Ad
introduction to database
- 1. Introduction to database Akif Department computer Science University of Peshawar Akifshexi 1
- 2. Contents of this chapter • Data • Information • Introduction to File processing system • Problems in file Processing System • Introduction to Database • Advantages of Database • Applications of Database • Database Management System • Common Database Management System • Components of DBMS Environment • Disadvantages of DBMS 2
- 3. Data 3 • Collection of raw facts and figures. • Data can be collect from different sources but it is not meaning for making decisions. • Data may be: Numbers, Characters, Symbols, pictures, sounds etc.. • Types of data: Numeric data, Alphabetic data and Alphanumeric data.
- 4. Information • Processed data is called information • It is more meaningful than data and is used for making decisions. • Data is used as input for the processing and information is output for this processing. 4 Data Processing Information
- 5. File Processing System • In past many organization stored data in files on tap or disk. • Data was managed using file-processing system. • Each organization has its own set of files. • Record in one file are not related to the record in other file. • No relation between files. 5
- 6. Problems in File Processing System 6
- 7. Data redundancy • In file processing system the same data may be duplicated in several files. • E.g. there are two files “Student” and “Library”. the file Student” contains the Roll No, name and address of all students. • The library contain the Roll No, name etc. • it means the data of one student appear in two files. • This is known as data redundancy. • Same data may appear in many files which is difficult to manage. 7
- 8. Redundancy example Student file Hostel File 8 Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Session:2012-16 RegNo: ab-3455 -------- ------- -------- Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Hostel: szic hostel Room: 5 Block B Hostel dues: 10000 ------- ------- ------- Redundant information
- 9. Inconsistency • Inconsistency means that two files may contain different data of the same student. • For example if address of the student is changed in one file then you will must change the address in other files. • if student information are stored in student file and same student information are stored in hostel file. • If any changed occur in one file then you must update the subsequent file as well. • In File processing system many files contains the data of same student 9
- 10. Inconsistency Example 10 Student file Hostel FileStudent file Hostel File Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Session:2012-16 RegNo: ab-3455 -------- ------- -------- Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Address: Swat Program: BCS Semester: 7th Hoste: szic hostel Room: 5 Block B Hostel dues: 10000 ------- ------- ------- Inconsistent address of the same student
- 11. Data Isolation • In file system data is stored in various files • It become very difficult to retrieve data. • For example student email are stored in student file and fee info are stored in Fee file. • To send an email message to inform a student about his/her fee you need retrieve data from both files which are difficult. 11
- 12. Data Isolation Example 12 Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Email:[email protected] RegNo: ab-3455 -------- Student File Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Hostel dues: 1000 Semester: 20000 -------- -------- Account File Roll No: 123 Name: Ali Books issued: 9 Card Exp: 1-12- 2013 ---- ---- Library File If we want to inform a student by email that clear his/her dues and return library Books • Then we will extract data from student file, account file and Hostel file which is difficult in file processing system.
- 13. Integrity Problems • Integrity means reliability and accuracy of data. • In File Processing System it is difficult to sustain the integrity of the data. • For example: the name of any student contains alphabets if any one by mistaken entered number instead of alphabets. • File Processing system has no integrity checking option. 13
- 14. Integrity Problem 14 Roll No: 123 Name: 12345 Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Email:[email protected] RegNo: ab-3455 -------- Student File Name should not be Composed of numbers File Processing System Does not prevent from This type mistake.
