000, NT 4.x - Enhanced kit for I2C control. 3. Clock source Internal External Less expensive and more Free updates from the Website flexible 4. Parallel interface Fast Slow Compatible with faster WIN-I2C: General Purpose legacy 16-bit I2C processors Software/Adapter kit - Basic Legacy Kit for I2C control with PCs running Windows 3.1x In addition, the PCA9564 has been made very similar to the Philips standard 80C51 microcontroller I2C I2CPORT: General Purpose I2C LPT Printer Port hardware so existing code can be utilized with a few Adapter v1.0 - Generic I2C adapter (Not compatible modifications. with Win-I2C/Win-I2CNT Software) Development Tools and Evaluation Board Evaluation Board 2002-1 Kit Overview Overview I2C Cable I2C 2002-1 Evaluation Kit 2 CD - ROM Purpose of the Development Tool and I C PC -Win95/98/2000/NT/XP Evaluation Board Win-I2CNT Win-I2CNT Parallel Port I2CPORT v2 Port I2CPORT v2 Adapter Card Port Adapter USB Adapter Software Software I2C Cable Card Card To provide a low cost platform that allows Field USB Cable 9V Application Engineers, designers and educators to Power Supply I2C 2002-1 Evaluation Board(s) easily test and demonstrate I2C devices in a platform that allows multiple operations to be performed in a I2C Cable setting similar to a real system environment. 9V Power Supply I2C 2002-1 Evaluation Board(s) USB Cable DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Board Kit 74 Slide 74 Slide 74 shows how the I2C 2002-1A kit is connected and shows how two evaluation boards can be used at the same time. I2CPORT v2 Adapter Card FEATURES - Converts Personal Computer parallel port to I2C bus master • The Win-I2CNT adapter connects to the standard DB-25 on any PC - Simple to use graphical interface for I2C commands - Win-I2CNT software compatible with Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, XP and 2000 • It can be powered by the PC or by the evaluation board - Order kits at www.demoboard.com DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 73 I2C 2Kbit EEPROM Slide 73 To the PC parallel port To the I2C The I2C 2002-1A I2C evaluation board can be Evaluation Board I2C bus signals purchased from http://www.demoboard.com for $199. Jumper JP2 I2C Voltage Selection (Bus voltage) Demo boards include at demoboard.com include: Open = 3.3 V bus Closed = 5.0 V bus DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview I2C-Trace: I2C Bus Tracer Kit - I2C Monitor captures 75 and displays I2C bus messages on any PC Slide 75 WIN-SMBUS: SMBUS Protocol S/W-H/W Kit - Supports SMBus ICs and the SMBus v1.0 protocol 26
- 27. AN10216-01 I2C Manual The I2CPORT v2 adapter card plugs into the parallel port and provides the interface between the Personal Computer and the I2C bus operating up to 150 kHz. 27
- 28. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Evaluation Board I2C 2002-1A Overview Device I/O Expanders PCA9501 GPIO register value SCL/SDA Main I2C Bus I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Board GPIO value GPIO Read / Write Options 1 1 GPIO programming GPIO PCA9550 PCA9551 PCA9554 PCA9543 PCA9555 PCA9561 PCA9515 P82B96 address EEPROM Auto Write PCA9501 PCF8582 address Feature RJ11 3 LM75A LM75A Selected byte USB A information 3 SCL1/SDA1 SCL2/SDA2 USB B Write Time 3 3.3 V 4 9V REGULATORS SCL0/SDA0 Byte 8BH 2 5.0 V EEPROM or 13910 Read / Write • 12 I2C devices on the evaluation board Options • 2 evaluation boards can be daisy chained without any address conflict Set the all EEPROM to EEPROM • Boards cascadable through I2C connectors, RJ11 phone cable or USB cable the same programming • On board regulators value DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 76 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 78 Slide 76 Slide 78 There are many new I2C devices on the evaluation Slide 78 shows the 8 bit GPIO and 2 kbit EEPROM board including GPIO, LED Blinkers, Switches, DIP selection for the PCA9501. Switches and Bus Buffers. Win-I2CNT Screen Examples Device Multiplexers/Switches PCA9543 Starting the Software Device address Clicking on the Win- I2CNT icon will start the software and will Control Register give the following window Value Working Window Read / Write Operation Selection Open the Open the device Channel Universal specific screen Selection modes screen 2 modes for the clock. Slow is adequate for slow ports and to solve Interrupt some potential Status compatibility issue I2C Indicates the Auto Write clock (SCL) Feature frequency Indicates that I2C communications can start DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 79 If problem, message “WIN-I2C hardware Help Hints Parallel Port not detected” displayed Action: check Adapter Card DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 77 Slide 79 Slide 77 Slide 79 shows the selection possibilities for the PCA9543/45/46/48 switches. Slide 77 shows the start screen from which all the other screens are selected. Device LED Drivers/Blinkers PCA9551 LED drivers states Register values Device address Auto Write Feature Read / Write Operation Frequencies and duty cycles programming DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 80 Slide 80 28
- 29. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Slide 80 shows the selections for the PCA9551 8 bit Device Non-Volatile Registers PCA9561 LED Blinker. The PCA9551 has two PWMs and controls for each bit (ON, OFF, BLINK1 and BLINK2). Device Address EEPROMs Read / Write Device I/O Expanders PCA9554 Operation Auto Write Output Read / Write MUX_IN Feature Register Operation (all Read registers) Operation Data (EEPROM, Device MUX_IN) address Multiplexing Input Configuratio n Register Note: MUX_IN, MUX_SELECT and WP pins are not controlled by the Software Register DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 83 Polarity Register Register Read / Write Slide 83 Programming Operation (specific register) Slide 83 shows the PCA9561 6 bit DIP Switch along with the 4 bit PCA8550 and 6 bit PCA9559/60. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 81 Slide 81 Device Thermal Management LM75A Auto Write Read / Write Temperature Feature Operation (all monitoring Slide 81 shows the 8 bit true output GPIO. Controls registers) allow to: Device - Program the bits a inputs or outputs address - Program the output state of output bits - Read the logic state in each input or output pin Read / Write Operation - Invert or not the bits that have been read (specific register) Device Device I/O Expanders PCA9555 modes Auto Write Polarity Input Read / Write Operation Feature Registers Registers (all registers) Temperature Monitoring Start Programming frequency Monitoring DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 84 Device Address Register Slide 84 Output Programming Registers Configuration Slide 84 allows control of the LM75A and monitoring Registers of the temperature on the graph. Read / Write Operation (specific Register) Device EEPROM 256 x 8 (2K) • Control window and operating scheme same as PCA9501’s 2KBit EEPROM DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 82 PCA9515 Slide 82 • Bus repeater - No software to control it • Buffered I2C connector available Slide 82 shows the 16 bit true output GPIO. • Enable Control pin accessible P82B96 • Bus buffer - No software to control it • I2C can come from the Port Adapter + USB Adapter through the USB cable • I2C can be sent through RJ11 and USB cables to others boards • 5.0 V and 9.0 V power supplies DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 85 Slide 85 29
- 30. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Slide 85 discusses the devices on the I2C 2002-1A evaluation board that is not controlled via the I2C bus. How to program the Universal Screen? They just provide the possibility to expand/extend the internal 3.3V I2C bus to external devices. • Length of the messages is variable: 20 instructions max • 5 different messages can be programmed PCA9515 allows connection using short wiring to • First START and STOP instructions can not be removed another 400 pF bus having 3.3-5 V standard I2C chips. • I2C Re-Start Command “S” key • I2C Write Command “W” key P82B96 allows options to demonstrate: • I2C Read Command “R” key 1. Linking to a second evaluation board using a • Add an Instruction “Insert” key USB cable to provide the power and I2C data • Remove an Instruction “Delete” key link to it. • Data: 0 to 9 + A to F keys 2. Linking two evaluation boards using a very DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview long telephony cable, say 10 m/33 ft or even 87 more. 3. Linking the evaluation board via a USB cable Slide 87 to the I2CPORT v2 adapter card. It allows a more convenient separation up to 5 m. Just Slide 87 shows how easy it is to program the universal include the USB adapter card. programming screen. 4. Expanding to another fully standard I2C bus operating at any desired voltage from 2 V to 15 V. Some others interesting Features See AN10146-01 for full details. • I2C clock frequency can be modified (Options Menu). • Acknowledge can be ignored for stand alone experiment (Options Menu). Universal Receiver / Transmitter Screen • Universal Transmitter/Receiver program can be saved in a file. • Device specific screens are different depending on the selected device. All the options are usually covered in those screens. Good tool to learn how the devices work and test all the features. Commands Programming • Possibility to build some small applications by connecting the devices together through the headers. I2C sequencing DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 88 parameters Slide 88 Sequencer Send selected Sequence programming Programmable delay between the messages There are many interesting features in the Win-I2CNT message DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 86 system that can help experiment with the new I2C devices. Slide 86 Slide 86 shows the universal screen where I2C command sequence can be used to program any device. 30
