Introduction to Arduino - Basics programming
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes22 views
Arduino Beginner
1 of 41
Download to read offline






































Ad
Recommended
Arduino_Beginner.pptx



Arduino_Beginner.pptxshivagoud45 The document provides an overview of a workshop on Arduino embedded development boards. It discusses the Arduino architecture and components, programming fundamentals using the Arduino IDE, and examples of projects including blinking an LED, controlling an RGB LED using PWM, interfacing sensors like light and temperature, and motor speed control. The document explains concepts like open and closed loop control systems, analog and digital signals, and serial communication. It also introduces the Arduino Uno board and shows examples of circuits using components like an L293D motor driver, temperature sensor, and potentiometer.
Arduino_Beginner.pptx



Arduino_Beginner.pptxaravind Guru The document provides an overview of an Arduino workshop that covers embedded systems and the Arduino development board. It includes sections on Arduino basics, architecture, components, programming fundamentals, and example projects interfacing LEDs, sensors and actuators. The workshop introduces concepts like open and closed loop control systems. It also explains the Arduino IDE, basic coding structures like setup and loop functions, and how to interface common electronic components like sensors, displays and motors to an Arduino board. Project examples include blinking an LED, controlling an RGB LED using PWM, reading from light and temperature sensors, and controlling motor speed.
arduinocourse-180308074529 (1).pdf



arduinocourse-180308074529 (1).pdfssusere5db05 This document provides an overview of an Arduino course covering embedded systems and programming. The summary includes:
- The course covers introduction to embedded systems including components, characteristics, and basic structure. It also covers introduction to computer programming concepts for Arduino like variables, operators, and control statements.
- The Arduino environment and programming is explained including the board, IDE, sensors, actuators and communication. Common electronic components and modules used with Arduino like LEDs, buttons, LCDs, ultrasonic sensors, and Bluetooth are described.
- The document concludes with a section on circuit diagrams for Arduino projects. Key concepts around pins, analog/digital input/output, pulse width modulation, delay, and
Arduino course



Arduino courseAhmed Shelbaya This document provides an overview of an Arduino course covering embedded systems and programming. The summary includes:
- The course covers introduction to embedded systems including components, characteristics, and basic structure. It also covers introduction to computer programming concepts for Arduino including variables, operators, control statements, functions, and C language basics.
- The document outlines the Arduino environment including boards, software IDE, sensors, actuators and provides examples of electronic components like LEDs, buttons, and code for digital input/output and serial communication.
- Finally, the course covers creating circuit diagrams and interfacing with common modules like LCD displays, ultrasonic sensors, relays, Bluetooth and DC motors.
Arduino Introduction PPT for school students



Arduino Introduction PPT for school studentsstusanthosh5195 Arduino (/ɑːrˈdwiːnoʊ/) is an Italian open-source hardware and software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a CC BY-SA license, while the software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL),[1] permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors.[2]
Arduino board designs use a variety of microprocessors and controllers. The boards are equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards ('shields') or breadboards (for prototyping) and other circuits. The boards feature serial communications interfaces, including Universal Serial Bus (USB) on some models, which are also used for loading programs. The microcontrollers can be programmed using the C and C++ programming languages (Embedded C), using a standard API which is also known as the Arduino Programming Language, inspired by the Processing language and used with a modified version of the Processing IDE. In addition to using traditional compiler toolchains, the Arduino project provides an integrated development environment (IDE) and a command line tool developed in Go.
Basics of arduino uno



Basics of arduino unoRahat Sood This document provides an overview of the Arduino Uno microcontroller board. It defines a microcontroller as a single-chip computer containing a CPU, memory, and input/output interfaces. The Arduino is an open-source electronics platform with easy-to-use hardware and software that allows anyone to develop interactive electronic projects. Key specifications of the Arduino Uno board are provided, including its microcontroller chip, memory, analog and digital pins. The process of analog to digital conversion is explained. Basic Arduino programming concepts like data types, statements, operators, and control structures are covered. The bare minimum code structure of setup() and loop() functions is described.
Arduino: Arduino starter kit



Arduino: Arduino starter kitSANTIAGO PABLO ALBERTO The document provides instructions for connecting an Arduino board to a Windows computer and uploading a simple "Blink" sketch. It outlines downloading the Arduino IDE software, connecting the board via USB, installing the correct USB drivers, opening the Blink example sketch, selecting the board and serial port in the IDE, and uploading the program to make an on-board LED blink.
Mechatronics material . Mechanical engineering



