Introduction to roof computing by Nishant Krishna
4 likes1,380 views
A new computing paradigm for the Internet of Things. ROOF is both a metaphor and acronym. Below the Cloud and Fog
1 of 28
Downloaded 76 times



























Ad
Recommended
IEEE P1931.1, The Roof Computing



IEEE P1931.1, The Roof ComputingSyam Madanapalli IEEE P1931.1 is an upcoming IEEE standard that defines an architectural framework, protocols and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for providing Real-time Onsite Operations Facilitation (ROOF). ROOF computing and networking for the data and the devices include next-hop connectivity for the devices, real-time context building and decision triggers, efficient backhaul connectivity to the cloud, and security & privacy.
Introduction to IoT Architecture



Introduction to IoT ArchitectureEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd IoT is an interconnectivity paradigm that aspires to connect everything in order to give a seamless user experience. Starting with end consumer, there are plenty of use cases for IoT solutions. Before building an end-to-end IoT solution, it is important for you to build an architectural understanding. This introductory module on IoT is aimed to provide you the necessary foundations like architecture to get you started. Added to that, this module also covers IoT workflow setup in some popular cloud platforms like AWS and non-functional considerations like performance and security.
Microsoft Smart Buildings White Paper



Microsoft Smart Buildings White PaperMicrosoft India Buildings are the largest contributor to
global carbon emissions, accounting
for about 40 percent of the world’s
total carbon footprint. Read this white paper to find out how how building owners, operators and occupants can achieve
significant energy and cost savings through the use of smart building solutions.
Comparison of MQTT and DDS as M2M Protocols for the Internet of Things



Comparison of MQTT and DDS as M2M Protocols for the Internet of ThingsReal-Time Innovations (RTI) Multiple protocols have been positioned as “the” application-layer messaging protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication. In fact, these protocols address different aspects of IoT messaging and are complementary more than competitive (other than for mindshare). This presentation compares two of these protocols, MQTT and DDS, and shows how they are designed and optimized for different communication requirements.
IOT gateways.pptx



IOT gateways.pptxPratik Gohel An IoT gateway bridges communication between devices, sensors, systems and the cloud. It offers local processing and storage, and can autonomously control devices based on sensor data. IoT gateways aggregate, process and filter data for secure transmission from the edge to the cloud. They bridge different sensing domain protocols with network domain protocols through protocol conversion and multi-interface connectivity to various wireless standards. Common features of IoT gateways include supporting multiple interfaces, protocol conversion, manageability, and acting as a bridge between sensing and network domains.
Ultimate list of 50 Best IoT platforms of 2019



Ultimate list of 50 Best IoT platforms of 2019ThingsCloud IoT has become a key driver of industrial growth in recent time. Along with that quite a lot of IoT platforms is coming in the market place. This is the comprehensive list of IoT Platforms we have classified IoT Platforms into
1. SaaS IoT Platforms
2. Open-Source IoT Platforms
3. Enterprise IoT Platforms
4. Self-Service IoT Platforms
This is a must read presentation for Developers, Students or anyone who is interested in IoT
Internet Of Things: Convergence



Internet Of Things: ConvergenceDaniel Kolodziej The legacy of industrial based networks is now evolving into the data infrastructure layer of the, 'Internet Of Things. With billions of devices about to be connected to the internet, there are signs of a convergence. A convergence between industrial and consumer, physical and virtual, man and machine. Everyday activities in the real world will have the potential to be augmented, improved and integrated into our digital lives by means of a smooth, flawless user experience. Welcome to the Internet Of Things.
basics of cloud computing



basics of cloud computingProf. Jacques Folon (Ph.D) Cours donné en décembre 2011 dans le cadre du diplôme en sécurité de l'information INFOSAFE (www.infosafe.be)
Internet of Things (IoT)



Internet of Things (IoT)Akanksha Prasad Iot: Introduction ,architecture ,application especially engineering ,software,hardware,protocols and challenges
nodered software code for Iot simulation
Internet of Things(IoT) Applications | IoT Tutorial for Beginners | IoT Train...



Internet of Things(IoT) Applications | IoT Tutorial for Beginners | IoT Train...Edureka! *** IoT Certification Training: https://www.edureka.co/iot-certificat... ***
This Edureka tutorial on "IoT Applications" takes you through the 6 domains which IoT has reinvented, namely,
1. IoT in Everyday LIfe
2. IoT in Healthcare
3. IoT in Smart Cities
4. IoT in Agriculture
5. IoT in Industrial Automation
6. IoT in Disaster Management
Know real-time examples of IoT applications in the most interesting use cases of today's world. Understand how they work and how can IoT be used to its complete potential.
Follow us to never miss an update in the future.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/edureka_learning/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/edurekaIN/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/edurekain
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/edureka
01 IoT Development History and Overview.pptx



01 IoT Development History and Overview.pptxbrian459388 The document provides an overview of the history and development of IoT, including key events and concepts. It discusses the origins of IoT in 1991 with the Trojan Room coffee pot and the development of concepts and standards over time. It also outlines the layers of the IoT architecture including sensing, network, platform and application layers. Finally, it introduces Huawei's 1+2+1 IoT solution architecture and components like NB-IoT, LiteOS, gateways and the IoT platform.
Best Practices for Killer Data Visualization



Best Practices for Killer Data VisualizationQualtrics There’s something special about simple, powerful visualizations that tell a story. In fact, 65% of people are visual learners.
Join Qualtrics and Sasha Pasulka from Tableau as we illuminate the world of data visualization and give you clear takeaways to help you tell a better story with data. Getting executive buy-in or that seat at the table may come down to who can visualize data in a way that excites and enlightens the audience.
Internet of things(IoT)



Internet of things(IoT)NAGUR SHAREEF SHAIK This PPT Covers the Basic Introductory part of IoT.
Gives a breif Explanation of Architechture of IoT
Specify Some of the Good Applications of IoT
IoT - module 4



IoT - module 4Syed Mustafa This document outlines a syllabus for a course on Internet of Things technology. It discusses several topics that will be covered in Module 4 on data and analytics for IoT, including an introduction to data analytics for IoT, structured versus unstructured data, data in motion versus data at rest, and an overview of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Specific techniques that will be examined include machine learning, big data analytics tools, edge streaming analytics, and network analytics. Examples are provided for each topic to illustrate key concepts relating to analyzing large amounts of IoT sensor data.
Internet of Things and its applications



Internet of Things and its applicationsPasquale Puzio A general overview about Internet of Things and its possible applications.
http://www.pasqualepuzio.it
Cloud Computing System models for Distributed and cloud computing & Performan...



