Interfacing android with embedded systems
- 2. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 1RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Contents Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................3 Android Development Tools (ADT):..........................................................................................................3 Software Development Kit (SDK):.............................................................................................................3 Android Packages......................................................................................................................................3 Download ADT bundle from Below link:...................................................................................................3 Getting Started..........................................................................................................................................4 Launching the eclipse for App Development:...........................................................................................4 Install Android Packages: .........................................................................................................................4 Creating your First App .................................................................................................................................7 Application Folders .....................................................................................................................................11 Adding Behavior..........................................................................................................................................12 Radio Buttons..............................................................................................................................................15 Alert Dialog .................................................................................................................................................18 Spinners ......................................................................................................................................................19 Android Manifest........................................................................................................................................22 Toggle Button..............................................................................................................................................24 Seek bar.......................................................................................................................................................27 Bluetooth Communication..........................................................................................................................28 Connecting to a remote Device ..............................................................................................................32 App for Bluetooth Communication.........................................................................................................34 Bluetooth and Relays interfacing using 8051 Microcontroller and Keil– AT89S52 ................................44 BLUETOOTH RELAY SHIELD .........................................................................................................................51 RELAY SHIELD ARDUINO CODE ...............................................................................................................52 4-RELAY SWITCH BOARD ANDROID APPLICATION..................................................................................56 8 channel Relay Bluetooth..........................................................................................................................57 OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................................................57 FEATURES................................................................................................................................................57 APPLICATION DIAGRAM..........................................................................................................................59 INTERFACE...............................................................................................................................................59 Circuit Diagram .......................................................................................................................................60 RELAY SWITCHBOARD SOFTWARE..........................................................................................................60
- 3. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 2RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Android APP link .....................................................................................................................................60 SERIAL 8 CHANNEL AC 230V SR AND DIMMER WITH BLUETOOTH INTERFACE..........................................61 FEATURES................................................................................................................................................61 Electrical Characteristics.........................................................................................................................62 TRIAC.......................................................................................................................................................63 Applications: ...........................................................................................................................................63 Electrical Characteristics.........................................................................................................................63 FIRING ANGLE .........................................................................................................................................64 CONNECTING 230V AC 8 CHANNELDIMMER WITH ELECTRONIC GADGETS...........................................65 UART INPUT FOR LOADS.........................................................................................................................65 Example...................................................................................................................................................65 BLOCK DIAGRAM.....................................................................................................................................67 BLUETOOTH ............................................................................................................................................68 Bluetooth Module HC 05 Specifications: ................................................................................................68 Bluetooth Module HC 05 Application:....................................................................................................68 PROCEDURE TO OPERATE......................................................................................................................69 RDL Wi-Fi Robo ...........................................................................................................................................74 RDL Wifi Relay.............................................................................................................................................77 Features: .................................................................................................................................................77 XBee Wifi configuration..............................................................................................................................84 SOFTWARE ..................................................................................................................................................84
- 4. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 3RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Introduction Android is a free and open operating system from Google that runs on all kinds of devices from phones, to tablets and even televisions. That’s a ton of different devices you can target with just one platform. (And the market share is gaining too). Google provides everything you need to get started building Android apps for free. And you can build your Android apps on Mac, Windows, or UNIX and publish your apps for next to nothing (and with no need for anyone’s approval). Ready to get started? You’re going to start building you’re first Android app, but first there are a few things to setup... Android already runs on a TON of different devices! With careful planning, you’re app can run on all of these Android powered devices. From phones and tablets, to TVs and even home automation There are a lot of mobile platforms out there, but with Android’s presence and growth, everyone is building out their Android apps. Android Development Environment: · Eclipse Integrated Development Environment (IDE): The Eclipse Integrated Development Environment (IDE for short) is where you’ll write your code. Eclipse is a generic IDE, not specific to Android development. It’s managed by the Eclipse foundation. Android DevelopmentTools (ADT): The Android Development Tools (ADT) is an Eclipse plug-in that adds Android specific functionality to Eclipse. Software Development Kit (SDK): The Android Software Development Kit (SDK) contains all of the lower level tools to build, run and test your Android apps. The ADT is really just a user interface, and The guts of the app building all happen here in the ADT. Android Packages: You can develop and support multiple versions of Android from the same development environment. These Packages add functionality to the base SDK to let you develop for that Android. Download ADT bundle from Below link: (http:developer.android.com/sdk/index.html#download)
- 5. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 4RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Getting Started: All you need to start developing android application is the ADT bundle which is downloaded from the developer’s site and Java Development Kit. Java IDE & Eclipse is particularly well supported to make development a little easier. Versions of the SDK, Java, and Eclipse Are available for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux, so you can explore Android from the comfort of whatever OS you favor. The SDK includes an emulator or all three OS environments, and because Android applications are run on a virtual machine, there’s no advantage to developing from any particular operating system. Android code is written using Java syntax, and the core Android libraries include most of the features from the core Java APIs. Before they can be run, though, your projects are first translated into Dalvik byte code. As a result, you get the benefits of using Java, while your applications have the advantage of running on a virtual machine optimized for Android devices. Launching the eclipse for App Development: After installing the Java-7 IDE in your system unzip the ADT bundle which you downloaded. It contains 2 folders SDK and Eclipse. Open the Eclipse folder and launch the Eclipse. · Launching Eclipse When you launch Eclipse for the first time, you will be prompted to enter a workspace Location.a directory where all of · your Eclipse projects and settings will be stored. Install Android Packages: The SDK is designed to allow you to work with multiple versions of Android in the same development environment. To keep downloads small, the SDK version packages are separated from the SDK. (This also allows you to update to new versions of Android without having to download the entire SDK) You can configure the installed packages in the SDK from the Android SDK and AVD Manager (another added bonus of the ADT).