Mechatronics material . Mechanical engineeringsachin chaurasia Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary field that refers to the skill sets needed in the contemporary, advanced automated manufacturing industry. At the intersection of mechanics, electronics, and computing, mechatronics specialists create simpler, smarter systems. Mechatronics is an essential foundation for the expected growth in automation and manufacturing.
Mechatronics deals with robotics, control systems, and electro-mechanical systems.
ARDUINO Presentation1.pptx



ARDUINO Presentation1.pptxSourabhSalunkhe10 The document discusses mechatronics and provides information on microprocessors, microcontrollers, Arduino, and interfacing devices with Arduino. It defines mechatronics as an interdisciplinary field focusing on integrating mechanical, electrical, and electronic engineering systems. It describes microprocessors and microcontrollers, highlighting the Atmega328 microcontroller used on the Arduino Uno board. It discusses analog and digital pins on Arduino and provides an example code for reading analog sensor values. It also lists some common input and output devices that can be interfaced with Arduino like buttons, motors, and LCD displays.
Arduino by yogesh t s'



Arduino by yogesh t s'tsyogesh46 1.Gives basic idea about what is arduino? and their funtionalites.
2. Applications of arduino
3. Adruino programming
4. what is Nodemcu ?
5. pindiagram of Nodemcu
Tinkercad Workshop PPT, Dept. of ECE.pptx



Tinkercad Workshop PPT, Dept. of ECE.pptxJayashreeSelvam5 The one-day workshop covers embedded system design using simulation tools. It discusses embedded systems, microcontrollers, microprocessors and Arduino. The technical specifications of Arduino and how to interface it with sensors like LCD, temperature sensor, ultrasonic sensor, IR sensor and soil moisture sensor are explained. The document emphasizes the need for simulation to safely and efficiently solve real-world problems. It also introduces Tinkercad as a free simulation tool to design interfaces between Arduino and various sensors. The code examples shared explain how to interface different sensors with Arduino and read their values.
Introduction to Arduino.pptx



Introduction to Arduino.pptxAkshat Bijronia By the end of this presentation you will be able to tell :
1. What is Arduino ?
2. Languages Supporting Arduino
3.Difference between microprocessor and microcontroller ?
4. Various different Arduino Boards
5. Arduino UNO R3 DataSheet
6. Parts and Functions of Arduino UNO R3 Board
7. Variables, functions and libraries used in Arduino board
8. Arduino Code: Blink Example
9. Applications of Arduino in real life
10. Simulators used for Arduino coding
Arduino & NodeMcu



Arduino & NodeMcuGuhan Ganesan The document discusses hardware programming concepts for Arduino and NodeMCU boards. It covers:
- The structure of Arduino programs with setup and loop functions. Setup runs once and loop runs continuously.
- Examples of blinking an LED on Arduino and reading light sensor input to display values.
- Pin configurations on NodeMCU and setting it up in Arduino IDE.
- Examples of blinking an LED and reading a sensor with NodeMCU and storing the sensor data in a MySQL database.
- Creating a Flask application to interface with the database and view the sensor data through templates.
Arduino Programming Basic



Arduino Programming BasicLITS IT Ltd,LASRC.SPACE,SAWDAGOR BD,FREELANCE BD,iREV,BD LAW ACADEMY,SMART AVI,HEA,HFSAC LTD. This document provides an overview of Arduino programming concepts including:
- Microcontrollers contain a CPU, memory, input/output pins and other peripherals on a single integrated circuit.
- Arduino is an open-source electronics platform with a microcontroller, pins to connect circuits, and software to program it.
- The core Arduino functions include setup(), loop(), pinMode(), digitalWrite(), digitalRead(), analogWrite(), analogRead(), and delay().
- Examples demonstrate blinking LEDs, reading input, using conditions and loops, arrays, LCD displays, and controlling servo motors.
- Arduino programming provides an accessible way to learn embedded systems and interact with circuits.
Introduction to Arduino session and basically it depends how you us and where...



Introduction to Arduino session and basically it depends how you us and where...YakshYadav2 This is arudhdbskaabd bzhsajajbzvs hshsbsbsbshus hsjshdbsjsjs
arduino uno



arduino uno20PA013BHOOMIKAP This document provides an overview of the Arduino Uno microcontroller board. It describes that the Arduino Uno contains an ATmega328 microprocessor and can be used to control electronics projects through input and output pins. The Arduino IDE software is used to write programs that can be compiled and uploaded to the board via a USB connection. The document explains the different pin types on the Arduino Uno and provides examples of how sensors and actuators can be connected to collect analog and digital data and control outputs.
Iot Workshop NITT 2015



