Internet Protocol Deep-Dive
- 1. www.glcnetworks.com Internet Protocol Deep dive GLC Webinar, 24 Feb 2022 Achmad Mardiansyah [email protected] GLC Networks, Indonesia
- 2. www.glcnetworks.com Agenda ● Introduction ● Review prerequisite knowledge ● Internet Protocol ● Troubleshooting ● Live practice ● Q & A 2
- 4. www.glcnetworks.com What is GLC? ● Garda Lintas Cakrawala (www.glcnetworks.com) ● Based in Bandung, Indonesia ● Areas: Training, IT Consulting ● Certified partner for: Mikrotik, Ubiquity, Linux foundation ● Product: GLC radius manager ● Regular event 4
- 5. www.glcnetworks.com Trainer Introduction ● Name: Achmad Mardiansyah ● Base: bandung, Indonesia ● Linux user since 1999, mikrotik user since 2007, UBNT 2011 ● Mikrotik Certified Trainer (MTCNA/RE/WE/UME/INE/TCE/IPv6) ● Mikrotik/Linux Certified Consultant ● Website contributor: achmadjournal.com, mikrotik.tips, asysadmin.tips ● More info: http://au.linkedin.com/in/achmadmardiansyah 5
- 6. www.glcnetworks.com Past experience ● 2020-2022 (Congo DRC, PNG, Malaysia): network support, radius/billing integration ● 2019, Congo (DRC): build a wireless ISP from ground-up ● 2018, Malaysia: network revamp, develop billing solution and integration, setup dynamic routing ● 2017, Libya (north africa): remote wireless migration for a new Wireless ISP ● 2016, United Kingdom: workshop for wireless ISP, migrating a bridged to routed network ● 2015, Kalimantan, wireless support ● See our website for more details 6
- 7. www.glcnetworks.com About GLC webinar? ● First webinar: january 1, 2010 (title: tahun baru bersama solaris - new year with solaris OS) ● As a sharing event with various topics: linux, networking, wireless, database, programming, etc ● Regular schedule ● Irregular schedule: as needed ● Checking schedule: http://www.glcnetworks.com/schedule ● You are invited to be a presenter ○ No need to be an expert ○ This is a forum for sharing: knowledge, experiences, information 7
- 8. www.glcnetworks.com Please introduce yourself ● Your name ● Your company/university? ● Your networking experience? ● Your mikrotik experience? ● Your expectation from this course? 8
- 9. www.glcnetworks.com Prerequisite ● This presentation requires some prerequisite knowledge ● We assume you already know: ○ Computer network ○ Mikrotik RouterOS 9
- 11. www.glcnetworks.com 7 OSI layer & protocol ● OSI layer Is a conceptual model from ISO (International Standard Organization) for project OSI (Open System Interconnection) ● When you send a message with a courier, you need to add more info to get your message arrived at the destination (This process is called encapsulation) ● What is protocol ○ Is a set of rules for communication ○ Available on each layer ● Communication consist of series encapsulation ○ SDU: service data unit (before PDU) ○ PDU: protocol data unit (after header is added) 11
- 12. www.glcnetworks.com Layered model (TCP/IP vs ISO) and encapsulation 12 / datagram
- 15. www.glcnetworks.com Layer 2 header, ethernet 15
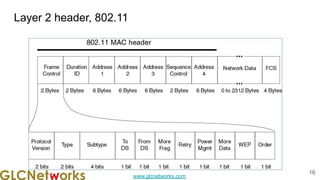
- 16. www.glcnetworks.com Layer 2 header, 802.11 16
- 17. www.glcnetworks.com Did you notice? ● There is a big overhead on encapsulation process ● More encapsulation means less payload? 17
- 19. www.glcnetworks.com IP spec (RFC 791) ● Defined long time ago (what 1981?) ● Defines how the IP header looks like ● Still used up to know ● New version -> IPv6 19
- 21. www.glcnetworks.com Layer 2 vs Layer 3 addressing 21 Layer 2 Layer 3 ● Burned-in address ● Adjacent communication ● Consist of 48 bit binary, written in HEX format. 1 HEX = 4 bit ● Unique for every physical port ● 6 first HEX digit -> represent the manufacturer ● Logical address ● End-to-end communication ● IPv4 32 bit long ● 2 versions: IPv4 (our focus) and IPv6 ● Consist of network part & host part ● Can be class based IP address (without subnet) ● Now it is classless IP address -> VLSM (variable length subnet mask) ● CIDR (classless inter domain routing)
- 22. www.glcnetworks.com Addressing, IANA, RIR ● Internet is based on IP (internet protocol) addressing scheme -> RFC791 ● Addressing has to be unique. ● We need an international body that regulates IP addressing -> IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority) ● IANA delegates (some of its authority) to RIR “Regional Internet Registry” ● RIR delegates to country’s ● Every organisation must have IP address block to join the internet and build a routing scheme among their equipment 22
