INTRO TO ML.pptx
- 2. What is Machine Learning? “Learning is any process by which a system improves performance from experience.” - Herbert Simon Definition by Tom Mitchell (1998): Machine Learning is the study of algorithms that • improve their performance P • at some task T • with experience E. A well-defined learning task is given by <P, T, E>. 3
- 3. Traditional Programming Machine Learning Computer Data Program Output Computer Data Output Program Slide credit: Pedro Domingos 4
- 4. When Do We Use Machine Learning? ML is used when: • Human expertise does not exist (navigating on Mars) • Humans can’t explain their expertise (speech recognition) • Models must be customized (personalized medicine) • Models are based on huge amounts of data (genomics) Learning isn’t always useful: • There is no need to “learn” to calculate payroll Based on slide by E. Alpaydin 5
- 5. A classic example of a task that requires machine learning: It is very hard to say what makes a 2 6 Slide credit: Geoffrey Hinton
- 6. 7 Slide credit: Geoffrey Hinton Some more examples of tasks that are best solved by using a learning algorithm • Recognizing patterns: – Facial identities or facial expressions – Handwritten or spoken words – Medical images • Generating patterns: – Generating images or motion sequences • Recognizing anomalies: – Unusual credit card transactions – Unusual patterns of sensor readings in a nuclear power plant • Prediction: – Future stock prices or currency exchange rates
- 7. 8 Slide credit: Pedro Domingos Sample Applications • Web search • Computational biology • Finance • E-commerce • Space exploration • Robotics • Information extraction • Social networks • Debugging software • [Your favorite area]
- 8. Samuel’s Checkers-Player “Machine Learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.” -Arthur Samuel (1959) 9
- 9. Defining the Learning Task Improve on task T,with respect to performance metric P , based on experience E T: Playing checkers P: Percentage of games won against an arbitrary opponent E: Playing practice games against itself T: Recognizing hand-written words P: Percentage of words correctly classified E: Database of human-labeled images of handwritten words T: Driving on four-lane highways using vision sensors P: Average distance traveled before a human-judged error E: A sequence of images and steering commands recorded while observing a human driver. T: Categorize email messages as spam or legitimate. P: Percentage of email messages correctly classified. E: Database of emails, some with human-given labels Slide credit: Ray Mooney 10
- 10. State of the Art Applications of Machine Learning 11
- 11. Autonomous Cars • Nevada made it legal for autonomous cars to drive on roads in June 2011 • As of 2013, four states (Nevada, Florida, California, and Michigan) have legalized autonomous cars Penn’s Autonomous Car (Ben Franklin Racing Team) 12
- 13. Autonomous Car Technology Laser Terrain Mapping Stanley Learning from Human Drivers Sebastian Adaptive Vision Path Planning Images and movies taken from Sebastian Thrun’s multimedia w1e4bsite.
- 14. Deep Learning in the Headlines 15
- 15. pixels edges object parts (combination of edges) object models Deep Belief Net on Face Images Based on materials by Andrew Ng 16
- 16. Learning of Object Parts 17 Slide credit: Andrew Ng
- 17. Training on Multiple Objects 18 Slide credit: Andrew Ng Trained on 4 classes (cars, faces, motorbikes, airplanes). Second layer: Shared-features and object-specific features. Third layer: More specific features.
