Logistic Regression in Case-Control Study
Download as PPT, PDF7 likes11,180 views
This document provides an introduction to using logistic regression in R to analyze case-control studies. It explains how to download and install R, perform basic operations and calculations, handle data, load libraries, and conduct both conditional and unconditional logistic regression. Conditional logistic regression is recommended for matched case-control studies as it provides unbiased results. The document demonstrates how to perform logistic regression on a lung cancer dataset to analyze the association between disease status and genetic and environmental factors.
1 of 28
Downloaded 277 times







![Data handling in R
Load data: mydata = read.csv(“/path/mydata.csv”)
See data on screen: data(mydata)
See top part of data: head(mydata)
Specific number of rows and column of data:
mydata[1:10,1:3]
To get a type of data: class(mydata)
Changing class of data: newdata = as.matrix(mydata)
Summary of data: summary(mydata)
Selecting (KEEPING) variables (columns)
newdata = mydata[c(1,3:5)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ihcclogisticregression-130728061733-phpapp02/85/Logistic-Regression-in-Case-Control-Study-9-320.jpg)
![Data handling in R
Selecting observations
newdata= subset(mydata, age>=20 | age <10,
select=c(ID, weight)
newdata= subset(mydata, sex==“Male” & age >25,
select=weight:income)
Excluding (DROPPING) variables (columns)
newdata = mydata[c(-3,-5)]
mydata$v3 = NULL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ihcclogisticregression-130728061733-phpapp02/85/Logistic-Regression-in-Case-Control-Study-10-320.jpg)

















Ad
Recommended
Basic survival analysis



Basic survival analysisMike LaValley This document provides an overview of survival analysis. It defines survival analysis as statistical methods for analyzing longitudinal data on the occurrence of events over time. Key features include events that may or may not occur for subjects and the length of time until an event can vary. Censoring, where subjects drop out before an event, is accommodated. The objectives, terms, and reasons for using survival analysis are described. Key concepts like hazard rates, survival functions, and the Kaplan-Meier estimate are also introduced.
Ch 11- Population Variances.pptx



Ch 11- Population Variances.pptxtharkistani This document discusses hypothesis testing for population variances. It covers testing for a single population variance, testing if two population variances are equal, and how to conduct these tests. The chi-square distribution is used to develop critical values and rejection regions for variance hypothesis tests. An example compares the variances of temperature readings from two thermostat models, testing if one has an "acceptable" variance below 0.5 and if their variances are equal.
Chapter 3 Confidence Interval



Chapter 3 Confidence Intervalghalan 1. Sampling error occurs because sample means are not equal to the population mean and differ from each other.
2. The distribution of sample means follows a normal distribution if drawn from a normal population, and approximates a normal distribution if drawn from a non-normal population as the sample size increases.
3. A confidence interval for the population mean or probability can be constructed given the sample size, mean or probability, and standard deviation. The confidence level indicates the probability the true population parameter falls within the interval.
Basic Biostatistics and Data managment 



Basic Biostatistics and Data managment Tadesse Awoke Ayele This course is designed to give students an overview of research versus biostatistics, Stata, test of association, comparisons of means, Correlation and regression, Generalized Linear Models (GLM).
The sessions are designed to introduce the de
nitions and basic
concepts of biostatistics, statistical inference, t-test, ANOVA, Correlation, Linear regression, logistic regression, Poisson regression, Negative binomial regression, and Zero in
ated poisson regression.
The overall emphasis will be placed on understanding the language of statistics and the art of statistical investigation.
Survival analysis



Survival analysisCollege of Fisheries, KVAFSU, Mangalore, Karnataka Survival analysis is a branch of statistics used to analyze time-to-event data, such as time until death or failure. It estimates the probability that an individual survives past a given time and compares survival times between groups. Objectives include estimating survival probabilities, comparing survival between groups, and assessing how covariates relate to survival time. Survival data can be complete or censored. The Kaplan-Meier estimator is used to estimate survival when there is censoring. The log-rank test compares survival curves between treatment groups, and Cox regression incorporates covariates to predict survival probabilities.
Survival analysis



Survival analysisSanjaya Sahoo This document provides an overview of survival analysis. It defines key terms like survival, censoring, and hazard functions. It describes the Kaplan-Meier method for estimating survival functions from censored data and comparing survival curves between groups using the log-rank test. Censoring occurs when subjects are lost to follow-up before the event of interest. The Kaplan-Meier method accounts for censoring to calculate the probability of surviving up to different time points.
Measures of association 2013



Measures of association 2013dinahoefer11 This document discusses measures of association used to quantify the relationship between an exposure and outcome in epidemiological studies. There are two types of measures: absolute measures, which are based on differences in disease frequency between exposed and unexposed groups, and relative measures, which are ratios of disease frequency. Common measures include risk difference, risk ratio, and odds ratio. Measures are calculated using data organized in 2x2 tables and can be interpreted as showing the strength and direction of association.
Association & causation (2016)



Association & causation (2016)Shyam Ashtekar The document discusses key concepts in establishing causation in epidemiology, including the difference between association and causation. It explains that causation requires determining if a factor A truly causes outcome B rather than being a spurious relationship. Several of Hill's criteria for establishing a causal relationship are described, such as strength of association, consistency of findings, specificity of the relationship, and examining alternative explanations through study design and accounting for potential confounding factors. The document emphasizes that multiple factors often interact to cause outcomes, and that proving causation involves considering the strength and consistency of evidence rather than any single study.
Poisson regression models for count data



Poisson regression models for count dataUniversity of Southampton This document provides an introduction to Poisson regression models for count data. It outlines that Poisson regression can be used to model count variables that have a Poisson distribution. A simple equiprobable model is presented where the expected count is equal across all categories. This equiprobable model establishes a null hypothesis that can be tested using likelihood ratio or Pearson's test statistics. Residual analysis is also discussed. Finally, the document introduces how a covariate can be added to a Poisson regression model to establish relationships between the count variable and explanatory variables.
Estimating risk



Estimating riskTarek Tawfik Amin This document provides definitions and examples of key concepts for estimating risk from epidemiological studies, including probability, odds, relative risk, and absolute risk. It discusses how relative risk is calculated from cohort and case-control study designs. Relative risk compares the risk of an outcome between exposed and unexposed groups to determine if exposure is associated with increased risk. The odds ratio, which estimates relative risk, is presented as the measure used to assess association in case-control studies. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating and interpreting these risk measures.
Binomial distribution