- 23. www.glcnetworks.com How the layer 3 address look like? ● IPv4 address is 32 bit long ● Written in binary -> always think in binary ● Displayed to human in decimal every 8 bit (octet). ● Has 2 parts: network part and host part ● Like a phone number 0812 XXXXXXXX -> hierarchical ● All devices in the network will have same network part ● First and last address cannot be used (for network id and broadcast id) 23 Network part host part
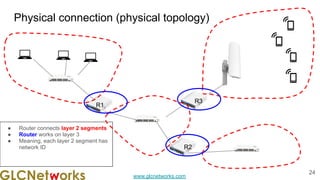
- 24. www.glcnetworks.com Physical connection (physical topology) 24 R2 R1 R3 ● Router connects layer 2 segments ● Router works on layer 3 ● Meaning, each layer 2 segment has network ID
- 25. www.glcnetworks.com Logical connection (logical topology) and routing table 25 Routing table: ● A table at router that is used to forward packet ● Available on every devices (router and host) ● Entry is executed sequentially 192.168.0.0/26 R1 192.168.0.1/26 192.168.0.3/26 192.168.0.2/26 R3 R2 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.3.3/24 192.168.3.9/24 192.168.2.9/24 192.168.2.2/24 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.9/24 destination gateway 192.168.0.0/26 direct 192.168.1.0/24 direct 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.0.2 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.0.3 192.168.16.3/32 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0/0 (default gw) 192.168.0.3
- 26. www.glcnetworks.com We need IP address planning ● Chopping a big network into smaller subnets ● Aggregate small subnets into bigger range ● make sure no ip addresses are overlap ● Dont use excel please… :-( 26
- 27. www.glcnetworks.com Forwarding packets using routing table ● It works like a firewall: match and action ● When a packet arrived, routing table is used to forward packets ● You should think in binary to understand how it works 27 destination gateway 192.168.16.3/32 11000000 10101000 00001000 00000011 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.0/26 11000000 10101000 00000000 00 direct 192.168.1.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000001 direct 192.168.2.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000010 192.168.0.2 192.168.3.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000011 192.168.0.3 0.0.0.0/0 (no match) 192.168.0.3
- 28. www.glcnetworks.com A packet arrived at R1… (example) Destination IP address of the packet is 192.168.2.6, which gateway do we use? A: 192.168.2.6 = (11000000 10101000 00000010 00000110) 28 destination gateway 192.168.16.3/32 11000000 10101000 00001000 00000011 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.0/26 11000000 10101000 00000000 00 direct 192.168.1.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000001 direct 192.168.2.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000010 192.168.0.2 192.168.3.0/24 11000000 10101000 00000011 192.168.0.3 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.3
- 29. www.glcnetworks.com Where routing table lookup happens? 29
- 30. www.glcnetworks.com Administrative distance (analogy) 30 30 CITY 1 100 km CITY 2 120 km CITY 2 90 km CITY 3 500 km CITY 4 250 km 10.10.10.0/24 192.168.0.1 10 10.10.20.0/24 192.168.0.2 12 10.10.20.0/24 192.168.0.3 9 10.10.30.0/24 192.168.0.3 50 10.10.40.0/24 192.168.0.4 25
- 31. www.glcnetworks.com Administrative distance ● Distance is considered when prefix length is same ● Lowest distance wins ● Administrative distance policy is depends on vendor ● Table on the right shows an example of administrative distance on cisco router 31
- 33. www.glcnetworks.com VLSM RFC ● Variable-Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) ● Can divide an IP address block into subnets of different sizes using / (slash) notation ● Solution the in efficient of classful IP address (fixed length). No more class A, B, C ● RFC: 1878 (1895) ● Basis for CIDR ● Example: 23.45.0.0/17 ○ 23.45.0.0/25 ○ 23.45.0.128/25 33
- 34. www.glcnetworks.com CIDR RFC ● CIDR: Classless Inter-Domain Routing ● Provides a new and more flexible way to specify network addresses in routers (using slash as notation) ● allow flexible allocation of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. ● CIDR lets a routing table entry represent an aggregation of networks that exist in the forward path ● Each IP address has a network prefix that identifies their network ● RFC: 1519 34