- 31. AN10216-01 I2C Manual How to Order the I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Kit http://300pinmsa.org/document/MSA_10G_40G_TRX_ I2C_Public_Document_02_19APR02.pdf So the idea is to look to any general systems that use How To Obtain the New Evaluation Kit dynamic address allocation (even including ones that do not use I2C hardware) to find the software design ideas • The I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Board Kit consists of the: – I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Board for building these systems. – I2CPort v2 Adapter Card for the PC parallel port – 4-wire connector cable – USB Adapter Card (no USB cable included) – 9 V power supply – CD-ROM with operating instructions and Win-I2CNT software on I2C Bus Vs SMBus - Electrical Differences that provides easy to use PC graphical interface specific to the I2C devices on the evaluation board but also with general purpose mode for all other I2C devices. Purchase the I2C 2002-1A Evaluation Board Kit at www.demoboard.com DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 89 Slide 89 Comparison of I2C with SMBus Low Power version of the SMBus Specification only The SMBus specification can be found on SMBus web site at www.SMBus.org DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 93 Some words on SMBus • Protocol derived from the I2C bus Slide 93 • Original purpose: define the communication link between: – an intelligent battery SMBus is used today as a system management bus in – a charger most PCs. Developed by Intel and others in 1995, it – a microcontroller modified some I2C electrical and software • Most recent specification: Version 2.0 – Include a low power version and a “normal” power version characteristics for better compatibility with the quickly – can be found at: www.SMBus.org decreasing power supply budget of portable equipment. • Some minor differences between I2C and SMBus: – Electrical SMBus also has a "High Power" version 2.0 that – Timing includes a "4 mA sink current" version that strictly – Operating modes cannot be driven by I2C chips. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 92 I2C Bus Vs SMBus - Timing and operating Slide 92 modes Differences The SMBus uses I2C hardware, and I2C hardware addressing, but adds second-level software for building • Timing: special systems. In particular its specifications include – Minimum clock frequency = 10 kHz "Address Resolution Protocol" that can make dynamic – Maximum clock frequency = 100 kHz – Clock timeout = 35 ms address allocations. • Operating modes "Dynamic reconfiguration: The hardware and software – slaves must acknowledge their address all the time allow bus devices to be "hot-plugged" and used (mechanism to detect a removable device’s presence) immediately, without restarting the system. The devices are recognized automatically and assigned unique addresses. This advantage results in a plug-and-play DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 94 user interface." In both those protocols there is a very useful distinction made between a System Host and all Slide 94 the other devices in the system that can have the names, and functions, of masters or slaves. I2C/SMBus compliancy I2C is also used as the hardware bus with some form of SMBus and I2C protocols are basically the same: A dynamic address assignment in the Optical network SMBus master will be able to control I2C devices and module specifications you can find at this website: vice-versa at the protocol level. The SMBus clock is defined from 10 kHz to 100 kHz while I2C can be a DC 31
- 32. AN10216-01 I2C Manual bus (0 to 100 kHz, 0 to 400 kHz, 0 to 3.4 MHz). This means that an I2C bus running at a frequency lower than Philips SMBus “high power” devices are also 10 kHz will not be SMBus compliant since the electrically compatible with I2C specifications but specification does not allow it. SMBus devices from others may not always be compatible with I2C. Philips I2C devices are electrically Logic levels are slightly different also: TTL for SMBus: compatible with low power SMBus specifications but low = 0.8V and high = 2.1V, 30%/70% VDD CMOS will not normally conform to all its software features level for I2C. This is not a big deal if VDD > 3.0 V. If the like time-out. I2C device is below 3.0 V then there is a problem since the logic hi/lo levels may not be recognized. Example for a typical I2C slave device, the PCA9552. It will be SMBus compliant if: Timeout feature: SMBus has a timeout feature, resetting - 10 kHz < Fclock < 100 kHz the devices if a communication takes too long (thus - It the device works in a 3.3V or higher explaining the min clock frequency at 10 kHz). I2C can environment be a "DC" bus meaning that a slave device stretches the master clock when performing some routine while the Note: the PCA9552 will not be able to reset itself if the master is accessing it. This will notify to the master: bus communication time is higher than the timeout "I'm busy right now but I do not want to loose the value. That is pretty much the case for all Philips communication with you, so hold on a little bit and I devices. Often the time-out feature can be added for a will let you continue when I'm done" ... and a "little bit" few cents in discrete hardware. See Slide 57. can be an eternity, (at least lower than 10 kHz). SMBus protocol just assumes that if something takes Intelligent Platform Management Interface too long, then it means that there is a problem in the bus (IPMI) and that everybody must reset in order to clear this mode. Slave devices are not then allowed to hold the Intel initiative in conjunction with hp, NEC and Dell clock low too long. and consists of three specifications: • IPMI for software extensions Differences SMBus 1.0 and SMBus 2.0 • Intelligent Platform Management Bus (IPMB) for Here is the statement from the SMBus 2.0 document: intra-chassis (in side the box) extensions This specification defines two classes of electrical • Inter Chassis Management Bus (ICMB) for inter- characteristics, low power and high power. The first chassis (outside of the box) extensions class, originally defined in the SMBus 1.0 and 1.1 specifications, was designed primarily with Smart Needed since as the complexity of systems increase, Batteries in mind, but could be used with other low- MTBF decreases. IPMI defines a standardized, power devices. abstracted, message-based interface to intelligent platform management hardware are defines This 2.0 version of the specification introduces an standardized records for describing platform alternative higher power set of electrical characteristics. management devices and their characteristics. IPMI This class is appropriate for use when higher drive provides a self monitoring capability increasing capability is required, for example with SMBus devices reliability of the systems on PCI add-in cards and for connecting such cards across the PCI connector between each other and to IPMI SMBus devices on the system board. Provides a self monitoring capability increasing reliability of the systems Devices may be powered by the bus VDD or by another Monitor server physical health characteristics: power source, VBus, (as with, for example, Smart • Temperatures Batteries) and will inter-operate as long as they adhere • Voltages to the SMBus electrical specifications for their class. • Fans • Chassis intrusion Philips devices have a higher power set of electrical characteristics than SMBus1.0. General system management: • Automatic alerting Main parameter is the current sink capability with Vol • Automatic system shutdown and re-start = 0.4V. - SMBus low power = 350 uA • Remote re-start - SMBus high power = 4 mA • Power control - I2C = 3 mA 32
- 33. AN10216-01 I2C Manual More information: www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/ipmi.htm Overall IPMI Architecture ICMB Standardized bus and protocol for extending management control, monitoring, and event delivery IPMB within the chassis: • I2C based • Multi-master BMC • Simple Request/Response Protocol • Uses IPMI Command sets • Supports non-IPMI devices • Physically I2C but write only (master capable devices), hot swap not required. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 100 • Enables the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) to accept IPMI request messages from Slide 100 other management controllers in the system. • Allows non-intelligent devices as well as Where IPMI is being used management controllers on the bus. • BMC serves as a controller to give system software Intel Server Management access to IPMB Servers today run mission-critical applications. There is literally no time for downtime. That is why Intel created Defines a standardized interface to intelligent platform Intel® Server Management – a set of hardware and management software technologies built right into most Intel® sever boards that monitors and diagnoses server health. Intel Hardware Server Management helps give you and your customers • Prediction and early monitoring of hardware more server uptime, increased peace of mind, lower failures support costs, and new revenue opportunities. • Diagnosis of hardware problems • Automatic recovery and restoration measures after More information: failure http://program.intel.com/shared/products/servers/boards • Permanent availability management /server_management • Facilitate management and recovery • Autonomous Management Functions: Monitoring, Event Logging, Platform Inventory, Remote PICMG Recovery PICMG (PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group) is a consortium of over 600 companies who Implemented using Autonomous Management collaboratively develop open specifications for high Hardware: performance telecommunications and industrial Designed for Microcontrollers based implementations computing applications. PICMG specifications include Hardware implementation is isolated from software CompactPCI® for Eurocard, rack mount applications implementation and PCI/ISA for passive backplane, standard format New sensors and events can then be added without any cards. Recently, PICMG announced it was beginning software changes development of a new series of specifications, called AdvancedTCA™, for next-generation telecommunications equipment, with a new form factor and based on switched fabric architectures. More information can be found at: http://www.picmg.org 33