- 18. Scene Labeling via Deep Learning [Farabet et al. ICML 2012, PAMI 2013] 19
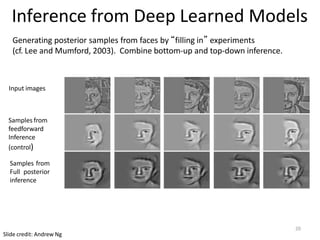
- 19. Input images Samples from feedforward Inference (control) Samples from Full posterior inference Inference from Deep Learned Models Generating posterior samples from faces by “filling in” experiments (cf. Lee and Mumford, 2003). Combine bottom-up and top-down inference. Slide credit: Andrew Ng 20
- 20. Machine Learning in Automatic Speech Recognition A Typical Speech Recognition System ML used to predict of phone states from the sound spectrogram Deep learning has state-of-the-art results # Hidden Layers 1 2 4 8 10 12 Word Error Rate % 16.0 12.8 11.4 10.9 11.0 11.1 Baseline GMM performance = 15.4% [Zeiler et al. “On rectified linear units for speech recognition” ICASSP 2013] 21
- 21. Impact of Deep Learning in Speech Technology Slide credit: Li Deng, MS Research 22
- 23. Types of Learning • Supervised (inductive) learning – Given: training data + desired outputs (labels) • Unsupervised learning – Given: training data (without desired outputs) • Semi-supervised learning – Given: training data + a few desired outputs • Reinforcement learning – Rewards from sequence of actions Based on slide by Pedro Domingos 24
- 24. Supervised Learning: Regression • Given (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn) • Learn a function f (x) to predict y given x – y is real-valued == regression 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 September Arctic Sea Ice Extent (1,000,000 sq km) Year Data from G. Witt. Journal of Statistics Education, Volume 21, Number 1 (2013) 26
- 25. Supervised Learning: Classification • Given (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn) • Learn a function f (x) to predict y given x – y is categorical == classification Breast Cancer (Malignant / Benign) 1(Malignant) 0(Benign) Tumor Size Based on example by Andrew Ng 27
- 26. Supervised Learning: Classification • Given (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn) • Learn a function f (x) to predict y given x – y is categorical == classification Breast Cancer (Malignant / Benign) 1(Malignant) 0(Benign) Tumor Size Tumor Size 28 Based on example by Andrew Ng
- 27. Supervised Learning: Classification • Given (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn) • Learn a function f (x) to predict y given x – y is categorical == classification Breast Cancer (Malignant / Benign) 1(Malignant) 0(Benign) Tumor Size Predict Benign Predict Malignant Tumor Size 29 Based on example by Andrew Ng
- 28. Supervised Learning Tumor Size Age - Clump Thickness - Uniformity of Cell Size - Uniformity of Cell Shape … • x can be multi-dimensional – Each dimension corresponds to an attribute Based on example by Andrew Ng 30
- 29. Unsupervised Learning • Given x1, x2, ..., xn (without labels) • Output hidden structure behind the x’s – E.g., clustering 31
- 30. [Source: Daphne Koller] Genes Individuals Unsupervised Learning Genomics application: group individuals by genetic similarity 32
- 31. Organize computing clusters Social network analysis Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/E. Churchwell (Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison) Astronomical data analysis Market segmentation Slide credit: Andrew Ng Unsupervised Learning 33
- 32. Unsupervised Learning • Independent component analysis – separate a combined signal into its original sources 34 Image credit: statsoft.com Audio from http://www.ism.ac.jp/~shiro/research/blindsep.html
- 33. Unsupervised Learning • Independent component analysis – separate a combined signal into its original sources 35 Image credit: statsoft.com Audio from http://www.ism.ac.jp/~shiro/research/blindsep.html
- 34. Reinforcement Learning • Given a sequence of states and actions with (delayed) rewards, output a policy – Policy is a mapping from states actions that tells you what to do in a given state • Examples: – Credit assignment problem – Game playing – Robot in a maze – Balance a pole on your hand 36
- 35. The Agent-Environment Interface Agent and environment interact at discrete time steps Agent observes state at step t: st S : t 0, 1, 2, K produces action at step t : at A(st ) gets resulting reward : and resulting next state : rt1 st1 . . . st at rt +1 st +1 at +1 rt +2 st +2 at +2 rt +3 st +3 . . . at +3 Slide credit: Sutton & Barto 37
- 36. Reinforcement Learning https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4cgWya-wjgY 38
- 37. Inverse Reinforcement Learning • Learn policy from user demonstrations Stanford Autonomous Helicopter http://heli.stanford.edu/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VCdxqn0fcnE 39
- 38. 40 Framing a Learning Problem
- 39. Designing a Learning System • Choose the training experience • Choose exactly what is to be learned – i.e. the target function • Choose how to represent the target function • Choose a learning algorithm to infer the target function from the experience Environment/ Experience Learner Knowledge Performance Element Based on slide by Ray Mooney Training data Testing data 41
- 40. Training vs. Test Distribution • We generally assume that the training and test examples are independently drawn from the same overall distribution of data – We call this “i.i.d” which stands for “independent and identically distributed” • If examples are not independent, requires collective classification • If test distribution is different, requires transfer learning Slide credit: Ray Mooney 42
- 41. ML in a Nutshell • Tens of thousands of machine learning algorithms – Hundreds new every year • Every ML algorithm has three components: – Representation – Optimization – Evaluation Slide credit: Pedro Domingos 43
- 42. 44 Slide credit: Ray Mooney Various Function Representations • Numerical functions – Linear regression – Neural networks – Support vector machines • Symbolic functions – Decision trees – Rules in propositional logic – Rules in first-order predicate logic • Instance-based functions – Nearest-neighbor – Case-based • Probabilistic Graphical Models – Naïve Bayes – Bayesian networks – Hidden-Markov Models (HMMs) – Probabilistic Context Free Grammars (PCFGs) – Markov networks
- 43. 45 Slide credit: Ray Mooney Various Search/Optimization Algorithms • Gradient descent – Perceptron – Backpropagation • Dynamic Programming – HMM Learning – PCFG Learning • Divide and Conquer – Decision tree induction – Rule learning • Evolutionary Computation – Genetic Algorithms (GAs) – Genetic Programming (GP) – Neuro-evolution
- 44. 47 Slide credit: Pedro Domingos Evaluation • Accuracy • Precision and recall • Squared error • Likelihood • Posterior probability • Cost / Utility • Margin • Entropy • K-L divergence • etc.