- 6. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 5RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Open the manager by selecting Window → Android SDK and AVD Manager. · When you expand the tree node, you’ll see a combination of SDK Tools, SDK platforms, samples documentation and more. These are all plugins to the SDK that you can add to expand the functionality of the SDK. (This way you can download and install the SDK once and keep adding new functionality to it as new version comes) · To create a new AVD go to window—>AVD manager —>new The process of updating the SDK and creating new AVD is as shown below.
- 7. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 6RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Fig3(a): Updating the SDK Manager Fig-3(b): Creating the AVD
- 8. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 7RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Creating your First App · Using Eclipse, create a new project by selecting File->Project (see Figure 4). · Expand android folder and select android app. project (see Figure 5). · A new dialog window will open give the application name and what is the minimum version of OS your app should support and then press next (see Figure 6). · Select the type of icon you want to give for your app and press next (See in Figure 7) · Give name of the activity and press finish see Figure 8. In the Package Explorer expand the project by clicking on arrows displayed to the left of each item in the project. In the res/layout folder, double-click the main.xml file Figure 4: Selecting project
- 9. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 8RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 5: Create android application project Figure 6: give the app name and API
- 10. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 9RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 7: select the icon Figure 8: Set the name of Activity
- 11. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 10RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 9: Layout when app is created Figure 10: Graphical Layout & XML Layout The .xml file in res/layout defines the user interface (UI) of your application. The default view is the Layout view, which lays out the activity graphically. To modify the UI, click the .xml tab located at the bottom. · Drag and drop the items which you need from palette on to your layout file
- 12. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 11RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Application Folders We have created our basic app successfully. Now we check about different types of folders or files supporting the app. Once you expand the app folder in package explorer it contains different folders. 1. Src 2. Assets 3. Res 4. Gen 5. Android versions 6. Bin 7. Libs 8. Android manifest Src It is the source folder which contains all the java files which are used in your project. Assets By default it is an empty folder. It is used to store raw data Res (Resource folder) The res folder contains the various resources that your application can use. Different types of folders present in the res folder include layout files which are front end of an app. Drawable which contains the images. Values which contains he strings, color, styles and dimensions for designing the front end of your app. The resource folder contains the above files as shown in Figure 11. Gen The gen folder contains Java files generated by ADT. The ADT creates an R.java file. When you write Java code in Android, you will come to a point when you need to reference the items in the res folder. You do this by using the R class. The R.java file is an index to all the resources defined in your res folder.
- 13. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 12RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Android Versions This item includes the android.jar file that your application builds against. The version of this file was determined by the build target that you chose the New Android Project . Expanding the item in the project displays the android.jar file and the path to where it’s installed. Libs The libs/ directory contain private libraries. Figure 11: Resource Folder Adding Behavior Drag and drop a button from palette into your layout file. Once you have added the button the layout file looks like as shown in the Figure 12. In the xml file add a · click event for the button as highlighted in the figure 13. Now open your source folder and open the java file. Create a method called as insert and writhe following code in that method as shown in Figure 14 and when you run the app you will get the output as shown in Figure 15.(The output is a Toast message which will give a message for a 30 seconds)
- 14. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 13RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 15: Click event in xml Figure 13 Figure 12: layout after adding a button Figure 14: Insert Method
- 15. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 14RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 15: o/p showing toast message after a button click
- 16. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 15RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Radio Buttons A radio button or option button is a graphical control element that allows the user to choose only one of a predefined set of options, an exclusive or. Drag and drop the radio buttons from the palette .the XML and graphical layout are as shown in Figures 16 & 17. Initialize the radio · Button in java code as shown in the Figure 18. · Add the click event for radio button as shown in Figure 19. · And the output of the app is as shown in the Figure 20. Run the application Figure 16: Graphical Layout of radio Buttons Figure 17: Xml file for Radio Buttons
- 17. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 16RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 18: Initializing RadioButton Figure 19: Click event for Radio button
- 18. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 17RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 20: O/P for radio button view on Emulator Figure 21: O/P when radio button click event
- 19. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 18RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Alert Dialog We will be using the alert dialog box whenever we want the permission for an action to take place An alert dialog can have two options they are to ask user to perform an action or not to perform an action The code for creating an alert dialog box is as shown in Figure 22 which is written in a button click event. The output of the application is as shown in Figures 23 for positive and negative buttons in alert dialog box. Figure 22: Code for Alert Dialog Box
- 20. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 19RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 23: Alert Dialog Box Spinners Spinners are similar to "combo boxes' in some GUI frameworks. Spinners provide a quick way to select one value from a set. In the default state, spinner shows its currently selected value. Touching the spinner displays a dropdown menu with all other available values, from which user can select a new one. You can add a spinner to your layout with the Spinner object shown in Figure 24.or you can add the code in xml as shown in Figure 25. Now go to strings.xml file in the res—>values and add the following code in the string.xml file as in Figure 26 Now add the following code in your java file to initialize the spinner and get the values from strings.xml file to the spinner in front end .the final o/p of the app is as shown in the figures 30 &31
- 21. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 20RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 25: Spinner added to xml file Figure 24: Spinner added to layout from Pallete Figure 26: Code for Spinner
- 22. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 21RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 27: Spinner Figure 28: Final Spinner Output
- 23. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 22RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Android Manifest The AndroidManifest.xml file contains information about your package, including components of the application such as activities, services etc. It performs some other tasks also: It is responsible to protect the application to access any protected parts by providing the permissions It is responsible to protect the application to access any protected parts by providing permissions It also declares the android API that the application going to use. It lists the instrumentation classes the instrumentation classes provide profiling and other informations.these information’s are removed just before the application is published etc. This is the required xml file for all the android application and located inside the root directory. The elements used in the above xml file are described below. <Manifest> Manifest is the root element of the AndroidManifest.xml file. It has package attribute that describes the package name of the activity class. <Application> Application is the sub-element of the manifest. It includes the namespace declaration. This element contains several sub elements that declares the application component such as activity etc. The commonly used attributes are of this elements are icons, label, theme etc. Android: icon It represents the icon for all the android application components. Android: label It works as the default label for all the application components.