- 34. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Use of IPMI within PICMG Slide 106 shows one of the two redundant buses that would interface through the PCA9511 or Known as Specification Based on Comments cPCI PICMG 2.0 NA No IPMB PCA9512/13/14. cPCI PICMG 2.9 IPMI 1.0 Single hot swap IPMB optional AdvancedTCA PICMG 3.x IPMI 1.5 Dual redundant hot swap IPMB mandatory VME • PICMG 2.0: CompactPCI Core • Motorola, Mostek and Signetics • PICMG 2.9: System Management cooperated to define the standard • PICMG 3.0: AdvancedTCA Core • Mechanical standard based on the • 3.1 Ethernet Star (1000BX and XAUI) – FC-PH links mixed with 1000BX Eurocard format. • 3.2 InfiniBand® Star & Mesh • Large body of mechanical • 3.3 StarFabric hardware readily available • 3.4 PCI Express • Pin and socket connector scheme is more resilient to mechanical wear than older printed circuit board DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 104 edge connectors. • Hundreds of component manufacturers support applications Slide 104 such as industrial controls, military, telecommunications, office automation and instrumentation systems. IPMI with additional extension is used as the basis for www.vita.com PICMG 2.9 and PICMG 3.x. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 107 Slide 107 Managed ATCA Board Example VMEbus VMEbus is a computer architecture. The term 'VME' stands for VERSAmodule Eurocard and was first coined in 1980 by the group of manufacturers who defined it. This group was composed of people from Motorola, Mostek and Signetics corporations who were PCA9511 PCA9511 • Dual, redundant -48VDC power distribution to each card w. high current, bladed power connector cooperating to define the standard. The term 'bus' is a • High frequency differential data connectors generic term describing a computer data path, hence the • Robust keying block • Two alignment pins name VMEbus. Actually, the origin of the term 'VME' • Robust, redundant system management • 8U x 280mm card size has never been formally defined. Other widely used • 1.2” (6HP) pitch definitions are VERSAbus-E, VERSAmodule Europe • Flexible rear I/O connector area DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 105 and VERSAmodule European. However, the term 'Eurocard' tends to fit better, as VMEbus was originally a combination of the VERSAbus electrical standard, Slide 105 and the Eurocard mechanical form factor. Slide 105 shows how IPMI is used within an VERSAbus was first defined by Motorola Corporation AdvancedTCA card. in 1979 for its 68000 microprocessor. Initially, it competed with other buses such as Multibus™, STD Bus, S-100 and Q-bus. However, it is rarely used Managed ATCA Shelf: Example 1 anymore. The microcomputer bus industry began with the advent of the microprocessor, and in 1980 many buses were showing their age. Most worked well with only one or two types of microprocessors, had a small addressing range and were rather slow. The VMEbus architects were charged with defining a new bus that PCA9511 PCA9511 would be microprocessor independent, easily upgraded from 16 to 32-bit data paths, implement a reliable PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 PCA9511 mechanical standard and allow independent vendors to build compatible products. No proprietary rights were assigned to the new bus, which helped stimulate third party product development. Anyone can make VMEbus DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 106 products without any royalty fees or licenses. Since much work was already done on VERSAbus it was Slide 106 used as a framework for the new standard. 34
- 35. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Device Overview In addition, a mechanical standard based on the Eurocard format was chosen. Eurocard is a term that loosely describes a family of products based around the I2C Device Categories DIN 41612 and IEC 603-2 connector standards, the IEEE 1101 PC board standards and the DIN 41494 and • TV Reception • General Purpose I/O IEC 297-3 rack standards. When VMEbus was first • Radio Reception • LED display control developed, the Eurocard format had been well • Audio Processing • Bus Extension/Control established in Europe for several years. A large body of • Infrared Control • A/D and D/A Converters mechanical hardware such as card cages, connectors • DTMF • EEPROM/RAM and sub-racks were readily available. The pin and socket connector scheme is more resilient to • LCD display control • Hardware Monitors mechanical wear than older printed circuit board edge • Clocks/timers • Microcontroller connectors. The marriage of the VERSAbus electrical specification DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 110 and the Eurocard format resulted in VMEbus Revision A. It was released in 1981. The VMEbus specification Slide 110 has since been refined through revisions B, C, C.1, IEC 821, IEEE 1014-1987 and ANSI/VITA 1-1994. The I2C devices can be broken down into different ANSI, VITA, IEC and IEEE standards are important categories. because they make VMEbus a publicly defined • TV reception: Provides TV tuning and reception specification. Since no proprietary rights are assigned to • Radio reception: Provides radio tuning and it, vendors and users need not worry that their products reception will become obsolete at the whim of any single • Audio Processing manufacturer. Since its introduction, VMEbus has • Infra-Red control generated thousands of products and attracted hundreds • DTMF: Dual Tone Multiple Frequency of manufacturers of boards, mechanical hardware, • LCD display control: Provides power to segments software and bus interface chips. It continues to grow of an LCD that are controlled via I2C bus and support diverse applications such as industrial • LED display control: Provides power to segments controls, military, telecommunications, office of an LED that are controlled via I2C bus automation and instrumentation systems. • Real time clocks and event counters: counting the passage of time, chronometer, periodic alarms for Use of IPMI in VME Architecture safety applications, system energy conservation, New VME draft standard indirectly calls for IPMI over time and date stamp for point of sales terminals or I2C for the system management protocol since there bank machines. was nothing to be gained by reinventing a different form of system management for VME. The only change • General Purpose Digital Input/Output (I/O): from the PICMG 2.9 system management specification monitoring of ‘YES’ or ‘NO’ information, such as is to redefine the backplane pins used for the I2C bus whether or not a switch is closed or a tank and to redefine the capacitance that a VME board can overflows; or controlling a contact, turning on an present on the I2C bus. The pin change was required LED, turning off a relay, starting or stopping a because the VME backplane connectors are different motor, or reading a digital number presented at the from cPCI. The capacitance change was required port (via a DIP switch, for example). because cPCI can have a maximum of 8 slots and VME • Bus Extension/Control: expends the I2C bus can have a maximum of 21 slots. System Management beyond the 400 pF limit, allows different voltage for VME Draft Standard VITA 38 – 200x Draft 0.5 9 devices on the same I2C bus or allows devices with May 02 draft at: the same I2C address to be selectively addressed on http://www.vita.com/vso/draftstd/vita38.d0.5.pdf the I2C bus. provides more information. • Analog/digital conversion: measurement of the size of a physical quantity (temperature, pressure…), proportional control; transformation of physical analog values into numerical values for calculation. • Digital/analog conversion: creation of particular control voltages to control DC motors or LCD contrast. • RAM: Random Access Memory 35
- 36. AN10216-01 I2C Manual • EEPROM: Electrically Erasable Programmable I2C devices are designed in the process that allows best Read Only Memory, retains digital information electrical and ESD performance and are manufactured even when powered down in Philips or third party fabs through out the world. • Hardware Monitors: monitoring of the temperature Philips has taken the initiative to offer the same process and voltage of systems in multiple internal fabs to provide redundancy and • Microprocessors: Provides the brains behind the continuation of supply in any market condition. I2C bus operation. TV Reception I2C Product Characteristics TV Reception • Package Offerings Typically DIP, SO, SSOP, QSOP, The SAA56xx family of microcontrollers are TSSOP or HVQFN packages a derivative of the Philips industry-standard • Frequency Range 80C51 microcontroller and are intended for Typically 100 kHz operation use as the central control mechanism in a Newer devices operating up to 400 kHz television receiver. They provide control Graphic devices up to 3.4 MHz functions for the television system, OSD and incorporate an integrated Data Capture and • Operating Supply Voltage Range display function for either Teletext or Closed 2.5 to 5.5 V or 2.8 to 5.5 V Caption. Newer devices at 2.3 to 5.5 V or 3.0 to 3.6 V with 5 V tolerance • Operating temperature range Typically -40 to +85 ºC Additional features over the SAA55xx family have been included, e.g. 100/120 Some 0 to +70 ºC Hz (2H/2V only) display timing modes, two page operation (50/60 Hz mode for • Hardware address pins 16:9, 4:3), higher frequency microcontroller, increased character storage, more 80C51 peripherals and a larger Display memory. For CC operation, only a Typically three (AO, A1, A2) are provided to allow up to eight of the 50/60 Hz display option is available. identical device on the same I2C bus but sometimes due to pin limitations there are fewer address pins Byte level I²C-bus up to 400 kHz dual port I/O DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 111 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 112 Slide 111 Slide 112 The frequency range of most of the newer I2C devices The I2C bus is used as a means to easily move control is up to 400 kHz and we are moving to 3.4 MHz for or status information on and off the devices. The future devices where typical uses would be in consumer SA56xx is given as an example of this type of device. electronics where a DSP is the master and the designer wants to rapidly send out the I2C information and then Radio Reception move on to other processing needs. Radio Reception The operating range of most of the newer CMOS devices is 2.3 to 5 V to allow operation at the 2.5, 3.3 and 5V nodes. Some processes restrict the voltage The TEA6845H is a range to the 3.3 V node. Most customers have moved single IC with car radio tuner for AM from 5 V and are now at 3.3 V but several are moving and FM intended for microcontroller rapidly to 2.5 V and even 1.8 V in the near future. We tuning with the I²C- bus. It provides the are working on next generation general purpose devices following functions: to support 1.8 V operation and currently have some LCD display drivers that operate down to 1 V. • AM double conversion receiver for LW, MW and SW (31 m, 41 m and 49 m bands) with IF1 = 10.7 MHz and IF2 = 450 kHz The operating temperature range is typically specified • FM single conversion receiver with integrated image rejection for IF = 10.7 MHz at the industrial temperature range but again depending capable of selecting US FM, US weather, Europe FM, East Europe FM and Japan FM bands. on process or application, the range may be specified DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 113 higher or lower. The automotive, military and aviation industries have expressed more interest in I2C devices Slide 113 due to the low cost and simplicity of operation so future devices temperature ranges may be expanded to meet Again, the I2C bus is used to control frequency their needs. selection or control the audio sound control and interface with the microcontroller. Special software I2C devices were typically offered in either DIP or SO programs, applied by connecting to the I2C bus during and limited their use in equipment where space is at a factory testing, automatically perform the alignment of premium. Newer I2C devices are typically offered in the RF sections of the receiver, eliminating the need for SO, TSSOP or near chip scale HVQFN packages. manual or mechanical adjustments. The alignment information will be stored in some non-volatile memory 36
