Introduction to SQL
Download as PPT, PDF1 like83 views
This document discusses database systems and SQL. It begins by defining key database concepts like data models, schemas, and instances. It then provides an introduction to SQL, explaining what SQL is used for and some of its main functions. The document goes on to describe database system architecture, languages, and interfaces. It discusses the three-schema architecture and concepts of data independence. It also covers database management system components, utilities, and classifications.
1 of 21
Download to read offline




















Ad
Recommended
SQL



SQLShunya Ram SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. The document provides an introduction to SQL basics including SQL statements to select, insert, update and delete data from database tables. It explains key SQL components like the WHERE clause for filtering records and the ORDER BY clause for sorting query results. Examples are given for each SQL statement and concept discussed.
SQL - DML and DDL Commands



SQL - DML and DDL CommandsShrija Madhu SQL is a standard language for querying and manipulating data in relational databases. It contains five categories of statements: data definition language (DDL) for defining data structure, data manipulation language (DML) for managing data, data control language (DCL) for privileges, transaction control statements for transactions, and session control statements for sessions. Common DDL commands include CREATE, ALTER, and DROP for databases and tables. Common DML commands include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE for querying and modifying data. Joins are used to combine data from two or more tables.
introdution to SQL and SQL functions



introdution to SQL and SQL functionsfarwa waqar This document provides an introduction to SQL (Structured Query Language). It defines SQL as a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. The key points covered include:
- SQL lets you perform queries against a database to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data. It can also be used to create and modify database structures.
- Common SQL commands covered are SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE.
- Additional SQL concepts explained are data types, WHERE clauses, ORDER BY clauses, GROUP BY clauses, and JOIN operations.
- RDBMS systems like MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, etc. use SQL to communicate with the databases they manage.
Sql Tutorials



Sql TutorialsPriyabrat Kar This document provides an overview of SQL (Structured Query Language). It defines SQL as a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. It describes what SQL can do, such as execute queries, retrieve, insert, update and delete data. It also covers important SQL statements (SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT), clauses (WHERE, ORDER BY), operators (LIKE), joins, and functions. In addition, it discusses SQL data types, constraints, creating tables and indexes.
Joins And Its Types



Joins And Its TypesWings Interactive This document discusses different types of joins in SQL including inner joins, self joins, outer joins, and cross joins. An inner join combines rows from two tables based on a common column and returns matched rows. A self join performs an inner join on a single table to match rows with itself. Outer joins return all rows from one or both tables whether or not they have a match. A cross join returns the Cartesian product of all rows in two tables.
SQL Joins.pptx



SQL Joins.pptxAnkit Rai This presentation gives a clear and concise description of joins in sql and several types of sql joins.
These slides also contains the pictorial representation as well as syntax for each type of joins.
PL/SQL TRIGGERS



PL/SQL TRIGGERSLakshman Basnet Triggers are stored programs that are automatically executed in response to events like data manipulation language (DML) statements or database definition language (DDL) statements. They can be used for purposes like enforcing referential integrity, auditing, and event logging. The syntax to create a trigger includes keywords like BEFORE, AFTER, INSTEAD OF to specify when it should be executed in relation to a triggering statement. PL/SQL packages are used to group related logic, types, variables and subprograms. A package has a specification that declares its elements and a body that defines them. Packages provide a way to encapsulate and organize code.
Oracle SQL Basics



Oracle SQL BasicsDhananjay Goel This document provides an overview and introduction to Oracle SQL basics. It covers topics such as installing Oracle software like the database, Java SDK, and SQL Developer tool. It then discusses database concepts like what a database and table are. It also covers database fundamentals including SQL queries, functions, joins, constraints, views and other database objects. The document provides examples and explanations of SQL statements and database components.
SQL Commands 



SQL Commands Sachidananda M H Consists of the explanations of the basics of SQL and commands of SQL.Helpful for II PU NCERT students and also degree studeents to understand some basic things.
Introduction to SQL



Introduction to SQLRam Kedem This document introduces SQL and its basic concepts. It defines SQL as the language used to communicate with relational databases and retrieve data. It discusses that SQL can be pronounced as "S-Q-L" or "sequel" and describes how different vendors have extended SQL with their own commands while maintaining standard SQL. It outlines the different types of SQL statements and gives examples. It concludes by listing some common data types used in columns like integer, money, varchar, and date.
Types Of Join In Sql Server - Join With Example In Sql Server