Cloud Computing System models for Distributed and cloud computing & Performan...hrmalik20 Advantage of Clouds over Traditional
Distributed Systems,Clouds,Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) Layered Architecture,Performance Metrics and Scalability Analysis,System Efficiency,Performance Challenges in Cloud Computing,What is cloud computing and why is it distinctive?,CLOUD SERVICE DELIVERY MODELS AND THEIR
PERFORMANCE CHALLENGES,Cloud computing security,What does Cloud Computing Security mean,Cloud Security Landscape,Distinctions between Security and Privacy,Energy Efficiency of Cloud Computing,How energy-efficient is cloud computing?
IoT: An introduction



IoT: An introductionJWORKS powered by Ordina This document provides an introduction to IoT including: defining IoT as connecting physical items to the internet via sensors to collect and communicate data; discussing how IoT can benefit businesses through optimizing workflows and lowering costs; and describing common IoT devices and technologies like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Intel Edison, Bluetooth LE, WiFi and distributed computing networks. The next session will focus on setting up the Raspberry Pi with an OS, using it for development, running Java programs, and controlling GPIO pins.
Fog computing



Fog computingMahantesh Hiremath ABSTRACT
Cloud computing promises to significantly change the way we use computers and access and store our personal and business information. With these new computing and communications paradigms arise new data security challenges. Existing data protection mechanisms such as encryption have failed in preventing data theft attacks, especially those perpetrated by an insider to the cloud provider.
For securing user data from such attacks a new paradigm called fog computing can be used. Fog Computing is a paradigm that extends Cloud computing and services to the edge of the network. Similar to Cloud, Fog provides data, compute, storage, and application services to end-users. The motivation of Fog computing lies in a series of real scenarios, such as Smart Grid, smart traffic lights in vehicular networks and software defined network This technique can monitor the user activity to identify the legitimacy and prevent from any unauthorized user access. Here we have discussed this paradigm for preventing misuse of user data and securing information.
CONCLUSION
This proposal of monitoring data access patterns by profiling user behavior to determine if and when a malicious insider illegitimately accesses someone’s documents in a Cloud service. Decoy documents stored in the Cloud alongside the user’s real data also serve as sensors to detect illegitimate access. Once unauthorized data access or exposure is suspected, and later verified, with challenge questions for instance, this inundate the malicious insider with bogus information in order to dilute the user’s real data. Such preventive attacks that rely on disinformation technology could provide unprecedented levels of security in the Cloud and in social networks.
Data Analytics for IoT 



Data Analytics for IoT Muralidhar Somisetty This document discusses analytics for IoT and making sense of data from sensors. It first provides an overview of Innohabit Technologies' vision and products related to contextual intelligence platforms, machine learning analytics, and predictive network health analytics. It then discusses how analytics can help make sense of the endless sea of data from IoT sensors, highlighting key applications of analytics in areas like industrial IoT, smart retail, autonomous vehicles, and more. The benefits of analytics adoption in industrial IoT contexts include optimized asset maintenance, production operations, supply chain management, and more.
JETSON : AI at the EDGE



JETSON : AI at the EDGESkolkovo Robotics Center NVIDIA's Jetson platform provides an AI computing solution for applications at the edge by running deep neural networks on low-power modules like the Jetson TX1. The Jetson TX1 module has powerful GPU processing capable of over 1 teraflop/s while consuming under 10 watts, making it suitable for applications in areas like industrial automation, robotics, smart cities, and more. Developers can use the Jetpack SDK and resources like the Deep Learning Institute to train models on servers and deploy them to Jetson modules for running AI inference in end products at the edge.
Data security in cloud computing



Data security in cloud computingPrince Chandu Cloud computing provides a way for organizations to share distributed resources over a network. However, data security is a major concern in cloud computing since data is stored remotely. The document discusses several techniques used for data security in cloud computing including authentication, encryption, data masking, and data traceability. The latest technologies discussed are a cloud information gateway that can control data transmission and secure logic migration that transfers applications to an internal sandbox for secure execution.
Iot and cloud computing



Iot and cloud computingeteshagarwal1 This presentation is based on the basic of IOT and Cloud computing and their application . This presentation will give a brief idea about this field .
Cloud computing



Cloud computingRupak Chaulagain Cloud Computing
1. Types of Cloud Computing
2. Service model of Clouds
3. Benefits of Cloud Computing
4. Examples of Cloud Computing
5. History of Cloud Computing
6. Disadvantages
Introduction to cloud computing



Introduction to cloud computingTEJVEER SINGH What is cloud computing?
Advantages of cloud computing.
Disadvantages of cloud computing.
Mainly Four Deployment Models.
What is private cloud?
DRAWBACK
Two models for cloud services can be delivered in a private cloud.
Cloud Computing Service Models.
Element Management Subsystem



Element Management Subsystemdevalnaik The document discusses different element management systems (EMS) used to manage network elements. It describes what an EMS is and its key functions like service provisioning, assurance, operations support, and automation. It then summarizes Nortel and Redback Networks' EMS architectures, features, and capabilities. Nortel's EMS focuses on managing VoIP media gateways while Redback's provides fault management, service provisioning, inventory management, and real-time statistics through an intuitive GUI. Both EMS systems are designed to scale with network growth and complexity.
Desktop virtualization customer presentation



Desktop virtualization customer presentationNuno Alves Para maiores detalhes:
http://condemalagueta.wordpress.com/
Twitter --> @ Nuno_Alves
Email --> [email protected]
Site da LCS - www.lcs.com.br
IoT on Azure



IoT on AzureVinoth Rajagopalan Internet of Things on Azure in Global Azure Bootcamp 2016 - Chennai. Session covered with Live Demo on Azure IoThub, stream Analytics, storage table and Power BI.
iot seminar topic 



iot seminar topic Kuldeep Suthar The document discusses the evolution and future of the Internet of Things (IoT). It describes the major eras in the development of the internet from the Internet of Boffins in the 1960s-70s to the modern Internet of Things. It explains how IoT works by connecting devices to collect and share data using embedded sensors. The document outlines the current status and future prospects of IoT, some of its applications, and technological challenges like security, interoperability and power supply. It concludes by stating that the potential of IoT is limited only by imagination.
FIWARE Tech Summit - FogFlow - New GE for IoT Edge Computing



FIWARE Tech Summit - FogFlow - New GE for IoT Edge ComputingFIWARE Presentation by Bin Cheng
Senior Researcher, NEC Laboratories Europe
FIWARE Tech Summit
28-29 November, 2017
Malaga, Spain
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Internet of Things (IoT)



Internet of Things (IoT)Akanksha Prasad Iot: Introduction ,architecture ,application especially engineering ,software,hardware,protocols and challenges
nodered software code for Iot simulation
Internet of Things(IoT) Applications | IoT Tutorial for Beginners | IoT Train...



