Innovation in CS/IT via Open Source Software
- 1. Innovation in CS/IT via Open Source Software Prepared by Dr. Maurice Eugene Dawson Jr.
- 2. Agenda Introduction Open Source Software Defined Linux Based Operating Systems Network Based Operating Systems OSALT & Sourceforge Virtualization Cloud Computing Cyber Security & Software Assurance
- 3. Introduction Degrees Received from CTU DCS-EIS in 2009 MBA in 2010 Assistant Professor of MIS at Alabama A&M University Editor-in-chief of the Journal of
- 5. Innovation in CS/IT via Open Source Software As costs around the world continue to rise for education, institutions must become innovative in the ways they teach and grow students. To do this effectively professors and administrative staff should push toward the utilization of Open Software (OSS) and virtual tools to enhance or supplement currently available tools. In developing countries OSS applications would allow students the ability to learn critical technological skills for success at small fraction of the cost. OSS also provides faculty members the ability to dissect source code and prepare students for low level software development. It is critical that all institutions look at alternatives in providing training and delivering educational material regardless of limitations going forward as the world continues to be more global due to the increased use of technologies everywhere. Doing this could provide a means of shortening the education gap in many countries. Through reviewing the available technology, possible implementations of these technologies, and the application of these items in graduate coursework could provide a starting point in integrating these tools into academia. When administrators or faculty debate the possibilities of OSS, gaming, and simulation tools this applied research provides a guide for changing the ability to develop students that will be competitive on a global level.
- 6. Open Source Software Defined
- 7. Before Linux In 80’s, Microsoft’s DOS was the dominated OS for PC Apple MAC was better, but expensive UNIX was much better, but much, much more expensive. Only for minicomputer for commercial applications People was looking for a UNIX based system, which is cheaper and can run on PC Both DOS, MAC and UNIX were proprietary, i.e., the source code of their kernel is protected No modification is possible without paying high license fees
- 8. GNU Project Established in 1984 by Richard Stallman, who believes that software should be free from restrictions against copying or modification in order to make better and efficient computer programs for “GNU's Not Unix” e Unix-like operating system which is free for copying and modification y by maintaining and distributing the software, e.g. optimally packaging the software with different too NU C Compiler in 1991. But still, an OS was yet to be developed
- 9. Beginning of Linux A famous professor Andrew Tanenbaum developed Minix, a simplified version of UNIX that runs on PC Minix is for class teaching only. No intention for commercial use In Sept 1991, Linus Torvalds, a second year student of Computer Science at the University of Helsinki, developed the preliminary kernel of Linux, known as Linux version 0.0.1
- 10. Message from Professor Andrew Tanenbaum " I still maintain the point that designing a monolithic kernel in 1991 is a fundamental error. Be thankful you are not my student. You would not get a high grade for such a design :-)“ (Andrew Tanenbaum to Linus Torvalds) Soon more than a hundred people joined the Linux camp. Then thousands. Then hundreds of thousands It was licensed under GNU General Public License, thus ensuring that the source codes will be free for all to copy, study and to change.