- 24. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 23RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Android: theme It represents a common theme for all the android activities. <Activity> Activity is the sub element of application and represents an activity that must be defined in the Manifest file. Android: label It represents a label i.e. displayed on the screen. Android: name It represents a name for the activity class. It is required attribute. <Intent-filter> Intent-filter is the sub-element of activity that describes the type of intent to which activity, service or broadcast receiver can respond to. <Action>
- 25. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 24RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM It adds an action for the intent-filter. The intent-filter must have at least one action element. <Category> It adds a category name to an intent-filter. Toggle Button A toggle button allows the user to change a setting between two states. You can add a basic toggle button to your layout with the Toggle Button object as shown in Figure 29. When the user selects a Toggle Button and Switch, the object receives an on-click Event. To define the click event handler, add the android:onClick attribute to the <ToggleButton> element in your XML layout. The value for this attribute must be the name of the method you want to call in response to a click event. The Activity hosting the layout must then implement the corresponding method. For example, here's a Toggle Button with the android:onClick attribute in the Figure 30 The final o/p can be seen in figure 31 & 32 Figure29: Toggle Button
- 26. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 25RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 30(a): Toggle Button XML Code Figure 30(b): Toggle Button Click Event
- 27. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 26RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 31: Toggle button off Figure 32: Toggle Button on
- 28. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 27RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Seek bar The seek bar is same like a progress bar but with added functionality .it can be easily dragged .The layout and xml files of seek bar are as shown in the Figures 33 &34For getting the value from seek bar first we need to initialize the seek bar. The initialization and the seek bar value changed are shown in the figure 35. The final o/p is as shown in the figure 36. Figure 33: Layout Figure 34: xml with seek Figure 35:CodeSeek
- 29. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 28RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 36: O/p when seek bar value is changed Bluetooth Communication Android offers APIs to manage and monitor your Bluetooth settings. Bluetooth is a communications protocol designed for short-range, low-bandwidth peer-to-peer communications. Using the Bluetooth APIs, you can search for, and connect to, other Bluetooth devices within range. By initiating a communications link using Bluetooth Sockets, you can then transmit and receive streams of data between devices from within your applications. Using the Bluetooth APIs, an Android application can perform the following: · Scan for other Bluetooth devices · Query the local Bluetooth adapter for paired Bluetooth devices · Establish RFCOMM channels · Connect to other devices through service discovery
- 30. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 29RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM · Transfer data to and from other devices Manage multiple connection. Bluetooth Adapter Represents the local Bluetooth adapter. Bluetooth Adapter is the entry-point for all Bluetooth interaction. Using this, you can discover other Bluetooth devices, query a list of bonded (paired) devices, instantiate a Bluetooth Device using a known MAC address, and create a Bluetooth Server Socket to listen for communications from other devices. To access the Bluetooth adapter we need to call the getdefaultadapter() as shown in the Figure 37 We need to give the required permissions in the manifest file to instantiate any process using Bluetooth. The permissions which needed to be given are shown in the figure 38 Once the permissions are given in the manifest file check whether is turned on by calling is enabled () if it is not turned on then it will take the user to settings menu to turn on the Bluetooth. The code for that is as shown in the Figure 39. Searching for Bluetooth Devices You can check if the local Bluetooth Adapter is already performing a discovery scan by using the Discovering method. To initiate the discovery process, call start Discovery on the Bluetooth Adapter Bluetooth.start discovery() Figure 37: Initializing the Bluetooth adapter Figure 38: Permission to be given in the manifest file
- 31. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 30RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 39: Check the Bluetooth state and enable it The discovery process is asynchronous so Android uses broadcast Intents to notify you of the start and end of discovery as well as remote devices discovered during the scan. You can monitor changes in the discovery process by creating Broadcast Receivers as shown in the Figure 40,41. Each broad cast intent includes name and address of the devices. So each name has to be received and must be placed in the array list. Once the values are completely received they must be placed in the List view using the list adapter. As shown in the figure 42. The output after searching for the devices and using the Bluetooth and displaying the values in a list view is as shown in the figure 43. Figure 40: Discovery receiver for Bluetooth
- 32. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 31RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 41: Receiver when the discovery finished be called Figure 42: getting the values to a list view
- 33. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 32RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 43: list view with name & Mac address Connecting to a remote Device You can establish an RFCOMM communication channel for bidirectional communications using the following classes. BluetoothServerSocketUsed to establish a listening socket for initiating a link between devices. To establish a handshake, one device acts as a server to listen for, and accept, incoming connection requests. Bluetooth Socket — used to create a new client to connect to a listening Bluetooth Server Socket. Also returned by the Bluetooth Server Socket after a connection is established. Once a connection is established, Bluetooth Sockets are used by both the server and client to transfer data streams. Connecting the devices In order for a Bluetooth Socket to establish a connection to a remote Bluetooth Device, the following conditions must be true: · The remote device must be discoverable.
