Introduction to C Programming
- 2. What is C ? C is a programming language developed at AT & T’s Bell Laboratories of USA in 1972. C language was designed and written by DENNIS RITCHIE.
- 3. Why to use C ? • C is a language which is Simple,Fast and Small. • C is very important language of programming and is a good base for learning C++,C# or JAVA later. • Unix, Linux, Windows are written C. • Gaming is also written in C. • Embedded and Mobile devices use C. • C offers better interaction with Hardware.
- 4. ENGLISH v/s C Engilsh C Alphabets, Digits Alphabets ,Digits ,Special Symbols Words, Numbers Constants , Variables, Keywords Sentences Statements or Instructions Paragraphs Programs
- 5. Alphabets, Digits, Special Symbols Alphabets – A to Z, a to z Digits – 0 to 9 Special Symbols - !,*,%,/….to32
- 7. Constants(Literals)Cannot Change Integers Real or Floats Characters Pointers Array String Structure Unions Enum Primary Secondary
- 8. Rules for Integer Constants I • Must have atleast one digits. II • No Decimal points. III • Either +ve or –ve. IV • If no sign precedes an integer constant, it is assumed to be +ve. V • No commas or blanks are allowed. VI • Valid range -2147483648 to 2147483648 Example: 421 -66 -7856 999 -69 1,200 1 2 3 42 -69 64.99 4
- 9. Rules for Real/Float Constants I • Must have atleast one digits. II • Must contain a decimal point. III • May be +ve or –ve. IV • Default is +ve. V • No commas or blanks are allowed. VI • Valid range -3.4x1038 to 3.4x1038 Examples: +325.34 426.0 -32.76 -48.5792
- 10. Real Constants • In exponential form the real constant is represented in two parts. • Part appearing : Before ‘e’ is called Mantissa After ‘e’ is called Exponent 3.24x10-4 Can be written in C as 3.24e-4
- 11. Rules for Real Constants Expressed in Exponential Form I • The mantissa part and exponential part should be separated by a letter e or E. II • Mantissa part may have a +ve or-ve sign(Default is +ve). III • Exponent must have alteast one digit, which must be +ve or -ve (Default is +ve). IV • Valid Range is -3.4e38 to 3.4e38 Examples: +3.2e-5 4.1e8 -0.2E+3 -3.2e-5
- 12. Rules for Character Constants I • It is a single alphabet, digit or special symbol II • Must be enclosed within a pair of ’ ’ • Both the inverted commas should point to the left. For example, ’A’ is valid whereas ‘A’ is not valid. Examples: ’A’ ’3’ ’m’ ’+’
- 13. C Variables It is an entity whose value can change. It is a name given to a location in memory. Example: x=3 y=4 z=x+y Therefore, z=7
- 14. Types of C Variables Integer Real Character Pointer Array String Structure Union Enum Primary Secondary
- 15. Constants & Variable Types int a float b char c a=3 b=3.0 c=’3’ Would this Work? 3 3.0 ’3’ a b Integer Constant Real Constant Char Constant ? ? c ? •int xyz •int abc123 • int 123abc
- 16. Rules For Building Variable Name I • First character must be alphabet II • Rest can be alphabets, digits or underscores(_) • Example:- hi69 si_int III • Length <=8(Usually) IV • No commas or spaces V • Variable names are case sensitive • Example:- ABC abc Abc aBc AbC si-int si_int All are different
- 17. C Keywords • Keywords are the words whose meaning has already been explained to the C compiler(or in a board sense to the computer). • There are only 32 keywords available in C. auto double int struct break else long switch case enum register typedef char extern return union const float short unsigned continue for signed void default goto sizeof volatile do if static while
- 18. Rules for FORM of C Program a) Each instruction in C program is written as a separate statement. b) The statement in a program must appear in the same order in which we wish them to be executed. c) Blank spaces may be inserted between two words to improve readability of the statement. d) All statement should be in lower case letters. e) Every C statement must end with a semicolon(;). Thus ; acts as a statement terminator.