Iot Workshop NITT 2015Srivignessh Pss This document provides information about microprocessors, microcontrollers, and the Intel 8085 and 8051 chips. It discusses how a microprocessor incorporates a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, and how microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications. Key aspects of microcontrollers covered include on-chip RAM, timers, serial ports, interrupt controllers, analog-to-digital converters, and pulse width modulation controllers. An example block diagram and features are given for the Intel 8051 microcontroller. Example Arduino/Freeduino programs are also summarized.
SKAD Electronics Training Manual.pdf



SKAD Electronics Training Manual.pdfKadiriIbrahim2 The document provides an overview of SKAD electronics training add-ons for universities and polytechnics in Nigeria. It describes various Arduino-based add-ons that are designed to improve existing science and engineering equipment. The add-ons cover topics like analog and digital electronics, digital logic, electricity and semiconductors simulation, greenhouse control, and modern technology systems. Each add-on includes components like the Arduino UNO board, sensors, displays, and jumper wires. The document then provides details of experiments that can be performed with each add-on to enhance student learning.
arduinoworkshop-160204051621.pdf



arduinoworkshop-160204051621.pdfAbdErrezakChahoub This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the Arduino platform. It discusses what a microcontroller is and some common types. It then introduces Arduino as an open-source prototyping platform using easy hardware and software. Several Arduino boards are described and the ATmega328p microcontroller chip is specified. The document outlines how to download the Arduino software and write programs. It provides examples of basic Arduino projects like blinking LEDs, reading sensors, and creating sounds.
Ardui no 



Ardui no Amol Sakhalkar This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the Arduino platform. It discusses what a microcontroller is and some common types. It then introduces Arduino as an open-source prototyping platform using easy hardware and software. Several Arduino boards are described and the ATmega328p microcontroller chip is specified. The document outlines how to download the Arduino software and write programs. It provides examples of basic Arduino projects like blinking LEDs, reading sensors, and creating sounds.
Internet of Things Unit 3 notes-Design and Development and Arduino.pptx



Internet of Things Unit 3 notes-Design and Development and Arduino.pptxDinola2 Embedded computing logic refers to the design and implementation of circuits, algorithms, and software within embedded systems to perform specific functions. It involves hardware design, software development, real-time processing, low power design, communication protocols, and security. Designers use techniques like simulation and testing to validate embedded system designs.
Arduino



ArduinoJerin John This document provides an overview of Arduino, an open-source hardware platform used for building interactive objects and prototypes. It describes Arduino as a single-board microcontroller intended to make electronics projects more accessible. Key topics covered include the Arduino programming environment, common Arduino boards and their features, examples of simple Arduino projects like blinking an LED and building a line-following robot, and comparisons to other prototyping platforms. The document encourages readers to get started with Arduino for its low cost, easy programming environment, and large community support.
Introduction to Arduino Hardware and Programming



Introduction to Arduino Hardware and ProgrammingEmmanuel Obot Introduction to Arduino Hardware and Programming:
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. It's intended for anyone making interactive projects.
Teachers and students use it to build low cost scientific instruments, to prove chemistry and physics principles, or to get started with programming and robotics. Designers and architects build interactive prototypes, musicians and artists use it for installations and to experiment with new musical instruments. Makers, of course, use it to build many of the projects exhibited at the Maker Faire. Arduino is a key tool to learn new things. Anyone - children, hobbyists, artists, programmers can use it to build an interactive device.
Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar.docx



Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar.docxRashidFaridChishti Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar
teststststststLecture_3_2022_Arduino.pptx



teststststststLecture_3_2022_Arduino.pptxethannguyen1618 The document provides an overview of learning objectives and topics for an introduction to Arduino lecture, including:
- How to use a potentiometer as a sensor and identify input/output ports of an Arduino.
- What an Arduino is, its boards and IDE software.
- Why Arduinos are popular for electronics projects.
- How Arduinos will be used in labs, including acquiring sensor data and sending signals to systems using code.
Embedded systems presentation



Embedded systems presentationRAJBALA PURNIMA PRIYA An Embedded system is a programmed controlling and operating system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system , often with real-time computing constrain.
It is a system that has software embedded into computer hardware , which makes a system dedicated for an applications or specific part of an application.
"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...