Types Of Join In Sql Server - Join With Example In Sql Serverprogrammings guru Do you know How many types of Joins in SQL. In this ppt presentation we are discussion about types of joins in sql server eg: INNER JOIN , SELF JOIN ,OUTER JOIN ,Right outer Join,Left outer Join,Full Outer Join,CROSS JOIN .
SQL Queries



SQL QueriesNilt1234 This document provides an introduction to SQL and database systems. It begins with example tables to demonstrate SQL concepts. It then covers the objectives of SQL, including allowing users to create database structures, manipulate data, and perform queries. Various SQL concepts are introduced such as data types, comparison operators, logical operators, and arithmetic operators. The document also discusses SQL statements for schema and catalog definitions, data definition, data manipulation, and other operators. Example SQL queries are provided to illustrate concepts around selecting columns, rows, sorting, aggregation, grouping, and more.
SQL JOINS



SQL JOINSSwapnali Pawar SQL Joins, Simple , equi , non-equi ,self , outer Joins- Primary Key,
Foreign Key, Equi -join, Non - Equi Join, Self Join, Inner Join ,Left OUTER Join, RIGHT OUTER Join,
FULL OUTER Join,
Introduction to-sql



Introduction to-sqlBG Java EE Course Introduction to SQL lecture - DDL and DML, creating and altering DB schema, inserting data and searching into existing content, joining tables
Group By, Having Clause and Order By clause 



Group By, Having Clause and Order By clause Deepam Aggarwal This presentation contains:
Definition of the group by, having and order by clauses
Examples with tables of the group by, having and order by clauses
SQL queries for the group by, having and order by clauses
Sql commands



Sql commandsBalakumaran Arunachalam The document discusses various SQL statements and functions used for managing databases and querying data. It provides the syntax for SQL statements like CREATE TABLE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and functions like COUNT, AVG, MIN, MAX, SUM to operate on data in database tables. It also covers statements for altering tables, joining tables, filtering rows with WHERE and HAVING clauses, removing duplicates with DISTINCT, and ordering results.
Introduction to sql



Introduction to sqlVARSHAKUMARI49 The document provides an introduction to the SQL language. It discusses the three main types of SQL statements: DDL, DML, and DCL. It also covers topics such as data types, constraints, functions, views, and how to create, modify and query tables. SQL is a language used to manage relational database management systems (RDBMS) and allows users to define, manipulate, and control access to data in a RDBMS.
Basic SQL and History



Basic SQL and HistorySomeshwarMoholkar SQL is a language used to communicate with databases and manage data. It allows users to create, update, and retrieve data from databases. The document outlines the history of SQL and its evolution over time. It also describes key SQL concepts like data types, commands, primary keys, database normalization, and techniques for ensuring data integrity.
Mysql



MysqlTSUBHASHRI MySQL is a popular and freely available open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). It stores data in tables and relationships between data are also stored in tables. MySQL uses SQL and works on many operating systems. It has commands for data definition (CREATE, ALTER, DROP), data manipulation (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE), transaction control (COMMIT, ROLLBACK), and data access control (GRANT, REVOKE). Joins allow retrieving data from multiple tables by linking rows together. Common join types are inner joins, outer joins, and self joins.
PL/SQL Introduction and Concepts 



PL/SQL Introduction and Concepts Bharat Kalia PL/SQL is a combination of SQL along with the procedural features of programming languages.
It provides specific syntax for this purpose and supports exactly the same datatypes as SQL.
Sql and Sql commands



Sql and Sql commandsKnowledge Center Computer This document provides an overview of MySQL, a relational database management system that uses SQL. It discusses the different languages used in SQL - Data Definition Language (DDL) for creating and modifying database objects, Data Manipulation Language (DML) for inserting, updating, selecting and deleting data, Data Control Language (DCL) for granting and revoking user privileges, and Transaction Control Language (TCL) for managing transactions. Each section provides examples of key commands used for each language type and their purposes.
Sql operators & functions 3