Internet of Things(IoT) Applications | IoT Tutorial for Beginners | IoT Train...Edureka! *** IoT Certification Training: https://www.edureka.co/iot-certificat... ***
This Edureka tutorial on "IoT Applications" takes you through the 6 domains which IoT has reinvented, namely,
1. IoT in Everyday LIfe
2. IoT in Healthcare
3. IoT in Smart Cities
4. IoT in Agriculture
5. IoT in Industrial Automation
6. IoT in Disaster Management
Know real-time examples of IoT applications in the most interesting use cases of today's world. Understand how they work and how can IoT be used to its complete potential.
Follow us to never miss an update in the future.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/edureka_learning/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/edurekaIN/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/edurekain
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/edureka
01 IoT Development History and Overview.pptx



01 IoT Development History and Overview.pptxbrian459388 The document provides an overview of the history and development of IoT, including key events and concepts. It discusses the origins of IoT in 1991 with the Trojan Room coffee pot and the development of concepts and standards over time. It also outlines the layers of the IoT architecture including sensing, network, platform and application layers. Finally, it introduces Huawei's 1+2+1 IoT solution architecture and components like NB-IoT, LiteOS, gateways and the IoT platform.
Best Practices for Killer Data Visualization



Best Practices for Killer Data VisualizationQualtrics There’s something special about simple, powerful visualizations that tell a story. In fact, 65% of people are visual learners.
Join Qualtrics and Sasha Pasulka from Tableau as we illuminate the world of data visualization and give you clear takeaways to help you tell a better story with data. Getting executive buy-in or that seat at the table may come down to who can visualize data in a way that excites and enlightens the audience.
Internet of things(IoT)



Internet of things(IoT)NAGUR SHAREEF SHAIK This PPT Covers the Basic Introductory part of IoT.
Gives a breif Explanation of Architechture of IoT
Specify Some of the Good Applications of IoT
IoT - module 4



IoT - module 4Syed Mustafa This document outlines a syllabus for a course on Internet of Things technology. It discusses several topics that will be covered in Module 4 on data and analytics for IoT, including an introduction to data analytics for IoT, structured versus unstructured data, data in motion versus data at rest, and an overview of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Specific techniques that will be examined include machine learning, big data analytics tools, edge streaming analytics, and network analytics. Examples are provided for each topic to illustrate key concepts relating to analyzing large amounts of IoT sensor data.
Internet of Things and its applications



Internet of Things and its applicationsPasquale Puzio A general overview about Internet of Things and its possible applications.
http://www.pasqualepuzio.it
Cloud Computing System models for Distributed and cloud computing & Performan...



Cloud Computing System models for Distributed and cloud computing & Performan...hrmalik20 Advantage of Clouds over Traditional
Distributed Systems,Clouds,Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) Layered Architecture,Performance Metrics and Scalability Analysis,System Efficiency,Performance Challenges in Cloud Computing,What is cloud computing and why is it distinctive?,CLOUD SERVICE DELIVERY MODELS AND THEIR
PERFORMANCE CHALLENGES,Cloud computing security,What does Cloud Computing Security mean,Cloud Security Landscape,Distinctions between Security and Privacy,Energy Efficiency of Cloud Computing,How energy-efficient is cloud computing?
IoT: An introduction



IoT: An introductionJWORKS powered by Ordina This document provides an introduction to IoT including: defining IoT as connecting physical items to the internet via sensors to collect and communicate data; discussing how IoT can benefit businesses through optimizing workflows and lowering costs; and describing common IoT devices and technologies like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Intel Edison, Bluetooth LE, WiFi and distributed computing networks. The next session will focus on setting up the Raspberry Pi with an OS, using it for development, running Java programs, and controlling GPIO pins.
Fog computing



Fog computingMahantesh Hiremath ABSTRACT
Cloud computing promises to significantly change the way we use computers and access and store our personal and business information. With these new computing and communications paradigms arise new data security challenges. Existing data protection mechanisms such as encryption have failed in preventing data theft attacks, especially those perpetrated by an insider to the cloud provider.
For securing user data from such attacks a new paradigm called fog computing can be used. Fog Computing is a paradigm that extends Cloud computing and services to the edge of the network. Similar to Cloud, Fog provides data, compute, storage, and application services to end-users. The motivation of Fog computing lies in a series of real scenarios, such as Smart Grid, smart traffic lights in vehicular networks and software defined network This technique can monitor the user activity to identify the legitimacy and prevent from any unauthorized user access. Here we have discussed this paradigm for preventing misuse of user data and securing information.
CONCLUSION
This proposal of monitoring data access patterns by profiling user behavior to determine if and when a malicious insider illegitimately accesses someone’s documents in a Cloud service. Decoy documents stored in the Cloud alongside the user’s real data also serve as sensors to detect illegitimate access. Once unauthorized data access or exposure is suspected, and later verified, with challenge questions for instance, this inundate the malicious insider with bogus information in order to dilute the user’s real data. Such preventive attacks that rely on disinformation technology could provide unprecedented levels of security in the Cloud and in social networks.
Data Analytics for IoT 



Data Analytics for IoT Muralidhar Somisetty This document discusses analytics for IoT and making sense of data from sensors. It first provides an overview of Innohabit Technologies' vision and products related to contextual intelligence platforms, machine learning analytics, and predictive network health analytics. It then discusses how analytics can help make sense of the endless sea of data from IoT sensors, highlighting key applications of analytics in areas like industrial IoT, smart retail, autonomous vehicles, and more. The benefits of analytics adoption in industrial IoT contexts include optimized asset maintenance, production operations, supply chain management, and more.
JETSON : AI at the EDGE



JETSON : AI at the EDGESkolkovo Robotics Center NVIDIA's Jetson platform provides an AI computing solution for applications at the edge by running deep neural networks on low-power modules like the Jetson TX1. The Jetson TX1 module has powerful GPU processing capable of over 1 teraflop/s while consuming under 10 watts, making it suitable for applications in areas like industrial automation, robotics, smart cities, and more. Developers can use the Jetpack SDK and resources like the Deep Learning Institute to train models on servers and deploy them to Jetson modules for running AI inference in end products at the edge.
Data security in cloud computing



Data security in cloud computingPrince Chandu Cloud computing provides a way for organizations to share distributed resources over a network. However, data security is a major concern in cloud computing since data is stored remotely. The document discusses several techniques used for data security in cloud computing including authentication, encryption, data masking, and data traceability. The latest technologies discussed are a cloud information gateway that can control data transmission and secure logic migration that transfers applications to an internal sandbox for secure execution.
Iot and cloud computing



Iot and cloud computingeteshagarwal1 This presentation is based on the basic of IOT and Cloud computing and their application . This presentation will give a brief idea about this field .
Cloud computing



Cloud computingRupak Chaulagain Cloud Computing
1. Types of Cloud Computing
2. Service model of Clouds
3. Benefits of Cloud Computing
4. Examples of Cloud Computing
5. History of Cloud Computing
6. Disadvantages
Introduction to cloud computing



Introduction to cloud computingTEJVEER SINGH What is cloud computing?
Advantages of cloud computing.
Disadvantages of cloud computing.
Mainly Four Deployment Models.
What is private cloud?
DRAWBACK
Two models for cloud services can be delivered in a private cloud.
Cloud Computing Service Models.
Element Management Subsystem



Element Management Subsystemdevalnaik The document discusses different element management systems (EMS) used to manage network elements. It describes what an EMS is and its key functions like service provisioning, assurance, operations support, and automation. It then summarizes Nortel and Redback Networks' EMS architectures, features, and capabilities. Nortel's EMS focuses on managing VoIP media gateways while Redback's provides fault management, service provisioning, inventory management, and real-time statistics through an intuitive GUI. Both EMS systems are designed to scale with network growth and complexity.
Desktop virtualization customer presentation



Desktop virtualization customer presentationNuno Alves Para maiores detalhes:
http://condemalagueta.wordpress.com/
Twitter --> @ Nuno_Alves
Email --> [email protected]
Site da LCS - www.lcs.com.br
IoT on Azure