- 37. AN10216-01 I2C Manual chip and re-sent to the receiver chip, where it is stored chip voltage reference the PCD3311C and PCD3312C in R.A.M., each time power is applied to the receiver. provide constant output amplitudes that are independent of the operating supply voltage and ambient Audio Processing temperature. An on-chip filtering system assures a very low total harmonic distortion in accordance with CEPT Audio Processing recommendations. In addition to the standard DTMF The SAA7740H is a function- specific digital signal processor. frequencies the devices can also provide: The device is capable of performing processing for • Twelve standard frequencies used in simplex listening-environments such as modem applications for data rates from 300 to equalization, hall-effects, reverberation, surround-sound 1200 bits per second and digital volume/balance control. The SAA7740H can • Two octaves of musical scales in steps of also be reconfigured (in a dual semitones. and quad filter mode) so that it can be used as a digital filter with programmable characteristics. LCD Display Driver The SAA7740H realizes most functions directly in hardware. The flexibility exists in the possibility to download function parameters, correction coefficients and various configurations from a host microcontroller. The parameters can be passed in real I2C LCD Display Driver time and all functions can be switched on simultaneously. The SAA7740H accepts LCD Display Control 2 digital stereo signals in the I2S-bus format at audio sampling frequency (fast ) Display size: and provides 2 digital stereo outputs. 2 line by 12 characters + 120 icons DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 114 DDRAM SDA Control logic CGRAM SCL Slide 114 CGROM Sequencer Row driver Bias voltage Voltage Supply The I2C bus is used to control the audio and sound generator multi- plier Column driver balance. The LCD Display driver is a complex device and is an Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) example of how "complete" a system an I2C chip can be – it generates the LCD voltages, adjusts the contrast, temperature compensates, stores the messages, has DTMF/Modem/Musical Tone Generators CGROM and RAM etc etc. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 116 Slide 116 The LCD display driver is a complex LCD driver and is an example of how "complete" a system an I2C chip can be - generates the LCD voltages, adjusts the contrast, temperature compensates, stores the messages, has CGROM and RAM etc. • Modem and musical tone generation • Telephone tone dialing • DTMF > Dual Tone Multiple Frequency • Low baud rate modem I2C LCD Segment Driver DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 115 Display sizes LCD Segment Control 1 x 24 … 2 x 40… single chip: 4 x 40 ... 16 x 24 Slide 115 Control logic SDA The PCD3311C and PCD3312C are single-chip silicon SCL RAM Backplane drivers gate CMOS integrated circuits. They are intended Sequencer principally for use in telephone sets to provide the dual- Supply Bias voltage generator tone multi-frequency (DTMF) combinations required Segment drivers for tone dialing systems. The various audio output frequencies are generated from an on-chip 3.58 MHz The LCD Segment driver is a less complex LCD driver quartz crystal-controlled oscillator. A separate crystal is (e.g., just a segment driver). used, and a separate microcontroller is required to control the devices. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 117 Both the devices can interface to I2C bus compatible Slide 117 microcontrollers for serial input. The PCD3311C can also interface directly to all standard microcontrollers, The LCD segment driver is a less complex LCD driver accepting a binary coded parallel input. With their on- (e.g., just a segment driver). Philips focus is for large 37
- 38. AN10216-01 I2C Manual volume consumer display apps, which is right now recently developed and is technically the most B&W and color STN LCD displays and in near future it advanced. The RTCs have one interrupt output and do will be TFT and OLED (organic LED displays). The not track the exact year. This must be done in software OLED drivers will most probably not be useable with by the customer. They do use a 4-year calendar base conventional LEDs. and can count 255 years. PCF8583 has the added advantage of 240 bytes of RAM integrated with the VGA is beyond our current roadmap that stretches only RTC. This could be important if such small RAM is up to about 1/4 VGA. This is simply because of the required then we replace two chips with one. requirements that we see in the mobile telecomm market, our main focus. We find already that I2C does General Purpose I/O Expanders not give us enough transmission rate for display data so serial bus is mainly intended for control and text I2C General Purpose I/O Expanders overlay signals in such displays. General Purpose I/O alternative analog Supply input configurations Interrupt POR ≠ Light Sensor Input/ output stages SDA I2C-bus interface Latches SCL Sub address decoder I2C Light Sensor • Transfers keyboard, ACPI Power switch, keypad, switch or other inputs to microcontroller via I2C bus The TSL2550 sensor converts the intensity of ambient light into digital signals • Expand microcontroller via I2C bus where I/O can be located near the that, in turn, can be used to control the backlighting of display screens found in source or on various cards portable equipment, such as laptops, cell phones, PDAs, camcorders, and GPS • Use outputs to drive LEDs, sensors, fans, enable and other input pins, systems. The device can also be used to monitor and control commercial and relays and timers residential lighting conditions. • Quasi outputs can be used as Input or Output without the use of a By allowing display brightness to be adjusted to ambient conditions, the sensor configuration register. is expected to bring about a significant reduction in the power dissipation of DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 120 portables. The TSL2550 all-silicon sensor combines two photodetectors, with one of the detectors sensitive to both visible and infrared light and the other sensitive only to IR light. The photodetectors’s output is converted to a digital format, in which Slide 120 form the information can be used to approximate the response of the human eye to ambient light conditions sans the IR element, which the eye cannot perceive. Let’s talk about some of the newer devices, such as DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 118 these new general-purpose input and output (GPIO) expansion for the I2C/SMBus. Slide 118 Slide 118 shows a new innovation in light detectors that Quasi Output I2C I/O Expanders - Registers uses the I2C bus to transfer information to and from the sensor. • To program the outputs Multiple writes are OUTPUT possible during the S Address W A A P DATA same communication Real Time Clock/Calendar • To read input values Multiple reads are INPUT possible during the I2C Real Time Clock/Calendar S Address R A DATA A P same communication Real time clocks and • Important to know event counters count – At power-up, all the I/O’s are HIGH; Only a current source to VDD is Real-Time Clock / Calendar 32kHz the passage of time and active Counters: act as a chronometer s, min, h, day, Oscillator / – An additional strong pull-up resistors allows fast rising edges prescaler month, year They are used in – I/O’s should be HIGH before using them as Inputs Alarm-, Timer- POR applications such as: Registers I2C-bus SDA • periodic alarms for DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 121 (240 Byte RAM 8583) interface SCL safety applications Sub • system energy Slide 121 Interrupt address decoder conservation • time and date stamp for point of sales The PCF8574 and PCA8575 are well known general terminals or bank purpose I/O expanders. The PCA9500 is a combination DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview machines 119 of the PCF8574 with a 2K EEPROM. The interrupt pin is replaced by the EEPROM write protect (WP). The Slide 119 EEPROM has a different fixed I2C address then the GPIO. The PCA9501 is a combination of the PCF8574 Philips offers four RTCs, these are PCF8593, PCF8583, with a 2K EEPROM. The device is offered in a 20-pin PCF8573 and PCF8563. The PCF8563 is the most TSSOP package and the four extra pins allow the 38
- 39. AN10216-01 I2C Manual interrupt output to be included in addition to the WP. The extra three pins are then used to offer a total of six True Output I2C I/O Expanders - Example address pins allowing up to 64 of these devices to share Input Polarity Config Output Reg# Reg# Reg# Reg# the same I2C bus. The PTN devices are design for 1 0 1 X 1 telecom maintenance and control applications. 1 0 0 1 1 The PCA9558 is a combination of the PCA9557 with a 0 0 0 0 0 2K EEPROM and 5-bit DIP Switch. 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 X 1 1 1 1 X 0 0 0 1 X 0 True Output I2C I/O Expanders - Registers 1 0 0 1 1 • To configure the device Read Read/ Read/ Read/ I/O’s CONFIG No need to access Write Write Write S Address W A 03H A A DATA Configuration and Polarity registers DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 124 POLARITY S Address W A 02H A A P DATA once programmed • To program the outputs Slide 124 Multiple writes are OUTPUT possible during the S Address W A 01H A A P DATA same communication Slide 124 shows an example of how the • To read input values PCA9554/54A/57 is programmable. INPUT S Address W A 00H A S Address R A A P DATA Multiple reads are possible DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview during the same communication 123 Signal monitoring and/or Control • Advantages of I2C Slide 123 – Easy to implement (Hardware and Software) – Extend microcontroller: I/O’s can be located near the source or on These newer device’s true outputs provide active source various cards and sink current sources and does not rely upon a pull – Save GPIO’s in the microcontroller up resistor to provide the source current. The four sets – Only 2 wires needed, independently of the numbers of signals – Signal(s) can be far from the masters of registers within the true outputs devices are – Fast enough to control keyboards programmable and provide for: Configuration (Input or – Simplify the PCB layout Output) control, Input (value), Output (value) or – Devices exist in the market and are massively used Polarity (active high or low). DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview The PCA9554/54A/55 devices have an interrupt output 125 and the 8 or 16 I/O pins can be configured for interrupt inputs. These newly released devices have the same I2C Slide 125 address and footprint as the PCF8574/74A/75 but require some software modifications due to the Signal Monitoring and/or Control first approach is to different I/O registers. The PCA9554 and PCA9555 use GPIO’s of the master(s) controlling the application. have the same I2C address while the PCA9554A has a In some applications, use of these GPIO’s is not the slightly different fixed address allowing 16 devices best approach. (eight 54A and eight 54/55 in any combination) to be on the same I2C/SMBus. The PCA9556/57 feature a Reasons can be the following: Hardware Reset pin instead of the interrupt output that • Number of signals to monitor/control is too allows the device to be reset remotely should the I2C important and requires a big amount of the bus become hung up. The PCA9557 is an improved master’s GPIO’s. version of the PCA9556 that has the electrical • Signals can be in a remote location implying a characteristics of the PCA9554/54A. Information on more complex PCB layout, with a lot of long traces GPIO selection is contained within application note (making the design more sensitive to noise) AN469. • Upgrade (more signals to monitor/control) requires a total re-layout of the PCB and is limited to the number of GPIO’s still available in the master. 39