- 34. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 33RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 44: Code for Connecting between the devices · The remote device must be accepting connections through a Bluetooth Server Socket. · The local and remote devices must be paired (bonded). If the devices are not paired, the users of each device will be prompted to pair them when the connection request is initiated. The code for creating a socket connection between the Bluetooth devices is as shown in figure 44 Transmitting & receiving the data from Sockets through Bluetooth is as shown in the figure45
- 35. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 34RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Figure 45: code for data Transfer or receive App for Bluetooth Communication In this example application we’ll see how to transfer and receive the data from the Bluetooth Devices.
- 36. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 35RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM publicclassMainActivityextends Activity { privatestaticfinal String TAG = "bluetooth2"; finalintRECIEVE_MESSAGE = 1; // Status for Handler privateBluetoothAdapterbtAdapter = null; privateBluetoothSocketbtSocket = null; privateStringBuildersb = newStringBuilder (); privateConnectedThreadmConnectedThread ; // SPP UUID service privatestaticfinal UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString ("00001101-0000-1000-8000- 00805F9B34FB"); // MAC-address of Bluetooth module which you want to connect(you must edit this line) privatestatic String address = "00:12:09:29:42:57"; //this is like a main activity in java @Override protectedvoidonCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super.onCreate (savedInstanceState ); setContentView (R.layout.terminal );// front end xml file which has to be displayed h= newHandler () { publicvoidhandleMessage (android.os.Messagemsg ) { switch (msg.what ) { caseRECIEVE_MESSAGE :// if receive massage byte[] readBuf = (byte[]) msg.obj;
- 37. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 36RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM String strIncom = newString (readBuf , 0, msg.arg1);// create string from bytes array sb.append (strIncom ); // append string intendOfLineIndex = sb.indexOf ("rn"); // determine the end-of-line if (endOfLineIndex > 0) {//if end-of-line, String sbprint = sb.substring (0, endOfLineIndex );// extract string Toast.makeText (getApplicationContext (), "received message"+"----"+sbprint , 30).show(); sb.delete (0, sb.length ());// and clear } break; } }; }; btAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter ();// get Bluetooth adapter checkBTState(); } privateBluetoothSocketcreateBluetoothSocket(BluetoothDevice device) throwsIOException { if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT>= 10){ try { final Method m = device.getClass().getMethod("createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord", new Class[] { UUID.class }); return (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(device, MY_UUID); } catch (Exception e) { Log.e(TAG, "Could not create Insecure RFCommConnection",e); } } returndevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
- 38. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 37RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM @Override publicvoidonPause() { super.onPause(); SharedPreferences preferences = getSharedPreferences("pref", 0); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = preferences.edit(); //"savedData" is the key that we will use in onCreate to get the saved data //mDataString is the string we want to save editor.putString("savedDatasd", sa); editor.putString("savedDatad", sakom); // commit the edits editor.commit(); Log.d(TAG, "...In onPause()..."); try{ btSocket.close(); } catch (IOException e2) { errorExit("Fatal Error", "In onPause() and failed to close socket." + e2.getMessage() + "."); } } privatevoidcheckBTState() { // Check for Bluetooth support and then check to make sure it is turned on // Emulator doesn't support Bluetooth and will return null if(btAdapter==null) { errorExit("Fatal Error", "Bluetooth not support"); } else { if (btAdapter.isEnabled()) { Log.d(TAG, "...Bluetooth ON...");
- 39. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 38RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM privatevoiderrorExit(String title, String message){ Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), message, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); finish(); } // writing a thread for read and write the data privateclassConnectedThreadextends Thread { privatefinalInputStreammmInStream;//initialising I/P Stream privatefinalOutputStreammmOutStream;// initializing the o/p Stream publicConnectedThread(BluetoothSocket socket) { InputStreamtmpIn = null; OutputStreamtmpOut = null; // Get the input and output streams, using temp objects because // member streams are final try {tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();//get values to i/p stream from socket tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();//get values to i/p stream from socket } catch (IOException e) { } mmInStream = tmpIn; mmOutStream = tmpOut; } publicvoid run() { byte[] buffer = newbyte[256]; // buffer store for the stream int bytes; // bytes returned from read() // Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs while (true) { try { // Read from the Input Stream bytes = mmInStream.read(buffer);// Get number of bytes and message in
- 40. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 39RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Log.d(TAG, "...Data to send: " + message + "..."); byte[] msgBuffer = message.getBytes();//get the data bytes try { mmOutStream.write(msgBuffer);//getting the data to o/p stream } catch (IOException e) { Log.d(TAG, "...Error data send: " + e.getMessage() + "..."); } } } //click events for buttons publicvoid b1(View v) { r1.setChecked(true);//Setting radio button to be checked mConnectedThread.write("1N");//Sending the data via bluetooth } publicvoid b2(View v) { r1.setChecked(false);//Setting radio button to be unchecked mConnectedThread.write("1F");//Sending the data via bluetooth } publicvoid b3(View v) { r2.setChecked(true);//Setting radio button to be checked mConnectedThread.write("2N");//Sending the data via bluetooth } publicvoid b4(View v) {r2.setChecked(false);//Setting radio button to be unchecked