Binomial distributionnumanmunir01 A random variable is a variable whose values are determined by the outcome of a random experiment and can be used to model probabilities. Examples of random variables include the sum of dice rolls or number of heads from coin tosses. A probability distribution assigns probabilities to each possible value of a random variable. It must satisfy the properties that probabilities are greater than or equal to 0 and sum to 1. Common probability distributions include the binomial and normal distributions.
Probability Distributions



Probability DistributionsCIToolkit A Probability Distribution is a way to shape the sample data to make predictions and draw conclusions about an entire population. It refers to the frequency at which some events or experiments occur. It helps finding all the possible values a random variable can take between the minimum and maximum statistically possible values.
Association and causation



Association and causationAparna Chaudhary A principal aim of epidemiology is to assess the cause of disease. However, since most epidemiological studies are by nature observational rather than experimental, a number of possible explanations for an observed association need to be considered before we can infer a cause-effect relationship exists.
Survival analysis



Survival analysisHar Jindal This document discusses survival analysis techniques. It begins with an overview of survival, censoring, and the need for survival analysis when not all patients have died or had the event of interest. It then describes the key techniques of life tables/actuarial analysis and the Kaplan-Meier method. Life tables involve constructing a hypothetical cohort and estimating survival at different ages based on mortality rates. The Kaplan-Meier method is commonly used to illustrate survival curves and gives partial credit to censored observations. A modified life table is also presented to analyze survival outcomes in different treatment groups.
Survival Data Analysis for Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Statistik Jakarta



Survival Data Analysis for Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Statistik JakartaSetia Pramana This document outlines a course on survival data analysis. It provides an overview of the course content which includes introduction to survival data, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, Cox proportional hazards models, parametric survival functions, and competing risks. It also describes the course workload which is 40% theory and 60% practice, including a group project, weekly presentations, and using R for analysis. Reference books and materials for learning R for survival analysis are also provided.
Attributable risk and population attributable risk



Attributable risk and population attributable riskAbino David This document defines risk factors and describes methods for identifying and quantifying risk. It defines a risk factor as an attribute or exposure associated with disease development. Epidemiological studies help identify risk factors and estimate degree of risk. Relative risk compares incidence between exposed and unexposed groups, while attributable risk indicates how much disease can be attributed to exposure by comparing incidence rates. Two examples are given to illustrate these concepts and how attributable risk informs potential public health interventions.
Epidemiological statistics



Epidemiological statisticsGarima Aggarwal This document provides an introduction to commonly used epidemiological and statistical terms that are important for clinicians. It defines terms like incidence, prevalence, sensitivity, specificity, mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and different types of epidemiological studies including observational studies like case reports, cross-sectional studies, case-control studies, and cohort studies as well as experimental studies like randomized controlled trials. It also discusses statistical measures used to analyze epidemiological data like relative risk, attributable risk, odds ratio, confidence intervals, p-values, meta-analysis, and correlation coefficients.
How to write a paper statistics



How to write a paper statisticsAmany El-seoud This document defines statistics and describes its uses in medical research. Statistics is the science of dealing with numbers to obtain objective, unbiased information from data. In medicine, statistics is used to descriptively summarize population data, prove associations between variables, compare study groups, and evaluate health programs. Data comes from records, surveys, and research studies. Statistical analysis involves collecting, summarizing, and presenting data in tables and graphs, then interpreting the information. Inferential statistics tests hypotheses using significance tests for means, correlations, regressions, and distributions to analyze relationships between variables and predict outcomes. Correlation does not necessarily indicate causation. Qualitative data is also analyzed using chi-squared and difference of proportions tests.
Survival Analysis Using SPSS



Survival Analysis Using SPSSNermin Osman The document discusses survival analysis techniques using SPSS. It defines key survival analysis terms and covers non-parametric and semi-parametric survival analysis methods like Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression. For Kaplan-Meier analysis, it provides an example to compare the effect of two drugs on time to effect. For Cox regression, it demonstrates how to identify attributes associated with customer churn. The document also discusses how to address time-dependent covariates in Cox regression models.
Modern epidemiology



Modern epidemiologyUE This document provides an overview of modern epidemiology. It defines epidemiology as the study of the occurrence and distribution of health-related diseases or events in populations, including their determinants and control. The purposes of epidemiology are described as investigating disease extent and priorities, studying disease progression, identifying causes and risks, recommending interventions, and informing public policy. John Snow is highlighted for his work tracing a cholera outbreak that improved public health systems.
Chapter 4 part2- Random Variables



Chapter 4 part2- Random Variablesnszakir Random Variable, Discrete Random Variables, Continuous Random Variables, Normal Distributions as Probability Distributions
Confidence interval & probability statements 



Confidence interval & probability statements DrZahid Khan This document discusses confidence intervals and probability. It defines confidence intervals as a range of values that provide more information than a point estimate by taking into account variability between samples. The document provides examples of how to calculate 95% confidence intervals for a proportion, mean, odds ratio, and relative risk using sample data and the appropriate formulas. It explains that confidence intervals convey the level of uncertainty associated with point estimates and allow estimation of how close a sample statistic is to the unknown population parameter.
Density Function | Statistics



Density Function | StatisticsTransweb Global Inc Density function in probability or density of any continuous instantly selected variable is a function in which the count provided at given point (sample) in the available set of possibilities random values can be predicted as giving a linked or dependent prospect for a continuous unplanned variable would the same of that sample. Copy the link given below and paste it in new browser window to get more information on Density Function:- www.transtutors.com/homework-help/statistics/density-function.aspx
Multiple regression presentation



Multiple regression presentationCarlo Magno This document discusses multiple regression analysis and its use in predicting relationships between variables. Multiple regression allows prediction of a criterion variable from two or more predictor variables. Key aspects covered include the multiple correlation coefficient (R), squared correlation coefficient (R2), adjusted R2, regression coefficients, significance testing using t-tests and F-tests, and considerations for using multiple regression such as sample size and normality assumptions.
Introduction to scoping reviews



Introduction to scoping reviewsRizwan S A A short introduction to the methods and principles of conducting a scoping review in health sciences.
5. Non parametric analysis



5. Non parametric analysisRazif Shahril This document outlines a lecture on non-parametric statistics. It begins by defining parametric and non-parametric tests, noting that non-parametric tests do not require assumptions of normality and can be used when data is not of sufficient quality for parametric tests. It then reviews the assumptions of common parametric t-tests and how to determine if the data violates assumptions. The document introduces several non-parametric tests: the Mann-Whitney U test for comparing two independent groups, the Wilcoxon test for comparing two related groups, and the Kruskal-Wallis H test for comparing three or more independent groups. It provides examples and outlines how to perform each test in SPSS.
Mortality rates & standardization