IoT on AzureVinoth Rajagopalan Internet of Things on Azure in Global Azure Bootcamp 2016 - Chennai. Session covered with Live Demo on Azure IoThub, stream Analytics, storage table and Power BI.
iot seminar topic 



iot seminar topic Kuldeep Suthar The document discusses the evolution and future of the Internet of Things (IoT). It describes the major eras in the development of the internet from the Internet of Boffins in the 1960s-70s to the modern Internet of Things. It explains how IoT works by connecting devices to collect and share data using embedded sensors. The document outlines the current status and future prospects of IoT, some of its applications, and technological challenges like security, interoperability and power supply. It concludes by stating that the potential of IoT is limited only by imagination.
Similar to Introduction to roof computing by Nishant Krishna (20)
FIWARE Tech Summit - FogFlow - New GE for IoT Edge Computing



FIWARE Tech Summit - FogFlow - New GE for IoT Edge ComputingFIWARE Presentation by Bin Cheng
Senior Researcher, NEC Laboratories Europe
FIWARE Tech Summit
28-29 November, 2017
Malaga, Spain
FogFlow: Cloud-Edge Orchestrator in FIWARE



FogFlow: Cloud-Edge Orchestrator in FIWAREBin Cheng fog computing framework with agile programming models. It allows IoT service providers to easily design and implement their services, meanwhile automatically launching dynamic data processing flows over cloud and edges in an optimized manner.
INTEROPERABILITY, FLEXIBILITY AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGN REQUIREMENTS IN THE IoT



INTEROPERABILITY, FLEXIBILITY AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGN REQUIREMENTS IN THE IoTMuhammad Ahad The document discusses several key requirements for Internet of Things (IoT) systems, including:
1. Interoperability and flexibility are important so that IoT devices can easily connect to different systems and components according to user needs. IoT devices should also be reusable in new contexts.
2. Industrial design focuses on user demands, comfort, functionality, and serviceability.
3. IoT devices need to be able to adapt to different situations and combine wireless technologies to improve connectivity and bandwidth. Standardized interfaces are also important for integration.
4. Managing complexity requires transparency rather than opaque "black box" components. Open source components and business models will become more common.
Wicsa2011 cloud tutorial



Wicsa2011 cloud tutorialAnna Liu This document provides an overview of cloud computing concepts and platforms from leading cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure. It discusses cloud characteristics like on-demand access and elastic scaling. It also covers the three main service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and four deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community). The document reviews features of each provider's cloud environment and compares their computing, storage, and database offerings. It provides an example cost calculation for storing and accessing data on different cloud platforms.
What is Your Edge From the Cloud to the Edge, Extending Your Reach



What is Your Edge From the Cloud to the Edge, Extending Your ReachSUSE As companies continue to take advantage of the benefits of cloud – increased flexibility, speed of innovation and quickly responding to business demands, it is no wonder that they want to extend these benefits to the edge. But there are still a lot of questions.
Telecom Clouds crossing borders, Chet Golding, Zefflin Systems



Telecom Clouds crossing borders, Chet Golding, Zefflin SystemsSriram Subramanian This document discusses how OpenStack can help telecom companies transform by enabling cross-border communication and applications. The author argues that with over 6.8 billion cellphone users worldwide, telecom networks must support global connectivity and cloud-based applications and services. OpenStack allows telecoms to build public, private and hybrid clouds that can scale enormously while integrating with other technologies. This represents a new era for telecom where they become cloud companies enabling ubiquitous communication and access to data anywhere in the world.
Digital transformation and AI @Edge



Digital transformation and AI @EdgeInstitute of Contemporary Sciences 1) The document discusses digital transformation and AI at the edge for industrial applications. It describes challenges like processing vast amounts of distributed data in real-time while ensuring security and reliability with limited resources.
2) Edge computing is important for industrial IoT as it allows data processing and AI inferencing close to where data is generated, improving latency, security, and scalability. The document outlines several open source edge computing projects and technologies being developed.
3) Achieving digital transformation requires bridging gaps between IT and operational systems through approaches like collecting telemetry data, predictive maintenance, and building a data-informed culture across the organization. Standards like OPC UA are also important for interoperability.
Control on Remote Sensing Network using Cloud Computing Services



Control on Remote Sensing Network using Cloud Computing ServicesIRJET Journal The document discusses using cloud computing services and ZigBee wireless technology to remotely monitor and control sensing devices over a network. It proposes a system where sensors in a home transmit data to a transmitter via ZigBee, which then sends the data to a receiver and cloud database for remote access and control of devices. The system aims to minimize power consumption and improve communication performance for real-time home automation and monitoring applications.
Walking through the fog (computing) - Keynote talk at Italian Networking Work...



Walking through the fog (computing) - Keynote talk at Italian Networking Work...FBK CREATE-NET "Walking through the fog (computing): trends, use-cases and open issues"
Despite its huge success in many IT-enabled application scenarios, cloud computing has demonstrated some intrinsic limitations that may severely limit its adoption in several contexts where constraints like e.g. preserving data locally, ensuring real-time reactivity or guaranteeing operation continuity despite lack of Internet connectivity (or a combination of them) are mandatory. These distinguishing requirements fostered an increased interest toward computing approaches that inherit the flexibility and adaptability of the cloud paradigm, while acting in proximity of a specific scenario. As a consequence, the emergence of this “proximity computing” approach has exploded into a plethora of architectural solutions (and novel terms) like fog computing, edge computing, dew computing, mist computing but also cloudlets, mobile cloud computing, mobile edge computing (and probably few others I may not be aware of…). The talk will initially make an attempt to introduce some clarity among these “foggy” definitions by proposing a taxonomy whose aim is to help identifying their peculiarities as well as their overlaps. Afterwards, the most important components of a generalized proximity computing architecture will be explained, followed by the description of few research works and use cases investigated within our Center and based on this emerging paradigm. An overview of open issues and interesting research directions will conclude the talk.
Cloud Computing.pptx



Cloud Computing.pptxLakshika Rasanjali Cloud computing provides IT capabilities as a service over the internet. There are different types including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Major cloud providers are Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud. Cloud computing goes through stages of development starting from time-sharing in the 1960s to modern technologies like containers. It offers advantages like reduced costs, scalability, and security but also has weaknesses regarding outages, vendor lock-in, and lack of control. Future trends include edge computing, disaster recovery, multi-cloud solutions, cloud security, Kubernetes, cloud gaming, and serverless computing.
Internet of things chapter2.pdf



Internet of things chapter2.pdfRupesh930637 This document discusses IoT network architecture and design. It explores drivers for new network architectures like scale, security, constrained devices, data, and legacy support. It compares the oneM2M and IoT World Forum IoT architectures, which divide functions into layers like applications, services, and networks. It also presents a simplified IoT architecture with two stacks: the data management and compute stack, and the core functional stack consisting of things, communications networks, and applications.
Cisco Keynote at NetApp Insight - Las Vegas



Cisco Keynote at NetApp Insight - Las VegasTim Stack This document discusses Cisco's vision for powering hybrid cloud through partnerships and innovation. It outlines how technology is enabling new applications and disruption across industries. Cisco is addressing new IT mandates around cloud, IoT, big data and mobility through its Application Centric Infrastructure approach. This allows powering applications at any scale from edge to cloud. Cisco and Intel are collaborating to deliver unified computing solutions to meet these needs through products like UCS servers and the Intercloud fabric, which allows consistent workload portability across hybrid clouds.
Businessday okt 2016 - Xirrus 



Businessday okt 2016 - Xirrus Marketing Team This document summarizes a presentation by Xirrus about their next generation wireless networking solutions. Xirrus is a Wi-Fi solutions provider that offers cloud-managed wireless access points. They highlight key trends driving wireless networking needs, including increased devices and emphasis on user experience. Xirrus' solution provides scalable access points with up to 8 radios, application intelligence to ensure reliability, and flexible cloud-based management. Their EasyPass solution simplifies wireless access. Xirrus presents case studies showing their solution can address varying density needs while reducing equipment requirements compared to traditional Wi-Fi.
AccML, co-located with HiPEAC 2021_Pedro Trancoso presentation



AccML, co-located with HiPEAC 2021_Pedro Trancoso presentationVEDLIoT Project VEDLIoT is a project that aims to develop a framework for the next generation internet of things (IoT) based on IoT devices that collaboratively solve complex deep learning applications across distributed systems. The project will improve the performance and cost ratio of AI processing by distributing hardware across the entire chain from embedded devices to the cloud. It will also increase the safety, health and well-being of users through accelerating AI methods for user-home interaction. The project will develop a cognitive IoT platform, deep learning toolchain, and DL accelerators to enable this vision over its three year timeline starting in November 2020.
OCC-Executive-Summary-20150323



OCC-Executive-Summary-20150323Les Williams This document discusses the benefits and challenges of cloud computing for service providers and network vendors. It outlines that Ethernet has emerged as the primary network connectivity for cloud infrastructure due to its ability to support automation, programmability, interoperability and cost effectiveness. However, challenges remain around security, network provisioning speed, interoperability between on-premise and cloud networks, and lack of bandwidth guarantees. The document recommends that OpenCloud Connect explore initiatives to apply network virtualization, SDN and NFV technologies to carrier Ethernet networks to improve agility, programmability and elastic scaling of cloud services across distributed data centers.
Ad
More from CodeOps Technologies LLP (20)
AWS Serverless Event-driven Architecture - in lastminute.com meetup



AWS Serverless Event-driven Architecture - in lastminute.com meetupCodeOps Technologies LLP This document discusses using event-driven architectures and serverless computing with AWS services. It begins with defining event-driven architectures and how serverless architectures relate to them. It then outlines several AWS services like EventBridge, Step Functions, SQS, SNS, and Lambda that are well-suited for building event-driven applications. The document demonstrates using S3, DynamoDB, API Gateway and other services to build a serverless hotel data ingestion and shopping platform that scales independently for static and dynamic data. It shows how to upload, store, and stream hotel data and expose APIs using serverless AWS services in an event-driven manner.
Understanding azure batch service



Understanding azure batch serviceCodeOps Technologies LLP This document provides an overview of the Azure Batch Service, including its core features, architecture, and monitoring capabilities. It discusses how Azure Batch allows uploading batch jobs to the cloud to be executed and managed, covering concepts like job scheduling, resource management, and process monitoring. The document also demonstrates Azure Batch usage through the Azure portal and Batch Explorer tool and reviews quotas and limits for Batch accounts, pools, jobs, and other resources.
DEVOPS AND MACHINE LEARNING



DEVOPS AND MACHINE LEARNINGCodeOps Technologies LLP In this session, we will take a deep-dive into the DevOps process that comes with Azure Machine Learning service, a cloud service that you can use to track as you build, train, deploy and manage models. We zoom into how the data science process can be made traceable and deploy the model with Azure DevOps to a Kubernetes cluster.
At the end of this session, you will have a good grasp of the technological building blocks of Azure machine learning services and can bring a machine learning project safely into production.
SERVERLESS MIDDLEWARE IN AZURE FUNCTIONS



SERVERLESS MIDDLEWARE IN AZURE FUNCTIONSCodeOps Technologies LLP When it comes to microservice architecture, sometimes all you wanted is to perform cross cutting concerns ( logging, authentication , caching, CORS, Routing, load balancing , exception handling , tracing, resiliency etc..) and also there might be a scenario where you wanted to perform certain manipulations on your request payload before hitting into your actual handler. And this should not be a repetitive code in each of the services , so all you might need is a single place to orchestrate all these concerns and that is where Middleware comes into the picture. In the demo I will be covering how to orchestrate these cross cutting concerns by using Azure functions as a Serverless model.
BUILDING SERVERLESS SOLUTIONS WITH AZURE FUNCTIONS



BUILDING SERVERLESS SOLUTIONS WITH AZURE FUNCTIONSCodeOps Technologies LLP In this talk, we will start with some introduction to Azure Functions, its triggers and bindings. Later we will build a serverless solution to solve a problem statement by using different triggers and bindings of Azure Functions.
Language to be used: C# and IDE - Visual Studio 2019 Community Edition"
APPLYING DEVOPS STRATEGIES ON SCALE USING AZURE DEVOPS SERVICES



APPLYING DEVOPS STRATEGIES ON SCALE USING AZURE DEVOPS SERVICESCodeOps Technologies LLP In this workshop, you will understand how Azure DevOps Services helps you scale DevOps adoption strategies in enterprise. We will explore various feature and services that can enable you to implement various DevOps practices starting from planning, version control, CI & CD , Dependency Management and Test planning.
BUILD, TEST & DEPLOY .NET CORE APPS IN AZURE DEVOPS



BUILD, TEST & DEPLOY .NET CORE APPS IN AZURE DEVOPSCodeOps Technologies LLP In this session, we will understand how to create your first pipeline and build an environment to restore dependencies and how to run tests in Azure DevOps followed by building an image and pushing it to container registry.
CREATE RELIABLE AND LOW-CODE APPLICATION IN SERVERLESS MANNER



CREATE RELIABLE AND LOW-CODE APPLICATION IN SERVERLESS MANNERCodeOps Technologies LLP In this session, we will discuss a use case where we need to quickly develop web and mobile front end applications which are using several different frameworks, hosting options, and complex integrations between systems under the hood. Let’s see how we can leverage serverless technologies (Azure Functions and logic apps) and Low Code/No code platform to achieve the goal. During the session we will go though the code followed by a demonstration.
CREATING REAL TIME DASHBOARD WITH BLAZOR, AZURE FUNCTION COSMOS DB AN AZURE S...