Sql operators & functions 3Dr. C.V. Suresh Babu This document summarizes various SQL operators and built-in functions. It describes arithmetic, relational, logical, and string operators. It also discusses different types of built-in functions including character, numeric, date, aggregate/group, conversion, and general functions. Examples are provided to demonstrate how each operator and function works.
AGGREGATE FUNCTION.pptx



AGGREGATE FUNCTION.pptxAnusha sivakumar This document discusses SQL aggregation functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MAX, and MIN. It provides examples of using each function to aggregate data from a sample table containing employee names and page counts. The COUNT function returns the number of rows, SUM adds values, AVG calculates the average, MAX returns the largest value, and MIN returns the smallest value. Syntax examples are given for each function applied to the sample data.
SQL Views



SQL Viewsbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers The document discusses various SQL concepts like views, triggers, functions, indexes, joins, and stored procedures. Views are virtual tables created by joining real tables, and can be updated, modified or dropped. Triggers automatically run code when data is inserted, updated or deleted from a table. Functions allow reusable code and improve clarity. Indexes allow faster data retrieval. Joins combine data from different tables. Stored procedures preserve data integrity.
MySQL Basics



MySQL Basicsmysql content Mysql is a popular open source database system. It can be downloaded from the mysql website for free. Mysql allows users to create, manipulate and store data in databases. A database contains tables which store data in a structured format. Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to perform operations like querying and manipulating data within mysql databases. Some common sql queries include select, insert, update and delete.
Chapter 1 introduction to sql server



Chapter 1 introduction to sql serverbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS) and SQL Server. It discusses what a database is and where databases are used. It then explains what a DBMS is and some examples of DBMS software. The document goes on to describe the relational database model including entities, attributes, relationships and keys. It also discusses the entity-relationship model. Finally, it covers SQL statements including DDL, DML, and DCL and provides examples of commands for creating tables, inserting and updating data, and setting privileges.
Sql commands



Sql commandsProf. Dr. K. Adisesha Structured Query Language
SQL Commands:
• The standard SQL commands to interact with relational databases are CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and DROP
Sql subquery



Sql subqueryRaveena Thakur A SQL subquery is a query nested inside another query. Subqueries can be used in the SELECT, WHERE, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE clauses. The subquery executes first and its results are then used by the outer query. There are three types of subqueries: single row, multiple row, and multiple column. Single row subqueries use comparison operators like =, <, > and return one row. Multiple row subqueries use operators like IN, ANY, ALL and return multiple rows. Multiple column subqueries compare more than one column between the outer and inner queries.
Database system



Database systemikjsamuel The document summarizes key concepts related to database systems, including data models, schemas, instances, DBMS architecture, languages, interfaces, environment, and classification of DBMSs. It defines data models as concepts to describe database structure and constraints. The three-schema architecture supports data independence through conceptual, internal, and external schemas. Database languages include DDL for schema definition and DML for data manipulation. DBMS interfaces provide access for different types of users.
Database system



Database systemikjsamuel The document provides an overview of key concepts in database systems, including data models, schemas, instances, DBMS architecture, languages, interfaces, and classification of DBMSs. It describes conceptual, physical, and implementation data models, and how schemas define database structure while instances capture the current stored data. The three-schema DBMS architecture is introduced to support data independence. Database languages include DDL for schema definition and DML for data manipulation. DBMS interfaces provide various ways to interact with databases. Utilities and tools support database management. DBMSs can be classified by data model, users, sites, and purpose.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
SQL Commands 



SQL Commands Sachidananda M H Consists of the explanations of the basics of SQL and commands of SQL.Helpful for II PU NCERT students and also degree studeents to understand some basic things.
Introduction to SQL



Introduction to SQLRam Kedem This document introduces SQL and its basic concepts. It defines SQL as the language used to communicate with relational databases and retrieve data. It discusses that SQL can be pronounced as "S-Q-L" or "sequel" and describes how different vendors have extended SQL with their own commands while maintaining standard SQL. It outlines the different types of SQL statements and gives examples. It concludes by listing some common data types used in columns like integer, money, varchar, and date.
Types Of Join In Sql Server - Join With Example In Sql Server



