Information and data security advanced encryption standard (aes)
- 2. Origins • The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is the block cipher algorithm chosen by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES). • Rijndael is an iterated block cipher. Therefore, the encryption or decryption of a block of data is accomplished by the iteration.
- 3. Cont. Origins • Rijndael was evaluated based on its security, its cost and its algorithm and implementation characteristics. The primary focus of the analysis was on the cipher's security, but the choice of Rijndael was based on its simple algorithm and implementation characteristics. There were several candidate algorithms but Rijndael was selected because based on the analyses, it had the best combination of security, performance, efficiency, ease of implementation and flexibility.
- 4. The AES Cipher - Rijndael • designed by Belgium academics Dr.Joan Daemen and Dr.Vincent Rijmen. • designed to be: • resistant against known attacks • speed and code compactness on many CPUs • design simplicity • AES is block cipher with ablock length of 128 bits. • AES allows for three different key lengths: 128 , 192 ,or 256 bits. V. Rijmen J. Daemen
- 6. AES Structure • data block of 4 columns of 4 bytes is state • key length: 10 rounds for a 16-byte key, 12 rounds for a 24-byte key, and 14 rounds for a 32-byte key. • state undergoes: • byte substitution (S-box used on every byte). • shift rows (permute bytes between groups/columns). • mix columns (subs using matrix multiply of groups). • add round key (XOR state with key material).
- 7. Data Unit
- 9. Some Comments on AES 1. an iterative rather than feistel cipher. 2. key expanded into array of 32-bit words. 3. 4 different stages are used. 4. has a simple structure. 5. only AddRoundKey uses key. 6. AddRoundKey a form of Vernam cipher. 7. each stage is easily reversible. 8. decryption uses keys in reverse order. 9. decryption does recover plaintext. 10.final round has only 3 stages
- 10. Substitute Bytes • a simple substitution of each byte. • uses one table of 16x16 bytes called an s-box. • each byte of state is replaced by byte indexed by row (left 4-bits) & column (right 4-bits). • eg. byte {95} is replaced by byte in row 9 column 5. • which has value {2A}. • S-box constructed using defined transformation of values in GF(28). • designed to be resistant to all known attacks.
- 11. Substitute Bytes
- 12. Example of S-box
- 13. Inverse s-box
- 14. Shift Rows • a circular byte shift in each row • 1st row is unchanged • 2nd row does 1 byte circular shift to left • 3rd row does 2 byte circular shift to left • 4th row does 3 byte circular shift to left • decrypt does shifts to right • this step permutes bytes between the columns
- 15. Shift Rows
- 16. Mix Columns • each column is processed separately • each byte is replaced by a value dependent on all 4 bytes in the column Constant matrix Old matrix New matrix
- 17. Mix Columns
- 19. AES Arithmetic • uses arithmetic in the finite field GF(28) • with irreducible polynomial m(x) = 𝑥8+ 𝑥4 + 𝑥3 + 𝑥 + 1 which is (100011011) or {11b} • e.g. {02} • {87}= (1 0000 1110) xor (1 0001 1011) = (0001 0101)
- 20. Add Round Key • The strength of this algorithm at this stage. • XOR state with 128-bits of the round key. • inverse for decryption identical. • designed to be as simple as possible. • requires other stages for complexity / security.
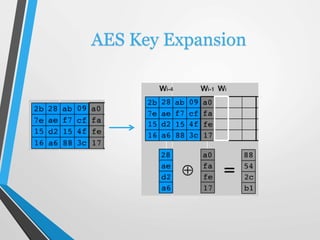
- 21. AES Key Expansion • takes 128-bit (16-byte) key and expands into array of 44, 32-bit words. • start by copying key into first 4 words. • then loop creating words that depend on values in previous & 4 places back. • in 3 of 4 cases just XOR these together. • 1st word in 4 has rotate + S-box + XOR round constant on previous, before XOR 4th back.
- 22. AES Key Expansion Shift 1byte to bottom
- 24. Key Expansion Rationale • designed to resist known attacks • design criteria included: • knowing part key insufficient to find many more. • invertible transformation. • fast on wide range of processor. • use round constants to eliminate symmetries. • diffuse key bits into round keys. • enough non-linearity to hinder analysis. • simplicity of description.
- 25. AES Decryption • AES decryption is not identical to encryption since steps done in reverse. • but can define an equivalent inverse cipher with steps as for encryption. • but using inverses of each step. • with a different key schedule. • works since result is unchanged when: • swap byte substitution & shift rows. • swap mix columns & add round key.
- 26. AES Decryption
- 27. Uses AES Since AES is an encryption algorithm therefore has many uses , which includes protecting the user via the Internet for up to protect and ensure the data in the banks and laboratories as that for -AES uses in the military , that is within the AES useful in all these applications is the lack of a way effective for breaking it , as some months programs and protocols based on AES resistance to electronic attacks , including : • AES is used in programs (WINZIP) in the event that the user request evidence after encryption compressed. • used in the TLS protocol , a protocol to establish a secure connection. • him as well as use in the IPsec protocol , a protocol to ensure safety in connections that are powered by IP via the Internet.