Introduction to communication systems
- 1. Communication PIC-Microcontroller Lab Course by JAOM Center, Feb. 2013 Introduction to Communication Systems Instructor: Mohsen Sarakbi
- 2. Definitions of Communication The word itself is derived from the Latin verb communicare, which means "to share" or "to make common". Communication is the transfer of information from one place to another. Simply: To connect source & destination.
- 3. Definitions of Communication For a best communication, connection should be: o As efficiently as possible o With as much fidelity/reliability as possible o As securely as possible
- 4. Communication System Communication Systems became essential, and gained an important position in our lives, we can touch its effect in every aspects of life. Examples: Networks, internet, satellites, mobile phone system, GPS, Radar ….. etc).
- 5. Parts of Communication System Communication systems consist of five parts: Source, Transmitter, Channel, Receiver, and Destination. Shannons Model of Communication
- 6. Parts of Communication System Source (input signal): o The source originates a message, such as (human voice, the television picture, data). o If the data is non-electrical (analogue) it must be converted by an input transducer (microphone, camera…) into an electrical waveform (baseband modulation) referred to as the baseband signal or message signal.
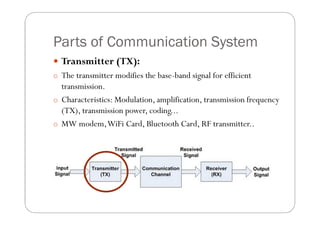
- 7. Parts of Communication System Transmitter (TX): o The transmitter modifies the base-band signal for efficient transmission. o Characteristics: Modulation, amplification, transmission frequency (TX), transmission power, coding... o MW modem,WiFi Card, Bluetooth Card, RF transmitter..
- 8. Parts of Communication System Channel: o The Channel is a medium, such as wire, coaxial cable, a waveguide, an optical fiber or a radio link (air interface), through which the transmitter output is sent. o Channel characteristics, ability for transmission, noise, interference, power needed, fading, multipath...
- 9. Parts of Communication System Receiver (RX): o The receiver reprocesses the signal received from the channel by undoing the signal modifications made at the transmitter and the channel. o Characteristics: Demodulation, receiver frequency (RX), receiving power (threshold), decoding... o MW modem,WiFi Card, Bluetooth Card, RF receiver..
- 10. Parts of Communication System Destination (output signal): The destination is the unit to which the message is communicated. The receiver output is fed to the output transducer (Monitor, Speaker…), which converts the electrical signal to its original form.
- 11. Parts of Communication System Transmitted/Received Signal o Modulated signal or encapsulated signal. This signal is modified by the transmitter/receiver o Examples: Ethernet frame: MW frame:
- 12. Parts of Communication System Transceiver Is a One devices (transmitter/receiver) that do the role of the two devices. o Bidirectional communication. o Higher Cost!
- 13. Modes of Channel Operation Simplex: o Simplex is one direction of communication, it requires only one line of communication. o Simplex channels are not often used in communication systems because it is not possible to send back error or control signals to the transmit end. o A good example would be TV or Radio Half-Duplex: o Two directions of communication (can send & receive) but only one direction is allowed through at a time. o Only one end transmits at a time, the other end receives. In addition, it is possible to send feedbacks. o An advantage is that the single lane is cheaper then the double lane (less connecters). o Example of half-duplex is talk-back radio, and CB Radio (Citizens Band). Full Duplex: o Two ways of communication with data can travel in both directions simultaneously. This is the most common channel operation in communication systems and networking. o It can perform feedbacks. o The most expensive (special devices and more connecters, as in case of fiber optics SFPs) o Example, is mobile phone line.
- 14. Modes of Channel Operation
- 15. Real Life Example, Telecommunication
- 16. Real Life Example, Satellite System
- 18. Our Course Data Transmission RF, Bluetooth, XBEE, Wi-Fi, GSM
- 19. Transmission Technology RF Bluetooth XBEE Wi-Fi GSM o All transmission methods are using TX/RX modules. o GSM, is not P-t-P directly connected channel (over existing mobile network)
- 20. Transmission
- 21. Transmission What is Transmission? Where is the Transmission Network exist (Topology)? What to Transmit (Media)?
- 22. Transmission What is Transmission? Transporting Traffic: Voice, Data, Signaling ... Connecting
- 23. Transmission Where is the Transmission Network exist? Between Network Elements Mobile Network
- 24. Transmission How to Transmit? Radio Link (Microwave) + Rapid installation + No "right of way" required -limited capacity Up to 1,2 GB/s IP capacity - Sensitive to ambient disturbance (rain and multipath fading) - Radio license fees Fiber Optics + High transmission capacity + High transmission quality + Resistant to ambient disturbance +Maximum distances 100 up 150 km between repeaters -Long implementation time
- 25. Transmission How to Transmit? Direct Cables (Coax) +Reliable -Low medium distance (decrease with capacity) Leased Lines High Cost!
- 26. Electromagnetic Spectrum • Transmission should be done using EM waves
- 28. Signal Bandwidth The bandwidth of a composite signal is the difference between the highest and the lowest frequencies contained in that signal.
- 29. History of communication systems Advanced electrical and electronic signals:: 1893: Wireless telegraphy 1896: Radio 1927: Television 1927: First commercial radio-telephone service, U.K.–U.S. 1936: World's first public videophone network 1946: Limited capacity Mobile Telephone Service for automobiles 1962: Commercial telecommunications satellite 1964: Fiber optical telecommunications 1969: Computer networking 1973: First modern-era mobile (cellular) phone 1981: First mobile (cellular) phone network 1982: SMTP email 1983: Internet 1998: Mobile satellite hand-held phones 2003: Skype Internet telephony