Ad
Introduction to R for data science
- 1. for Data Science September 2017 Long Nguyen
- 2. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20172 Why R? • R is the most preferred programming tool for statisticians, data scientists, data analysts and data architects • Easy to develop your own model. • R is freely available under GNU General Public License • R has over 10,000 packages (a lot of available algorithms) from multiple repositories. http://www.burtchworks.com/2017/06/19/2017-sas-r-python-flash-survey-results/
- 3. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20173 R & Rstudio IDE Go to: • https://www.r-project.org/ • https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/
- 4. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20174 Essentials of R Programming • Basic computations • Five basic classes of objects – Character – Numeric (Real Numbers) – Integer (Whole Numbers) – Complex – Logical (True / False) • Data types in R – Vector: a vector contains object of same class – List: a special type of vector which contain elements of different data types – Matrix: A matrix is represented by set of rows and columns. – Data frame: Every column of a data frame acts like a list 2+3 sqrt(121) myvector<- c("Time", 24, "October", TRUE, 3.33) my_list <- list(22, "ab", TRUE, 1 + 2i) my_list[[1]] my_matrix <- matrix(1:6, nrow=3, ncol=2) df <- data.frame(name = c("ash","jane","paul","mark"), score = c(67,56,87,91)) df name score 1 ash NA 2 jane NA 3 paul 87 4 mark 91
- 5. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20175 Essentials of R Programming • Control structures – If (condition){ Do something }else{ Do something else } • Loop – For loop – While loop • Function – function.name <- function(arguments) { computations on the arguments some other code } x <- runif(1, 0, 10) if(x > 3) { y <- 10 } else { y <- 0 } for(i in 1:10) { print(i) } mySquaredFunc<-function(n){ # Compute the square of integer `n` n*n } mySquaredVal(5)
- 6. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20176 Useful R Packages • Install packages: install.packages('readr‘, ‘ggplot2’, ‘dplyr’, ‘caret’) • Load packages: library(package_name) Importing Data •readr •data.table •Sqldf Data Manipulation •dplyr •tidyr •lubridate •stringr Data Visualization •ggplot2 •plotly Modeling •caret •lm, •randomForest, rpart •gbm, xgb Reporting •RMarkdown •Shiny
- 7. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20177 Importing Data • CSV file mydata <- read.csv("mydata.csv") # read csv file library(readr) mydata <- read_csv("mydata.csv") # 10x faster • Tab-delimited text file mydata <- read.table("mydata.txt") # read text file mydata <- read_table("mydata.txt") • Excel file: library(XLConnect) wk <- loadWorkbook("mydata.xls") df <- readWorksheet(wk, sheet="Sheet1") • SAS file library(sas7bdat) mySASData <- read.sas7bdat("example.sas7bdat") • Other files: – Minitab, SPSS(foreign), – MySQL (RMySQL) Col1,Col2,Col3 100,a1,b1 200,a2,b2 300,a3,b3 100 a1 b1 200 a2 b2 300 a3 b3 400 a4 b4
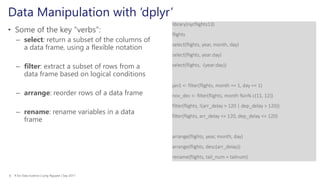
- 8. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20178 Data Manipulation with ‘dplyr’ • Some of the key “verbs”: – select: return a subset of the columns of a data frame, using a flexible notation – filter: extract a subset of rows from a data frame based on logical conditions – arrange: reorder rows of a data frame – rename: rename variables in a data frame library(nycflights13) flights select(flights, year, month, day) select(flights, year:day) select(flights, -(year:day)) jan1 <- filter(flights, month == 1, day == 1) nov_dec <- filter(flights, month %in% c(11, 12)) filter(flights, !(arr_delay > 120 | dep_delay > 120)) filter(flights, arr_delay <= 120, dep_delay <= 120) arrange(flights, year, month, day) arrange(flights, desc(arr_delay)) rename(flights, tail_num = tailnum)