- 15. Security Problems • File Processing System does not provide any security on data. • There is not mechanism in File Processing System for data to be secured from un authorized access. • No authentication facility in file processing system. • Any one can easily access and changed the data. 15
- 16. Security Problem 16 Roll No: 123 Name: 12345 Address: Dir Program: BCS Semester: 7th Email:[email protected] RegNo: ab-3455 -------- Authorized User Can Change The file data Un Authorized User In file processing system no security was defined Student File
- 18. What is Database? • Database can be defined as an organized collection of related data. • The word organized means that data is stored in such a way that the user can: • Store, manipulate and retrieve data easily • The word “related” means that a database is normally created to store the data about a particular topic. • e.g. Student database contain information about the student i.e his name, rollno, address, cellno, class etc. • All data in data base is arranged in tables. Inayatkhan 18
- 19. What is Database? • A database is a repository of data, designed to support efficient data storage, retrieval and maintenance. • Multiple types of databases exist to suit various industry requirements. • A database may be specialized to store: • binary files • Documents • Images • videos • geographic data • etc. Inayatkhan 19
- 20. Database forms • Data can be stored in various forms like: • relational database • If data is stored in a tabular form then it is called a relational database • hierarchical database • When data is organized in a tree structure form • It is called a hierarchical database. • network database • Data stored as graphs representing relationships between objects is referred to as a network database. • In this course, we will focus on relational databases. Inayatkhan 20
- 21. Table • In relational Database data can be store in the form of Tables. • Tables is the fundamental object of the database structure. • The basic purpose of a table is to store data. • A table consists of rows and columns. • A table is a very convenient way to store data. • In the Table you can easily: • Retrieve data • Delete data • Insert data • Update data Inayatkhan 21
- 22. Table Inayatkhan 22 Roll No Name Address Email CellNo 1 Ali khan Peshawar [email protected] 03451122113 2 Adnan Charsada [email protected] m 03331122114 3 Jan Mardan [email protected] 03132255254 STUDENT TABLE
- 23. Rows/Record • Rows are the horizotal part of the table. • It is a collection of related fields. • For example: • In the student table, we have three rows. • Each row contain a record of different student. Inayatkhan 23 Roll No Name Address Email CellNo 1 Ali khan Peshawar [email protected] 03451122113 2 Adnan Charsada adnan@yahoo. com 03331122114 3 Jan Mardan [email protected] 03132255254
- 24. Columns/Field • Columns are the vertical part of the table. • For example: • In the Student table, all values under “Name” field make a column. Inayatkhan 24 Roll No Name Address Email CellNo 1 Ali khan Peshawar [email protected] 03451122113 2 Adnan Charsada adnan@yahoo. com 03331122114 3 Jan Mardan [email protected] 03132255254
- 25. Types of Database Systems • PC databases • Centralized database • Client/server databases • Distributed databases
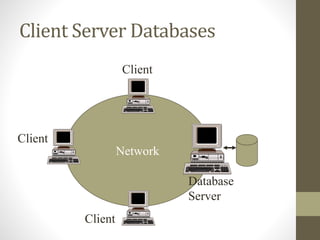
- 29. Distributed Databases computer computer computer Location A Location C Location B Homogeneous Databases
- 30. Distributed Databases Local Network Database Server Client Client Comm Server Remote Comp. Remote Comp. Heterogeneous Or Federated Databases
- 32. Phone Directory • Phone directory is a simple example of a database. • A phone directory stores the phone numbers of different persons . • you can search any phone number from the phone directory easily because all phone numbers are stored in an organized way . Inayatkhan 32
- 33. Library • A library contains thousands of books . • It is very difficult to handle the records of all these books without database . • A database system can be used to store the records of books members of the library ,issuance and recovery of the books etc. • You can use this database to search the required books eaily. • This database can help you a lot for doing research work. Inayatkhan 33
- 34. Accounts • A database is used to control the accounts system of an organization . • The account database keeps the record of all financial transactions of the organization. • You can easily perform different calculations to find the information about your business such as your annual etc. Inayatkhan 34
- 35. College • A college has many students in different classes. • A database may be used to keep the records of the students fee transaction ,examination information and other data of the college. • You can also store the attendance of the student in the database. Inayatkhan 35
- 36. Airplane ticket reservation • Database can be used to store passenger information • A passenger can reserved his/her seat online. Inayatkhan 36
- 37. NADRA • NADRA have its own database • One of the most secure database in the world • It store Pakistan citizen information • Normally Nation Identity Card information Inayatkhan 37
- 38. Other databases • YouTube • Facebook • Yahoo • Google • Hotmail • Amazon • etc. Inayatkhan 38
- 40. Redundancy Control • The data in a database appears only once and is not duplicated. • for example the data of a student in the college database is store in one table we access this table for different purposes . for example : • if we want to store the marks of the student in a table ,only roll NO of the student will be used . the second table will be connected to the student table for accessing the information about the student as follow Inayatkhan 40
- 41. Redundancy Control Inayatkhan 41 Roll NO Name Address Email Phone 1 Naveed Mardan Naveed@yahoo. 03469119099 2 Imran Peshawar [email protected] 03469322089 RollNo Subject Marks 1 Math 90 1 English 60 2 Math 80 2 English 70 Student Table Marksl table In the above figure , the details of the student are stored in the student table. The Marks table store only the rollno of the student . the remaining data is not duplicated . RollNo in the marks table is duplicated for the joining two tables.