"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...Infopitaara A Boiler Feed Pump (BFP) is a critical component in thermal power plants. It supplies high-pressure water (feedwater) to the boiler, ensuring continuous steam generation.
⚙️ How a Boiler Feed Pump Works
Water Collection:
Feedwater is collected from the deaerator or feedwater tank.
Pressurization:
The pump increases water pressure using multiple impellers/stages in centrifugal types.
Discharge to Boiler:
Pressurized water is then supplied to the boiler drum or economizer section, depending on design.
🌀 Types of Boiler Feed Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps (most common):
Multistage for higher pressure.
Used in large thermal power stations.
Positive Displacement Pumps (less common):
For smaller or specific applications.
Precise flow control but less efficient for large volumes.
🛠️ Key Operations and Controls
Recirculation Line: Protects the pump from overheating at low flow.
Throttle Valve: Regulates flow based on boiler demand.
Control System: Often automated via DCS/PLC for variable load conditions.
Sealing & Cooling Systems: Prevent leakage and maintain pump health.
⚠️ Common BFP Issues
Cavitation due to low NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head).
Seal or bearing failure.
Overheating from improper flow or recirculation.
Ad
More Related Content
Similar to Introduction to Arduino - Basics programming (20)
ARDUINO Presentation1.pptx



ARDUINO Presentation1.pptxSourabhSalunkhe10 The document discusses mechatronics and provides information on microprocessors, microcontrollers, Arduino, and interfacing devices with Arduino. It defines mechatronics as an interdisciplinary field focusing on integrating mechanical, electrical, and electronic engineering systems. It describes microprocessors and microcontrollers, highlighting the Atmega328 microcontroller used on the Arduino Uno board. It discusses analog and digital pins on Arduino and provides an example code for reading analog sensor values. It also lists some common input and output devices that can be interfaced with Arduino like buttons, motors, and LCD displays.
Arduino by yogesh t s'



Arduino by yogesh t s'tsyogesh46 1.Gives basic idea about what is arduino? and their funtionalites.
2. Applications of arduino
3. Adruino programming
4. what is Nodemcu ?
5. pindiagram of Nodemcu
Tinkercad Workshop PPT, Dept. of ECE.pptx



Tinkercad Workshop PPT, Dept. of ECE.pptxJayashreeSelvam5 The one-day workshop covers embedded system design using simulation tools. It discusses embedded systems, microcontrollers, microprocessors and Arduino. The technical specifications of Arduino and how to interface it with sensors like LCD, temperature sensor, ultrasonic sensor, IR sensor and soil moisture sensor are explained. The document emphasizes the need for simulation to safely and efficiently solve real-world problems. It also introduces Tinkercad as a free simulation tool to design interfaces between Arduino and various sensors. The code examples shared explain how to interface different sensors with Arduino and read their values.
Introduction to Arduino.pptx



Introduction to Arduino.pptxAkshat Bijronia By the end of this presentation you will be able to tell :
1. What is Arduino ?
2. Languages Supporting Arduino
3.Difference between microprocessor and microcontroller ?
4. Various different Arduino Boards
5. Arduino UNO R3 DataSheet
6. Parts and Functions of Arduino UNO R3 Board
7. Variables, functions and libraries used in Arduino board
8. Arduino Code: Blink Example
9. Applications of Arduino in real life
10. Simulators used for Arduino coding
Arduino & NodeMcu



Arduino & NodeMcuGuhan Ganesan The document discusses hardware programming concepts for Arduino and NodeMCU boards. It covers:
- The structure of Arduino programs with setup and loop functions. Setup runs once and loop runs continuously.
- Examples of blinking an LED on Arduino and reading light sensor input to display values.
- Pin configurations on NodeMCU and setting it up in Arduino IDE.
- Examples of blinking an LED and reading a sensor with NodeMCU and storing the sensor data in a MySQL database.
- Creating a Flask application to interface with the database and view the sensor data through templates.
Arduino Programming Basic



Arduino Programming BasicLITS IT Ltd,LASRC.SPACE,SAWDAGOR BD,FREELANCE BD,iREV,BD LAW ACADEMY,SMART AVI,HEA,HFSAC LTD. This document provides an overview of Arduino programming concepts including:
- Microcontrollers contain a CPU, memory, input/output pins and other peripherals on a single integrated circuit.
- Arduino is an open-source electronics platform with a microcontroller, pins to connect circuits, and software to program it.
- The core Arduino functions include setup(), loop(), pinMode(), digitalWrite(), digitalRead(), analogWrite(), analogRead(), and delay().
- Examples demonstrate blinking LEDs, reading input, using conditions and loops, arrays, LCD displays, and controlling servo motors.
- Arduino programming provides an accessible way to learn embedded systems and interact with circuits.
Introduction to Arduino session and basically it depends how you us and where...