Mortality rates & standardizationVaishnavi Madhavan Comparison of mortality rates are important in public health. hence standardisation is of important value in public health
Stat 3203 -multphase sampling



Stat 3203 -multphase samplingKhulna University This document discusses double sampling and multiphase sampling techniques. It provides examples of using double sampling to estimate population means and variances when auxiliary information is collected from the full sample and primary study variables from a subsample. Optimal allocation formulas are presented to minimize variance for a given cost. Difference, ratio, and regression estimators are also discussed using the double sampling framework.
Spatial Data Science with R



Spatial Data Science with Ramsantac Slide show for the webinar on "Spatial Data Science with R" organized for the GeoDevelopers.org community. The video of the webinar and all the related materials including source code and sample data can be downloaded from this link: http://amsantac.co/blog/en/2016/08/07/spatial-data-science-r.html
In this webinar I talked about Data Science in the context of its application to spatial data and explained how we can use the R language for the analysis of geographic information within the different stages of a data science workflow, from the import and processing of spatial data to visualization and publication of results.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Poisson regression models for count data



Poisson regression models for count dataUniversity of Southampton This document provides an introduction to Poisson regression models for count data. It outlines that Poisson regression can be used to model count variables that have a Poisson distribution. A simple equiprobable model is presented where the expected count is equal across all categories. This equiprobable model establishes a null hypothesis that can be tested using likelihood ratio or Pearson's test statistics. Residual analysis is also discussed. Finally, the document introduces how a covariate can be added to a Poisson regression model to establish relationships between the count variable and explanatory variables.
Estimating risk



Estimating riskTarek Tawfik Amin This document provides definitions and examples of key concepts for estimating risk from epidemiological studies, including probability, odds, relative risk, and absolute risk. It discusses how relative risk is calculated from cohort and case-control study designs. Relative risk compares the risk of an outcome between exposed and unexposed groups to determine if exposure is associated with increased risk. The odds ratio, which estimates relative risk, is presented as the measure used to assess association in case-control studies. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating and interpreting these risk measures.
Binomial distribution



Binomial distributionnumanmunir01 A random variable is a variable whose values are determined by the outcome of a random experiment and can be used to model probabilities. Examples of random variables include the sum of dice rolls or number of heads from coin tosses. A probability distribution assigns probabilities to each possible value of a random variable. It must satisfy the properties that probabilities are greater than or equal to 0 and sum to 1. Common probability distributions include the binomial and normal distributions.
Probability Distributions



Probability DistributionsCIToolkit A Probability Distribution is a way to shape the sample data to make predictions and draw conclusions about an entire population. It refers to the frequency at which some events or experiments occur. It helps finding all the possible values a random variable can take between the minimum and maximum statistically possible values.
Association and causation



Association and causationAparna Chaudhary A principal aim of epidemiology is to assess the cause of disease. However, since most epidemiological studies are by nature observational rather than experimental, a number of possible explanations for an observed association need to be considered before we can infer a cause-effect relationship exists.
Survival analysis



Survival analysisHar Jindal This document discusses survival analysis techniques. It begins with an overview of survival, censoring, and the need for survival analysis when not all patients have died or had the event of interest. It then describes the key techniques of life tables/actuarial analysis and the Kaplan-Meier method. Life tables involve constructing a hypothetical cohort and estimating survival at different ages based on mortality rates. The Kaplan-Meier method is commonly used to illustrate survival curves and gives partial credit to censored observations. A modified life table is also presented to analyze survival outcomes in different treatment groups.
Survival Data Analysis for Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Statistik Jakarta



Survival Data Analysis for Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Statistik JakartaSetia Pramana This document outlines a course on survival data analysis. It provides an overview of the course content which includes introduction to survival data, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, Cox proportional hazards models, parametric survival functions, and competing risks. It also describes the course workload which is 40% theory and 60% practice, including a group project, weekly presentations, and using R for analysis. Reference books and materials for learning R for survival analysis are also provided.
Attributable risk and population attributable risk



Attributable risk and population attributable riskAbino David This document defines risk factors and describes methods for identifying and quantifying risk. It defines a risk factor as an attribute or exposure associated with disease development. Epidemiological studies help identify risk factors and estimate degree of risk. Relative risk compares incidence between exposed and unexposed groups, while attributable risk indicates how much disease can be attributed to exposure by comparing incidence rates. Two examples are given to illustrate these concepts and how attributable risk informs potential public health interventions.
Epidemiological statistics



Epidemiological statisticsGarima Aggarwal This document provides an introduction to commonly used epidemiological and statistical terms that are important for clinicians. It defines terms like incidence, prevalence, sensitivity, specificity, mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and different types of epidemiological studies including observational studies like case reports, cross-sectional studies, case-control studies, and cohort studies as well as experimental studies like randomized controlled trials. It also discusses statistical measures used to analyze epidemiological data like relative risk, attributable risk, odds ratio, confidence intervals, p-values, meta-analysis, and correlation coefficients.
How to write a paper statistics



How to write a paper statisticsAmany El-seoud This document defines statistics and describes its uses in medical research. Statistics is the science of dealing with numbers to obtain objective, unbiased information from data. In medicine, statistics is used to descriptively summarize population data, prove associations between variables, compare study groups, and evaluate health programs. Data comes from records, surveys, and research studies. Statistical analysis involves collecting, summarizing, and presenting data in tables and graphs, then interpreting the information. Inferential statistics tests hypotheses using significance tests for means, correlations, regressions, and distributions to analyze relationships between variables and predict outcomes. Correlation does not necessarily indicate causation. Qualitative data is also analyzed using chi-squared and difference of proportions tests.
Survival Analysis Using SPSS



Survival Analysis Using SPSSNermin Osman The document discusses survival analysis techniques using SPSS. It defines key survival analysis terms and covers non-parametric and semi-parametric survival analysis methods like Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression. For Kaplan-Meier analysis, it provides an example to compare the effect of two drugs on time to effect. For Cox regression, it demonstrates how to identify attributes associated with customer churn. The document also discusses how to address time-dependent covariates in Cox regression models.
Modern epidemiology



Modern epidemiologyUE This document provides an overview of modern epidemiology. It defines epidemiology as the study of the occurrence and distribution of health-related diseases or events in populations, including their determinants and control. The purposes of epidemiology are described as investigating disease extent and priorities, studying disease progression, identifying causes and risks, recommending interventions, and informing public policy. John Snow is highlighted for his work tracing a cholera outbreak that improved public health systems.
Chapter 4 part2- Random Variables



