Ad
introduction to cloud computing and basic
- 2. 1. Cloud Computing 2. History 3. Characteristics 4. Model 2
- 3. What is Cloud Computing? • Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network based computing that takes place over the Internet, • basically a step on from Utility Computing • a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Internet infrastructure (called a platform). • Using the Internet for communication and transport provides hardware, software and networking services to clients • Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) • These platforms hide the complexity and details of the underlying infrastructure from users and applications by providing very simple graphical interface or API (Applications Programming Interface). 3
- 4. What is Cloud Computing? • In addition, the platform provides on demand services, that are always on, anywhere, anytime and any place. • Pay for use and as needed, elastic • scale up and down in capacity and functionalities • The hardware and software services are available to • general public, enterprises, corporations and businesses markets 4
- 5. Cloud Summary •Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet based development and services •A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infrastructure: • Remotely hosted: Services or data are hosted on remote infrastructure. • Ubiquitous: Services or data are available from anywhere. • Commodified: The result is a utility computing model similar to traditional that of traditional utilities, like gas and electricity - you pay for what you would want! 5
- 6. •In short we can say that •Cloud computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resources, software and information are provided to computers and other devices on- demand, like the electricity grid. •The cloud computing is a culmination of numerous attempts at large scale computing with seamless access to virtually limitless resources. 6
- 7. • The cloud symbol is typically used to represent the internet. • Cloud computing is now commonly used to describe the delivery of software, infrastructure and storage services over the internet. • Users of the cloud can benefit from other organizations delivering services associated with their data, software and other computing needs on their behalf, without the need to own or run the usual physical hardware (such as servers) and software (such as email) themselves. • Cloud computing is the next stage in the evolution of the internet, it provides the means through which everything from computing power to computing infrastructure, applications and business processes — can be delivered to you as a service wherever and whenever you need them. 7
- 8. Why use cloud computing? 1. Reduce capex costs and improve the predictability of on- going operating expenses. 2. Enable your employees to work from anywhere. 3. Access your data anytime, without risks associated with physical storage since this is managed by cloud providers. 4. Avoid complex disaster recovery planning; let cloud computing vendors take care of this for you. 5. Access the same class of technology as your bigger, more established competitors . 6. Let cloud computing vendors do your server maintenance for you, freeing up your resources for more important tasks 7. Improve your document control, with all your files in one central location, allowing everyone to work from one central copy . 8
- 9. HISTORY AND EVOLUTION • Cloud computing is one the most innovative technology of our time. Following is a brief history of Cloud computing. 9
- 10. • EARLY 1960S:- The computer scientist John McCarthy, come up with concept of timesharing, and enabling Organization to simultaneously use an expensive mainframe. This computing is described as a significant contribution to the development of the Internet, and a pioneer of Cloud computing. • IN 1969:- The idea of an “Intergalactic Computer Network” or “Galactic Network” (a computer networking concept similar to today’s Internet) was introduced by J.C.R. Licklider, who was responsible for enabling the development ofAdvanced ARPANET (Research Projects Agency Network). His vision was for everyone on the globe to be interconnected and being able to access programs and data at any site, from anywhere. • IN 1970:- Using virtualization software like VMware. It become possible to run more than one Operating System simultaneously in an isolated environment. It was possible to run a completely different Computer (virtual machine) inside a different Operating System. • IN 1997:- The first known definition of the term “Cloud Computing” seems to be by Prof. Ramnath Chellappa in Dallas in 1997 – “A computing paradigm where the boundaries of computing will be determined by economic rationale rather than technical limits alone.” 10
- 11. • IN 1999 • The arrival of Salesforce.com in 1999 pioneered the concept of delivering enterprise applications via simple website. The services firm covered the way for both specialist and mainstream software firms to deliver applications over the Internet. • IN 2003:- The first public release of Xen, which creates a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) also known as a hypervisor, a software system that allows the execution of multiple virtual guest operating systems simultaneously on a single machine. • IN 2006:- In 2006, Amazon expanded its cloud services. First was its Elastic Compute cloud (EC2), which allowed people to access computers and run their own applications on them, all on the cloud. Then they brought out Simple Storage Service (S3). This introduced the pay-as-you-go model to both users and the industry as a whole, and it has basically become standard practice now. • IN 2013:-The Worldwide Public Cloud Services Market totalled £78bn, up 18.5 per cent on 2012, with IaaS (infrastructure-as-a-service) the fastest growing market service. • IN 2014:- In 2014, global business spending for infrastructure and services related to the cloud will reach an estimated £103.8bn, up 20% from the amount spent in 2013 (Constellation Research). 11