- 35. www.glcnetworks.com Router and Routing ● Router is a network device that is used to forward packets, based on layer 3 information (layer 3 header) ● Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network, or between or across multiple networks 35 Physical router Router icon
- 36. www.glcnetworks.com Static routing 36 ● Entries on routing table is created manually ● Admin must manage routing table in all routers ● Admin have full control 192.168.0.0/26 R1 192.168.0.1/26 192.168.0.3/26 192.168.0.2/26 R3 R2 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.3.3/24 192.168.3.9/24 192.168.2.9/24 192.168.2.2/24 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.9/24 destination gateway 192.168.0.0/26 direct 192.168.1.0/24 direct 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.0.2 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.0.3 192.168.16.3/32 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.3
- 37. www.glcnetworks.com Dynamic routing 37 ● Router will talk to each other with routing protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) ● Entries on routing table is created automatically ● Admin must have a good knowledge about routing protocol 192.168.0.0/26 R1 192.168.0.1/26 192.168.0.3/26 192.168.0.2/26 R3 R2 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.3.3/24 192.168.3.9/24 192.168.2.9/24 192.168.2.2/24 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.9/24 destination gateway 192.168.0.0/26 direct 192.168.1.0/24 direct 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.0.2 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.0.3 192.168.16.3/32 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.3
- 38. www.glcnetworks.com Routing is one-way ● Currently, routing is done one-way only ● Forwarding process on router is based on destination IP address ● There is no guarantee incoming path is similar to outgoing path ● We can only control outgoing forwarding 38 R1 192.168.0.1/26 192.168.0.3/26 R3 R2 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/24 192.168.3.0/24 192.168.3.3/24 192.168.3.9/24 192.168.2.9/24 192.168.2.2/24 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.9/24
- 39. www.glcnetworks.com Autonomous system (AS) ● Is a collection of routers and networks under one administration and apply single routing policy ● AS is identified by a number (ASN), given by RIR (Regional Internet Registry: APNIC, ARIN, RIPE, etc) 39 AS1 AS4 AS3 AS2
- 40. www.glcnetworks.com Interior vs exterior routing 40
- 41. www.glcnetworks.com IGP vs EGP 41 AS1 IGP: Interior Gateway Protocols ● Routing protocol that runs internally within AS (intra-AS) ● Connecting networks within AS ● Example: RIP, OSPF EGP: Exterior Gateway Protocol ● Routing protocol that runs between AS ● Connecting an AS to other ASes ● Example: BGP AS4 AS3 AS2
- 42. www.glcnetworks.com Multiple routing protocol: scope and target scope ● Route scope and target scope attributes can be used to resolve nexthop router. ● Normally nexthops can be resolved only through routes that are on link. ● It is very useful when the gateway is not directly connected 42 AS1 R1 AS3 AS2 Indirect gateway R1
- 44. www.glcnetworks.com Troubleshooting layer 3 ● Always starts from lowest layer. ○ Make sure layer 1 and 2 are OK ● Reachability test: ping ● Path analysis: traceroute 44
- 45. www.glcnetworks.com Live practice ● SSH client ● SSH parameters ○ SSH address ○ SSH port ○ SSH username ○ SSH password 45
- 47. www.glcnetworks.com Interested? Just come to our training... ● Topics are arranged in systematic and logical way ● You will learn from experienced teacher ● Not only learn the materials, but also sharing experiences, best-practices, and networking 47
- 48. www.glcnetworks.com End of slides ● Thank you for your attention ● Please submit your feedback: http://bit.ly/glcfeedback ● Find our further event on our website : https://www.glcnetworks.com ● Like our facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/glcnetworks ● Slide: https://www.slideshare.net/glcnetworks/ ● Discord (bahasa indonesia): (https://discord.gg/6MZ3KUHHBX ) ● Recording (youtube): https://www.youtube.com/c/GLCNetworks ● Stay tune with our schedule 48