Internet Protocol Version 6 in computer Networks
- 1. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 27 IPv6 Protocol
- 2. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 2 OBJECTIVES: OBJECTIVES: To give the format of an IPv6 datagram composed of a base header and a payload. To discuss different fields used in an IPv6 datagram based header and compare them with the fields in IPv4 datagram. To show how the options in IPv4 header are implemented using the extension header in IPv6. To show how security is implemented in IPv6. To discuss three strategies used to handle the transition from IPv4 to IPv6: dual stack, tunneling, and header translation.
- 3. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 3 Chapter Chapter Outline Outline 27.1 Introduction 27.1 Introduction 27.2 Packet Format 27.2 Packet Format 27.3 Transition to IPv6 27.3 Transition to IPv6
- 4. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 4 27-1 INTRODUCTION In this introductory section, we discuss two topics: rationale for a new protocol and the reasons for delayed adoption.
- 5. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 5 Topics Discussed in the Section Topics Discussed in the Section Rationale for Change Reason for Delay in Adoption
- 6. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 6 27-2 PACKET FORMAT The IPv6 packet is shown in Figure 27.1. Each packet is composed of a mandatory base header followed by the payload. The payload consists of two parts: optional extension headers and data from an upper layer. The base header occupies 40 bytes, whereas the extension headers and data from the upper layer contain up to 65,535 bytes of information.
- 7. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 7 Topics Discussed in the Section Topics Discussed in the Section Base Header Flow Label Comparison between IPv4 and IPv6 Headers Extension Headers Comparison between IPv4 and IPv6 Options
- 8. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 8 Figure 27.1 IPv6 datagram
- 9. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 9 Figure 27.2 Format of the base header
- 10. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 10
- 11. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 11 Figure 27.3 Extension header format
- 12. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 12 Figure 27.4 Extension header types
- 13. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 13 Figure 27.5 Hop-by-hop option header format
- 14. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 14 Figure 27.6 The format of the option in a hop-by-hop option header Action C Type 1 bit 2 bits 5 bits Action: if the option not recognized 00 Skip this option 01 Discard datagram, no more action 10 Discard datagram and send ICMP message 11 Discard datagram send ICMP message if not multicast C: Change in option value 0 Does not change in transit 1 May be changed in transit Type 00000 Pad1 00001 PadN 00010 Jumbo payload
- 15. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 15 Figure 27.7 Pad1
- 16. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 16 Figure 27.8 PadN
- 17. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 17 Figure 27.9 Jumbo payload
- 18. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 18 Figure 27.10 Source routing
- 19. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 19 Figure 27.11 Source routing example Source: A Destination: R1 Left: 3 R2 R3 B Source: A Destination: R2 Left: 2 R1 R3 B Source: A Destination: R3 Left: 1 R1 R2 B Source: A Destination: B Left: 0 R1 R2 R3
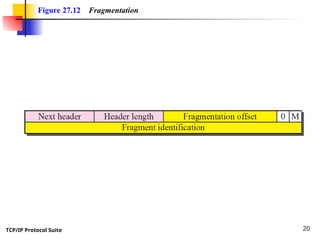
- 20. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 20 Figure 27.12 Fragmentation
- 21. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 21 Figure 27.13 Authentication
- 22. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 22 Figure 27.14 Calculation of authentication data
- 23. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 23 Figure 27.15 Encrypted security payload
- 24. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 24 27-3 TRANSITION FROM IPv4 TO IPv6 Because of the huge number of systems on the Internet, the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 cannot happen suddenly. It will take a considerable amount of time before every system in the Internet can move from IPv4 to IPv6. The transition must be smooth to prevent any problems between IPv4 and IPv6 systems. Three strategies have been devised by the IETF to help the transition (see Figure 27.16).
- 25. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 25 Topics Discussed in the Section Topics Discussed in the Section Dual Stack Tunneling Header Translation
- 26. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 26 Figure 27.16 Three transition strategies
- 27. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 27 Figure 27.17 Dual stack
- 28. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 28 Figure 27.18 Tunneling strategy Payload IPv6 header IPv4 header
- 29. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 29 Figure 27.19 Header translation strategy Payload IPv6 header Payload IPv4 header