- 40. AN10216-01 I2C Manual tied up by sending repeated transmissions to blink Signal monitoring and/or Control LEDs as is currently done when a GPIO is used. The • Proposed devices PCA9530/31/32/33 and the PCA9550/51/52/53 provide # o f O u tp u ts In te rru p t a n d P O R a n d 2K In te rru p t, P O R the same amount of electrical sink capability as the POR EEP RO M a n d 2K EEP RO M Q u a si O u tp u t (20-25 m a sin k a n d 100 u A so u rce ) PCA9554/55/57 but have a built in oscillator and two 8 P CF 8574/74A P CA9500/58 P CA9501 I2C programmable blink rates. 16 P CF 8575/75C - - # of Outputs Reset and POR Interrupt and POR Two user definable blink rates and duty cycles True Output (20-25 ma sink and 10 mA source) 8 PCA9556/57 PCA9534/54/54A programmed via the I2C/SMBus. These are 16 - PCA9535/55 programmed during the initial set up and can range • Advantages between 160 Hz and every 1.6 seconds for the LED – Number of I/O scalable – Programmable I2C address allowing more than one device in the bus Dimmers and between 40 Hz and every 6.4 seconds for – Interrupt output to monitor changes in the inputs the LED Blinkers. Thereafter only a single transmission – Software controlling the device(s) easy to implement is required to turn individual LEDs: on, off or blink at DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 126 one of the two programmable blink rates. The duty cycle can be used to ‘dim’ the LEDs using the LED Slide 126 Dimmers by setting the blink rate to 160 Hz (faster than the eye can see the blinking) and then changing the The I2C GPIO device approach provides an elegant average current through the LED by changing the duty solution with minimum hardware and software changes: cycle. • The device(s) can be plugged to an existing I2C bus in the application The internal oscillator is regulated to +/- 10% accuracy • Minor software change is required to control the and no external components are required. The +/- 10% new device(s) tolerance was recommended by human factor • Easily upgradeable (by adding more I2C GPIO engineers. These devices allow you to program two devices) specific blink rates and then command a LED to blink • Remote signals can be easily controlled (requires at one of these rates without sending any further I2C only a longer I2C bus trace - 2 wires only) commands. If you use normal GPIOs to blink LEDs, • Changes in the monitored input signals can be you must send an ON command followed by an OFF propagated to the master through a single Interrupt command followed by an ON command for the line. The master can be easily interrogate the I2C duration of the blink. This is OK if you do not have GPIO to determine which input(s) generated the many LEDs to blink or much traffic on the I2C bus, or Interrupt have microcontroller overhead to burn, but if you do this for many LEDs you will tie up the I2C bus and your See Application Note AN469 for more information on micro controller. Hence the need for dedicated LED GPIOs. blinkers as a stand alone part option. Unused pins can be used as normal GP input or output, but since they are LED Dimmers and Blinkers open-drain, a pull up resistor will be needed for logic high outputs. I2C LED Dimmers and Blinkers alternative analog input configurations A Hardware Reset pin is included, allowing the LED blinker to be reset independently from the rest of the Supply Reset POR I2C/SMBus or higher level system. Each open drain ≠ Input/ output stages SDA I2C-bus interface output can sink 25 mA of current with total package Oscillator SCL Sub address sinking capacity limited to 100 mA for the 2, 4 and 8 bit devices and 200 mA for the 16 bit device (100 mA decoder for each byte). Typical LEDs take 10-25 mA of current • I2C/SMBus is not tied up by sending repeated transmissions to turn LEDs when in operation. on and then off to “blink” LEDs. • Frees up the micro’s timer • Continues to blink LEDs even when no longer connected to bus master • Can be used to cycle relays and timers • Higher frequency rate allows LEDs to be dimmed by varying the duty cycle for Red/Green/Blue color mixing applications. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 127 Slide 127 These new devices are useful for LED driving and blinking. The I2C/SMBus or the micro controller is not 40
- 41. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C LED Blinkers and Dimmers I2C GPIO’s can be used to control LEDs in order to Frequency 0 (00H) 40 Hz 255 (FFH) 6.4 s visual status, like for example blink slowly when in 0 Input 0 0 0 0 0 Register(s) Duty Cycle 100 % 0.4 % normal condition, blink faster in an alarm mode. The 0 (00H) 255 (FFH) Frequency 160 Hz 1.6 s main disadvantages of this method are the following: 0 0 PWM0 0 0 0 0 • ON/OFF commands need to be sent all the time by Duty Cycle 0% 99.6 % PWM0 256 - PWM 0 Blinkers 0 0 PSC0 0 0 0 0 256 256 Dimmers the master ON OFF ON OFF • I2C bus can be tied by sending the ON/OFF 0 0 PWM1 0 0 0 0 PSC0 + 1 PSC0 + 1 commands when a lot of LEDs needs to be 160 40 0 0 PSC1 0 0 0 0 controlled PWM1 256 256 - PWM1 256 • At least one timer in the master needs to be ON OFF ON OFF ON 0 LED0Selector 0 0 0 0 dedicated for this purpose PSC1 + 1 160 PSC1 + 1 40 ON = OFF = LED ON LED OFF ON, OFF, BR1, BR2 ON, • Blinking is lost if the I2C bus hangs or if the master DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 128 fails Slide 128 Using I2C for visual status Slide 128 shows the register configuration of the LED • Products: Blinkers and Dimmers. # of Outputs Reset and POR LED Blinkers 2 PCA9550 4 PCA9553 Blinking between 40 times a second to 8 PCA9551 once every 6.4 seconds 16 PCA9552 I2C Blinkers and Dimmers - Programming • To program the 2 blinking rates # of Outputs Reset and POR LED Dimmers 2 PCA9530 S Address W A PSC0 A A Blinking between 160 times a second to pointer PSC0 PWM0 A 4 PCA9533 once every 1.6 seconds. 8 PCA9531 P Can be used for dimming/brightness or PSC1 A PWM1 A 16 PCA9532 PWM for stepper motor control PSC0 pointer = 01H for 2, 4 and 8-bit devices PSC0 pointer = 02H for the 16-bit devices • To program the drivers LED SEL0 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 131 S Address W A A LEDSEL0 A LEDSEL1 A pointer LEDSEL2 A LEDSEL3 A P Slide 131 LEDSEL0 pointer = 05H for 2, 4 and 8-bit devices LEDSEL0 pointer = 06H for the 16-bit devices Only the 16-bit devices have 4 LED selector registers (8-bit devices have I2C LED blinkers provide an elegant autonomous 2 registers, 2 and 4-bit devices have only one) DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 129 solution: • They have an built-in accurate oscillator requiring no external components Slide 129 • They can be programmed in one I2C access (2 Slide 129 shows the programming sequence for the selectable fully programmable blinking rates) LED Dimmers and Blinkers. • Output state (Blinking rate 1, Blinking rate 2, Permanently ON, Permanently OFF) is programmed in one I2C access anytime. Using I2C for visual status Blinking is not lost, once the device is programmed, in • Use LEDs to give visual interpretation of a specific action: case the bus hangs or the master fails. – alarm status (using different blinking rates) – battery charging status • 1st approach: I2C GPIO’s See Application Note AN264 for more information on – Advantage: the LED Dimmers/Blinkers. – Simple programming – Easy to implement – Inconvenient: – Need to continually send ON/OFF commands through I2C – 1 microcontroller’s timer required to perform the task – I2C bus can be tied up by commands if many LEDs to be controlled – Blinking is lost if the I2C bus hangs • 2nd approach: I2C LED Blinkers – Advantage: – One time programmable (frequency, duty cycle) – Internal oscillator – Easy to implement – Device does not need I2C bus once programmed and turned on DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 130 Slide 130 41
- 42. AN10216-01 I2C Manual DIP Switch I2C Dip Switches Mux Select I2C DIP Switches I2C Bus I2C INTERFACE / MUX Select Pin Mode Selection Non MUX Output Pin Write EEPROM Control I2C Bus Protect Hardware Output EEPROM Pins 0 0EEPROM 0 0 0 0 0 Mux 0 0EEPROM 1 0 0 0 0 0 0EEPROM 2 0 0 0 0 MUX Hardware Input Pins 0 0EEPROM 3 0 0 0 0 • Non-volatile EEPROM retains values when the device is powered down • Used for Speed Step™ notebook processor voltage changes when on 0HARDWARE Value 0 0 0 0 0 AC/battery power or when in deep sleep mode • Also used as replacement for jumpers or DIP switches since there is no PCA9561 requirement to open the equipment cabinet to modify the jumpers/DIP 6 Bits DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 133 switch settings DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 132 Slide 133 Slide 132 The PCA9561 shown in Slide 133 is unique in that it These devices were designed for use with Intel® has 6 hardware input pins and four internal 6-bit processors to implement the Speed Step™ technology EEPROM registers. Output selection is possible for notebook computers (selects different processor between any one of these five 6-bit values at any time voltages when connected to AC power, the battery or in via the I²C bus. The EEPROMs have a 10 year memory a deep sleep/deeper sleep mode), Dual BIOS selection retention and are rated for 3000 write cycles in the data (select different operating systems during start-up). sheet but have been tested to 50,000 cycles with no failures. Designers have however found other uses for these devices such as; VGA/Tuner cards (select the The hardware pins may not be used at all or may be appropriate transmission standard), in inkjet printers used for a default manufacturing address. At and are being used as replacement for jumpers or dip manufacturing, the I2C address of the targeted device switches since the I²C controlled integrated EEPROM may be the one given by the default EEPROM values and Multiplexer eliminates the need to open equipment (all Zero’s). If the customer wants to change the I2C to modify the settings by hand, making it easier to address, he has to Address the Multiplexed/Latched change settings and less likely to damage the EEPROM device (PCA8550, PCA9559, PCA9560 or equipment. PCA9561) and program the EEPROM to the new value they want. I²C commands and/or hardware pins are used to select between the default values or the setting programmed If they use the PCA9560 or PCA9561, 2 or 4 different from the I2C bus and stored in the onboard I2C values can be already pre-programmed. Put the right EEPROM register. These onboard values can be logic level(s) on the Mux_select pin(s) if necessary (to changed at any time via the I²C bus. The non-volatile select the EEPROM values at the Mux input and I²C EEPROM register values stay resident even when propagate them to the outputs (connected to the the device is powered down. The devices power up with Address pins of the targeted I2C device). Address the either the hardware pin inputs or the EEPROM0 targeted I2C device (programmed with the new I2C register retained value on the hardware output pins address). Nice thing about using Multiplexed/Latched depending on the position (H or L) of the Mux select EEPROM is that the configuration is not lost each time pins. supply is powered down. The PCA9560 is footprint identical to the PCA9559 but has two internal EEPROM registers to allow for three preprogrammed setting (e.g., AC power/battery power, deep sleep or deeper sleep mode). 42