Introduction to Arduino session and basically it depends how you us and where...YakshYadav2 This is arudhdbskaabd bzhsajajbzvs hshsbsbsbshus hsjshdbsjsjs
arduino uno



arduino uno20PA013BHOOMIKAP This document provides an overview of the Arduino Uno microcontroller board. It describes that the Arduino Uno contains an ATmega328 microprocessor and can be used to control electronics projects through input and output pins. The Arduino IDE software is used to write programs that can be compiled and uploaded to the board via a USB connection. The document explains the different pin types on the Arduino Uno and provides examples of how sensors and actuators can be connected to collect analog and digital data and control outputs.
Iot Workshop NITT 2015



Iot Workshop NITT 2015Srivignessh Pss This document provides information about microprocessors, microcontrollers, and the Intel 8085 and 8051 chips. It discusses how a microprocessor incorporates a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, and how microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications. Key aspects of microcontrollers covered include on-chip RAM, timers, serial ports, interrupt controllers, analog-to-digital converters, and pulse width modulation controllers. An example block diagram and features are given for the Intel 8051 microcontroller. Example Arduino/Freeduino programs are also summarized.
SKAD Electronics Training Manual.pdf



SKAD Electronics Training Manual.pdfKadiriIbrahim2 The document provides an overview of SKAD electronics training add-ons for universities and polytechnics in Nigeria. It describes various Arduino-based add-ons that are designed to improve existing science and engineering equipment. The add-ons cover topics like analog and digital electronics, digital logic, electricity and semiconductors simulation, greenhouse control, and modern technology systems. Each add-on includes components like the Arduino UNO board, sensors, displays, and jumper wires. The document then provides details of experiments that can be performed with each add-on to enhance student learning.
arduinoworkshop-160204051621.pdf



arduinoworkshop-160204051621.pdfAbdErrezakChahoub This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the Arduino platform. It discusses what a microcontroller is and some common types. It then introduces Arduino as an open-source prototyping platform using easy hardware and software. Several Arduino boards are described and the ATmega328p microcontroller chip is specified. The document outlines how to download the Arduino software and write programs. It provides examples of basic Arduino projects like blinking LEDs, reading sensors, and creating sounds.
Ardui no 



Ardui no Amol Sakhalkar This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the Arduino platform. It discusses what a microcontroller is and some common types. It then introduces Arduino as an open-source prototyping platform using easy hardware and software. Several Arduino boards are described and the ATmega328p microcontroller chip is specified. The document outlines how to download the Arduino software and write programs. It provides examples of basic Arduino projects like blinking LEDs, reading sensors, and creating sounds.
Internet of Things Unit 3 notes-Design and Development and Arduino.pptx



Internet of Things Unit 3 notes-Design and Development and Arduino.pptxDinola2 Embedded computing logic refers to the design and implementation of circuits, algorithms, and software within embedded systems to perform specific functions. It involves hardware design, software development, real-time processing, low power design, communication protocols, and security. Designers use techniques like simulation and testing to validate embedded system designs.
Arduino



ArduinoJerin John This document provides an overview of Arduino, an open-source hardware platform used for building interactive objects and prototypes. It describes Arduino as a single-board microcontroller intended to make electronics projects more accessible. Key topics covered include the Arduino programming environment, common Arduino boards and their features, examples of simple Arduino projects like blinking an LED and building a line-following robot, and comparisons to other prototyping platforms. The document encourages readers to get started with Arduino for its low cost, easy programming environment, and large community support.
Introduction to Arduino Hardware and Programming



Introduction to Arduino Hardware and ProgrammingEmmanuel Obot Introduction to Arduino Hardware and Programming:
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. It's intended for anyone making interactive projects.
Teachers and students use it to build low cost scientific instruments, to prove chemistry and physics principles, or to get started with programming and robotics. Designers and architects build interactive prototypes, musicians and artists use it for installations and to experiment with new musical instruments. Makers, of course, use it to build many of the projects exhibited at the Maker Faire. Arduino is a key tool to learn new things. Anyone - children, hobbyists, artists, programmers can use it to build an interactive device.
Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar.docx



Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar.docxRashidFaridChishti Lab Manual Arduino UNO Microcontrollar
teststststststLecture_3_2022_Arduino.pptx



teststststststLecture_3_2022_Arduino.pptxethannguyen1618 The document provides an overview of learning objectives and topics for an introduction to Arduino lecture, including:
- How to use a potentiometer as a sensor and identify input/output ports of an Arduino.
- What an Arduino is, its boards and IDE software.
- Why Arduinos are popular for electronics projects.
- How Arduinos will be used in labs, including acquiring sensor data and sending signals to systems using code.
Embedded systems presentation



Embedded systems presentationRAJBALA PURNIMA PRIYA An Embedded system is a programmed controlling and operating system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system , often with real-time computing constrain.
It is a system that has software embedded into computer hardware , which makes a system dedicated for an applications or specific part of an application.
Arduino Programming Basic



Arduino Programming BasicLITS IT Ltd,LASRC.SPACE,SAWDAGOR BD,FREELANCE BD,iREV,BD LAW ACADEMY,SMART AVI,HEA,HFSAC LTD.
Recently uploaded (20)
"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...