- 41. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 40RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="60dp"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textViewd1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="0.53" android:background="@drawable/rec" android:onClick="b1" android:text="ON"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="0.53"
- 42. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 41RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2"android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <RadioButton android:id="@+id/radioButton1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="60dp"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textViewf1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <Button android:id="@+id/button3"
- 43. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 42RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM <TextView android:id="@+id/textView3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <Button android:id="@+id/button4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="0.53" android:background="@drawable/rec" android:onClick="b4" android:text="OFF"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <RadioButton android:id="@+id/radioButton2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView
- 44. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 43RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM <RadioButton android:id="@+id/radioButton3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="60dp"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=" "/> <Button android:id="@+id/button7" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="0.53" android:background="@drawable/rec" android:onClick="b7"
- 45. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 44RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Bluetooth and Relays interfacing using 8051 Microcontroller and Keil– AT89S52 Circuit and Working: Fig.6 shows the circuit of simple 8051 Microcontroller interfaced with Bluetooth and 4 relays. The following interface could be used along with an android app to turn ON/OFF appliances connected to relays. Program 6 demonstrates how to receive data through Bluetooth. Components/modules required : 1) 8051 project board (assembled/non assembled kit). 2) 5V and 12V DC source. 3) Bluetooth Module. 4) 12V 4 Relay board. 5) IC AT89S52. 6)8051 IC burner 7) Connectors and cables. The android APK file could be downloaded from here
- 46. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 45RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Fig6: Circuit Diagram for Bluetooth and 4 Relay interfacing
- 47. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 46RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Program 6: #include<reg52.h>//special function register declarations //for the intended 8051 derivative void delay(); //Function prototype declaration // Relay Connections sbit Relay1=P2^3; //Relay 1 is connected to Port 2 pin 3 sbit Relay2=P2^2; //Relay 2 is connected to Port 2 pin 2 sbit Relay3=P2^1; //Relay 3 is connected to Port 2 pin 1 sbit Relay4=P2^0; //Relay 4 is connected to Port 2 pin 0 unsigned char byte1,byte2;// Variable declarations // MAIN CODE void main() { //Serial Initialization TMOD=0X20; //use Timer 1, mode 2 SCON=0X50; //indicating serial mode 1,where an 8-bit data //is framed with start and stop bits TH1=0XFD; //9600 baud rate TR1=1; //Start timer delay(); //Wait for some time for serial initialization to finish // Transmit 'S' to check whether the setup is ready TI=0; //Forcibly change the Transmit //Interrupt Flag of 8051 to 0 SBUF='S'; //Move 'S' to serial buffer memory
- 48. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 47RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM TI=0; //Forcibly change the Transmit //Interrupt Flag of 8051 to 0 SBUF='S'; //Move 'S' to serial buffer memory While (TI==0); //Wait until TI flag is set by hardware //when an entire byte has been transmitted TI=0; // forcibly clear TI flag delay (); //A small delay for relaxation P2=0x00; //Set Port 2 all bits to 0 while(1) // continuous loop { RI=0; //Forcibly clear the Receive //Interrupt Flag of 8051 to 0 while(RI==0); //Wait until RI flag is set by hardware //when an entire byte has been received byte1=SBUF; //Move the received byte of data into variable 'byte1' RI=0; //Forcibly clear RI flag while(RI==0); //Wait until RI flag is set by hardware //when an entire byte has been received byte2=SBUF; //Move the received byte of data into variable 'byte2' RI=0; //Forcibly clear RI flag if(byte1=='1') //Check whether the 1st byte of data is 'A' { if(byte2=='N') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '1'
- 49. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 48RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM { Relay1=1; //Turn ON Relay1 } else if(byte2=='F') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '0' { Relay1=0; //Turn OFF Relay1 } } else if(byte1=='2') //Check whether the 1st byte of data is 'B' { if(byte2=='N') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '1' { Relay2=1; //Turn ON Relay2 } else if(byte2=='F') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '0' { Relay2=0; //Turn OFF Relay2 } } else if(byte1=='3') //Check whether the 1st byte of data is 'C' { if(byte2=='N') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '1' { Relay3=1; //Turn ON Relay3 }
- 50. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 49RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM else if(byte2=='F') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '0' { Relay3=0; //Turn OFF Relay3 } } } else if(byte1=='4') //Check whether the 1st byte of data is 'D' { if(byte2=='N') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '1' { Relay4=1; //Turn ON Relay4 } else if(byte2=='F') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '0' { Relay4=0; //Turn OFF Relay4 } } else if(byte1=='X') //Check whether the 1st byte of data is 'D' { if(byte2=='N') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '1' { P2=0xFF; //Turn ON all the Relays } else if(byte2=='F') //Check whether the 2nd byte of data is '0' {