- 11. Linux Today Linux has been used for many computing platforms PC, PDA, Supercomputer,… Not only character user interface but graphical user interface is available Commercial vendors moved in Linux itself to provide freely distributed code. They make their money by compiling up various software and gathering them in a distributable format Red Hat, Slackware, etc
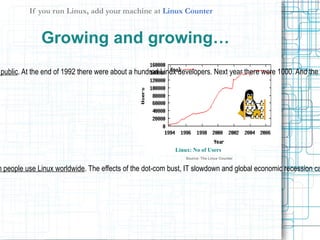
- 12. If you run Linux, add your machine at Linux Counter Growing and growing… public. At the end of 1992 there were about a hundred Linux developers. Next year there were 1000. And the Linux: No of Users Source: The Linux Counter n people use Linux worldwide. The effects of the dot-com bust, IT slowdown and global economic recession ca
- 13. Linux Based Operating Systems Over 400 Linux OS available! Popular distros are Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat, SuSE, Puppy Linux, Damn Small Linux Distrowatch List
- 14. Linux Based Operating Systems Over 400 Linux OS available! Popular distros are Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat, SuSE, Puppy Linux, Damn Small Linux Distrowatch List
- 15. GNU Linux Distrobution Timeline
- 16. Fedora
- 17. Fedora Spins
- 18. Gentoo Linux
- 19. Puppy Linux
- 20. Damn Small Linux
- 21. Ubuntu Desktop
- 23. Ubuntu & Fedora Live Disk DEMO
- 24. Edubuntu Demo
- 25. Open SuSE Demo
- 26. Network Based Operating Systems
- 27. Ubuntu Server
- 28. Centos DEMO
- 29. Blackbuntu
- 30. Backtrack Demo
- 31. OSALT & Sourceforge Open Source an an Alternative (OSALT) has 100's of open source replacements for popular software such as Adobe Photoshop, IBM Rational Rose, Microsfot Project, Microsoft Office, and many more. Sourceforge has over 300,000 active OSS projects.
- 32. OSALT
- 33. Sourceforge
- 34. Virtualization
- 36. Cloud Computing
- 37. Cyber Security & Software Assurance NIST Special Publications IASE DISA
- 38. Movement In Linux Other countries are supporting the OSS movement as well. In China, Red Flag Linux commands over thirty percent of the market (Pan and Bonk, 2007). China is actively looking for an OS to combat Windows OS thus the momentum for OSS continues to grow. In Russia, Linux may become a national OS by 2015 as they are as well looking for lower cost solutions in all levels of education. The Edubuntu OS, which has roots in South Africa, is being utilized by The Republic of Macedonia in all k-12 schools. With software packages such as LibreOffice students and faculty have the ability to perform similar functions as those found in the Microsoft Office suite without having to spend any money to obtain the software.
- 39. OSS in K-12 Education Current Research Topics
- 40. Abstract As many areas in America are rapidly losing funding for technological advances in education, we as educators have to be innovative. The Republic of Macedonia is utilizing Edubuntu in all primary and secondary schools for a program titled Computer for Every Child which started in 2008. Open Source Software (OSS) could be the answer in providing lower socio economic schools a competitive edge to continue to compete for a technological standpoint. OSS is software developed in a collaborative and public environment. OSS is freely available software that is generally under the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL). With this license there is never a charge however any modifications must follow the associated license with the software. This research is to provide an alternative solution to resource limited schools and ensure the competitiveness of American children as our society becomes more global.
- 41. PAST RESEARCH: Introduction This paper is part of a larger study on methods for creating the educational environment of the future. Edubuntu, which is one of the most well known OSS education packages, shall be utilized as the OSS of choice for implementation in the school system. This software package shall be deployed in a school with the deemed minimal technological resources. This study shall take place within the metros of Huntsville, AL, Montgomery, AL, and Saint Louis, MO. This study shall last over the duration of approximately half a year. The expectation is that this study shall change the way we as educators view OSS and use this technology to lower overall operating costs while raising the level of competency.
- 42. Problem In lower socio economic areas there is a lack of technology being used in the classroom. Due to constantly cut budgets how can technology be implemented in the classroom environment?
- 43. Edubuntu Edubuntu is an Operating Systems (OS) that is distributed as free and Open Source Software (OSS). This OS holds a global usage of more than 12 million users.