- 43. AN10216-01 I2C Manual • I2C sub-branch isolation I2C DIP Switches - PCA9561 • I2C bus level shifting (e.g., each individual • To program the 4 EEPROMS SCx/SDx channel can be operated at 1.8 V, 2.5 V, S Address W A 00H A EEPROM 0 A EEPROM 1 A 3.3 V or 5.0 V if the device is powered at 2.5 V). A EEPROM 2 A EEPROM 3 A P Interrupt logic inputs for each channel and a combined • To read the 4 EEPROMS output are included on every multiplexer and provide a S Address W A 00H A S Address R A EEPROM 0 A flag to the master for system monitoring. These devices EEPROM 1 A EEPROM 2 A EEPROM 3 A P do not isolate the capacitive loading on either side of • To read the Hardware value the device so the designer must take into account all S Address W A FFH A S Address R A HW VALUE A P trace and device capacitance on both sides of the device •To select the mode (any active channels). Pull up resistors must be used on S Address W A FXH A P all channels. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 134 I2C Switches Slide 134 Side 134 shows the typical program sequence for the I2C Bus 0 I2C Bus OFF PCA9561. See Application Note AN250 for more I2C Bus 1 OFF information on the DIP Switches. Reset I2 C Interrupt 0 Interrupt Out Controller Interrupt 1 Multiplexers and Switches • Switches allow the master to communicate to one channel or multiple I2C Multiplexers downstream channels at a time • Switches don’t isolate the bus capacitance • Other Applications include: sub-branch isolation and I2C/SMBus level I2C Bus I2 C Bus 0 OFF shifting (1.8, 2.5, 3.3 or 5.0 V) I2C Bus 1 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 136 I2 C Interrupt 0 Interrupt Out Controller Interrupt 1 Slide 136 FEATURES KEY POINTS -Fan out main I2C/SMBus to multiple channels -Many specialized devices have only one I2C -Select off or individual downstream channel address and sometimes many are needed in the The Switches allow multiplexing but also allow -I2C/SMBus commands used to select channel same system. -Multiplexers allow the master to communicate to multiple downstream channels to be active at the same -Power On Reset (POR) opens all channels -Interrupt logic provides flag to master for one downstream channel at a time but don’t isolate the bus capacitance time that allows voltage level translation or load sharing system monitoring. -Other Applications include sub-branch isolation. applications. The I2C SCL/SDA upstream channel to fan out to multiple SCx/SDx channels that are selected DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 135 by the programmable control register. The Switches can select individual SCx/SDx channels one at a time, Slide 135 all at once or in any combination through I2C commands and very primary designed for sub-branch The multiplexer allows multiplexing multiple I2C isolation and level shifting but also work fine for devices with the same I2C address. The I2C SCL/SDA address conflict resolution (Just make sure you do not upstream channel to fan out to multiple SCx/SDx select two channels at the same time). Applications are channels that are selected by the programmable control the same as for the multiplexers but since multiple register. The I²C command is sent via the main I²C bus channels can be selected at the same time the switches and is used to select or deselect the downstream are really great for I2C bus level shifting (e.g., channels. The Multiplexers can select none or only one individual SCx/SDx channels at 1.8 V, 2.5 V, 3.3 V or SCx/SDx channels at a time since they were designed 5.0 V if the device is powered at 2.5 V). primarily for address conflict resolution such as when multiple devices with the same I2C address need to be A hardware reset pin has been added to all the switches. attached to the same I2C bus and you can only talk to It provides a means of resetting the bus should it hang one of the devices at a time. up, without rebooting the entire system and is very useful in server applications where it is impractical to These devices are used in video projectors and server reset the entire system when the I2C bus hangs up. The applications. Other applications include: switches reset to no channels selected. Address conflict resolution (e.g., SPD EEPROMs on DIMMs). 43
- 44. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Interrupt logic inputs and output are available on the The PCA9541/01 defaults to channel 0 on start up/reset. PCA9543 and PCA9545 and provide a flag to the The device was designed for a company that wanted the master for system monitoring. The PCA9546 is a lower device to connect master 0 to shared resources at start cost version of the PCA9545 without Interrupt Logic. up so they wouldn't have to send any commands. The PCA9548 provides eight channels and are more convenient to use then dual 4 channel devices since the The PCA9541/02 defaults to channel 0 on start up/reset device address does not have to shift. only after it has seen a stop command on bus 0. This is our hot swap version, a requirement the company using These devices do not isolate the capacitive loading on the PCA9541/01 didn't have (since they power down either side of the device so the designer must take into the system before cards are inserted or removed). This account all trace and device capacitance on both sides feature on the PCA9541/02 allows you to insert and of the device (active channels only). Pull up resistors remove cards without confusing the slave devices on must be used on all channels. the card by them being caught midway into an I2C transmission if there is an active transmission on the backplane/main bus. I2C Multiplexers & Switches - Programming The PCA9541/03 defaults to no channels selected on • To connect the upstream channel to the selected start up/reset and one of the masters needs to command downstream channel(s) the PCA9541/03 to select bus 0 or 1. We had some S PCA954x Address W A CHANNEL SELECTION A P Selection is done at the STOP command customers interested in not connecting any bus until the master was ready. This feature also allows the • To access the downstream devices on the selected channel PCA9541/03 to be used as a 'gatekeeper" multiplexer as S Device Address W A Command A P described in the data sheet specific applications section. Once the downstream channel selection is done, there is no need to access (Write) the PCA954x Multiplexer or Switch The device will keep the configuration until a new configuration is required (New Write operation on the PCA954x) Master Selector in Multi-Point Application DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 140 Slide 137 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 PCA9541 Master 0 Master 1 Slide 137 shows a typical programming sequence. See Application Note AN262 for more information on the switch/multiplexers. I2C 2 to 1 Master Selector DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 138 Master 0 I2C Bus Slave Card Master 1 I2C Bus I2C Bus Slide 139 Interrupt 0 Out I2 C Interrupt In Interrupt In Interrupt 1 Out Controller Reset PCA9541 in a multi-point application were all cards use the same two buses. Master 0 is the primary master and • Master Selector selects from two I2C/SMBus masters to a single channel master 1 is the back up master. • I2C/SMBus commands used to select master • Interrupt outputs report demultiplexer status • Sends 9 clock pulses/stop to clear slaves prior to transferring master DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 137 Slide 138 The PCA9541 is designed for applications where there are two bus masters controlling the same slaves and the masters need to be isolated for redundancy. 44
- 45. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Bus Repeaters and Hubs Master Selector in Point-Point Application I2C Bus Repeater and Hub PCA9541 Master 0 Master 1 400 pF SCL0 SCL1 400 pF 400 pF 400 pF 400 pF SDA1 PCA9541 SDA0 Master 0 Master 1 400 pF 400 pF Enable I2C Bus Repeater PCA9541 5-Channel I2C Hub Master 0 Master 1 PCA9515 PCA9516 • Bi-directional I2C drivers isolate the I2C bus capacitance to each segment. PCA9541 • Multi-master capable (e.g., repeater transparent to bus arbitration and Master 0 Master 1 contention protocols) with only one repeater delay between segments. • Segments can be individually isolated • Voltage Level Translation DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 139 • 3.3 V or 5 V voltage levels allowed on the segment DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 142 Slide 140 Slide 142 PCA9541 in a point to point application where there are two dedicated buses to each slave card for even higher These bi-directional I2C drivers enable designers to redundancy, such as a bent pin would not disable all the isolate the I2C bus capacitance into smaller sections, cards. accommodating more I2C devices or a longer bus length. The I2C specification only allows 400 pF load Voltage Level Translators on the I2C bus and these devices can break the I2C bus into multiple 400 pF segments. I2C Bus Bi-Directional Voltage Level Translation PCA9515 and PCA9516 applications include 1.8 V 5V supporting the PCI management bus, > 8 PCI slots, 200 KΩ 1.5 V 1.2 V 1.0 V GTL2002 isolating SMBus to hot plug PCI slots and driving I2C VCORE GND GREF VCC to multiple system boards. Either 3.3 V or 5 V voltages SREF DREF S1 D1 are allowed on each segment to allow devices with CPU I/O Chipset I/O S2 D2 different voltages ranges to be used on the same bus. The devices are transparent to bus arbitration and • Voltage translation between any voltage from 1.0 V to 5.0 V • Bi-directional with no direction pin contention protocols in a multi-master environment. • Reference voltage clamps the input voltage with low propagation delay • Used for bi-directional translation of I2C buses at 3.3 V and/or 5 V to The PCA9518 expandable hub is designed to allow the processor I2C port at 1.2 V or 1.5 V or any voltage in-between • BiCMOS process provides excellent ESD performance more multiple groups of 4 downstream channels. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 141 Hot Swap Bus Buffers Slide 141 I2C Hot Swap Bus Buffer These devices are very useful in translation of I2C bus voltages as a lower and lower core voltages are used. The GTL2000 is 22 bits wide, the GTL2002 is 2 bits wide and the GTL2010 is 10 bits wide. See Application PCA9511 PCA9512 Note AN10145 for more information. PCA9513 PCA9514 SCL SDA • Allows I/O card insertion into a live backplane without corruption of busses • Control circuitry connects card after stop bit or idle occurs on the backplane • Bi-directional buffering isolates capacitance, allows 400 pF on either side • Rise time accelerator allows use of weaker DC pull-up currents while still meeting rise time requirements • SDA and SCL lines are precharged to 1V, minimizing current required to charge chip parasitic capacitance DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 143 Slide 143 45