- 12. How Cloud Computing works? • For understanding How Cloud computing works, first you must understand – What is Cloud computing? and Benefits of Cloud computing, second you should understand the different types of Cloud offering like Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS) or must say “X as a Service, (XaaS)” or “Anything as a Service”. 12
- 13. The first building block of Cloud is infrastructure where The Cloud will be implemented. It is a wrong assumption that environment should be virtualized, but cloud is a way to request resource in on- demand way. If you have a solution to provide resource in on- demand way on bare metal, then it is also a Cloud service. This infrastructure supports different types of Cloud Service like IaaS, PaaS, SaaS etc. To provide these services you need Operating System Service, which will be charged with requested service. Business System Service (BSS) – This is mainly used to validate the request and create the invoice for the consumed services. There are multiple metrics, which are used to create the invoice like Number of users, CPUs, Memory, Storage, I/Os usage hours/month etc. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. • How Cloud computing works in reality • For accessing Cloud services, first step is to register on Cloud service provider portal and create an account. Now login into portal and you can order your services though the Cloud service consumer area. These services had been created by Cloud service provider. These services can be a simple virtual machine (VM), some network component, an Application service or any platform service etc. • Business System Service (BSS) • The Cloud provider will validate your request through Business System Service (BSS), if the validation is OK (like Credit Card detail, Contract etc.), Service provider will provide the requested service through Operating System Service. • To access these all service Cloud service provider will provide you a credentials to access or make any request for service. Monthly invoice get generate for services used by you. 15
- 16. Do you Use the Cloud?
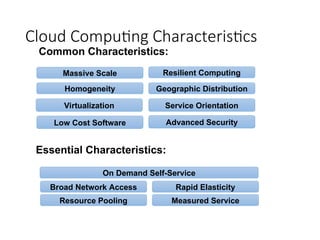
- 17. Cloud Computing Characteristics 17 Common Characteristics: Low Cost Software Virtualization Service Orientation Advanced Security Homogeneity Massive Scale Resilient Computing Geographic Distribution Essential Characteristics: Resource Pooling Broad Network Access Rapid Elasticity Measured Service On Demand Self-Service Adopted from: Effectively and Securely Using the Cloud Computing Paradigm by peter Mell, Tim Grance
- 18. 1. Shared / Pooled Resources: • Resources are drawn from a common pool • Common resources build economies of scale • Common infrastructure runs at high efficiency 2. Broad Network Access: •Open standards and APIs •Almost always IP, HTTP, and REST •Available from anywhere with an internet connection 18
- 19. 3. On-Demand Self-Service: . Completely automated • Users abstracted from the implementation • Near real-time delivery (seconds or minutes) • Services accessed through a self-serve web interface 4. Scalable and Elastic: Resources dynamically-allocated between users • Additional resources dynamically-released when needed • Fully automated 5. Metered by Use: Services are metered, like a utility • Users pay only for services used • Services can be cancelled at any time 19
- 20. Deployment Models Public cloud •Public cloud (off-site and remote) describes cloud computing where resources are dynamically provisioned on an on-demand, self-service basis over the Internet, via web applications/web services, open API, from a third-party provider who bills on a utility computing basis. Private cloud •A private cloud environment is often the first step for a corporation prior to adopting a public cloud initiative. Corporations have discovered the benefits of consolidating shared services on virtualized hardware deployed from a primary datacenter to serve local and remote users. Hybrid cloud •A hybrid cloud environment consists of some portion of computing resources on-site (on premise) and off-site (public cloud). By integrating public cloud services, users can leverage cloud solutions for specific functions that are too costly to maintain on-premise such as virtual server disaster recovery, backups and test/development environments. Community cloud •A community cloud is formed when several organizations with similar requirements share common infrastructure. Costs are spread over fewer users than a public cloud but more than a single tenant.
Editor's Notes
- #16: Take the poll Have you used the cloud For one, two, three, or more of these services
- #17: ScalabilityInfrastructure capacity allows for traffic spikes and minimizes delays. ResiliencyCloud providers have mirrored solutions to minimize downtime in the event of a disaster. This type of resiliency can give businesses the sustainability they need during unanticipated events. Homogeneity: No matter which cloud provider and architecture an organization uses, an open cloud will make it easy for them to work with other groups, even if those other groups choose different providers and architectures. On-demand self-service. A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service’s provider. Broad network access. Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, and PDAs). Resource pooling. Multi-tenant model.. There is a sense of location independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or datacenter). Examples of resources include storage, processing, memory, network bandwidth, and virtual machines. Rapid elasticity. Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases automatically, to quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be purchased in any quantity at any time. Measured Service. Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts).