Introduction to Computer MBA SEM I - Copy (4).ppt
- 2. Introduction to Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
- 3. Functionalities Of A Computer • Any digital computer carries out five functions in gross terms. – Takes Data as Input – Stores the data/Instructions in its memory and use them when required. – Processes the data and coverts it into useful Information. – Generates the Output. – Control all the above four steps.
- 4. Computer Components Any kind of computers consists of HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE.
- 5. Hardware Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that constitutes a computer system. Computer hardware refers to the physical parts or components of a computer such as the monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, hard drive disk (HDD), system unit (graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard and chips), etc. all of which are physical objects that can be touched.
- 6. Input Devices Input device is any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. Input device Translate data from form that humans understand to one that the computer can work with. Most common are keyboard and mouse
- 7. Example of Input Devices:- 1. Keyboard 2. Mouse (pointing device) 3. Microphone 4. Touch screen 5. Scanner 6. Webcam 7. Touchpads 8. MIDI keyboard 10.Graphics Tablets 11.Cameras 12.Pen Input 13.Video Capture Hardware 14.Microphone 15.Trackballs 16.Barcode reader 17.Digital camera 18.Joystick 19.Gamepad 20.Electronic Whiteboard Note: The most common use keyboard is the QWERTY keyboard. Generally standard Keyboard has 104 keys.
- 8. Central Processing Unit (CPU) A CPU is brain of a computer. It is responsible for all functions and processes. Regarding computing power, the CPU is the most important element of a computer system.
- 9. Central Processing Unit (CPU) The CPU is comprised of three main parts : 1. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Executes all arithmetic and logical operations. Arithmetic calculations like as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical operation like compare numbers, letters, or special characters 2. Control Unit (CU): controls and co-ordinates computer components. – Read the code for the next instruction to be executed. – Increment the program counter so it points to the next instruction. – Read whatever data the instruction requires from cells in memory. – Provide the necessary data to an ALU or register. – If the instruction requires an ALU or specialized hardware to complete, instruct the hardware to perform the requested operation. 3. Registers :Stores the data that is to be executed next, "very fast storage area".
- 10. Primary Memory • RAM: Random Access Memory (RAM) is a memory scheme within the computer system responsible for storing data on a temporary basis, so that it can be promptly accessed by the processor as and when needed. It is volatile in nature, which means that data will be erased once supply to the storage device is turned off. RAM stores data randomly and the processor accesses these data randomly from the RAM storage. RAM is considered "random access" because you can access any memory cell directly if you know the row and column that intersect at that cell. • ROM (Read Only Memory): ROM is a permanent form of storage. ROM stays active regardless of whether power supply to it is turned on or off. ROM devices do not allow data stored on them to be modified.
- 11. Secondary Memory • Stores data and programs permanently: its retained after the power is turned off • Hard drive (HD): A hard disk is part of a unit, often called a "disk drive," "hard drive," or "hard disk drive," that store and provides relatively quick access to large amounts of data on an electromagnetically charged surface or set of surfaces. • Optical Disk: an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disk drive that uses laser light as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from discs, but recent drives are commonly both readers and recorders, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Optical drive is the generic name; drives are usually described as "CD" "DVD", or "Bluray", followed by "drive", "writer", etc. There are three main types of optical media: CD, DVD, and Blu-ray disc. CDs can store up to 700 megabytes (MB) of data and DVDs can store up to 8.4 GB of data. Blu-ray discs, which are the newest type of optical media, can store up to 50 GB of data. This storage capacity is a clear advantage over the floppy disk storage media (a magnetic media), which only has a capacity of 1.44 MB.
- 12. Secondary Memory Flash Disk A storage module made of flash memory chips. A Flash disks have no mechanical platters or access arms, but the term "disk" is used because the data are accessed as if they were on a hard drive. The disk storage structure is emulated.
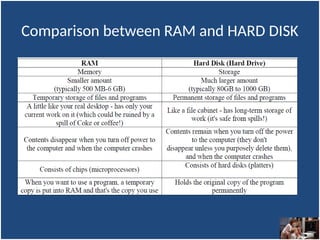
- 13. Comparison between RAM and HARD DISK
- 14. Output Devices An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system (such as a computer) which converts the electronically generated information into human- readable form.
- 15. Software Software is a generic term for organized collections of computer data and instructions, often broken into two major categories: 1. system software that provides the basic non- task-specific functions of the computer, and 2. application software which is used by users to accomplish specific tasks.
- 17. System software System software is responsible for controlling, integrating, and managing the individual hardware components of a computer system so that other software and the users of the system see it as a functional unit without having to be concerned with the low-level details such as transferring data from memory to disk, or rendering text onto a display. Generally, system software consists of an operating system and some fundamental utilities such as disk formatters, file managers, display managers, text editors, user authentication (login) and management tools, and networking and device control software.
- 18. Application software Application software is used to accomplish specific tasks other than just running the computer system. Application software may consist of a single program, such as an image viewer; a small collection of programs (often called a software package) that work closely together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet or text processing system; a larger collection (often called a software suite) of related but independent programs and packages that have a common user interface or shared data format, such as Microsoft Office, which consists of closely integrated word processor, spreadsheet, database, etc.; or a software system, such as a database management system, which is a collection of fundamental programs that may provide some service to a variety of other independent applications.
- 19. Comparison Application Software and System Software System Software Application Software Computer software, or just software is a general term primarily used for digitally stored data such as computer programs and other kinds of information read and written by computers. App comes under computer software though it has a wide scope now. Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Example: 1) Microsoft Windows 2) Linux 3) Unix 4) Mac OSX 5) DOS 1) Opera (Web Browser) 2) Microsoft Word (Word Processing) 3) Microsoft Excel (Spreadsheet software) 4) MySQL (Database Software) 5) Microsoft PowerPoint (Presentation Software) 6) Adobe Photoshop (Graphics Software) Interaction: Generally, users do not interact with system software as it works in the background. Users always interact with application software while doing different activities. Dependency: System software can run independently of the application software. Application software cannot run without the presence of the system software.
- 20. Unit of Measurements Storage measurements: The basic unit used in computer data storage is called a bit (binary digit). Computers use these little bits, which are composed of ones and zeros, to do things and talk to other computers. All your files, for instance, are kept in the computer as binary files and translated into words and pictures by the software (which is also ones and zeros). This two number system, is called a “binary number system” since it has only two numbers in it. The decimal number system in contrast has ten unique digits, zero through nine.