- 42. Data Consistency • One benefit of the controlling redundancy is that the data is consistent. • If a data item appears only at once place ,it is easy to maintain it. • You need to update the data , you will update it at only one place. • This change will automatically take effect at all place where this data is used. Inayatkhan 42
- 43. Data Security • Data security is the protection of the database from unauthorized access. The database management system provide several procedures to maintain data security .the security is maintained by allowing access to the database through the use of passwords .not every use of database system should be able to access all the data . • Database managemen system provides different levels of security options for different user . Inayatkhan 43
- 44. Reduced Development Time • A database organize data more efficiently than a file processing system. it is often easier and faster to develop program that use this data. • Many database management system also provide several tools to assist in program development. so it reduces the overall time for developing application. Inayatkhan 44
- 45. Compactness • The data base management system store data with compact and efficient manner. • it required less storage space than the file system. so it saves the storage resoures of th system and memory is not wasted. Inayatkhan 45
- 47. Database Managment System • A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of programs that are used to create and mantian a database. DBMS is a general-Purpose software system that provide the following facilities : • 1 It provide the facility to define the structure of the database. the user can specify the data types, format, and constraints for the data to be stored in the database • 2 it provide the facility to store the data on some storage medium that is controlled by the DBMS • 3 it provide the facilities to insert ,delete , update and retrive specfic data for generation reports etc.
- 48. Common DBMS • MS Access • MySQL • SQLite • SQL Sever • Oracale • DB2 Inayatkhan 48
- 49. Microsoft Access • Familiar look and feel of Windows • Easy to start building simple databases • Can build sophisticated systems • It’s already on your computer • True relational database Inayatkhan 49
- 50. Creating Database in Access Inayatkhan 50
- 51. Inayatkhan 51
- 52. Inayatkhan 52
- 53. Inayatkhan 53
- 54. Inayatkhan 54
- 55. Inayatkhan 55
- 56. Inayatkhan 56
- 58. Inayatkhan 58
- 59. Inayatkhan 59
- 60. Inayatkhan 60
- 61. Inayatkhan 61 Select * from student This Query will display All the record of the Student table.
- 62. Inayatkhan 62 This Query will display The record of Roll No 1.
- 63. • MySQL is a very popular, open source database. • Officially pronounced “my Ess Que Ell” (not my sequel). • Handles very large databases; very fast performance. • Why are we using MySQL? • Free (much cheaper than Oracle!) • Each student can install MySQL locally. • Easy to use Shell for creating tables, querying tables, etc. • Easy to use with Java JDBC Inayatkhan 63
- 64. Database Components DBMS =============== Design tools Table Creation Form Creation Query Creation Report Creation Procedural language compiler (4GL) ============= Run time Form processor Query processor Report Writer Language Run time User Interface Applications Application Programs Database Database contains: User’s Data Metadata Application Metadata
- 66. Components of DBMS Environment • Hardware • PC, workstation, mainframe, a network of computers. • Software • DBMS, operating system, network software (if necessary) and also the application programs. • Data • Used by the organization and a description of this data called the schema. • Procedures • Instructions and rules that should be applied to the design and use of the database and DBMS. • People
- 67. Disadvantages of DBMSs • Complexity • Size • Cost of DBMS • Additional hardware costs • Performance • Higher impact of a failure