- 19. The First C Program #include<stdio.h> int main() { float p,r,si; int n; p=1000; r=8.5; n=3; si=p*n*r/100; printf(“S.I.=%f”,si); return 0; } All variable must be declared + - * / are Arithmetic Operators ; is a statement terminator
- 20. Printing Values float p,r,si; int n; p=1000; r=8.5; n=3; si=p*n*r/100; printf(“S.I.=%f”,si); Format String Format Specifier ( ) Parantheses { } Braces [ ] Brackets 1000 3 8.5 255.00 p n r si
- 21. General Form of printf() printf(“format string”,list of variables); Ex. printf(“%f%i%f%f”,p,n,r,si); • %i - integer • %f - float • %c - char Format String can contain Sequence is Important
- 22. What to Execute #include<stdio.h> int main() { float p,r,si; int n; p=1000; r=8.5; n=3; si=p*n*r/100; printf(“S.I.=%f”,si); return 0; } Return type Function For printf() to work Scope Delimiters Success return(0); Optional
- 23. Comments are used in a C program to clarify the purpose of the program or statement in program. Tips About Comments:- Any number of comments anywhere /*formula*/ si=p*n*r/100; /*formula*/ Multi-line comments are OK /* Hi welcome to C programming Calculate Simple Interest*/ Nested comments are NOT OK /*…………………./* …………..*/…………………*/ Comments
- 24. Comments Are Useful /*Calculation of simple interest*/ #include<stdio.h> int main() { float p,r,si; int n; p=1000; r=8.5; n=3; si=p*n*r/100; printf(“S.I.=%f”,si); return 0; } Comment
- 25. What is main()? • main() is a function • A function is container for a set of statements. • All statements that belong to main() are enclosed within a pair of braces{ } . • main() always returns a an integer value,hence there is an int before main(). The integer value that we are returning is 0. 0 indicates success. • Some compliers like Turbo C/C++ even permits us to return nothing from main( ). In this case we use the keyword void. But it is non-standard way of writing int main( ) { statement 1; statement 2; statement 3; }
- 26. scanf( ) To make the program general, i.e. the program itself should ask the user to supply the values through the keyboard during execution. This can be achieved using a function called scanf( ) . printf( ) outputs the value to the screen whereas scanf( ) receives them from the keyboard. General Form:- scanf(“%d”,&ch); • The format specifier %d is used in scanf() statement. • Address of operatoris used before variable name “ch” in scanf() statement as &ch. Format Specifier Ampersand or Address of Operator
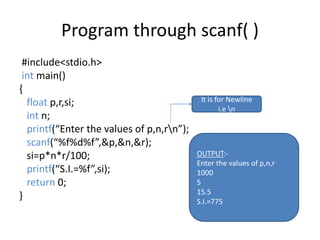
- 27. Program through scanf( ) #include<stdio.h> int main() { float p,r,si; int n; printf(“Enter the values of p,n,rn”); scanf(“%f%d%f”,&p,&n,&r); si=p*n*r/100; printf(“S.I.=%f”,si); return 0; } OUTPUT:- Enter the values of p,n,r 1000 5 15.5 S.I.=775 It is for Newline i.e n
- 28. One More Program /*Calculation of average*/ #include<stdio.h> int main() { int n1,n2,n3,avg; printf(“Enter values of n1,n2,n3n”); scanf(“%d%d%d”,&n1,&n2,&n3); avg=(n1+n2+n3)/3; printf(“Average=%d”,avg); return 0; } OUTPUT:- Enter values of n1, n2, n3 3 5 4 Average=4
- 29. SUMMARY • 3 top reasons for learning C: - Good base for learning C++,C# or JAVA later - Unix, Linux, Windows, Gaming frameworks are written in C -C offers better interaction with H/W. • Constants=Literals->Cannot Change Variables=Identifiers->May Change • Types of variables and constants: 1)Primary 2)Secondary • 3 types of primary: 1)integer 2)Real(float) 3)character • Ranges: 1) 2-byte integers: -32768 to 32768 2) 4-byte integers: -2147483648 to 2147483648 3) floats: -3.4x1038 to 3.4x1038 • In a char constant both quotes must slant to left like ’A’ • Variables has 2 meanings: 1) It is an entity whose value can change 2)It is a name given to a location in memory • Variable names are case-sensitive and must begin with an alphabet
- 30. • Total keyword=32.Example int, char, float • printf( ) is a function that can print multiple constants, variables and expressions • Format specifiers in printf( ),scanf( ): int - %i float - %f char - %c • main( ) is a function that must always return an integer value: 0 – if it meets success non zero – if it encounters failuire • Use/*………………*/for a comment in a program • & is “address of operator ” and must be used before a variable in scanf( )


















![Printing Values
float p,r,si;
int n;
p=1000;
r=8.5;
n=3;
si=p*n*r/100;
printf(“S.I.=%f”,si);
Format
String
Format
Specifier
( ) Parantheses
{ } Braces
[ ] Brackets
1000 3 8.5
255.00
p n r
si](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoc-170912164503/85/Introduction-to-C-Programming-20-320.jpg)