Chapter 4 part2- Random Variablesnszakir Random Variable, Discrete Random Variables, Continuous Random Variables, Normal Distributions as Probability Distributions
Confidence interval & probability statements 



Confidence interval & probability statements DrZahid Khan This document discusses confidence intervals and probability. It defines confidence intervals as a range of values that provide more information than a point estimate by taking into account variability between samples. The document provides examples of how to calculate 95% confidence intervals for a proportion, mean, odds ratio, and relative risk using sample data and the appropriate formulas. It explains that confidence intervals convey the level of uncertainty associated with point estimates and allow estimation of how close a sample statistic is to the unknown population parameter.
Density Function | Statistics



Density Function | StatisticsTransweb Global Inc Density function in probability or density of any continuous instantly selected variable is a function in which the count provided at given point (sample) in the available set of possibilities random values can be predicted as giving a linked or dependent prospect for a continuous unplanned variable would the same of that sample. Copy the link given below and paste it in new browser window to get more information on Density Function:- www.transtutors.com/homework-help/statistics/density-function.aspx
Multiple regression presentation



Multiple regression presentationCarlo Magno This document discusses multiple regression analysis and its use in predicting relationships between variables. Multiple regression allows prediction of a criterion variable from two or more predictor variables. Key aspects covered include the multiple correlation coefficient (R), squared correlation coefficient (R2), adjusted R2, regression coefficients, significance testing using t-tests and F-tests, and considerations for using multiple regression such as sample size and normality assumptions.
Introduction to scoping reviews



Introduction to scoping reviewsRizwan S A A short introduction to the methods and principles of conducting a scoping review in health sciences.
5. Non parametric analysis



5. Non parametric analysisRazif Shahril This document outlines a lecture on non-parametric statistics. It begins by defining parametric and non-parametric tests, noting that non-parametric tests do not require assumptions of normality and can be used when data is not of sufficient quality for parametric tests. It then reviews the assumptions of common parametric t-tests and how to determine if the data violates assumptions. The document introduces several non-parametric tests: the Mann-Whitney U test for comparing two independent groups, the Wilcoxon test for comparing two related groups, and the Kruskal-Wallis H test for comparing three or more independent groups. It provides examples and outlines how to perform each test in SPSS.
Mortality rates & standardization



Mortality rates & standardizationVaishnavi Madhavan Comparison of mortality rates are important in public health. hence standardisation is of important value in public health
Stat 3203 -multphase sampling



Stat 3203 -multphase samplingKhulna University This document discusses double sampling and multiphase sampling techniques. It provides examples of using double sampling to estimate population means and variances when auxiliary information is collected from the full sample and primary study variables from a subsample. Optimal allocation formulas are presented to minimize variance for a given cost. Difference, ratio, and regression estimators are also discussed using the double sampling framework.
Viewers also liked (15)
Spatial Data Science with R



Spatial Data Science with Ramsantac Slide show for the webinar on "Spatial Data Science with R" organized for the GeoDevelopers.org community. The video of the webinar and all the related materials including source code and sample data can be downloaded from this link: http://amsantac.co/blog/en/2016/08/07/spatial-data-science-r.html
In this webinar I talked about Data Science in the context of its application to spatial data and explained how we can use the R language for the analysis of geographic information within the different stages of a data science workflow, from the import and processing of spatial data to visualization and publication of results.
Confounder and effect modification



Confounder and effect modificationAl-YAQIN DIAGNOSTIC ULTRASONIC CLINIC BAGHDAD 1. Effect modification and confounding are two aspects to consider when examining the relationship between an exposure and outcome. Effect modification provides useful information about how a third variable impacts the relationship, while confounding can distort the observed effect.
2. Stratifying the data and calculating stratum-specific odds ratios is a way to check for effect modification and confounding. Effect modification is present if the odds ratios differ substantially between strata. Confounding is present if the crude odds ratio differs from the stratified odds ratios.
3. It is important to measure potential confounding factors so they can be controlled for through stratification or multivariate analysis. This prevents confounding from distorting the observed effect between the exposure and outcome.
手把手教你 R 語言分析實務



手把手教你 R 語言分析實務Helen Afterglow 2016-09-04
本課程針對對 R 語言有基本認識但想更進一步擁有實務經驗的夥伴們。若您 R 語言翻轉教室 的內容都熟悉了,卻苦無實戰機會,最適合來和我們一起實作練習。
Bias and confounding



Bias and confoundingIkram Ullah This document discusses bias and confounding in epidemiological studies. It defines bias as systematic error that results in incorrect estimation of exposure-outcome associations. Selection bias and information bias are two common types of bias. Confounding occurs when another exposure is associated with both the disease and exposure being studied, independently of the exposure-disease relationship. Methods to control for confounding include restriction, matching, randomization, stratification, and multivariate analysis at the design and analysis stages of a study.
Research Methodology



Research MethodologyAneel Raza This chapter discusses variables and different types of variables. It defines a variable as something that can be measured and can take on different values. Variables are derived from concepts and indicators are used to convert concepts into measurable variables. There are several types of variables including independent and dependent variables, and variables can be classified based on their causal relationship, study design, or unit of measurement. Measurement scales include nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales, with each scale building upon the previous one and allowing for different types of statistical analysis.
Dummy variable



Dummy variableAkram Ali Dummy variables are used to represent qualitative or categorical variables that take on only two values, usually 0 and 1. A dummy variable indicates the presence or absence of a particular attribute. For example, a dummy variable could represent gender where 1 = male and 0 = female. Dummy variables allow qualitative variables to be used in regression models. However, there is a "dummy variable trap" where including dummy variables for all categories of a qualitative variable leads to perfect multicollinearity. To avoid this, only n-1 dummy variables should be included where there are n categories.
R programming



R programmingShantanu Patil hey guys this is ppt of R programming which will provide you detail knowledge of language by IT Expert
Antenatal care



Antenatal careMeklelle university This document outlines antenatal care (ANC), including its objectives to reduce maternal and infant morbidity and mortality through early detection of complications, health education, and preventive interventions. It describes traditional and focused ANC models, with the focused model recommending 4 routine visits and evidence-based activities. The initial ANC visit includes a detailed history, exam, and diagnostic workup to identify risks and plan care. Subsequent visits monitor progress and new issues. Strategies to assure fetal well-being include assessing growth, movements, and tests after 28 weeks. Health interventions emphasize education, nutrition, and psychological support.
Variables