- 44. Child Monitoring Ability to monitor the following: Instant messages Email Browser history Time on computer
- 45. Libre Office LibreOffice Writer is the word processor in LibreOffice, with similar functionality and file support to Microsoft Word or WordPerfect. It also can act as a basic WYSIWYG editor. LibreOffice Calc is the included spreadsheet program, similar to Microsoft Excel or Lotus 1-2-3. It has a number of unique features, including a system which automatically defines series of graphs, based on information available to the user. LibreOffice Impress is the presentation program in the suite, resembling Microsoft Powerpoint. Presentations can be exported as SWF files, allowing them to be viewed on any computer with Adobe Flash installed. LibreOffice Base is the software's database management program, similar to Microsoft Access. LibreOffice Base allows the creation and management of databases, preparation of forms and reports that provide end users easy access to data. Like Access, it can be used as a front-end for various database systems, including Access databases (JET), ODBC data sources, and MySQL or PostgreSQL. LibreOffice Draw is a vector graphics editor and diagramming tool similar to Microsoft Visio and comparable in features to early versions of CorelDRAW. It provides connectors between shapes, which are available in a range of line styles and facilitate building drawings such as flowcharts. It also includes features similar to desktop publishing software such as Scribus and Microsoft Publisher. LibreOffice Math is an application designed for creating and editing mathematical formulae. The application uses a variant of XML for creating formulas, as defined in the Open Document specification. These formulas can be incorporated into other documents in the LibreOffice suite, such as those created by Writer or Calc, by embedding the formulas into the document.
- 46. Engineering Sweet Home 3d Uml Modeling Tools
- 48. Schooltool
- 49. Other OSS Alternatives & Implementations Edulinux Debian-Edu Fedora Education Spin Guadalinux-Edu OpenSuse-Edu UberStudent
- 50. Operating Systems Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard [Cost $1029.00]
- 51. Libre Office
- 52. Project Tools
- 54. Engineering
- 55. Virtualization
- 56. Open Source Software Healthcare
- 57. Strategic and Operation Plan under the State Cooperative Agreement Phase 0 Phase 1 Phase 4 Phase 3 Feasibility Strategy & Phase Implementation Operations 2 Planning PMO set-up Stakeholder Identification Needs Assessment Governance Clinical Processes Solution Deployment Framework Clinical Analysis Integration engine Operational Processes Initiatives Ranking Financial projections deployment Service Deployment Gap Analysis and Community Readiness Service Deployment Solutions Development Technical Infrastructure Assessment Clinical Process Financial Modeling and Business Operations Current State Reengineering Realignment Assessment Operational Processes Support Services Technical Framework Live Support Definition of Optimal Adoption Strategy Future State Definition of Optimal Decision Definition of Optimal Future State Future State Decision Decision Operational Business Plan Live Exchange Exchange Business Case
- 58. Open Source Healthcare Software The healthcare industry is seeking alternatives to expensive health information systems to lower costs. To do this the following must occur. Partnership with academia Encourage more developers for this industry Sponsor open source development Develop open standards to ensure interoperability
- 59. Open Source Healthcare Software Public health and biosurveillance Dental management and patient record Electronics health or medical record Medical practice management software Health system management Imaging/visualization Medical information systems
- 60. Life Beyond Your Doctorate PUBLISH OR PARISH! Research is essential!
- 63. Wiki CFP
- 64. Intellectbase International Consortium
- 65. Intellectbase International Consortium Intellectbase International Consortium promotes broader intellectual resources and publishes reviewed papers from all disciplines. Researchers are invited to exchange ideas, share experiences on research challenges, research findings and state-of-the-art solutions. To achieve this, Intellectbase currently publishes the following nine journals with an additional five journals scheduled for future
- 66. AACE
- 67. Inderscience
- 70. Any Questions You can follow me on Twitter at www.twitter.com/#!/drmauricedawson Or connect on LinkedIn at Www.linkedin.com/in/mauricedawson
Editor's Notes
- #55: http://brlcad.org

















































![Operating Systems
Windows Server 2008 R2
Standard [Cost $1029.00]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ossdawson-120722025041-phpapp02/85/Innovation-in-CS-IT-via-Open-Source-Software-50-320.jpg)

































































![Linux [2005]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/linuxgsi640final1-12005-120430024710-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)








































