Introduction to Arduino Hardware and Programming
- 2. • Introduction: 1. What is Microcontroller? 2. What is Arduino? 3. Types of Arduino 4. Arduino Uno Board 5. Arduino Shields 6. What is Arduino used for? 7. What can Arduino do? 8. Why Arduino? 9. Input/output 10. Analog/digital 11. Sensor 12. Communication • Programming structure: 1. Data types 2. Statement and operators. 3. Control statements [if, if…else, switch case] 4. Loop statement [while, for, do …while] 5. What is function? 6. What is Arduino Libraries Basic Process Arduino IDE Arduino Language Reference Technical Section [Handling Event Using the in-build millis() function] Questions??? Agenda
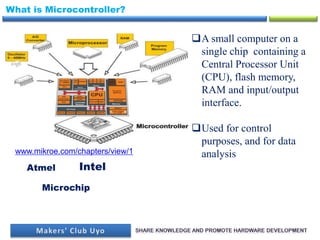
- 4. What is Microcontroller? A small computer on a single chip containing a Central Processor Unit (CPU), flash memory, RAM and input/output interface. Used for control purposes, and for data analysis Microchip Atmel Intel www.mikroe.com/chapters/view/1
- 5. What is Arduino? An open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware (electronic board) and software (IDE). www.arduino.cc A electronic board, with on-board regulated power supply, USB port to communicate with PC, and an Atmel microcontroller chip. Anyone can get the details of its design and modify it or make his own.
- 6. Types of Arduino Arduino Uno : 16MHz Arduino Mega2560 : 16MHz Arduino Ethernet : 16MHz Arduino Nano : 16MHz LilyPad Arduino : 8MHz Arduino Pro Mini : 8 (3.3 V)/16 (5 V) MHz
- 7. Arduino MKR1000 : 48MHz Arduino 101 : 32MHz Arduino Zero : 48MHz Arduino Due : 84MHz Arduino Yún : 16MHz and 400MHz Types of Arduino Arduino Leonardo : 16MHz
- 8. Arduino Pro : 16MHz Arduino Fio : 8MHz Arduino Mega ADK : 16MHz Arduino Esplora : 16MHz Arduino Micro : 16MHz Types of Arduino
- 10. Arduino Shields Boards plugged on top of the Arduino PCB to extend its capacities.
- 11. What is Arduino used for? Physical Computing projects / research Interactive Design Rapid prototyping
- 12. What can Arduino do? Sensors ( sense things) Push buttons, touch pads, tilt switches. Variable resistors (volume knob / sliders) Photo-resistors (light intensity) Thermistors (temperature) Ultrasound (proximity range finder) Actuators ( do things) • Lights, LED’s • Motors • Speakers • Displays (LCD)
- 13. Why Arduino? It is Open Source, both in terms of Hardware and Software. It can communicate with a computer via serial connection over USB. It can be powered from USB or standalone DC power. It can run standalone from a computer (chip is programmable) and it has memory (a small amount). It can work with both Digital and Analog electronic signals. Sensors and Actuators. You can build robots, drone, home automation, IoT application, farm management system with Arduino.
- 14. Input/output Examples: Buttons Switches, Light Sensors, Flex Sensors, Humidity Sensors, Temperature Sensors, Photo-transistor, etc. Examples: LEDs, DC motor, Servo motor, Relay, Stepper motor, Piezo, Buzzer, RGB LED, etc. Input is a signal / information going into the board. Output is any signal exiting the board.
- 15. Analog/digital Digital signal are anything that can take specific levels of values with specific offset between each other. Ex: Square waves Analog signal are anything that take value between its minimum value and maximum value. Ex: Temperature, Sine waves, etc.