- 9. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20179 Data Manipulation with ‘dplyr’ • Some of the key “verbs”: – mutate: add new variables/columns or transform existing variables – summarize: generate summary statistics of different variables in the data frame – %>%: the “pipe” operator is used to connect multiple verb actions together into a pipeline flights_sml <- select(flights, year:day, ends_with("delay"), distance, air_time ) mutate(flights_sml, gain = arr_delay - dep_delay, speed = distance / air_time * 60 ) by_dest <- group_by(flights, dest) delay <- summarise(by_dest, count = n(), dist = mean(distance, na.rm = TRUE), delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE) ) delay <- filter(delays, count > 20, dest != "HNL") ggplot(data = delay, mapping = aes(x = dist, y = delay)) + geom_point(aes(size = count), alpha = 1/3) + geom_smooth(se = FALSE)
- 10. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201710 library(tidyr) tidy4a <- table4a %>% gather(`1999`, `2000`, key = "year", value = "cases") tidy4b <- table4b %>% gather(`1999`, `2000`, key = "year", value = "population") left_join(tidy4a, tidy4b) spread(table2, key = type, value = count) separate(table3, year, into = c("century", "year"), sep = 2) separate(table3, rate, into = c("cases", "population")) unite(table5, "new", century, year, sep = "") Data Manipulation with ‘tidyr’ • Some of the key “verbs”: – gather: takes multiple columns, and gathers them into key-value pairs – spread: takes two columns (key & value) and spreads in to multiple columns – separate: splits a single column into multiple columns – unite: combines multiple columns into a single column
- 11. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201711 Data Visualization with ‘ggplot2’ • Scatter plot library(ggplot2) ggplot(midwest, aes(x=area, y=poptotal)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method="lm") ggplot(midwest, aes(x=area, y=poptotal)) + geom_point(aes(col=state, size=popdensity)) + geom_smooth(method="loess", se=F) + xlim(c(0, 0.1)) + ylim(c(0, 500000)) + labs(subtitle="Area Vs Population", y="Population", x="Area", title="Scatterplot", caption = "Source: midwest")
- 12. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201712 Data Visualization with ‘ggplot2’ • Correlogram library(ggplot2) library(ggcorrplot) # Correlation matrix data(mtcars) corr <- round(cor(mtcars), 1) # Plot ggcorrplot(corr, hc.order = TRUE, type = "lower", lab = TRUE, lab_size = 3, method="circle", colors = c("tomato2", "white", "springgreen3"), title="Correlogram of mtcars", ggtheme=theme_bw)
- 13. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201713 Data Visualization with ‘ggplot2’ • Histogram on Categorical Variables ggplot(mpg, aes(manufacturer)) + geom_bar(aes(fill=class), width = 0.5) + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=65, vjust=0.6)) + labs(title="Histogram on Categorical Variable", subtitle= "Manufacturer across Vehicle Classes")
- 14. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201714 Data Visualization with ‘ggplot2’ • Density plot ggplot(mpg, aes(cty)) + geom_density(aes(fill=factor(cyl)), alpha=0.8) + labs(title="Density plot", subtitle="City Mileage Grouped by Number of cylinders", caption="Source: mpg", x="City Mileage", fill="# Cylinders") Other plots: • Box plot • Pie chart • Time-series plot
- 15. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201715 Interactive Visualization with ‘plotly’ library(plotly) d <- diamonds[sample(nrow(diamonds), 1000), ] plot_ly(d, x = ~carat, y = ~price, color = ~carat, size = ~carat, text = ~paste("Clarity: ", clarity)) Plotly library makes interactive, publication-quality graphs online. It supports line plots, scatter plots, area charts, bar charts, error bars, box plots, histograms, heat maps, subplots, multiple-axes, and 3D charts.