"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...Infopitaara A Boiler Feed Pump (BFP) is a critical component in thermal power plants. It supplies high-pressure water (feedwater) to the boiler, ensuring continuous steam generation.
⚙️ How a Boiler Feed Pump Works
Water Collection:
Feedwater is collected from the deaerator or feedwater tank.
Pressurization:
The pump increases water pressure using multiple impellers/stages in centrifugal types.
Discharge to Boiler:
Pressurized water is then supplied to the boiler drum or economizer section, depending on design.
🌀 Types of Boiler Feed Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps (most common):
Multistage for higher pressure.
Used in large thermal power stations.
Positive Displacement Pumps (less common):
For smaller or specific applications.
Precise flow control but less efficient for large volumes.
🛠️ Key Operations and Controls
Recirculation Line: Protects the pump from overheating at low flow.
Throttle Valve: Regulates flow based on boiler demand.
Control System: Often automated via DCS/PLC for variable load conditions.
Sealing & Cooling Systems: Prevent leakage and maintain pump health.
⚠️ Common BFP Issues
Cavitation due to low NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head).
Seal or bearing failure.
Overheating from improper flow or recirculation.
Data Structures_Introduction to algorithms.pptx



Data Structures_Introduction to algorithms.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Concept of Problem Solving, Introduction to Algorithms, Characteristics of Algorithms, Introduction to Data Structure, Data Structure Classification (Linear and Non-linear, Static and Dynamic, Persistent and Ephemeral data structures), Time complexity and Space complexity, Asymptotic Notation - The Big-O, Omega and Theta notation, Algorithmic upper bounds, lower bounds, Best, Worst and Average case analysis of an Algorithm, Abstract Data Types (ADT)
theory-slides-for react for beginners.pptx



theory-slides-for react for beginners.pptxsanchezvanessa7896 Everything you need to know about react.
DT REPORT by Tech titan GROUP to introduce the subject design Thinking



DT REPORT by Tech titan GROUP to introduce the subject design ThinkingDhruvChotaliya2 This a Report of a Design Thinking
ELectronics Boards & Product Testing_Shiju.pdf



ELectronics Boards & Product Testing_Shiju.pdfShiju Jacob This presentation provides a high level insight about DFT analysis and test coverage calculation, finalizing test strategy, and types of tests at different levels of the product.
Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...



Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering In tube drawing process, a tube is pulled out through a die and a plug to reduce its diameter and thickness as per the requirement. Dimensional accuracy of cold drawn tubes plays a vital role in the further quality of end products and controlling rejection in manufacturing processes of these end products. Springback phenomenon is the elastic strain recovery after removal of forming loads, causes geometrical inaccuracies in drawn tubes. Further, this leads to difficulty in achieving close dimensional tolerances. In the present work springback of EN 8 D tube material is studied for various cold drawing parameters. The process parameters in this work include die semi-angle, land width and drawing speed. The experimentation is done using Taguchi’s L36 orthogonal array, and then optimization is done in data analysis software Minitab 17. The results of ANOVA shows that 15 degrees die semi-angle,5 mm land width and 6 m/min drawing speed yields least springback. Furthermore, optimization algorithms named Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Simulated Annealing (SA) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) are applied which shows that 15 degrees die semi-angle, 10 mm land width and 8 m/min drawing speed results in minimal springback with almost 10.5 % improvement. Finally, the results of experimentation are validated with Finite Element Analysis technique using ANSYS.
ADVXAI IN MALWARE ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK: BALANCING EXPLAINABILITY WITH SECURITY



ADVXAI IN MALWARE ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK: BALANCING EXPLAINABILITY WITH SECURITYijscai With the increased use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in malware analysis there is also an increased need to
understand the decisions models make when identifying malicious artifacts. Explainable AI (XAI) becomes
the answer to interpreting the decision-making process that AI malware analysis models use to determine
malicious benign samples to gain trust that in a production environment, the system is able to catch
malware. With any cyber innovation brings a new set of challenges and literature soon came out about XAI
as a new attack vector. Adversarial XAI (AdvXAI) is a relatively new concept but with AI applications in
many sectors, it is crucial to quickly respond to the attack surface that it creates. This paper seeks to
conceptualize a theoretical framework focused on addressing AdvXAI in malware analysis in an effort to
balance explainability with security. Following this framework, designing a machine with an AI malware
detection and analysis model will ensure that it can effectively analyze malware, explain how it came to its
decision, and be built securely to avoid adversarial attacks and manipulations. The framework focuses on
choosing malware datasets to train the model, choosing the AI model, choosing an XAI technique,
implementing AdvXAI defensive measures, and continually evaluating the model. This framework will
significantly contribute to automated malware detection and XAI efforts allowing for secure systems that
are resilient to adversarial attacks.
Resistance measurement and cfd test on darpa subboff model