- 45. ML in Practice • Understand domain, prior knowledge, and goals • Data integration, selection, cleaning, pre-processing, etc. • Learn models • Interpret results • Consolidate and deploy discovered knowledge Loop 48 Based on a slide by Pedro Domingos
- 46. 49 Lessons Learned about Learning • Learning can be viewed as using direct or indirect experience to approximate a chosen target function. • Function approximation can be viewed as a search through a space of hypotheses (representations of functions) for one that best fits a set of training data. • Different learning methods assume different hypothesis spaces (representation languages) and/or employ different search techniques. Slide credit: Ray Mooney
- 47. A Brief History of Machine Learning 50
- 48. 51 Slide credit: Ray Mooney History of Machine Learning • 1950s – Samuel’s checker player – Selfridge’s Pandemonium • 1960s: – Neural networks: Perceptron – Pattern recognition – Learning in the limit theory – Minsky and Papert prove limitations of Perceptron • 1970s: – Symbolic concept induction – Winston’s arch learner – Expert systems and the knowledge acquisition bottleneck – Quinlan’s ID3 – Michalski’s AQ and soybean diagnosis – Scientific discovery with BACON – Mathematical discovery with AM
- 49. 52 Slide credit: Ray Mooney History of Machine Learning (cont.) • 1980s: – Advanced decision tree and rule learning – Explanation-based Learning (EBL) – Learning and planning and problem solving – Utility problem – Analogy – Cognitive architectures – Resurgence of neural networks (connectionism, backpropagation) – Valiant’s PAC Learning Theory – Focus on experimental methodology • 1990s – Data mining – Adaptive software agents and web applications – Text learning – Reinforcement learning (RL) – Inductive Logic Programming (ILP) – Ensembles: Bagging, Boosting, and Stacking – Bayes Net learning
- 50. 53 Based on slide by Ray Mooney History of Machine Learning (cont.) • 2000s – Support vector machines & kernel methods – Graphical models – Statistical relational learning – Transfer learning – Sequence labeling – Collective classification and structured outputs – Computer Systems Applications (Compilers, Debugging, Graphics, Security) – E-mail management – Personalized assistants that learn – Learning in robotics and vision • 2010s – Deep learning systems – Learning for big data – Bayesian methods – Multi-task & lifelong learning – Applications to vision, speech, social networks, learning to read, etc. – ???
- 51. What We’ll Cover in this Course • Supervised learning – Decision tree induction – Linear regression – Logistic regression – Support vector machines & kernel methods – Model ensembles – Bayesian learning – Neural networks & deep learning – Learning theory • Unsupervised learning – Clustering – Dimensionality reduction • Reinforcement learning – Temporal difference learning – Q learning • Evaluation • Applications Our focus will be on applying machine learning to real applications 54






![8
Slide credit: Pedro Domingos
Sample Applications
• Web search
• Computational biology
• Finance
• E-commerce
• Space exploration
• Robotics
• Information extraction
• Social networks
• Debugging software
• [Your favorite area]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoml-230329133301-d6354f8c/85/INTRO-TO-ML-pptx-7-320.jpg)










![Scene Labeling via Deep Learning
[Farabet et al. ICML 2012, PAMI 2013] 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoml-230329133301-d6354f8c/85/INTRO-TO-ML-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![Machine Learning in
Automatic Speech Recognition
A Typical Speech Recognition System
ML used to predict of phone states from the sound spectrogram
Deep learning has state-of-the-art results
# Hidden Layers 1 2 4 8 10 12
Word Error Rate % 16.0 12.8 11.4 10.9 11.0 11.1
Baseline GMM performance = 15.4%
[Zeiler et al. “On rectified linear units for speech
recognition” ICASSP 2013]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoml-230329133301-d6354f8c/85/INTRO-TO-ML-pptx-20-320.jpg)









![[Source: Daphne Koller]
Genes
Individuals
Unsupervised Learning
Genomics application: group individuals by genetic similarity
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoml-230329133301-d6354f8c/85/INTRO-TO-ML-pptx-30-320.jpg)




