- 46. AN10216-01 I2C Manual The PCA9511 hot swappable 2-wire bus buffer allows product’s internal I2C bus, will require safety I/O card insertion into a live backplane without isolation. corruption of the data and clock busses. Control • Medical equipment requires safety isolation of the circuitry prevents the backplane from being connected patient connections. Any power for the isolated to the card until a stop bit or bus idle occurs on the circuitry must be passed via isolating transformers. backplane without bus contention on the card. When The data paths are sometimes transformer coupled the connection is made, the PCA9511 provides bi- using carrier tones, but they could also be via opto- directional buffering, keeping the backplane and card isolated I2C. capacitances isolated. Rise time accelerator circuitry • Lamp dimmers and switches can be controlled over allows the use of weaker DC pull-up currents while still I2C data links. meeting rise time requirements. • Each light in a disco or live stage production could have its own identity and be individually computer During insertion, the SDA and SCL lines are controlled from a control desk or computer via I2C. precharged to 1 V to minimize the current required to Dimming (phase control) can be done with small charge the parasitic capacitance of the chip. micros or TCA280B from IES. Putting the phase controller inside each lamp will make it easier to The PCA9511 incorporates a digital ENABLE input meet EMC rules - lower power wiring radiation. pin, which forces the part into a low current mode when asserted low, and an open drain READY output pin, Applications requiring extension of the I2C bus (both which indicates that the backplane and card sides are P82B715 and P82B96): connected together. • Almost any application where a remote control needs to be located some distance from the main The PCA9512/13/14 are variants on the PCA9511. equipment cabinet, e.g. in medical or industrial applications. Some safe distances the P82B715 or The PCA9511DP is an alternate source for the Linear P82B96 can transmit I2C signals are: Tech LTC4300-1I and the PCA9512DP is an alternate o P82B715: 50 Ω coax cable or twisted- source for the Linear Tech LTC4300-2I. pair cables - 50 meters, 85 kHz o P82B96: Telephone cable pairs or Flat Ribbon Cable - 100 meters at 71 kHz or 1 Bus Extenders kilometer at 31 kHz I2C Bus Extenders Changing I2C bus signals for multi-point applications 3.3/5V 12V 12V Twisted-pair telephone wires, USB or flat ribbon cables Up to 15V logic levels, Include VCC & GND SCL NO LIMIT to the number of 3.3/5 12V connected bus devices ! Note: Schottky diode or Zener clamps may be 3.3V needed to limit spurious signals on very long wiring SDA P82B96 P82B96 P82B96 P82B96 SCL KEY POINTS P82B96 SDA/SCL SDA/SCL SDA/SCL SDA High drive outputs are used to extend the reach of the I2C bus and exceed the 400 pF/system limit. Link parking meters Link vending machines Warehouse Possible distances range from 50 and pay stations to save cell phone links pick/pack •-- systems •-- meters at 85kHz to 1km at 31kHz over •-- •-- •-- • Factory automation twisted-pair phone cable. •-- •-- Bus Buffer has split high drive outputs •-- •-- • Access/alarm systems I2C Bus Extender allowing differential transmission or •-- •-- Dual Bi-Directional Bus Buffer •-- • Video, LCD & LED display signs Opto-isolation of the I2C Bus. •-- •-- P82B715 •-- P82B96 • Hotel/motel management systems DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 144 • Monitor emergency lighting/exit signs DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 145 Slide 144 Slide 145 Applications requiring opto-isolation of the I2C bus (P82B96 only): The buffered 12V bus has exactly the same multi-drop • Digital telephone answering machines (Philips characteristic as a standard I2C but the restriction to 400 PCD6001), Fax machines, feature phones and pF has been removed so there is no longer any security system auto-dialers are connected to the restriction on the number of connected devices. P82B96 phone line and often powered from the 110/230 V alone can sink at least 30 mA (static specification, > 60 mains via double-insulated ‘plug-pack’ DC power mA dynamic) and there is no theoretical limitation to packs. Many use Microcontrollers (e.g. providing further amplification. Just adding a simple PCD33xx), and some will already have I2C buses. 2N2907A emitter-follower enables 500 mA bus sink Any other interfaces, e.g. connecting to the capability. 46
- 47. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Just adding a simple 2N2907A emitter-follower enables With large sink currents it is possible to drive a special 500 mA sink capability. type of low impedance “I2C” bus - say at 500 Ω, or even down to 50 Ω. With the ability to use logic This allows longer distance communication on the I2C voltages up to 15 V it is possible to drive hundreds of bus. See Application Note AN255 for more meters of cable, providing the clock rate is decreased to information. allow time for the signals to travel the long distances. It’s possible to run 100 meters with at least 70 kHz and Electro-Optical Isolation 1kilometer at 30 kHz. That beats CAN bus, based on useful byte rate! Changing I2C bus signals for Opto-isolation 3.3/5V Vcc 1 Vcc 2 Note the special bus formed when the P82B96 Tx and SCL Rx outputs are linked has all the usual properties of an SCL I2C bus -- it IS an I2C bus, but with some of the 3.3/5V P82B96 limitations removed. So it is a ‘multi-drop’ bus that can SDA support ANY NUMBER of physical connection nodes. SDA Of course the method of addressing of individual nodes must be designed but it’s easy with microcontrollers, Bi-directional data streams Low cost Optos can be directly driven 4N36 Optos for ~5kHz 6N137 for 100kHz Re-combined to I2C I2C compatible levels and possible using hardware, to achieve sub-addressing. Special logic levels (10-30mA) HCPL-060L for 400 kHz e.g. Vcc 2 = 5V ( I2C compatible 5V) VCC 1 = 2 to 12V Controlling equipment on phone lines Application examples: Parking meters and vehicle I2C currents (3mA) Higher current option, up to 30mA static sink AC Mains switches, lamp dimmers sensors are linked to a pay station, some have credit Isolating medical equipment card and pay-by-phone options. Groups of vending DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 147 machines can be linked so only one in a group needs a cell phone link for payment facility or reporting the Slide 147 stock/sales/faults situation. Warehouse systems transmit requirements to workstations, print labels, have real- Here the 30mA drive capability at Tx is used to directly time visibility of work status. Motel systems control drive low cost opto-couplers to achieve isolation of the access, air-con, messages via teletext on TV screen, I2C bus signals. This allows I2C nodes in industrial report room status. applications (e.g. factory automation) to have their grounds at different potentials. It allows I2C chips inside telephones to interface to external devices that Changing I2C bus signals for driving long distances Remote Control need to be grounded, for example to a PC to log Faxed information. It allows driving I2C chips connected to Enclosure 12V 12V 3.3 -5V Long cables the AC power mains with a safety isolation barrier. The SCL P82B96 allows operation up to 400 kHz. 3.3-5V 12V Rise Time Accelerators SDA P82B96 Rise Time Accelerators P82B96 Bi-directional Simply link the pins Twisted-pair telephone wires, Re-combine to data streams for Bi-directional USB or flat ribbon cables bi-directional I2C data streams Special logic levels 2V through 12V logic levels Convert the logic The LTC®1694-1 is a dual SMBus active pull- (I2C compatible 5V) Conventional CMOS signal levels back logic levels (2-15V) Able to send VCC and GND to I2C compatible up designed to enhance data transmission I2C currents (3mA) 100 meters at 70kHz speed and reliability under all specified SMBus Hot Swap Higher current option, NO LIMIT to the number of Protection loading conditions. The LTC1694-1 is also up to 30mA static sink connected devices ! compatible with the Philips I2C Bus. DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 146 The LTC1694-1allows multiple device connections or a longer, more capacitive interconnect, without compromising slew rates or bus Slide 146 performance, by supplying a high pull-up current of 2.2 mA to slew the SMBus or I2C lines during positive bus transitions During negative transitions or steady DC levels, the LTC1694-1 sources It is allowed to simply join the two unidirectional logic zero current. External resistors, one on each bus line, trigger the pins Tx and Rx to form a bi-directional bus with all the LTC1694-1 during positive bus transitions and set the pull-down current level. These resistors determine the slew rate during negative bus same features as I2C but with freedom to choose transitions and the logic low DC level. different logic voltages and sink larger currents than the DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 148 3 mA limitation of the I2C specifications. P82B96 alone can sink at least 30 mA (static Slide 148 specification, >60 mA dynamic) and there is no theoretical limitation to providing further amplification. Rise time accelerators like the LTC1694 and LCT1694- 1 are used to help control the rise time of the I2C bus. 47