Types Of Join In Sql Server - Join With Example In Sql Serverprogrammings guru Do you know How many types of Joins in SQL. In this ppt presentation we are discussion about types of joins in sql server eg: INNER JOIN , SELF JOIN ,OUTER JOIN ,Right outer Join,Left outer Join,Full Outer Join,CROSS JOIN .
SQL Queries



SQL QueriesNilt1234 This document provides an introduction to SQL and database systems. It begins with example tables to demonstrate SQL concepts. It then covers the objectives of SQL, including allowing users to create database structures, manipulate data, and perform queries. Various SQL concepts are introduced such as data types, comparison operators, logical operators, and arithmetic operators. The document also discusses SQL statements for schema and catalog definitions, data definition, data manipulation, and other operators. Example SQL queries are provided to illustrate concepts around selecting columns, rows, sorting, aggregation, grouping, and more.
SQL JOINS



SQL JOINSSwapnali Pawar SQL Joins, Simple , equi , non-equi ,self , outer Joins- Primary Key,
Foreign Key, Equi -join, Non - Equi Join, Self Join, Inner Join ,Left OUTER Join, RIGHT OUTER Join,
FULL OUTER Join,
Introduction to-sql



Introduction to-sqlBG Java EE Course Introduction to SQL lecture - DDL and DML, creating and altering DB schema, inserting data and searching into existing content, joining tables
Group By, Having Clause and Order By clause 



Group By, Having Clause and Order By clause Deepam Aggarwal This presentation contains:
Definition of the group by, having and order by clauses
Examples with tables of the group by, having and order by clauses
SQL queries for the group by, having and order by clauses
Sql commands



Sql commandsBalakumaran Arunachalam The document discusses various SQL statements and functions used for managing databases and querying data. It provides the syntax for SQL statements like CREATE TABLE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and functions like COUNT, AVG, MIN, MAX, SUM to operate on data in database tables. It also covers statements for altering tables, joining tables, filtering rows with WHERE and HAVING clauses, removing duplicates with DISTINCT, and ordering results.
Introduction to sql



Introduction to sqlVARSHAKUMARI49 The document provides an introduction to the SQL language. It discusses the three main types of SQL statements: DDL, DML, and DCL. It also covers topics such as data types, constraints, functions, views, and how to create, modify and query tables. SQL is a language used to manage relational database management systems (RDBMS) and allows users to define, manipulate, and control access to data in a RDBMS.
Basic SQL and History



Basic SQL and HistorySomeshwarMoholkar SQL is a language used to communicate with databases and manage data. It allows users to create, update, and retrieve data from databases. The document outlines the history of SQL and its evolution over time. It also describes key SQL concepts like data types, commands, primary keys, database normalization, and techniques for ensuring data integrity.
Mysql



MysqlTSUBHASHRI MySQL is a popular and freely available open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). It stores data in tables and relationships between data are also stored in tables. MySQL uses SQL and works on many operating systems. It has commands for data definition (CREATE, ALTER, DROP), data manipulation (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE), transaction control (COMMIT, ROLLBACK), and data access control (GRANT, REVOKE). Joins allow retrieving data from multiple tables by linking rows together. Common join types are inner joins, outer joins, and self joins.
PL/SQL Introduction and Concepts 



PL/SQL Introduction and Concepts Bharat Kalia PL/SQL is a combination of SQL along with the procedural features of programming languages.
It provides specific syntax for this purpose and supports exactly the same datatypes as SQL.
Sql and Sql commands



Sql and Sql commandsKnowledge Center Computer This document provides an overview of MySQL, a relational database management system that uses SQL. It discusses the different languages used in SQL - Data Definition Language (DDL) for creating and modifying database objects, Data Manipulation Language (DML) for inserting, updating, selecting and deleting data, Data Control Language (DCL) for granting and revoking user privileges, and Transaction Control Language (TCL) for managing transactions. Each section provides examples of key commands used for each language type and their purposes.
Sql operators & functions 3



Sql operators & functions 3Dr. C.V. Suresh Babu This document summarizes various SQL operators and built-in functions. It describes arithmetic, relational, logical, and string operators. It also discusses different types of built-in functions including character, numeric, date, aggregate/group, conversion, and general functions. Examples are provided to demonstrate how each operator and function works.
AGGREGATE FUNCTION.pptx