Resistance measurement and cfd test on darpa subboff modelINDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR this ppt is about DARPA submarine resistance measurement , i cinduct a cfd test on star ccm and open foam also
Data Structures_Linear data structures Linked Lists.pptx



Data Structures_Linear data structures Linked Lists.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Concept of Linear Data Structures, Array as an ADT, Merging of two arrays, Storage
Representation, Linear list – singly linked list implementation, insertion, deletion and searching operations on linear list, circularly linked lists- Operations for Circularly linked lists, doubly linked
list implementation, insertion, deletion and searching operations, applications of linked lists.
IntroSlides-April-BuildWithAI-VertexAI.pdf



IntroSlides-April-BuildWithAI-VertexAI.pdfLuiz Carneiro ☁️ GDG Cloud Munich: Build With AI Workshop - Introduction to Vertex AI! ☁️
Join us for an exciting #BuildWithAi workshop on the 28th of April, 2025 at the Google Office in Munich!
Dive into the world of AI with our "Introduction to Vertex AI" session, presented by Google Cloud expert Randy Gupta.
"Feed Water Heaters in Thermal Power Plants: Types, Working, and Efficiency G...



"Feed Water Heaters in Thermal Power Plants: Types, Working, and Efficiency G...Infopitaara A feed water heater is a device used in power plants to preheat water before it enters the boiler. It plays a critical role in improving the overall efficiency of the power generation process, especially in thermal power plants.
🔧 Function of a Feed Water Heater:
It uses steam extracted from the turbine to preheat the feed water.
This reduces the fuel required to convert water into steam in the boiler.
It supports Regenerative Rankine Cycle, increasing plant efficiency.
🔍 Types of Feed Water Heaters:
Open Feed Water Heater (Direct Contact)
Steam and water come into direct contact.
Mixing occurs, and heat is transferred directly.
Common in low-pressure stages.
Closed Feed Water Heater (Surface Type)
Steam and water are separated by tubes.
Heat is transferred through tube walls.
Common in high-pressure systems.
⚙️ Advantages:
Improves thermal efficiency.
Reduces fuel consumption.
Lowers thermal stress on boiler components.
Minimizes corrosion by removing dissolved gases.
RICS Membership-(The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors).pdf



RICS Membership-(The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors).pdfMohamedAbdelkader115 Glad to be one of only 14 members inside Kuwait to hold this credential.
Please check the members inside kuwait from this link:
https://www.rics.org/networking/find-a-member.html?firstname=&lastname=&town=&country=Kuwait&member_grade=(AssocRICS)&expert_witness=&accrediation=&page=1
Data Structures_Searching and Sorting.pptx



Data Structures_Searching and Sorting.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Sorting Order and Stability in Sorting.
Concept of Internal and External Sorting.
Bubble Sort,
Insertion Sort,
Selection Sort,
Quick Sort and
Merge Sort,
Radix Sort, and
Shell Sort,
External Sorting, Time complexity analysis of Sorting Algorithms.
Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...



Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering Analysis of reinforced concrete deep beam is based on simplified approximate method due to the complexity of the exact analysis. The complexity is due to a number of parameters affecting its response. To evaluate some of this parameters, finite element study of the structural behavior of the reinforced self-compacting concrete deep beam was carried out using Abaqus finite element modeling tool. The model was validated against experimental data from the literature. The parametric effects of varied concrete compressive strength, vertical web reinforcement ratio and horizontal web reinforcement ratio on the beam were tested on eight (8) different specimens under four points loads. The results of the validation work showed good agreement with the experimental studies. The parametric study revealed that the concrete compressive strength most significantly influenced the specimens’ response with the average of 41.1% and 49 % increment in the diagonal cracking and ultimate load respectively due to doubling of concrete compressive strength. Although the increase in horizontal web reinforcement ratio from 0.31 % to 0.63 % lead to average of 6.24 % increment on the diagonal cracking load, it does not influence the ultimate strength and the load-deflection response of the beams. Similar variation in vertical web reinforcement ratio leads to an average of 2.4 % and 15 % increment in cracking and ultimate load respectively with no appreciable effect on the load-deflection response.
Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...