VariablesHiba Armouche This document discusses different types of variables that are important to consider when studying relationships. It defines a variable as any characteristic that can vary, and a constant as a characteristic that is the same for all members of a group. The document outlines independent and dependent variables, quantitative and categorical variables, moderator variables, mediator variables, and extraneous variables. Understanding the relationships between these different types of variables is essential for explaining phenomena in research.
Variables



Variablesshoffma5 This document discusses key concepts in research variables including:
1) Independent variables are those that influence or explain variation in the dependent variable, while dependent variables are outcomes measured.
2) Variables can be categorical (taking a small set of values) or continuous (quantitative and measured on a scale).
3) Scales of measurement include nominal (labels), ordinal (ordered ranks), interval (equal intervals), and ratio (true zero point).
4) Identifying the independent and dependent variables and their properties (categorical vs. continuous, scale of measurement) is important for research questions.
Logistic regression



Logistic regressionsaba khan Logistic regression allows prediction of discrete outcomes from continuous and discrete variables. It addresses questions like discriminant analysis and multiple regression but without distributional assumptions. There are two main types: binary logistic regression for dichotomous dependent variables, and multinomial logistic regression for variables with more than two categories. Binary logistic regression expresses the log odds of the dependent variable as a function of the independent variables. Logistic regression assesses the effects of multiple explanatory variables on a binary outcome variable. It is useful when the dependent variable is non-parametric, there is no homoscedasticity, or normality and linearity are suspect.
SAMPLING AND SAMPLING ERRORS



SAMPLING AND SAMPLING ERRORSrambhu21 This document discusses various sampling methods used for data collection. It defines key terms like population, sample, parameter, and statistic. It describes probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, and multistage sampling. It also discusses non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, purposive sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, and self-selection sampling. The document concludes by explaining the different types of sampling errors like sample errors and non-sample errors.
Ad
Similar to Logistic Regression in Case-Control Study (20)
7. logistics regression using spss



7. logistics regression using spssDr Nisha Arora This document provides guidance on performing and interpreting logistic regression analyses in SPSS. It discusses selecting appropriate statistical tests based on variable types and study objectives. It covers assumptions of logistic regression like linear relationships between predictors and the logit of the outcome. It also explains maximum likelihood estimation, interpreting coefficients, and evaluating model fit and accuracy. Guidelines are provided on reporting logistic regression results from SPSS outputs.
Essay on-data-analysis



Essay on-data-analysisRaman Kannan Introduction to Data Analytics starting with
OLS.
This is the first of a series of essays. I will share essays on unsupervised learning, dimensionality reduction and anomaly/outlier detection.
Interpreting Logistic Regression.pptx



Interpreting Logistic Regression.pptxGairuzazmiMGhani This document discusses logistic regression for categorical response variables. It provides examples of binary and ordinal categorical response variables like whether someone smokes (yes/no) or the success of a medical treatment (survives/dies). It then demonstrates how to perform binary logistic regression in R to predict a binary outcome like gender from height. Key aspects covered include interpreting the logistic regression coefficients, plotting the logistic curve, and calculating odds ratios to compare two groups.
Data mining with R- regression models



Data mining with R- regression modelsHamideh Iraj Data mining with R - Regression Models
a curation from:Data Analysis Course
Weeks 4-5-6
https://www.coursera.org/course/dataanalysis
Statistics for Data Analytics



Statistics for Data AnalyticsABHISHEKDAHALE 1. Multiple regression analysis was conducted to predict river water pH based on temperature and alkalinity using over 500 data points. The regression model was found to fit the data well and both independent variables were statistically significant predictors of pH.
2. Logistic regression analysis was performed on diabetes data to predict gender based on age, cholesterol, height, and weight. The logistic regression model showed good fit to the data and high predictive accuracy of over 84%. Age and height were found to be statistically significant predictors of gender in the model.
3. Both analyses involved checking assumptions, interpreting output, and evaluating model fit and predictive ability using various statistical tests in the R programming language.
Accounting serx



Accounting serxzeer1234 The document outlines a presentation on regression analysis using Stata. It discusses Stata's features and windows. It covers data structure types like cross-sectional, panel, and time series data. Regression diagnostics like normality, heteroskedasticity, multicollinearity, and specification are explained. Other regression models like logistic, probit, and Poisson are also covered. The presentation concludes with suggestions for presenting results and suggested readings.
Accounting serx



Accounting serxzeer1234 The document outlines a presentation on regression analysis using Stata. It discusses Stata's features and windows. It covers data structure types like cross-sectional, panel, and time series data. Regression diagnostics like normality, heteroskedasticity, multicollinearity, and specification are explained. Other regression models like logistic, probit, and Poisson are also covered. The presentation concludes with suggestions for presenting results and suggested readings.
Gene expression profiling ii



Gene expression profiling iiPrasanthperceptron The document discusses dimensionality reduction techniques for microarray data analysis, specifically principal component analysis (PCA). PCA automatically detects redundancies in data and defines a new set of components that are guaranteed to be non-redundant. It reduces the complexity of data by removing or consolidating features. The document also discusses using supervised machine learning algorithms like nearest neighbor classification and linear discriminant analysis to incorporate external information like known gene expression profiles into microarray data analysis.
spss teaching



spss teachinglalit pratpa singh singh This document provides an overview of the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) software. It describes the main components and windows in SPSS, including the data window, variable view window, output window, and chart editor window. It also outlines several statistical techniques that can be performed in SPSS, such as descriptive statistics, correlations, t-tests, and chi-square tests of independence. SPSS is a tool that allows users to manage and analyze data, as well as generate graphs and conduct a wide range of statistical procedures.
Mini-lab 1: Stochastic Gradient Descent classifier, Optimizing Logistic Regre...



Mini-lab 1: Stochastic Gradient Descent classifier, Optimizing Logistic Regre...Yao Yao https://github.com/yaowser/data_mining_group_project
https://www.kaggle.com/c/zillow-prize-1/data
From the Zillow real estate data set of properties in the southern California area, conduct the following data cleaning, data analysis, predictive analysis, and machine learning algorithms:
Mini-lab 1: Stochastic Gradient Descent classifier, Optimizing Logistic Regression Model Performance, Optimizing Support Vector Machine Classifier, Accuracy of results and efficiency, Logistic Regression Feature Importance, interpretation of support vectors, Density Graph
ML MODULE 2.pdf



ML MODULE 2.pdfShiwani Gupta Data Cleaning (Missing value, Outlier)
EDA (Descriptive Stats, Visualization)
Feature Engineering (Data Transformation (Encoding, Skew, Scale), Feature Selection)
PCA and LDA in machine learning



PCA and LDA in machine learningAkhilesh Joshi Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) illustration and code in python
Logistic regression vs. logistic classifier. History of the confusion and the...