- 48. AN10216-01 I2C Manual See Application Note AN255 Appendix 6 for Digital Potentiometers differences between the LTC1694 and LCT1694-1. Digital Potentiometers Parallel Bus to I2C Bus Controller • DS1846 nonvolatile (NV) tri- potentiometer, memory, and Parallel Bus to I2C Bus Controller MicroMonitor. The DS1846 is a highly integrated chip that combines three linear-taper potentiometers, 256 bytes of EEPROM memory, and a MicroMonitor. Chip Enable The part communicates over the Microcontroller Write Strobe I2C Interface Operation industry-standard 2-wire interface and is Read Strobe I2C Bus Control Reset available in a 20-pin TSSOP. Address Inputs Control Interrupt Request • The DS1846 is optimized for use in a variety of embedded systems Bus Buffer Data (8-bits) where microprocessor supervisory, NV storage, and control of analog functions are required. Common applications include gigabit transceiver modules, portable instrumentation, PDAs, cell phones, and • Controls all the I2C bus specific sequences, protocol, arbitration and a variety of personal multimedia products. timing DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 150 • Serves as an interface between most standard parallel-bus microcontrollers/ microprocessors and the serial I2C bus. • Allows the parallel bus system to communicate with the I2C bus Slide 150 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 149 Digital potentiometers are similar to the potentiometers Slide 149 you used to adjust with the screwdriver but these are adjusted via the I2C bus. Some digital potentiometers The PCF8584 and PCA9564 serve as an interface include onboard EEPROM so that settings are retained between most standard parallel-bus microcontrollers/ with the device is powered down. microprocessors and the serial I2C bus and allow the parallel bus system to communicate bi-directionally Analog to Digital Converters with the I2C bus. This commonly is referred as the bus master. Communication with the I2C bus is carried out on a byte-wise basis using interrupt or polled Analog to Digital Converter handshake. It controls all the I2C bus specific These devices translate between digital information communicated sequences, protocol, arbitration and timing. Supply - via the I2C bus and analog POR Oscillator, intern / + extern - information measured by a INT Interrupt + voltage. The PCA9564 is similar to the PCF8584 but operates at SDA SCL I2C-bus interface ADC / DAC - - + Analog to digital conversion is 2.3 to 3.6 V VCC and up to 400 kHz (slave mode) with - + + - used for measurement of the size of a physical quantity various enhancements added that were requested by Sub + address decoder Analog reference (temperature, pressure …), proportional control or engineers. transformation of physical amplitudes into numerical values for calculation. PCA9564 PCF8584 Comments Digital to analog conversion is • 4 channel Analog to Digital 1. Voltage range 2.3-3.6V 4.5-5.5V PCA9564 is 5V tolerant • 1 channel Digital to Analog used for creation of particular 2. Max I2C freq. 360 kHz 90 kHz Faster I2C control voltages to control DC motors or LCD contrast. 3. Clock source Internal External Less expensive/more flexible DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 151 4. Parallel interface Fast Slow Compatible with faster processors Slide 151 In addition, the PCA9564 has been made very similar to The PCF8591 is capable of converting four different the Philips standard 80C51 microcontroller I2C analog voltages to the digital values for processing in hardware so existing code can be utilized with a few the microcontroller. It can also generate one analog modifications. voltage by converting an 8-bit digital value provided by the microcontroller. Several kinds of analog information in your applications, such as temperature, pressure, battery level, signal strength, etc can be processed by such a device. These are digitally processed and can be subsequently displayed, used to control contacts, switches, relay, etc. for example using the previously discussed I/O expander PCA9554. The D/A output is useful for such jobs as LCD contrast control. 48
- 49. AN10216-01 I2C Manual Serial RAM/EEPROM 2 is identical to the PCF85102C-2 except that the fixed I2C address is different, allowing up to eight of each I2C Serial CMOS RAM/EEPROMs device to be used on the same I2C bus. EEPROM Standard Sizes Supply 128 x 8-byte (1 kbit) 24C01 RAM Address pointer POR SDA Hardware Monitors/Temp & Voltage Sensors Address POR I2C-bus pointer interface SCL 256 x 8-byte (2 kbit) 24C02 256 I2C-bus 512 x 8-byte (4 kbit) 24C04 Byte address Sub interface I2C Hardware Monitors decoder Sub E2PROM 256 address 1024 x 8-byte (8 kbit) 24C08 Byte decoder Sub 2048 x 8-byte (16 kbit) 24C16 RAM address decoder 4096 x 8-byte (32 kbit) 24C32 8192 x 8-byte (64 kbit) 24C64 Remote 16384 x 8-byte (128 kbit) 24C128 Sensor 32768 x 8-byte (256 kbit) 24C256 65536 x 8-byte (512 kbit) 24C512 Digital Temperature • I²C bus is used to read and write information to and from the memory Sensor and Thermal • Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory I2C Temperature Monitor Watchdog™ I2C Temperature and Voltage • 1,000,000 write cycles, unlimited read cycles NE1617A LM75A Monitor(Heceta4) • 10 year data retention NE1618 NE1619 DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 153 – Sense temperature and/or monitor voltage via I²C Slide 153 – Remote sensor can be internal to microprocessor There are different kinds of memories in the line of I²C DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 154 bus compatible components such as: RAM, EEPROM, video memories and Flash memories. Slide 154 • RAM is Random Access Memory • EEPROM is Electrically Erasable Programmable Hardware monitors such as the NE1617A, NE1618, Read Only Memory NE1619 and LM75A use the I²C bus to report • Common small serial memories (RAM and temperature and/or voltage. Some of the temperature EEPROM) are often used in applications. monitors include hardware pins that allow external EEPROMs are particularly useful in applications transistors/diodes to be located in external components where data retention during power-off is essential (e.g., processors) that sense the temperature much more (for example: meter readings, electronic key, accurately then if the sensor was mounted externally on product identification number, etc). the package. The test pins are used at the factory to • A single pinning is used for these ICs because they calibrate/set the temperature sensor and are left floating are very similar and their pinouts have been by the customer. intentionally designed for interchangeability. • EEPROMs store data (2kbits organized in 256 x 8 Microcontrollers in the PCF8582C-2 for example), including set points, temperature, alarms, and more, for a I2C Microcontroller guaranteed minimum storage time of ten years in The master can be either a the absence of power. EEPROMs change values bus controller or µcontroller Timer + − + − 8K ISP 512B and provides the brains 100,000 to 1,000,000 times and have an infinite Analog Comparators Ports 0, 1, 2, 3 IAP Data Flash EEPROM 768B SRAM 0/1 16-bit behind the I2C bus operation. number of read cycles, while consuming only 10 600% Accelerated C51 Core Power Management, RTC, WDT, power-on-reset, brownout detect A bus controller adds I2C bus micro amperes of current. capability to a regular 32xPLL Keypad/ Internal ±2.5% 16-bit Enh. Pattern Match 7.3728 MHz I2C SPI Interrupt RC Oscillator PWM CCU UART µcontroller without I2C, or to add more I2C ports to For example, the PCA8581 is organized as 128 words µcontrollers already equipped with an I2C port of 8-bytes. Addresses and data are transferred serially Microcontrollers with Multiple Serial ports can such as the: via a two-line bi-directional bus (I2C bus). The built-in convert from: P87LPC76x P89C55x 100 kHz I2C 100 kHz I2C I2C to UART/RS232 – LPC76x, 89C66x and word address register is incremented automatically after 89LPC9xx P89C65x 100 kHz I2C each data byte is written or read. All bytes can be read I2C to SPI - P87C51MX and 89LPC9xx family I2C to CAN - 8 bit P87C591 and 16 bit PXA-C37 P89C66x P89LPC932 100 kHz I2C 400 kHz I2C in a single addressing operation. Up to 8 bytes can be written in one operation, reducing the total write time DesignCon 2003 TecForum I2C Bus Overview 155 per byte. Slide 155 The PCA8582C-2 is pin and address compatible to: PCF8570, PCF8571, PCF8572 and PCF8581. The Microcontrollers are the brains behind the I2C bus PCF85102C-2 is identical to the PCF8582C-2 with pin operation. More and more micros include at least one 7 (Programming time control output) as a ‘no connect’ I2C port if not more to allow multiple I2C buses to be to allow it to be used in competitors sockets since PTC controlled from the same microcontroller. should be left floating or held at VCC. The PCF85103C- 49
- 50. AN10216-01 I2C Manual I2C Patent and Legal Information whatever. This also applies to FPGAs. However, since the FPGAs are programmed by the user, the user is The I2C bus is protected by patents held by Philips. considered a company that builds an I2C-IC and would Licensed IC manufacturers that sell devices need to obtain the license from Philips. incorporating the technology already have secured the rights to use these devices, relieving the burden from Apply for a license or text of the Philips I2C Standard the purchaser. A license is required for implementing License Agreement an I2C interface on a chip (IC, ASIC, FPGA, etc). • US and Canadian companies: contact Mr. Piotrowski ([email protected]) It is Philips's position that all chips that can talk to the • All other companies: contact Mr. Hesselmann I2C bus must be licensed. It does not matter how this ([email protected]) interface is implemented. The licensed manufacturer may use its own know how, purchased IP cores, or ADDITIONAL INFORMATION The latest datasheets for both released and sampling general purpose I2C devices and other Specialty Logic products can be found at the Philips Logic Product Group website: http://www.philipslogic.com/i2c Datasheets for all released Philips Semiconductors I2C devices can be found at the Philips Semiconductors website: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/i2c More information or technical support on I2C devices can be provided by e-mail: [email protected] APPLICATION NOTES AN168 Theory and Practical Consideration using PCF84Cxx and PCD33xx Microcontrollers AN250 PCA8550 4-Bit Multiplexed/1-Bit Latched 5-Bit I2C E2PROM AN255 I2C/SMBus Repeaters, Hubs, and Expanders AN256 PCA9500/01 Provides Simple Card Maintenance and Control Using I2C AN262 PCA954X Family OF I2C/SMBus Multiplexers and Switches AN264 I2C Devices for LED Display Control AN444 Using the P82B715 I2C Extender on Long Cables AN460 Using the P82B96 for Bus Interface AN469 I2C I/O Ports AN10145 Bi-directional Low Voltage Translators GTL2000, GTL2002, GTL2010 AN10146 I2C 2002-1 Evaluation Board AN95068 C Routines for the PCx8584 AN96119 I2C with the XA-G3 AN97055 Bi-Directional Level Shifter for I2C-Bus and Other Systems ANP82B96 Introducing the P82B96 I2C Bus Buffer 50
- 51. AN10216-01 I2C Manual ANZ96003 Using the PCF8584 with Non-Specified Timings and Other Frequently Asked Questions 51