- 51. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 50RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM P2=0x00; //Turn OFF all the Relays } } else { P2=0x00; //Clear Port 2 all bits to 0 if any other variable has been received } } //Function for delay routine void delay() //Delay Routine { unsignedint x=60000; // larger the value of x the more is the delay. while (x--); // executes this statement until x decrements to 0 }
- 52. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 51RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM BLUETOOTH RELAY SHIELD OVERVIEW Bluetooth technology is a short distance communication technology used by almost all phones including smart phones and al laptops. This technology find very wide uses including that of Home & Industrial automation. The Relay shield is capable of controlling 4 relays. The max switching power could be 12A/250VAC or 15A/24VDC. It could be directly controlled by Arduino through digital IOs. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT Controlling relay shield from Bluetooth enabled device (Android APK) EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
- 53. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 52RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Note: remove USB after uploading the code, DC 12V 1A must be plugged in RELAY SHIELD ARDUINO CODE /* Software serial multiple serial test Receives from the hardware serial, sends to software serial. Receives from software serial, sends to hardware serial. The circuit: * RX is digital pin 10 (connect o TX of other device) * TX is digital pin 1 (connect o RX of other device) Note: Not all pins on the Mega and Mega 2560 support change interrupts, so only the following can be used for RX: 10, 1, 12, 13, 50, 51, 52, 53, 62, 63, 64, 65, 6, 67, 68, 69 Not all pins on the Leonardo support change interrupts, so only the following can be used for RX: 8, 9, 10, 1, 14 (MISO), 15 (SCK), 16 (MOSI). Software serial multiple serial test Receives from the hardware serial, sends to software serial. Receives from software serial, sends to hardware serial. The circuit: * RX is digital pin 2 (connect o TX of other device) * TX is digital pin 3 (connect o RX of other device) SENDING DATA FORMAT 1N TO ON RELAY1 1F TO OF RELAY1 2N TO ON RELAY2
- 54. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 53RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM 2F TO OF RELAY2 3N TO ON RELAY3 3F TO OF RELAY3 4N TO ON RELAY4 4F TO OF RELAY4 This example code is in the public domain. */ #include <SoftwareSerial.h> Software Serial my Serial(2, 3); / RX, TX int rec; void setup() { pin Mode(4, OUTPUT); pin Mode(5, OUTPUT); pin Mode(6, OUTPUT); pin Mode(7, OUTPUT); mySerial.begin(960); } void lop() / run over and over { while(!mySerial.available(); rec=mySerial.read(); if(rec='1') { while(!mySerial.available(); rec=mySerial.read();
- 55. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 54RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM if(rec='N') digitalWrite(4, HIGH); else if(rec='F') digitalWrite(4, LOW); } else if(rec='2') { while(!mySerial.available(); rec=mySerial.read(); if(rec='N') digitalWrite(5, HIGH); else if(rec='F') digitalWrite(5, LOW); } else if(rec='3') { while(!mySerial.available(); rec=mySerial.read(); if(rec='N') digitalWrite(6, HIGH); else if(rec='F') digitalWrite(6, LOW); } else if(rec='4') {
- 56. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 55RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM while(!mySerial.available(); rec=mySerial.read(); if(rec='N') digitalWrite(7, HIGH); else if(rec='F') digitalWrite(7, LOW); } }
- 57. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 56RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM 4-RELAY SWITCH BOARD ANDROID APPLICATION
- 58. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 57RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM 8 channel Relay Bluetooth OVERVIEW This is Eight Chanel relay board controlled by Bluetooth Module. The Bluetooth relay board is with 8 SPDT relays rated up to 7A each. You can control devices 230V / 120V (up to 8) directly with one such relay unit. Suitable for home automation applications, hobby projects, industrial Automation. Bluetooth module enables you to wireless transmit & receive serial data. FEATURES Brand: RDL Order No: RDL/8RB/14/001/V1.0 Product Datasheet: 8 Channel Relay Board 8 SPDT Relay channels (7A 250V,12A 120V,10A 125VAC, 10A 28VDC). Power suply:12VDC 1AMP Current consumption: 40 mA.
- 59. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 58RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM LED indication for relay & power supply. Design based on highly proven IC ULN2803 as Driver. TL output. Status LEDs Android apk file will be given High quality PCB FR4 Grade with FPT Certified.
- 60. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 59RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM APPLICATION DIAGRAM INTERFACE
- 61. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 60RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Circuit Diagram RELAY SWITCHBOARD SOFTWARE AndroidAPP link https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=rdl.relayswitchboard
- 62. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 61RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM SERIAL 8 CHANNEL AC 230V SR AND DIMMER WITH BLUETOOTH INTERFACE Brand: RDL Order No: RDL/8SD/13/001/V1.0 Product Datasheet: 8-Channel Bluetooth Dimmer Datasheet The board can be used in application where dimming of 10-20v AC power is required like dimming of bulb or fan. The board can be control with Serial data from any microcontroller 0- 10% dimming or ON/OF control Main power(230v) completely isolated from microcontroller. FEATURES Works on AC power supply 230V. Load Capacity 12 Amp AC(Up to 200 Watt) Isolated from mains power Works from any microcontroller. Serial Control (TTL) Simultaneous 8 load control with 0-10% dimming. Act as 8 channel solid state relay with ON/OF and dimming. Optional input for Microcontroller or Bluetooth, XBEE, and USB interface pin TX, RX, 5V, GND.