Process Parameter Optimization for Minimizing Springback in Cold Drawing Proc...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering
Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...



Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering
Ad
Introduction to Arduino - Basics programming
- 1. The Arduino life Workshop on Arduino Embedded Development Board 1
- 2. The heart of engineering isn’t calculation; It’s problem solving. Schools may teach the numbers first, but calculation is neither the front end of engineering note its end goal. Calculation is one means among many to finding a solution that provides useful, objectively measurable improvement. 2
- 3. Embedded Systems Arduino Basics Arduino Architecture Arduino board layout. What are the resources available Arduino IDE Programming fundamentals Learn by Doing – Sense, Control & Actuate Project 1: LED Blinking Project 2: RGB LED Interfacing & PWM Control Project 3: Interfacing Sensors (Light, Temperature, etc.,) Project 4: Interfacing Actuators (Motor Speed Control using PWM) Introduction 3
- 4. Industry / Robot / System Industry / System 4
- 5. System & Control System / Plant: “A system may be a piece of equipment, perhaps just a set of machine parts functioning together, the purpose of which is to perform a particular operation”. Control System: “A control system is an interconnection of components forming a system configuration that provide a desired system performance” 5
- 10. Embedded Systems "It is a combination of hardware and software to perform a specific task" “An embedded system is a computer system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today.” 10
- 11. Components of Embedded Systems Power Supply Processor Memory Timers & Counters Communication Ports Input & Output Application Specific Circuits Software Components 11
- 18. arduino ( arrr-dween-oh ) (n.) It's an open-source physical computing platform based on a simple microcontroller board, and a development environment for writing software for the board. Arduino Basics 18
- 19. Arduino Nano Arduino Mega Arduino LilyPad Arduino Mini Arduino Leonardo Arduino Uno Types of Arduino Boards 19
- 20. Arduino Uno Digital pins: 14 digital IO pins 6 are PWM pins (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11). Analog pins: 6 analog pins(A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5) Takes analog values as an input 20
- 21. 21
- 22. VERIFY UPLOAD NEW TAB OPEN SAVE SERIAL MONITOR BOARD & SERIAL PORT SELECTIONS CODE GOES HERE Arduino IDE 22
- 24. setup() function •Called when a sketch starts. •To initialize variables, pin modes, start using libraries, etc. •Will only run once, after each power-up or reset of the Arduino board. loop() function •Loops consecutively. •Code in the loop() section of the sketch is used to actively control the Arduino board. Commenting •Any line that starts with two slashes (//) will not be read by the compiler, so you can write anything you want after it. Basic Coding structure 24
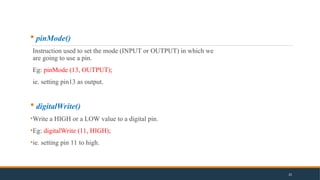
- 25. pinMode() Instruction used to set the mode (INPUT or OUTPUT) in which we are going to use a pin. Eg: pinMode (13, OUTPUT); ie. setting pin13 as output. digitalWrite() •Write a HIGH or a LOW value to a digital pin. •Eg: digitalWrite (11, HIGH); •ie. setting pin 11 to high. 25
- 26. digitalRead() •Reads the value from a specified digital pin, either HIGH or LOW •Eg: int inPin=7; val = digitalRead(inPin); •ie. reads the value from inPin and assigns it to val. delay() •Pauses the program for the amount of time (in milliseconds) specified as parameter. •Eg: delay(1000); •ie. waits for a second (1000 ms = 1 s) 26
- 27. Component List Arduino Uno USB cable LED, RGB LED LDR POT(10k) Resistors Temp sensor LM-35 Motor Driver L293D, DC Motor Connecting wire 27
- 28. LED Blink 28
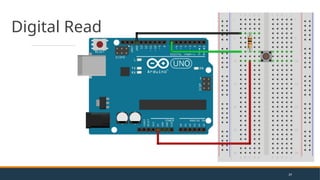
- 29. Digital Read 29
- 30. Analog Read 30
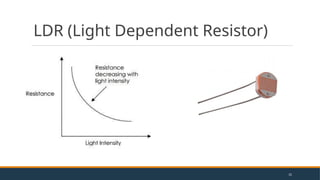
- 31. LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) 31
- 32. LDR - Wiring 32
- 34. 34
- 35. Motor Driver Circuit (L293D) The L293 and L293D devices are quadruple high current half-H drivers. Output Current of 600 mA per channel for L293D) DC Motor Drive – L293D 35
- 37. 37
- 38. DC Motor Control using L293D 38
- 40. “How much more Arduino can do is only left to your imagination” 40
- 41. Thank you 41







