Introduction to Android.ppt
- 2. What is Android? • A software platform and operating system for mobile devices • Based on the Linux kernel • Developed by Google and later the Open Handset Alliance (OHA) • Allows writing managed code in the Java language Unveiling of the Android platform was announced on 5 November 2007 with the founding of OHA Introduction
- 3. History of Android • Google acquired the startup company Android Inc. in 2005 to start the development of the Android Platform. The key players at Android Inc. included Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White. • In late 2007, a group of industry leaders came together around the Android Platform to form the Open Handset Alliance (http://www.openhandsetalliance.com). • The Android SDK was first issued as an “early look” release in November 2007. • In September 2008 T-Mobile announced the availability of the T- Mobile G1, the first smartphone based on the Android Platform. • A few days after that, Google announced the availability of Android SDK Release Candidate 1.0. • In October 2008, Google made the source code of the Android Platform available under Apache’s open source license.
- 5. What is Open Handset Alliance? • Quoting from www.OpenHandsetAlliance.com page • “… Open Handset Alliance™, a group of 47 technology and mobile companies have come together to accelerate innovation in mobile and offer consumers a richer, less expensive, and better mobile experience. • Together we have developed Android™, the first complete, open, and free mobile platform. • We are committed to commercially deploy handsets and services using the Android Platform. “
- 6. Introduction What is the Open Handset Alliance (OHA)? → It's a consortium of several companies Google Android
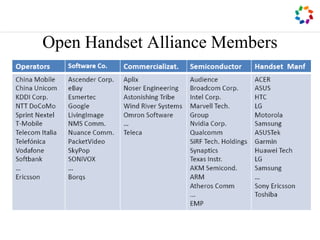
- 7. Open Handset Alliance Members
- 8. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 8 Phones HTC G1, Droid, Tattoo Motorola Droid (X) Suno S880 Samsung Galaxy Sony Ericsson
- 9. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 9 Tablets Velocity Micro Cruz Gome FlyTouch Acer beTouch Dawa D7 Toshiba Android SmartBook Cisco Android Tablet
- 10. Hardware Android is not a single piece of hardware; it's a complete, end-to- end software platform that can be adapted to work on any number of hardware configurations. Everything is there, from the bootloader all the way up to the applications. Platform Google Android
- 11. Android’s Context: Mobile Market Player$ Stakeholders: • Mobile network operators want to lock down their networks, controlling and metering traffic. • Device manufacturers want to differentiate themselves with features, reliability, and price points. • Software vendors want complete access to the hardware to deliver cutting-edge applications.
- 12. The Maturing Mobile Experience • Tomorrow?
- 13. The Maturing Mobile Experience
- 15. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 15 Platform - The Android Software Stack
- 16. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 16 Android S/W Stack - Application • Android provides a set of core applications: Email Client SMS Program Calendar Maps Browser Contacts Etc • All applications are written using the Java language.
- 17. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 17 Android S/W Stack – App Framework • Most of the application framework accesses these core libraries through the Dalvik VM, the gateway to the Android Platform
- 18. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 18 Android S/W Stack – App Framework (Cont) Feature Role View System Used to build an application, including lists, grids, text boxes, buttons, and embedded web browser Content Provider Enabling applications to access data from other applications or to share their own data Resource Manager Providing access to non-code resources (localized string , graphics, and layout files) Notification Manager Enabling all applications to display customer alerts in the status bar Activity Manager Managing the lifecycle of applications and providing a common navigation backstack
- 19. Location Manager
- 21. Notification Manager • How background app interact with users • Consistent notification presentation
- 22. View System
- 23. View System
- 24. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 24 Android S/W Stack - Libraries • Including a set of C/C++ libraries used by components of the Android system • Exposed to developers through the Android application framework
- 25. Android S/W Stack - Libraries • The media libraries are based on PacketVideo’s (http://www.packetvideo.com/) OpenCORE. These libraries are responsible for recording and playback of audio and video formats. A library called Surface Manager controls access to the display system and supports 2D and 3D. • The WebKit library is responsible for browser support; it is the same library that supports Google Chrome and Apple Inc.’s Safari. The FreeType library is responsible for font support. SQLite (http://www.sqlite.org/) is a relational database that is available on the device itself. SQLite is also an independent open source effort for relational databases and not directly tied to Android. You can acquire and use tools meant for SQLite for Android databases as well.
- 26. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 26 Android S/W Stack - Runtime • Core Libraries Providing most of the functionality available in the core libraries of the Java language APIs Data Structures Utilities File Access Network Access Graphics Etc
- 27. Bruce Scharlau, University of Aberdeen, 2010 The Dalvik runtime is optimised for mobile applications Run multiple VMs efficiently Each app has its own VM Minimal memory footprint
- 28. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 28 Android S/W Stack – Runtime (Cont) • Dalvik Virtual Machine (Cont) Executing the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format .dex format is optimized for minimal memory footprint. Compilation Relying on the Linux Kernel for: Threading Low-level memory management
- 29. Bruce Scharlau, University of Aberdeen, 2010 Android applications are compiled to Dalvik bytecode Write app in Java Compiled in Java Transformed to Dalvik bytecode Linux OS Loaded into Dalvik VM
- 30. @2010 Mihail L. Sichitiu 30 Android S/W Stack – Linux Kernel Relying on Linux Kernel 2.6 for core system services Memory and Process Management Network Stack Driver Model Security • The supplied device drivers include Display, Camera, Keypad, WiFi, Flash Memory, Audio, and IPC (interprocess communication). Providing an abstraction layer between the H/W and the rest of the S/W stack
- 31. Network Connectivity It supports wireless communications using: GSM mobile-phone technology 3G Edge 802.11 Wi-Fi networks Platform Google Android
- 32. Development requirements • Java • Android SDK Software development Google Android
- 33. IDE and Tools Android SDK • Class Library • Developer Tools • Emulator and System Images • Documentation and Sample Code Eclipse IDE + ADT (Android Development Tools) • Reduces Development and Testing Time • Makes User Interface-Creation easier • Makes Application Description Easier Software development Google Android
- 34. Here are a few other advantages Android offers you as a developer: • The Android SDK is available for Windows, Mac and Linux, so you don’t need to pay for new hardware to start writing applications. • An SDK built on Java. If you’re familiar with the Java programming language, you’re already halfway there. • By distributing your application on Android Market, it’s available to hundreds of thousands of users instantly. You’re not just limited to one store, because there are alternatives, too. For instance, you can release your application on your own blog. Amazon have recently been rumoured to be preparing their own Android app store also. • As well as the technical SDK documentation, new resources are being published for Android developers as the platform gains popularity among both users and developers. Advantages Google Android
- 35. Application Building Blocks • Activity • IntentReceiver • Service • ContentProvider
- 36. Activities • Typically correspond to one UI screen • But, they can: – Be faceless – Be in a floating window – Return a value
- 37. IntentReceivers • Components that respond to broadcast ‘Intents’ • Way to respond to external notification or alarms • Apps can invent and broadcast their own Intent
- 38. Intents • Think of Intents as a verb and object; a description of what you want done – E.g. VIEW, CALL, PLAY etc.. • System matches Intent with Activity that can best provide the service • Activities and IntentReceivers describe what Intents they can service
- 40. Services • Faceless components that run in the background – E.g. music player, network download etc…
- 41. ContentProviders • Enables sharing of data across applications – E.g. address book, photo gallery • Provides uniform APIs for: – querying – delete, update and insert. • Content is represented by URI and MIME type