- 63. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 62RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Electrical Characteristics Average Power Dissipation of 0.5W Operating Temperature +120 dregs Holding Current (maximum)-30mA Latching Current(maximum)-60mA It is a 6pin Random Phase opt isolators TRIAC driver output
- 64. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 63RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM TRIAC From Triode for Alternating Current, is a generic zed trade name for an electronic component hat Can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a Bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor. Applications: • Solenoid/Valve Controls • Static ac Power Switch • Lamp Ballasts • Solid State Relays • Interfacing Microprocessors to 15 Vac Peripherals • Incandescent Lamp Dimmer • Motor Controls Electrical Characteristics Total Power Dissipation @ TA is 25°is 4.4mW Storage Temperature Range is -40 to +150 dregs
- 65. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 64RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM FIRING ANGLE Phase angle of applied voltage at which the Thyristor conduct
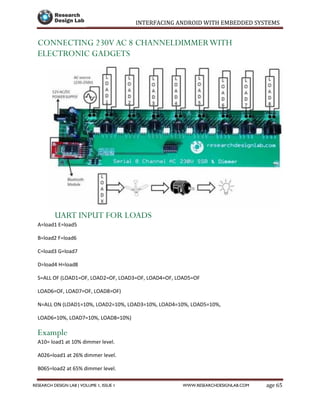
- 66. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 65RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM CONNECTING 230V AC 8 CHANNELDIMMERWITH ELECTRONIC GADGETS UART INPUT FOR LOADS A=load1 E=load5 B=load2 F=load6 C=load3 G=load7 D=load4 H=load8 S=ALL OF (LOAD1=OF, LOAD2=OF, LOAD3=OF, LOAD4=OF, LOAD5=OF LOAD6=OF, LOAD7=OF, LOAD8=OF) N=ALL ON (LOAD1=10%, LOAD2=10%, LOAD3=10%, LOAD4=10%, LOAD5=10%, LOAD6=10%, LOAD7=10%, LOAD8=10%) Example A10= load1 at 10% dimmer level. A026=load1 at 26% dimmer level. B065=load2 at 65% dimmer level.
- 67. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 66RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM C089=load3 at 89% dimmer level. LOAD1
- 68. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 67RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 69. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 68RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM BLUETOOTH Brand: RDL Order No: RDL/BLT/13/001/V1.0 Bluetooth Module HC 05 Specifications: Bluetooth protocol: Bluetooth Specification v2.0+ED Frequency: 2.4GHz ISM band Modulation: GFSK(Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) Emission power: =4dBm, Class 2 Sensitivity: =-84dBm at 0.1% BER Sped: Asynchronous: 2.1Mbps(Max) /160 kbps, Synchronous: 1Mbps/1Mbps Security: Authentication and encryption Profiles: Bluetooth serial port Power supply: +3.3VDC 50mA Working temperature: -20 ~ +75 Centigrade Dimension: 26.9mm x 13mm x 2.2 mm Bluetooth Module HC 05 Application: Computer and peripheral devices GPS receiver Industrial control MCU projects
- 70. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 69RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM PROCEDURE TO OPERATE Download the Bluetooth SP app of Research design lab from play store
- 71. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 70RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 72. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 71RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 73. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 72RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 74. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 73RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM NOTE: Since this module working with live 230V AC, while experimenting user has to take Proper safety precautions.
- 75. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 74RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM RDL Wi-Fi Robo Use your Android phone to control a robot via Wi-Fi and drives it like an RC car. It controls the direction of a Robot, and also allows rotating clockwise and counter-clockwise. The Robot Control app works like a joystick. Press the buttons FORWARD, BACKWARD for acceleration and moving forward and backward. Left and Right buttons to move left and right, and a Mid button to stop the robot. The quit button exits you from the app successfully. The app will be able to run on android devices with Ice-cream Sandwich and higher versions. The following data will be transmitted via Wi-Fi while performing below given Button press event. Forward ->>> 1 Backward ->>> 2 Left ->>> 3 Right ->>> 4 Stop ->>> 5
- 76. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 75RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 77. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 76RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Brand: RDL
- 78. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 77RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM RDL Wi-Fi Relay This app acts as a remote controller for controlling the appliance via Wi-Fi enabled Android devices. It enables to control eight appliances (ON / OFF) Features: 1. Support TCP/IP connection 2. It can control max eight devices. 3. The minimum version of Android OS required for this app is Ice-cream Sandwich (4.0 API). 4. When the button is pressed on it sends value: 1N, when button is pressed OFF it sends value: 1F SW1 -> ON ………> 1N SW1 -> OFF ………> 1F SW2 -> ON ………> 2N SW2 -> OFF ………> 2F ………. ……… SW8 -> ON ………> 8N SW8 -> OFF ………> 8F
- 79. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 78RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Brand: RDL Order No: RDL/WiFi-R/14/001/v1.0
- 80. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 79RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 81. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 80RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 82. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 81RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 83. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 82RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 84. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 83RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 85. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 84RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM XBee Wi-Fi Configuration XBee is very easy and popular wireless device. It is a transceiver, it can transmit and it receives data wirelessly. There are several types of XBee module. The very popular XBee is Series 1 (802.15.4), comes with the firmware to create connection for point to point or star network. But bear in mind, many people actually thought it is using ZigBee protocol, but it is not compliance to ZigBee because it uses the low layer of ZigBee protocol only SOFTWARE XCTU V6.1.0.