AGGREGATE FUNCTION.pptxAnusha sivakumar This document discusses SQL aggregation functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MAX, and MIN. It provides examples of using each function to aggregate data from a sample table containing employee names and page counts. The COUNT function returns the number of rows, SUM adds values, AVG calculates the average, MAX returns the largest value, and MIN returns the smallest value. Syntax examples are given for each function applied to the sample data.
SQL Views



SQL Viewsbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers The document discusses various SQL concepts like views, triggers, functions, indexes, joins, and stored procedures. Views are virtual tables created by joining real tables, and can be updated, modified or dropped. Triggers automatically run code when data is inserted, updated or deleted from a table. Functions allow reusable code and improve clarity. Indexes allow faster data retrieval. Joins combine data from different tables. Stored procedures preserve data integrity.
MySQL Basics



MySQL Basicsmysql content Mysql is a popular open source database system. It can be downloaded from the mysql website for free. Mysql allows users to create, manipulate and store data in databases. A database contains tables which store data in a structured format. Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to perform operations like querying and manipulating data within mysql databases. Some common sql queries include select, insert, update and delete.
Chapter 1 introduction to sql server



Chapter 1 introduction to sql serverbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS) and SQL Server. It discusses what a database is and where databases are used. It then explains what a DBMS is and some examples of DBMS software. The document goes on to describe the relational database model including entities, attributes, relationships and keys. It also discusses the entity-relationship model. Finally, it covers SQL statements including DDL, DML, and DCL and provides examples of commands for creating tables, inserting and updating data, and setting privileges.
Sql commands



Sql commandsProf. Dr. K. Adisesha Structured Query Language
SQL Commands:
• The standard SQL commands to interact with relational databases are CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and DROP
Sql subquery



Sql subqueryRaveena Thakur A SQL subquery is a query nested inside another query. Subqueries can be used in the SELECT, WHERE, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE clauses. The subquery executes first and its results are then used by the outer query. There are three types of subqueries: single row, multiple row, and multiple column. Single row subqueries use comparison operators like =, <, > and return one row. Multiple row subqueries use operators like IN, ANY, ALL and return multiple rows. Multiple column subqueries compare more than one column between the outer and inner queries.
Similar to Introduction to SQL (20)
Database system



Database systemikjsamuel The document summarizes key concepts related to database systems, including data models, schemas, instances, DBMS architecture, languages, interfaces, environment, and classification of DBMSs. It defines data models as concepts to describe database structure and constraints. The three-schema architecture supports data independence through conceptual, internal, and external schemas. Database languages include DDL for schema definition and DML for data manipulation. DBMS interfaces provide access for different types of users.
Database system



Database systemikjsamuel The document provides an overview of key concepts in database systems, including data models, schemas, instances, DBMS architecture, languages, interfaces, and classification of DBMSs. It describes conceptual, physical, and implementation data models, and how schemas define database structure while instances capture the current stored data. The three-schema DBMS architecture is introduced to support data independence. Database languages include DDL for schema definition and DML for data manipulation. DBMS interfaces provide various ways to interact with databases. Utilities and tools support database management. DBMSs can be classified by data model, users, sites, and purpose.
Database system-DBMS



Database system-DBMSikjsamuel The document discusses database system concepts and architecture. It covers topics such as data models, schemas and instances; DBMS architecture and data independence; database languages and interfaces; the database system environment; and classification of database management systems. Specifically, it describes the three-schema architecture used to support data independence, different types of database languages, interfaces for users and programmers, components of a DBMS, and utilities used in database systems.
Database system



Database systemikjsamuel The document discusses database system concepts and architecture. It covers topics such as data models, schemas and instances; DBMS architecture and data independence; database languages and interfaces; the database system environment; and classification of database management systems. The key points are data models define a database's structure and constraints, schemas describe a database, and instances are the actual stored data. DBMSs use a three-schema architecture to provide data independence and multiple views of data.
Chapter02



Chapter02sasa_eldoby This document discusses database system concepts and architecture. It covers data models and their categories, including conceptual, physical and implementation models. It describes the history of data models such as network, hierarchical, relational, object-oriented and object-relational models. It also discusses schemas, instances, states, the three-schema architecture, data independence, DBMS languages, interfaces, utilities, centralized and client-server architectures, and classifications of DBMSs.
Database Management system, database architecture unikkkkkkkkkkkkkkk