CREATING REAL TIME DASHBOARD WITH BLAZOR, AZURE FUNCTION COSMOS DB AN AZURE S...CodeOps Technologies LLP In this talk people will get to know how we can use change feed feature of Cosmos DB and use azure functions and signal or service to develop a real time dashboard system
WRITE SCALABLE COMMUNICATION APPLICATION WITH POWER OF SERVERLESS



WRITE SCALABLE COMMUNICATION APPLICATION WITH POWER OF SERVERLESSCodeOps Technologies LLP Imagine a scenario, where you can launch a video call or chat with an advisor, agent, or clinician in just one-click. We will explore application patterns that will enable you to write event-driven, resilient and highly scalable applications with Functions that too with power of engaging communication experience at scale. During the session, we will go through the use case along with code walkthrough and demonstration.
Training And Serving ML Model Using Kubeflow by Jayesh Sharma



Training And Serving ML Model Using Kubeflow by Jayesh SharmaCodeOps Technologies LLP We will walk through the exploration, training and serving of a machine learning model by leveraging Kubeflow's main components. We will use Jupyter notebooks on the cluster to train the model and then introduce Kubeflow Pipelines to chain all the steps together, to automate the entire process.
Deploy Microservices To Kubernetes Without Secrets by Reenu Saluja



Deploy Microservices To Kubernetes Without Secrets by Reenu SalujaCodeOps Technologies LLP It is difficult to deploy interloop Kubernetes development in current state. Know these open-source projects that can save us from the burden of various tools and help in deploying microservices on Kubernetes cluster without saving secrets in a file.
Leverage Azure Tech stack for any Kubernetes cluster via Azure Arc by Saiyam ...



Leverage Azure Tech stack for any Kubernetes cluster via Azure Arc by Saiyam ...CodeOps Technologies LLP Learn the concepts of Azure Arc through a demo on how to connect an existing kubernetes cluster to Azure via Azure Arc.
YAML Tips For Kubernetes by Neependra Khare



YAML Tips For Kubernetes by Neependra KhareCodeOps Technologies LLP Learn the basics of YAML like spacing, maps, lists and some tips and tricks that will help you to write and verify YAMLs for Kubernetes.
Must Know Azure Kubernetes Best Practices And Features For Better Resiliency ...



Must Know Azure Kubernetes Best Practices And Features For Better Resiliency ...CodeOps Technologies LLP Running day-1 Ops on your Kubernetes is somewhat easy, but it is quite daunting to manage day two challenges. Learn about AKS best practices for your cloud-native applications so that you can avoid blow up your workloads.
Monitor Azure Kubernetes Cluster With Prometheus by Mamta Jha



Monitor Azure Kubernetes Cluster With Prometheus by Mamta JhaCodeOps Technologies LLP Prometheus is a popular open source metric monitoring solution and Azure Monitor provides a seamless onboarding experience to collect Prometheus metrics. Learn how to configure scraping of Prometheus metrics with Azure Monitor for containers running in AKS cluster.
Jet brains space intro presentation



Jet brains space intro presentationCodeOps Technologies LLP What if you could combine Trello, GitLab, JIRA, Calendar, Slack, Confluence, and more - all together into one solution?
Yes, we are talking about Space - the latest tool from JetBrains famous for its developer productivity-enhancing tools (esp. IntelliJ IDEA).
Here we have explained about JetBrains' space and its functionalities.
Functional Programming in Java 8 - Lambdas and Streams



Functional Programming in Java 8 - Lambdas and StreamsCodeOps Technologies LLP This document provides an overview of functional programming concepts in Java 8 including lambdas and streams. It introduces lambda functions as anonymous functions without a name. Lambdas allow internal iteration over collections using forEach instead of external iteration with for loops. Method references provide a shorthand for lambda functions by "routing" function parameters. Streams in Java 8 enhance the library and allow processing data pipelines in a functional way.
Distributed Tracing: New DevOps Foundation



Distributed Tracing: New DevOps FoundationCodeOps Technologies LLP This talk will serve as a practical introduction to Distributed Tracing. We will see how we can make best use of open source distributed tracing platforms like Hypertrace with Azure and find the root cause of problems and predict issues in our critical business applications beforehand.
"Distributed Tracing: New DevOps Foundation" by Jayesh Ahire 



"Distributed Tracing: New DevOps Foundation" by Jayesh Ahire CodeOps Technologies LLP This talk serves as a practical introduction to Distributed Tracing. We will see how we can make best use of open source distributed tracing platforms like Hypertrace with Azure and find the root cause of problems and predict issues in our critical business applications beforehand.
Presentation part of Open Source Days on 30 Oct - ossdays.konfhub.com
CREATING REAL TIME DASHBOARD WITH BLAZOR, AZURE FUNCTION COSMOS DB AN AZURE S...



CREATING REAL TIME DASHBOARD WITH BLAZOR, AZURE FUNCTION COSMOS DB AN AZURE S...CodeOps Technologies LLP
Leverage Azure Tech stack for any Kubernetes cluster via Azure Arc by Saiyam ...



Leverage Azure Tech stack for any Kubernetes cluster via Azure Arc by Saiyam ...CodeOps Technologies LLP
Must Know Azure Kubernetes Best Practices And Features For Better Resiliency ...



Must Know Azure Kubernetes Best Practices And Features For Better Resiliency ...CodeOps Technologies LLP
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Linux Professional Institute LPIC-1 Exam.pdf



Linux Professional Institute LPIC-1 Exam.pdfRHCSA Guru Introduction to LPIC-1 Exam - overview, exam details, price and job opportunities
Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For Devs



Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For DevsBrian McKeiver May 2nd, 2025 talk at StirTrek 2025 Conference.
#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025



#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, transcript, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD



Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure ADVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD
AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...



AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...SOFTTECHHUB I started my online journey with several hosting services before stumbling upon Ai EngineHost. At first, the idea of paying one fee and getting lifetime access seemed too good to pass up. The platform is built on reliable US-based servers, ensuring your projects run at high speeds and remain safe. Let me take you step by step through its benefits and features as I explain why this hosting solution is a perfect fit for digital entrepreneurs.
How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?



How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?Daniel Lehner 𝙄𝙨 𝘼𝙄 𝙟𝙪𝙨𝙩 𝙝𝙮𝙥𝙚? 𝙊𝙧 𝙞𝙨 𝙞𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙜𝙖𝙢𝙚 𝙘𝙝𝙖𝙣𝙜𝙚𝙧 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙗𝙪𝙨𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙨𝙨 𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙙𝙨?
Everyone’s talking about AI but is anyone really using it to create real value?
Most companies want to leverage AI. Few know 𝗵𝗼𝘄.
✅ What exactly should you ask to find real AI opportunities?
✅ Which AI techniques actually fit your business?
✅ Is your data even ready for AI?
If you’re not sure, you’re not alone. This is a condensed version of the slides I presented at a Linkedin webinar for Tecnovy on 28.04.2025.
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat The MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a framework designed to manage context and interaction within complex systems. This SlideShare presentation will provide a detailed overview of the MCP Model, its applications, and how it plays a crucial role in improving communication and decision-making in distributed systems. We will explore the key concepts behind the protocol, including the importance of context, data management, and how this model enhances system adaptability and responsiveness. Ideal for software developers, system architects, and IT professionals, this presentation will offer valuable insights into how the MCP Model can streamline workflows, improve efficiency, and create more intuitive systems for a wide range of use cases.
tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdf



tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdffjgm517 descaripcion detallada del avance de las tecnologias en mesopotamia, egipto, roma y grecia.
Mobile App Development Company in Saudi Arabia