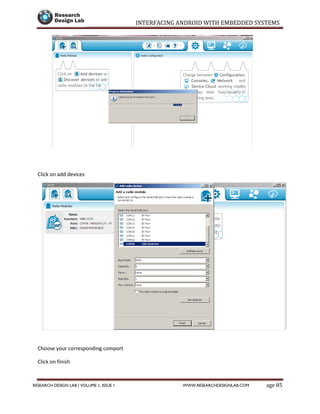
- 86. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 85RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Click on add devices Choose your corresponding comport Click on finish
- 87. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 86RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 88. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 87RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM Click on update firmware
- 89. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 88RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 90. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 89RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 91. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 90RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 92. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 91RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 93. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 92RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
- 94. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 93RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM In order to make sure the Soft AP mode working on the Xbee WiFi module. First, I search the WiFi with “RDL WIFI” SSID using my Android phone, and connect to it. Click on connect
- 95. INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Page 94RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM



































![INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Page 35RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
publicclassMainActivityextends Activity {
privatestaticfinal String TAG = "bluetooth2";
finalintRECIEVE_MESSAGE = 1; // Status for Handler
privateBluetoothAdapterbtAdapter = null;
privateBluetoothSocketbtSocket = null;
privateStringBuildersb = newStringBuilder ();
privateConnectedThreadmConnectedThread ;
// SPP UUID service
privatestaticfinal UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString ("00001101-0000-1000-8000-
00805F9B34FB");
// MAC-address of Bluetooth module which you want to connect(you must edit this line)
privatestatic String address = "00:12:09:29:42:57";
//this is like a main activity in java
@Override
protectedvoidonCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
super.onCreate (savedInstanceState );
setContentView (R.layout.terminal );// front end xml file which has to be displayed
h= newHandler () {
publicvoidhandleMessage (android.os.Messagemsg ) {
switch (msg.what ) {
caseRECIEVE_MESSAGE :// if receive massage
byte[] readBuf = (byte[]) msg.obj;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-150912043928-lva1-app6891/85/Interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-36-320.jpg)
![INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Page 36RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
String strIncom = newString (readBuf , 0, msg.arg1);// create string from bytes array
sb.append (strIncom ); // append string
intendOfLineIndex = sb.indexOf ("rn"); // determine the end-of-line
if (endOfLineIndex > 0) {//if end-of-line,
String sbprint = sb.substring (0, endOfLineIndex );// extract string
Toast.makeText (getApplicationContext (), "received message"+"----"+sbprint , 30).show();
sb.delete (0, sb.length ());// and clear
}
break;
}
};
};
btAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter ();// get Bluetooth adapter
checkBTState();
}
privateBluetoothSocketcreateBluetoothSocket(BluetoothDevice device) throwsIOException {
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT>= 10){
try {
final Method m = device.getClass().getMethod("createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord",
new Class[] { UUID.class });
return (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(device, MY_UUID);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Could not create Insecure RFCommConnection",e);
}
}
returndevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-150912043928-lva1-app6891/85/Interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-37-320.jpg)

![INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Page 38RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
privatevoiderrorExit(String title, String message){
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), message, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
finish();
} // writing a thread for read and write the data
privateclassConnectedThreadextends Thread {
privatefinalInputStreammmInStream;//initialising I/P Stream
privatefinalOutputStreammmOutStream;// initializing the o/p Stream
publicConnectedThread(BluetoothSocket socket) {
InputStreamtmpIn = null;
OutputStreamtmpOut = null;
// Get the input and output streams, using temp objects because
// member streams are final
try {tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();//get values to i/p stream from socket
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();//get values to i/p stream from socket
} catch (IOException e) { }
mmInStream = tmpIn;
mmOutStream = tmpOut;
}
publicvoid run() {
byte[] buffer = newbyte[256]; // buffer store for the stream
int bytes; // bytes returned from read()
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs
while (true) {
try {
// Read from the Input Stream
bytes = mmInStream.read(buffer);// Get number of bytes and message in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-150912043928-lva1-app6891/85/Interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-39-320.jpg)
![INTERFACING ANDROID WITH EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Page 39RESEARCH DESIGN LAB | VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 WWW.RESEARCHDESIGNLAB.COM
Log.d(TAG, "...Data to send: " + message + "...");
byte[] msgBuffer = message.getBytes();//get the data bytes
try {
mmOutStream.write(msgBuffer);//getting the data to o/p stream
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "...Error data send: " + e.getMessage() + "...");
}
}
}
//click events for buttons
publicvoid b1(View v)
{ r1.setChecked(true);//Setting radio button to be checked
mConnectedThread.write("1N");//Sending the data via bluetooth
}
publicvoid b2(View v)
{
r1.setChecked(false);//Setting radio button to be unchecked
mConnectedThread.write("1F");//Sending the data via bluetooth
}
publicvoid b3(View v)
{
r2.setChecked(true);//Setting radio button to be checked
mConnectedThread.write("2N");//Sending the data via bluetooth
}
publicvoid b4(View v)
{r2.setChecked(false);//Setting radio button to be unchecked](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-150912043928-lva1-app6891/85/Interfacing-android-with-embedded-systems-40-320.jpg)