Logistic regression vs. logistic classifier. History of the confusion and the...Adrian Olszewski Despite the wrong (yet widespread) claim, that "logistic regression is not a regression", it's one of the key regression tool in experimental research, like the clinical trials. It is used also for advanced testing hypotheses.
The logistic regression is part of the GLM (Generalized Linear Model) regression framework. I expanded this topic here: https://medium.com/@r.clin.res/is-logistic-regression-a-regression-46dcce4945dd
analysis part 02.pptx



analysis part 02.pptxefrembeyene4 This document provides an overview of quantitative data analysis techniques including descriptive statistics, reliability analysis, factor analysis, and various statistical tests. Descriptive statistics involve calculating frequencies, percentages, means, and cross-tabulations to summarize demographic and other variables. Reliability analysis using Cronbach's alpha is described to measure the internal consistency of scales. The steps for conducting an exploratory factor analysis are outlined. Finally, guidance is provided on selecting appropriate statistical tests such as t-tests, ANOVA, regression, chi-square, and Mann-Whitney U based on the variables' levels of measurement and number of groups being compared.
working with python



working with pythonbhavesh lande Linear regression and logistic regression are two machine learning algorithms that can be implemented in Python. Linear regression is used for predictive analysis to find relationships between variables, while logistic regression is used for classification with binary dependent variables. Support vector machines (SVMs) are another algorithm that finds the optimal hyperplane to separate data points and maximize the margin between the classes. Key terms discussed include cost functions, gradient descent, confusion matrices, and ROC curves. Code examples are provided to demonstrate implementing linear regression, logistic regression, and SVM in Python using scikit-learn.
R for Statistical Computing



R for Statistical ComputingMohammed El Rafie Tarabay This document provides an overview of statistical concepts and analysis techniques in R, including measures of central tendency, data variability, correlation, regression, and time series analysis. Key points covered include mean, median, mode, variance, standard deviation, z-scores, quartiles, standard deviation vs variance, correlation, ANOVA, and importing/working with different data structures in R like vectors, lists, matrices, and data frames.
Supervised Learning.pdf



Supervised Learning.pdfgadissaassefa This document discusses supervised learning. Supervised learning uses labeled training data to train models to predict outputs for new data. Examples given include weather prediction apps, spam filters, and Netflix recommendations. Supervised learning algorithms are selected based on whether the target variable is categorical or continuous. Classification algorithms are used when the target is categorical while regression is used for continuous targets. Common regression algorithms discussed include linear regression, logistic regression, ridge regression, lasso regression, and elastic net. Metrics for evaluating supervised learning models include accuracy, R-squared, adjusted R-squared, mean squared error, and coefficients/p-values. The document also covers challenges like overfitting and regularization techniques to address it.
2014-mo444-practical-assignment-04-paulo_faria



2014-mo444-practical-assignment-04-paulo_fariaPaulo Faria The document discusses applying machine learning techniques to identify compiler optimizations that impact program performance. It used classification trees to analyze a dataset containing runtime measurements for 19 programs compiled with different combinations of 45 LLVM optimizations. The trees identified optimizations like SROA and inlining that generally improved performance across programs. Analysis of individual programs found some variations, but also common optimizations like SROA and simplifying the control flow graph. Precision, accuracy, and AUC metrics were used to evaluate the trees' ability to classify optimizations for best runtime.
logistic regression.............................................................



logistic regression.............................................................muhammadbsee749 LR.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan. This chapter provides an in-depth overview of the viscosity of macromolecules, an essential concept in biophysics and medical sciences, especially in understanding fluid behavior like blood flow in the human body.
Key concepts covered include:
✅ Definition and Types of Viscosity: Dynamic vs. Kinematic viscosity, cohesion, and adhesion.
⚙️ Methods of Measuring Viscosity:
Rotary Viscometer
Vibrational Viscometer
Falling Object Method
Capillary Viscometer
🌡️ Factors Affecting Viscosity: Temperature, composition, flow rate.
🩺 Clinical Relevance: Impact of blood viscosity in cardiovascular health.
🌊 Fluid Dynamics: Laminar vs. turbulent flow, Reynolds number.
🔬 Extension Techniques:
Chromatography (adsorption, partition, TLC, etc.)
Electrophoresis (protein/DNA separation)
Sedimentation and Centrifugation methods.
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services Clare Doyle - Cork City Libraries
LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini Updates



LDMMIA Reiki Master Spring 2025 Mini UpdatesLDM Mia eStudios As of Mid to April Ending, I am building a new Reiki-Yoga Series. No worries, they are free workshops. So far, I have 3 presentations so its a gradual process. If interested visit: https://www.slideshare.net/YogaPrincess
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
Blessings and Happy Spring. We are hitting Mid Season.
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
Social Problem-Unemployment .pptx notes for Physiotherapy Students



Social Problem-Unemployment .pptx notes for Physiotherapy StudentsDrNidhiAgarwal Unemployment is a major social problem, by which not only rural population have suffered but also urban population are suffered while they are literate having good qualification.The evil consequences like poverty, frustration, revolution
result in crimes and social disorganization. Therefore, it is
necessary that all efforts be made to have maximum.
employment facilities. The Government of India has already
announced that the question of payment of unemployment
allowance cannot be considered in India
K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schools



K12 Tableau Tuesday - Algebra Equity and Access in Atlanta Public Schoolsdogden2 Algebra 1 is often described as a “gateway” class, a pivotal moment that can shape the rest of a student’s K–12 education. Early access is key: successfully completing Algebra 1 in middle school allows students to complete advanced math and science coursework in high school, which research shows lead to higher wages and lower rates of unemployment in adulthood.
Learn how The Atlanta Public Schools is using their data to create a more equitable enrollment in middle school Algebra classes.
To study Digestive system of insect.pptx



To study Digestive system of insect.pptxArshad Shaikh Education is one thing no one can take away from you.”
SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptx



SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptxRonisha Das SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS - XTASY 2025
Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdf



Exploring-Substances-Acidic-Basic-and-Neutral.pdfSandeep Swamy Exploring Substances:
Acidic, Basic, and
Neutral
Welcome to the fascinating world of acids and bases! Join siblings Ashwin and
Keerthi as they explore the colorful world of substances at their school's
National Science Day fair. Their adventure begins with a mysterious white paper
that reveals hidden messages when sprayed with a special liquid.
In this presentation, we'll discover how different substances can be classified as
acidic, basic, or neutral. We'll explore natural indicators like litmus, red rose
extract, and turmeric that help us identify these substances through color
changes. We'll also learn about neutralization reactions and their applications in
our daily lives.
by sandeep swamy
Handling Multiple Choice Responses: Fortune Effiong.pptx