Mobile App Development Company in Saudi ArabiaSteve Jonas EmizenTech is a globally recognized software development company, proudly serving businesses since 2013. With over 11+ years of industry experience and a team of 200+ skilled professionals, we have successfully delivered 1200+ projects across various sectors. As a leading Mobile App Development Company In Saudi Arabia we offer end-to-end solutions for iOS, Android, and cross-platform applications. Our apps are known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, high performance, and strong security features. We tailor each mobile application to meet the unique needs of different industries, ensuring a seamless user experience. EmizenTech is committed to turning your vision into a powerful digital product that drives growth, innovation, and long-term success in the competitive mobile landscape of Saudi Arabia.
2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptx



2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptxSamuele Fogagnolo Cloudflare Q4 Financial Results Presentation
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungen



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungenpanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-und-verwaltung-von-multiuser-umgebungen/
HCL Nomad Web wird als die nächste Generation des HCL Notes-Clients gefeiert und bietet zahlreiche Vorteile, wie die Beseitigung des Bedarfs an Paketierung, Verteilung und Installation. Nomad Web-Client-Updates werden “automatisch” im Hintergrund installiert, was den administrativen Aufwand im Vergleich zu traditionellen HCL Notes-Clients erheblich reduziert. Allerdings stellt die Fehlerbehebung in Nomad Web im Vergleich zum Notes-Client einzigartige Herausforderungen dar.
Begleiten Sie Christoph und Marc, während sie demonstrieren, wie der Fehlerbehebungsprozess in HCL Nomad Web vereinfacht werden kann, um eine reibungslose und effiziente Benutzererfahrung zu gewährleisten.
In diesem Webinar werden wir effektive Strategien zur Diagnose und Lösung häufiger Probleme in HCL Nomad Web untersuchen, einschließlich
- Zugriff auf die Konsole
- Auffinden und Interpretieren von Protokolldateien
- Zugriff auf den Datenordner im Cache des Browsers (unter Verwendung von OPFS)
- Verständnis der Unterschiede zwischen Einzel- und Mehrbenutzerszenarien
- Nutzung der Client Clocking-Funktion
Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded Developers



Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded DevelopersToradex Toradex brings robust Linux support to SMARC (Smart Mobility Architecture), ensuring high performance and long-term reliability for embedded applications. Here’s how:
• Optimized Torizon OS & Yocto Support – Toradex provides Torizon OS, a Debian-based easy-to-use platform, and Yocto BSPs for customized Linux images on SMARC modules.
• Seamless Integration with i.MX 8M Plus and i.MX 95 – Toradex SMARC solutions leverage NXP’s i.MX 8 M Plus and i.MX 95 SoCs, delivering power efficiency and AI-ready performance.
• Secure and Reliable – With Secure Boot, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and LTS kernel support, Toradex ensures industrial-grade security and longevity.
• Containerized Workflows for AI & IoT – Support for Docker, ROS, and real-time Linux enables scalable AI, ML, and IoT applications.
• Strong Ecosystem & Developer Support – Toradex offers comprehensive documentation, developer tools, and dedicated support, accelerating time-to-market.
With Toradex’s Linux support for SMARC, developers get a scalable, secure, and high-performance solution for industrial, medical, and AI-driven applications.
Do you have a specific project or application in mind where you're considering SMARC? We can help with Free Compatibility Check and help you with quick time-to-market
For more information: https://www.toradex.com/computer-on-modules/smarc-arm-family
Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven Insights



Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven InsightsAndrew Marnell With expertise in data architecture, performance tracking, and revenue forecasting, Andrew Marnell plays a vital role in aligning business strategies with data insights. Andrew Marnell’s ability to lead cross-functional teams ensures businesses achieve sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptx



Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptxshyamraj55 We’re bringing the TDX energy to our community with 2 power-packed sessions:
🛠️ Workshop: MuleSoft for Agentforce
Explore the new version of our hands-on workshop featuring the latest Topic Center and API Catalog updates.
📄 Talk: Power Up Document Processing
Dive into smart automation with MuleSoft IDP, NLP, and Einstein AI for intelligent document workflows.
Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...



Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, presentation slides, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environments



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environmentspanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-and-managing-multiuser-environments/
HCL Nomad Web is heralded as the next generation of the HCL Notes client, offering numerous advantages such as eliminating the need for packaging, distribution, and installation. Nomad Web client upgrades will be installed “automatically” in the background. This significantly reduces the administrative footprint compared to traditional HCL Notes clients. However, troubleshooting issues in Nomad Web present unique challenges compared to the Notes client.
Join Christoph and Marc as they demonstrate how to simplify the troubleshooting process in HCL Nomad Web, ensuring a smoother and more efficient user experience.
In this webinar, we will explore effective strategies for diagnosing and resolving common problems in HCL Nomad Web, including
- Accessing the console
- Locating and interpreting log files
- Accessing the data folder within the browser’s cache (using OPFS)
- Understand the difference between single- and multi-user scenarios
- Utilizing Client Clocking
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in Business



Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in BusinessDr. Tathagat Varma My talk for the Indian School of Business (ISB) Emerging Leaders Program Cohort 9. In this talk, I discussed key issues around adoption of GenAI in business - benefits, opportunities and limitations. I also discussed how my research on Theory of Cognitive Chasms helps address some of these issues
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat
Introduction to roof computing by Nishant Krishna
- 1. IEEE P1931.1 Introduction to ROOF Computing Nishant Krishna Software Architect and Consulting Engineer, Avaya Member, P1931.1 Working Group (Slides reused from Syam Madanapalli, Chair, P1931.1)
- 2. 2 About Nishant Krishna Ø Software Architect, Innovator and Inventor with ~17 years of experience working on Network Management Systems (NMS), Cloud and Virtualization, Software-Defined Network (SDN), API Development and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. Ø 2 patent granted and 5 patents filed/pending with US Patent Office in the areas of Network Management Systems, Cloud, Virtualization and SDN Technologies. Ø I participate actively in User Experience (UX) and Wireframing related activities. Ø My areas of interest include Cloud and Virtualization, SDN, IoT, UX, User Interfaces, Network Security, Cryptography, public speaking and latest tech and gadgets. Ø Nishant has a Master of Science (MS) in Software Engineering degree from BITS, Pilani, along with many technical certifications. https://in.linkedin.com/in/nishantkrishna https://twitter.com/nishantkrishna
- 3. 3 “There are two types of organizations in today’s world, those that have been breached and those that just don’t know it yet.”
- 4. 6/18/174 Standards Title: Standard for an Architectural Framework for Real-time Onsite Operations Facilitation (ROOF) for the Internet of Things • Technical and functional interoperability for IoT systems that operate and co-operate in a secure and independent manner within the context of a local environment such as home, factory, office or airport, etc. • Defines an architectural framework, protocols and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for providing Real-time Onsite Operations Facilitation (ROOF). • ROOF computing and networking for the data and the devices include next-hop connectivity for the devices, real-time context building and decision triggers, efficient backhaul connectivity to the cloud, and security & privacy. • Defines how an end user is able to securely provision, commission and decommission the devices. Working Group Chair: Syam Madanapalli, Dell IEEE P1931.1: ROOF Computing
- 5. 6/18/175 Standards Title: Standard for Harmonization of Internet of Things (IoT) Devices and Systems • Define a metadata bridge to facilitate IoT protocol transport for sensors, actuators, and devices. • The standard addresses issues of security, scalability, and interoperability. This standard can provide significant cost savings and reduce complexity, and offer a data sharing approach leveraging current instrumentation and devices used in industry • The backend of such a globally scalable, secure and interoperable network would be based on the eXtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP), • Key components and needs of a successful Smart City infrastructure will be identified and addressed. This standard does not develop Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for existing IoT or legacy protocols. Working Group Chair: Dr. William Miller, MACT-USA, Dr. Muzzammil Hussain, Samsung (India Focus Group for 1451) IEEE P1451-99: IoT Harmonisation
- 7. History of Computing Paradigms 1960s Server Computing 1990s Distributed Computing 2000s Cloud Computing Server VPN Cloud Headquarters Subsidiaries Remote users Remote users Headquarters Subsidiaries Terminals
- 8. Roof, Humans and the Internet of Things 8 Roof protects people and their possessions.* * "Roof". Wikipedia. N.p., 2016. Web. The Internet of Things, the constrained devices, require an environment wherein they can operate, build trust, collaborate and be protected. Need a Roof for the Internet of Things.
- 9. IoT and the Autonomy 9 An IoT system should have various decision and automation tools that operate and cooperate autonomously within the context of a local environment.
- 10. What is Roof? 10 The ROOF • A new computing paradigm for the Internet of Things • ROOF is both a metaphor and acronym • Below the Cloud and Fog The Primary goal • To provide Autonomous and Realtime Response over a period of time • Context building using edge analytics Others • To support plug and play connectivity for the Things • Efficient connectivity to the Cloud/Service providers • Security by default with contextual analysis • Local storage
- 11. The Roof – for the Better Internet of Things 11 Cloud Hundreds Up to 1000s of kilometers away Fog Tens of thousands Few kilometers away ROOF Millions to billions Few meters/one-hop away Things Billions to trillions ROOF – Realtime Onsite Operations Facilitation for the Internet of Things
- 12. Motivation for the Roof 12 Various access & data protocols Realtime and offline support Constrained nodes, and device & data protection Variety of sensor & data and evolving infrastructure Connectivity Context Security Data Framework for interoperabilit y Realtime computing Computing for security and privacy Flexible backhaul and services
- 13. Roof Computing Data/Service Context Security Connectivity 13 Roof is a computational paradigm for the Internet of Things to provide • Next-hop connectivity for the Things • Realtime context building and actions • Efficient data & service connectivity to the Cloud/service provider • Framework and computing for security & privacy
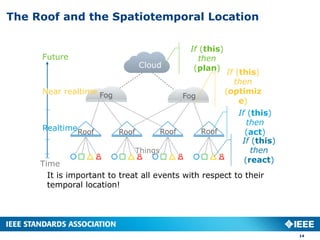
- 14. The Roof and the Spatiotemporal Location 14 It is important to treat all events with respect to their temporal location! If (this) then (react) If (this) then (act) If (this) then (optimiz e) If (this) then (plan) Time Realtime Near realtime Future Things Fog Cloud Roof Fog Roof Roof Roof
- 15. Roof Functional Model 15 IoT Services Device&Network Management Security&Privacy Management Thing Connectivity Cloud Connectivity & Service Management Context Building Local Storage Physical world (Things) Intruders Users Cyber world/Service Providers
- 16. Roof Applications 16 Roof is essential for any IoT application, including: • Connected homes • Connected industries • Connected vehicles • Connected healthcare services • Connected public authorities • Clusters of IoT deployments in the smart cities • Other highly distributed IoT application deployments Clou d Gateway Things Mobile App Internet
- 17. Roof with Blockchain 17 Cloud Blockchain • Establish peer-to-peer trust & reputation • Information sharing and collaboration • Move away on security from passive prevention to cooperative distributed assurance
- 18. Roof vs. Fog vs. Cloud 18 Consideration Computing Model Roof Fog Cloud Distance to Things Few meters Upto few kilometers Upto thousands of kilometers Deployment numbers Millions to billions Tens of thousands Few hundreds Technology complexity Simple Complex Simple Implementation complexity Easy Difficult Easy Content Machine data The Internet fringe Big data Drivers The things - constrained devices Support for mobility and to reduce the latency Big Data storage and analytics Applications All IoT applications Large distributed IoT applications Appcesory, storage and analytics Cost of implementation Low High Medium
- 19. Goals for the Roof 1. Enable the devices under the Roof to collaborate and act in realtime 2. Bridge the physical and cyber world, and allow horizontal integration 3. Confirming to Roof requires security & privacy by design 4. Lower operational and maintenance cost with ease of configuration, commissioning, use and maintenance 5. Easy to build and repeatable – hence increased reliability, resilience and scalability for IoT deployments 6. Allow innovation for new business models and lower the barrier for entry for device manufacturers and service providers 19
- 20. Goal 1: Context Building Context Action Devices Sensor Fusion Cn=2^s – 1 Cn = Max. no. of contexts S= No. of States/services Compute Context Aggregate the data Route the data Data condensing is critical because of the sheer volumes of Data being generated.
- 21. Goal 2: Hormonization Service A Vendor IoT Platform Vendor IoT Hub Service B Vendor IoT Platform Vendor IoT Hub Service A IoT Platform Service B Roof Service C Vendor specific vertical solutions Roof harmonization
- 22. Goal 3: Security by Design Security fusion, combining multiple security touchpoints, helps curb security threats. Device manufacturers and Service providers require support Security by design to fit into the Roof Model. Context Authorization Authentication Network Security Role Based
- 23. Goal 4: Better User Experience Configuration Commissioning and decommissioning Software updates Coherent services and distributed user experience User aware security & privacy
- 24. Goal 5: Reuse & Scalability A model that can be replicated easily Be able to build large scale IoT applications, e.g. a Smart City A model that can be used across multiple applications and verticals Act autonomously in realtime Connect to the Cloud for more value creation Cloud
- 25. Goal 6: Innovation Roof allows evolution of common IoT platforms for rapid application/service delivery Applications can evolve independently & enables an environment for rapid innovation Devices can evolve independently Open IoT Platform Service BService A Service N
- 26. What’s happening right now? ¾ Working group is meeting once every month. On an average close to 50 members join the meeting. The group has representation from industry, standards body, device manufacturers, academia and many more areas, from around the world. ¾ Sub-groups are already formed for various smaller sections of the standard and they are activity working. ¾ Discussions about creating reference and open-source implementation are going on. ¾ Use cases and areas where ROOF can be applicable are actively identified in many of the sectors and are being expanded. 26
- 27. Few parting thoughts… ¾ Interoperability can be achieved through mandating a common set of API, ontology and data semantics. ¾ We need to consider capability of establishing secure ownership of all “things” including ROOF infrastructure. A “Software Roof of Trust” may need to be established. ¾ We must allow ROOF and things to be private/business owned or rented (owner maintains final control) and/or provided by an internet provider. ¾ May need to use blockchain to control both ownership and allowed administrator/user along with a kill switch. ¾ We can’t leave out requirements for safety conformance of things, communications, and processing of so many of the ROOFs and Things that will be (already are) safety critical. ¾ Billions of ”things” out there use variety of protocols and standards. We need to work towards developing protocols and strategies to integrate such vast diversity of communication technologies. 27
- 28. Thank You! 28