- 16. Sensors Devices that transforms the physical quantity in electrical value. The physical quantity could be Light Heat Motion Moisture Pressure Temperature Blood pressure Humidity Speed And others environmental phenomena
- 17. Communication Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART): is a form of serial communication because data is transmitted as sequential bits Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI): is a master-slave model, where there is one master device and multiple slave devices. Inter-integrated circuit (I2C): it connect multiple masters to multiple slaves. Hardware connection for UART SPI multiple-slaves connected to a single master I2C hardware connection
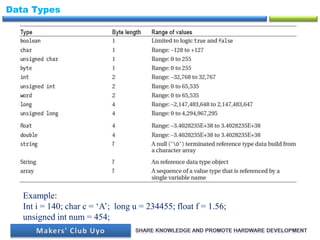
- 19. Data Types Example: Int i = 140; char c = ‘A’; long u = 234455; float f = 1.56; unsigned int num = 454;
- 20. Statement and Operators Statement represents a command, it ends with ‘;’ Example: int i; i=49; Operators are symbols that used to indicate a specific function: • Math operators: [+,-,*,/,%,^] • Logic operators: [==, !=, &&, ||] • Comparison operators: [==, >, <, !=, <=, >=] Syntax: • ‘;’ Semicolon (end statement) • ‘{ }’ curly braces (block of statement) • ‘//’ single line comment, • /*Multi-line comments*/
- 21. Statement and Operators Compound Operators: • ++ (increment) • -- (decrement) • += (compound addition) • -= (compound subtraction) • *= (compound multiplication) • /= (compound division)
- 22. Control Statements If statement: if(condition) { statements; } else if(condition2) { Statements; } Else{ statements; }
- 23. Control Statements Switch statement: switch (x) { case 1: //do something when x equals 1 break; case 2: //do something when x equals 2 break; default: // if nothing else matches, do the default // default is optional }
- 24. Loop Statement Do… while: do { Statements; }while(condition); // the statements are run at least once. While: While(condition) { statements; } for for (int i=0; i <= var; i++){ statements; }
- 25. What is functions? A body of code designed to solve a particular task. void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: }
- 26. What is Arduino Library? Arduino environment can be extended through the use of libraries. Libraries provide extra functionality for use in sketches. Working with hardware Manipulating data. A number of libraries come installed with the IDE. Download Create your own.
- 27. Basic Process Design the circuit: o What are electrical requirements of the sensors or actuators? o Identify inputs (analog inputs) o Identify digital outputs Write the code o Build incrementally • Get the simplest piece to work first • Add complexity and test at each stage • Save and Backup frequently o Use variables, not constants o Comment explicitly
- 28. Arduino IDE Download the Arduino IDE (The program used to write code and uploading it to arduino boards) from: http://arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
- 30. Technical Session Handling Multiple Event Using the Arduino in-build millis() function: Make a 4 LEDs to blink at different rate of 1 sec, 0.5 sec, 0.25 sec and 0.1sec in an infinite loop. Download the demo code from https://github.com/emotexplanet/Arduino_Multiple_Event_with_millis_function
- 31. Questions??? ?
- 32. Thank You

![• Introduction:
1. What is Microcontroller?
2. What is Arduino?
3. Types of Arduino
4. Arduino Uno Board
5. Arduino Shields
6. What is Arduino used for?
7. What can Arduino do?
8. Why Arduino?
9. Input/output
10. Analog/digital
11. Sensor
12. Communication
• Programming structure:
1. Data types
2. Statement and operators.
3. Control statements [if, if…else, switch case]
4. Loop statement [while, for, do …while]
5. What is function?
6. What is Arduino Libraries
Basic Process
Arduino IDE
Arduino Language Reference
Technical Section [Handling Event Using the in-build millis() function]
Questions???
Agenda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoarduinoonslideshare-171208101551/85/Introduction-to-Arduino-Hardware-and-Programming-2-320.jpg)














![Statement and Operators
Statement represents a command, it ends with ‘;’
Example: int i;
i=49;
Operators are symbols that used to indicate a specific
function:
• Math operators: [+,-,*,/,%,^]
• Logic operators: [==, !=, &&, ||]
• Comparison operators: [==, >, <, !=, <=, >=]
Syntax:
• ‘;’ Semicolon (end statement)
• ‘{ }’ curly braces (block of statement)
• ‘//’ single line comment,
• /*Multi-line comments*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoarduinoonslideshare-171208101551/85/Introduction-to-Arduino-Hardware-and-Programming-20-320.jpg)