- 16. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201716 Data Modeling - Linear Regression data(mtcars) mtcars$am = as.factor(mtcars$am) mtcars$cyl = as.factor(mtcars$cyl) mtcars$vs = as.factor(mtcars$vs) mtcars$gear = as.factor(mtcars$gear) #Dropping dependent variable mtcars_a = subset(mtcars, select = -c(mpg)) #Identifying numeric variables numericData <- mtcars_a[sapply(mtcars_a, is.numeric)] #Calculating Correlation descrCor <- cor(numericData) # Checking Variables that are highly correlated highlyCorrelated = findCorrelation(descrCor, cutoff=0.7) highlyCorCol = colnames(numericData)[highlyCorrelated] #Remove highly correlated variables and create a new dataset dat3 = mtcars[, -which(colnames(mtcars) %in% highlyCorCol)] #Build Linear Regression Model fit = lm(mpg ~ ., data=dat3) #Extracting R-squared value summary(fit)$r.squared library(MASS) #Stepwise Selection based on AIC step <- stepAIC(fit, direction="both") summary(step)
- 17. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201717 Data modeling with ‘caret’ • Loan prediction problem • Data standardization and imputing missing values using kNN preProcValues <- preProcess(train, method = c("knnImpute","center","scale")) library('RANN') train_processed <- predict(preProcValues, train) • One-hot encoding for categorical variables dmy <- dummyVars(" ~ .", data = train_processed,fullRank = T) train_transformed <- data.frame(predict(dmy, newdata = train_processed)) • Prepare training and testing set index <- createDataPartition(train_transformed$Loan_Status, p=0.75, list=FALSE) trainSet <- train_transformed[ index,] testSet <- train_transformed[-index,] • Feature selection using rfe predictors<-names(trainSet)[!names(trainSet) %in% outcomeName] Loan_Pred_Profile <- rfe(trainSet[,predictors], trainSet[,outcomeName], rfeControl = control)
- 18. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201718 • Take top 5 variables predictors<-c("Credit_History", "LoanAmount", "Loan_Amount_Term", "ApplicantIncome", "CoapplicantIncome") • Train different models model_gbm<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='gbm') model_rf<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='rf') model_nnet<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='nnet') model_glm<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='glm') • Variable important plot(varImp(object=model_gbm),main="GBM - Variable Importance") plot(varImp(object=model_rf),main="RF - Variable Importance") plot(varImp(object=model_nnet),main="NNET - Variable Importance") plot(varImp(object=model_glm),main="GLM - Variable Importance") • Prediction predictions<-predict.train(object=model_gbm,testSet[,predictors],type="raw") confusionMatrix(predictions,testSet[,outcomeName]) #Confusion Matrix and Statistics #Prediction 0 1 # 0 25 3 # 1 23 102 #Accuracy : 0.8301 Data modeling with ‘caret’
- 19. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201719 Reporting R Markdown files are designed: (i) for communicating to decision makers, (ii) collaborating with other data scientists, and (iii) an environment in which to do data science, where you can capture what you were thinking. Text formatting *italic* or _italic_ **bold** __bold__ `code` superscript^2^ and subscript~2~ Headings # 1st Level Header ## 2nd Level Header ### 3rd Level Header Lists * Bulleted list item 1 * Item 2 * Item 2a * Item 2b 1. Numbered list item 1 2. Item 2. The numbers are incremented automatically in the output. Links and images <http://example.com>[linked phrase](http://example.com)
- 20. R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201720 Thank you!




![R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 20174
Essentials of R Programming
• Basic computations
• Five basic classes of objects
– Character
– Numeric (Real Numbers)
– Integer (Whole Numbers)
– Complex
– Logical (True / False)
• Data types in R
– Vector: a vector contains object of same class
– List: a special type of vector which contain
elements of different data types
– Matrix: A matrix is represented by set of rows
and columns.
