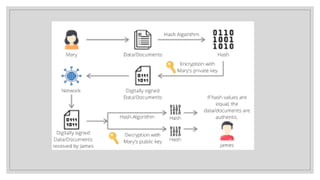
The Information Technology Act of 2000 was enacted in India to provide legal recognition for electronic transactions and digital communication, following the UN's recommendations for uniformity in cyber law. It grants legal validity to digital signatures, facilitates electronic filing and storage of data, and ensures the security and integrity of digital communications through encryption methods. The Act also emphasizes the importance of authentication and non-repudiation in electronic transactions.