Handling Multiple Choice Responses: Fortune Effiong.pptxAuthorAIDNationalRes INTRO TO STATISTICS
INTRO TO SPSS INTERFACE
CLEANING MULTIPLE CHOICE RESPONSE DATA WITH EXCEL
ANALYZING MULTIPLE CHOICE RESPONSE DATA
INTERPRETATION
Q & A SESSION
PRACTICAL HANDS-ON ACTIVITY
UNIT 3 NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE. SOCIAL AND PREVENTIVE PHARMACY



UNIT 3 NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE. SOCIAL AND PREVENTIVE PHARMACYDR.PRISCILLA MARY J NATIONAL HEALTH PROGRAMMEE
How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odoo



How to Set warnings for invoicing specific customers in odooCeline George Odoo 16 offers a powerful platform for managing sales documents and invoicing efficiently. One of its standout features is the ability to set warnings and block messages for specific customers during the invoicing process.
How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POS



How to Manage Opening & Closing Controls in Odoo 17 POSCeline George In Odoo 17 Point of Sale, the opening and closing controls are key for cash management. At the start of a shift, cashiers log in and enter the starting cash amount, marking the beginning of financial tracking. Throughout the shift, every transaction is recorded, creating an audit trail.
One Hot encoding a revolution in Machine learning



One Hot encoding a revolution in Machine learningmomer9505 A brief introduction to ONE HOT encoding a way to communicate with machines
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport This version of the lectures is provided free of charge to graduate students studying the Operations Management course at the MBA level.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 795 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 95 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
The ever evoilving world of science /7th class science curiosity /samyans aca...



The ever evoilving world of science /7th class science curiosity /samyans aca...Sandeep Swamy The Ever-Evolving World of
Science
Welcome to Grade 7 Science4not just a textbook with facts, but an invitation to
question, experiment, and explore the beautiful world we live in. From tiny cells
inside a leaf to the movement of celestial bodies, from household materials to
underground water flows, this journey will challenge your thinking and expand
your knowledge.
Notice something special about this book? The page numbers follow the playful
flight of a butterfly and a soaring paper plane! Just as these objects take flight,
learning soars when curiosity leads the way. Simple observations, like paper
planes, have inspired scientific explorations throughout history.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdf



Biophysics Chapter 3 Methods of Studying Macromolecules.pdfPKLI-Institute of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Lahore , Pakistan.
Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...



Marie Boran Special Collections Librarian Hardiman Library, University of Gal...Library Association of Ireland
Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...



Phoenix – A Collaborative Renewal of Children’s and Young People’s Services C...Library Association of Ireland
Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdf



Operations Management (Dr. Abdulfatah Salem).pdfArab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 4-30-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Logistic Regression in Case-Control Study
- 1. Logistic Regression in Case- Control study using – A statistical tool Satish Gupta
- 2. What is R? The R statistical programming language is a free open source package. The language is very powerful for writing programs. Many statistical functions are already built in. Contributed packages expand the functionality to cutting edge research.
- 3. Getting Started Go to www.r-project.org Downloads: CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network) Set your Mirror: location close to you. Select Windows 95 or later, MacOS or UNIX platforms
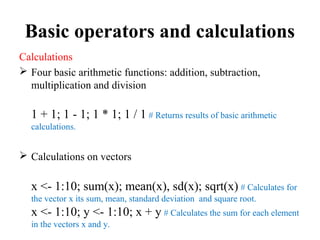
- 5. Basic operators and calculations Comparison operators equal: == not equal: != greater/less than: > < greater/less than or equal: >= <= Example: 1 == 1 # Returns TRUE
- 6. Basic operators and calculations Logical operators AND: & x <- 1:10; y <- 10:1 # Creates the sample vectors 'x' and 'y'. x > y & x > 5 # Returns TRUE where both comparisons return TRUE. OR: | x == y | x != y # Returns TRUE where at least one comparison is TRUE. NOT: ! !x > y # The '!' sign returns the negation (opposite) of a logical vector.
- 7. Basic operators and calculations Calculations Four basic arithmetic functions: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division 1 + 1; 1 - 1; 1 * 1; 1 / 1 # Returns results of basic arithmetic calculations. Calculations on vectors x <- 1:10; sum(x); mean(x), sd(x); sqrt(x) # Calculates for the vector x its sum, mean, standard deviation and square root. x <- 1:10; y <- 1:10; x + y # Calculates the sum for each element in the vectors x and y.
- 8. R-Graphics R provides comprehensive graphics utilities for visualizing and exploring scientific data. It includes: Scatter plots Line plots Bar plots Pie charts Heatmaps Venn diagrams Density plots Box plots
- 9. Data handling in R Load data: mydata = read.csv(“/path/mydata.csv”) See data on screen: data(mydata) See top part of data: head(mydata) Specific number of rows and column of data: mydata[1:10,1:3] To get a type of data: class(mydata) Changing class of data: newdata = as.matrix(mydata) Summary of data: summary(mydata) Selecting (KEEPING) variables (columns) newdata = mydata[c(1,3:5)]
- 10. Data handling in R Selecting observations newdata= subset(mydata, age>=20 | age <10, select=c(ID, weight) newdata= subset(mydata, sex==“Male” & age >25, select=weight:income) Excluding (DROPPING) variables (columns) newdata = mydata[c(-3,-5)] mydata$v3 = NULL
- 11. R-Library There are many tools defined as “package” are present in R for different kind of analysis including data from genetics and genomics. Depending upon the availability of library, it can be downloaded from two sources Using CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network) as: install.packages(“package_name”) Using Bioconductor as: source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R") biocLite(“package_name”)
- 12. R-Library To load a package, library() #Lists all libraries/packages that are available on a system. library(genetics) #Package for genetics data analysis library(help=genetics) #Lists all functions/objects of “genetics” package ?function #Opens documentation of a function
- 13. What is Logistic Regression? Logistic regression describes the relationship between a dichotomous response variable and a set of explanatory variables. Logistic regression is often used because the relationship between the DV (a discrete variable) and a predictor is non-linear.
- 14. A General Model: Logistic Regression JJ disease disease disease XX p p p βββ +++= − = 110) 1 log()logit( Where: pdisease is the probability that an individual has a particular disease. β0 is the intercept β1, β2 …βJ are the coefficients (effects) of genetic factors X1, X2 …XJ are the variables of genetic factors
- 15. Assumptions Logistic regression does not make any assumptions of normality, linearity, and homogeneity of variance for the independent variables. Because it does not impose these requirements, it is preferred to discriminant analysis when the data does not satisfy these assumptions.
- 16. Questions ?? What is the relative importance of each predictor variable? How does each predictor variable affect the outcome? Does a predictor variable make the solution better or worse or have no effect? Are there interactions among predictors? Does adding interactions among predictors (continuous or categorical) improve the model? What is the strength of association between the outcome variable and a set of predictors? Often in model comparison you want non-significant differences so strength of association is reported for even non-significant effects.
- 17. Types of Logistic Regression Unconditional logistic regression Conditional logistic regression ** Rule of thumbs Use conditional logistic regression if matching has been done, and unconditional if there has been no matching. When in doubt, use conditional because it always gives unbiased results. The unconditional method is said to overestimate the odds ratio if it is not appropriate.
- 18. Data Format Status Matset Se_Quartiles GPX1 GPX4 SEP15 TXN2 1 1 <60 CT TT AG AG 0 1 >60 – 70 CC CC GG GG 1 2 <60 TT CC AG AA 0 2 >70 – 80 CC CT GG GG 1 3 >80 CC CC AA AA 0 3 >60 – 70 CT TT GG GG 1 4 <60 CC CC AA AG 0 4 >70 – 80 TT TT GG GG 1 5 >80 CC CC AG AA 0 5 <60 CC CC GG GG 1 6 >70 – 80 CT TT AA AA 0 6 >80 CC CC GG AG 1 7 >60 – 70 TT CC AA AG
- 19. Data and Library loading Load and use data in R (Using Lung cancer data from PLoS One 2013, 8(3):e59051). lung = read.csv(“/path/lung.csv”, sep= “t”, header = TRUE) Load the library and use data for analysis library(epicalc) use(lung)
- 20. Data Analysis Performing conditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control) clogit_lung = clogit(Status ~ Se_Quartiles + strata(Matset), data = .data) clogistic.display(clogit_lung) OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) Quartiles: ref.=<60 <0.001 >60 – 70 0.4(0.15 – 1.09) 0.074 >70 – 80 0.11(0.03 – 0.33) <0.001 >80 0.10(0.03 – 0.34) <0.001
- 21. Data Analysis Performing conditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control), clogit_lung = clogit(Status ~ GPX1+ strata(Matset), data = .data) clogistic.display(clogit_lung) OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) GPX1: ref.=CC 0.032 CT 0.44(0.22 – 0.86) 0.017 TT 0.42(0.13 – 1.38) 0.151
- 22. Data Analysis Performing conditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control), clogit_lung = clogit(Status ~ Se_Quartiles + GPX1+ strata(Matset), data = .data) clogistic.display(clogit_lung) crude OR(95%CI) adj. OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) Quartiles: ref.=<60 <0.001 >60 – 70 0.4(0.15 – 1.09) 0.32(0.11 – 0.96) 0.042 >70 – 80 0.11(0.03 – 0.33) 0.09(0.02 – 0.3) <0.001 >80 0.1(0.03 – 0.34) 0.05(0.01 – 0.23) <0.001 GPX1:ref.=CC 0.006 CT 0.44(0.22 – 0.86) 0.26(0.11 – 0.65) 0.004 TT 0.42(0.13 – 1.38) 0.44(0.09 – 2.18) 0.313 Environmental Factor Genetic Factor
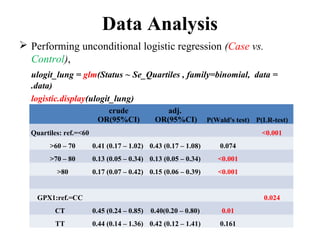
- 23. Data Analysis Performing unconditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control), ulogit_lung = glm(Status ~ Se_Quartiles , family=binomial, data = .data) logistic.display(ulogit_lung) OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) Quartiles: ref.=<60 <0.001 >60 – 70 0.41 (0.17 – 1.02) 0.054 >70 – 80 0.13 (0.05 – 0.34) <0.001 >80 0.17 (0.07 – 0.42) <0.001
- 24. Data Analysis Performing unconditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control), ulogit_lung = glm(Status ~ GPX1 , family=binomial, data = .data) logistic.display(ulogit_lung) OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) Quartiles: ref.=CC 0.034 CT 0.45 (0.24 – 0.85) 0.014 TT 0.44 (0.14 – 1.36) 0.156
- 25. Data Analysis Performing unconditional logistic regression (Case vs. Control), ulogit_lung = glm(Status ~ Se_Quartiles , family=binomial, data = .data) logistic.display(ulogit_lung) crude OR(95%CI) adj. OR(95%CI) P(Wald's test) P(LR-test) Quartiles: ref.=<60 <0.001 >60 – 70 0.41 (0.17 – 1.02) 0.43 (0.17 – 1.08) 0.074 >70 – 80 0.13 (0.05 – 0.34) 0.13 (0.05 – 0.34) <0.001 >80 0.17 (0.07 – 0.42) 0.15 (0.06 – 0.39) <0.001 GPX1:ref.=CC 0.024 CT 0.45 (0.24 – 0.85) 0.40(0.20 – 0.80) 0.01 TT 0.44 (0.14 – 1.36) 0.42 (0.12 – 1.41) 0.161
- 26. Something More Changing the default reference GPX1 = relevel(GPX1, ref = "TT") pack() Saving the result result = clogistic.display(clogit_lung) write.csv(result$table, file=“path/result.csv“, sep = “t”) write.table(result$table, file=“path/result.xls“, sep = “t”)
- 27. Summary: regression models Regression models can be used to describe the average effect of predictors on outcomes in your data set. They can tell how likely that the effect is just be due to chance. They can look at each predictor “adjusting for” the others (estimating what would happen if all others were held constant.)
- 28. Thanks to, Prof. Virasakdi Chongsuvivatwong Epidemiology Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand
Editor's Notes
- #15: Coeffcients are calculated my MLE
- #21: In order to test hypotheses in logistic regression, we have used the likelihood ratio test and the Wald test.
- #22: If the confidence interval includes 0 we can say that there is no significant difference between the means of the two populations, at a given level of confidence. The width of the confidence interval gives us some idea about how uncertain we are about the difference in the means. A very wide interval may indicate that more data should be collected before anything definite can be said. A confidence interval that includes 1.0 means that the association between the exposure and outcome could have been found by chance alone and that the association is not statistically significant.
- #26: Binomial is specifying a choice of variance and link functions. Variance is binomial and link is logit function.