– Data frame: Every column of a data frame acts
like a list
2+3
sqrt(121)
myvector<- c("Time", 24, "October", TRUE, 3.33)
my_list <- list(22, "ab", TRUE, 1 + 2i)
my_list[[1]]
my_matrix <- matrix(1:6, nrow=3, ncol=2)
df <- data.frame(name = c("ash","jane","paul","mark"), score =
c(67,56,87,91))
df
name score
1 ash NA
2 jane NA
3 paul 87
4 mark 91](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-4-320.jpg)









![R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201715
Interactive Visualization with ‘plotly’
library(plotly)
d <- diamonds[sample(nrow(diamonds), 1000), ]
plot_ly(d, x = ~carat, y = ~price, color = ~carat,
size = ~carat, text = ~paste("Clarity: ", clarity))
Plotly library makes interactive, publication-quality graphs online. It supports line plots, scatter plots, area
charts, bar charts, error bars, box plots, histograms, heat maps, subplots, multiple-axes, and 3D charts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-15-320.jpg)
![R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201716
Data Modeling - Linear Regression
data(mtcars)
mtcars$am = as.factor(mtcars$am)
mtcars$cyl = as.factor(mtcars$cyl)
mtcars$vs = as.factor(mtcars$vs)
mtcars$gear = as.factor(mtcars$gear)
#Dropping dependent variable
mtcars_a = subset(mtcars, select = -c(mpg))
#Identifying numeric variables
numericData <- mtcars_a[sapply(mtcars_a, is.numeric)]
#Calculating Correlation
descrCor <- cor(numericData)
# Checking Variables that are highly correlated
highlyCorrelated = findCorrelation(descrCor, cutoff=0.7)
highlyCorCol = colnames(numericData)[highlyCorrelated]
#Remove highly correlated variables and create a new dataset
dat3 = mtcars[, -which(colnames(mtcars) %in% highlyCorCol)]
#Build Linear Regression Model
fit = lm(mpg ~ ., data=dat3)
#Extracting R-squared value
summary(fit)$r.squared
library(MASS) #Stepwise Selection based on AIC
step <- stepAIC(fit, direction="both")
summary(step)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-16-320.jpg)
![R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201717
Data modeling with ‘caret’
• Loan prediction problem
• Data standardization and imputing missing values using kNN
preProcValues <- preProcess(train, method = c("knnImpute","center","scale"))
library('RANN')
train_processed <- predict(preProcValues, train)
• One-hot encoding for categorical variables
dmy <- dummyVars(" ~ .", data = train_processed,fullRank = T)
train_transformed <- data.frame(predict(dmy, newdata = train_processed))
• Prepare training and testing set
index <- createDataPartition(train_transformed$Loan_Status, p=0.75, list=FALSE)
trainSet <- train_transformed[ index,]
testSet <- train_transformed[-index,]
• Feature selection using rfe
predictors<-names(trainSet)[!names(trainSet) %in% outcomeName]
Loan_Pred_Profile <- rfe(trainSet[,predictors], trainSet[,outcomeName], rfeControl = control)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-17-320.jpg)
![R for Data Science | Long Nguyen | Sep 201718
• Take top 5 variables
predictors<-c("Credit_History", "LoanAmount", "Loan_Amount_Term", "ApplicantIncome", "CoapplicantIncome")
• Train different models
model_gbm<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='gbm')
model_rf<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='rf')
model_nnet<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='nnet')
model_glm<-train(trainSet[,predictors],trainSet[,outcomeName],method='glm')
• Variable important
plot(varImp(object=model_gbm),main="GBM - Variable Importance")
plot(varImp(object=model_rf),main="RF - Variable Importance")
plot(varImp(object=model_nnet),main="NNET - Variable Importance")
plot(varImp(object=model_glm),main="GLM - Variable Importance")
• Prediction
predictions<-predict.train(object=model_gbm,testSet[,predictors],type="raw")
confusionMatrix(predictions,testSet[,outcomeName])
#Confusion Matrix and Statistics
#Prediction 0 1
# 0 25 3
# 1 23 102
#Accuracy : 0.8301
Data modeling with ‘caret’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-18-320.jpg)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontorfordatasciencelongnguyen-180430055136/85/Introduction-to-R-for-data-science-19-320.jpg)




































