Database Management system, database architecture unikkkkkkkkkkkkkkksandhyakiran10 The document provides an overview of database system concepts and architecture. It discusses the key concepts of database schema and instance, the three schema architecture consisting of the internal, conceptual and external schemas, and the goals of data independence. It also describes database languages like DDL and DML used at different levels, common DBMS interfaces, components and utilities. Finally, it covers centralized and client-server architectures and classifications of DBMS based on data model, number of users/sites, software, cost and purpose.
INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE



INTRODUCTION TO DATABASEMuhammad Bilal Tariq This document discusses database concepts and architecture. It covers data models including conceptual, physical and implementation models. It discusses the history of relational, network and hierarchical data models. It also covers the three-level database architecture including the external, conceptual and internal schemas. The architecture supports logical and physical data independence. The document discusses database languages like DDL and DML and different database interfaces and systems.
Db architecture



Db architectureMr Patrick NIYISHAKA The document defines key concepts related to database schemas including:
- A schema defines the structure and data in a database including entities, relationships, and constraints.
- A schema diagram provides a visual representation of the database schema.
- Database schemas have three levels: external, conceptual, and internal. The conceptual schema hides physical storage details.
Fundamentals of database system - Database System Concepts and Architecture



Fundamentals of database system - Database System Concepts and ArchitectureMustafa Kamel Mohammadi In this chapter you will learn
DBMS evolution
Data model
Three schema architecture
DBMS language
DBMS interfaces
DBMS components
Classification of DBMS
Lec02_Database System Concepts and Architecture_part1.pptx



Lec02_Database System Concepts and Architecture_part1.pptxAhmedSalama337512 Lec02_Database System Concepts and Architecture_part1.pptx
DATABASE FUNCTIONS



DATABASE FUNCTIONSghazi103 This document discusses database management systems (DBMS) and their functions. It begins by describing the functions of a DBMS, including data dictionary management, data storage management, data transformation and presentation, security management, and more. It then discusses how managing database systems has shifted the focus from programming to managing organizational resources. The document ends by explaining the three-schema architecture of databases, which includes external, conceptual, and physical schemas that separate the user application from the physical database.
Database concepts and Archeticture Ch2 with in class Activities



Database concepts and Archeticture Ch2 with in class ActivitiesZainab Almugbel This is the slides of chapter 2 of the book Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant Navathe, "Fundamentals of Database Systems" 6th Edition, 2010
I did not include the activities in the slides. I printed them out in separate papers. Then, I asked students: who liked to participate in activity 1 (the interview) in the class. I selected 2 students for the first activity (one was the interviewer and another was the guest). I did the same for the other activities.
Database Design Slide 1



Database Design Slide 1ahfiki This document provides an overview of key database concepts, including:
- Types of databases and database management systems (DBMS) functions
- Data models like relational, hierarchical, and object-oriented
- The three-schema architecture with conceptual, internal, and external schemas
- Languages used to define and manipulate database structures and data
- Centralized and client-server database system architectures
2 database system concepts and architecture



2 database system concepts and architectureKumar This document provides an overview of database system concepts and architecture. It discusses data models, schemas, instances, and states. It also describes the three-schema architecture, data independence, DBMS languages and interfaces, database system utilities and tools, and centralized and client-server architectures. Key classification of DBMSs are also covered.
Dbms module i



Dbms module iSANTOSH RATH This document provides an overview of database management systems and related concepts. It discusses the three schema architecture including external, conceptual, and internal schemas. It also covers data models, data definition and manipulation languages, database administrators, keys such as primary keys and foreign keys, and integrity constraints including referential integrity, check constraints, and NOT NULL constraints. The goal of these concepts is to provide a structured and standardized way to define, manipulate, and manage database systems and data.
2nd chapter dbms.pptx



2nd chapter dbms.pptxkavitha623544 The document discusses various data models, database system architectures, database languages, and components of database management systems. It provides details on hierarchical, network, and relational data models including their advantages and disadvantages. It also describes physical centralized and distributed database architectures. Key database languages covered are DDL, DML, DCL, and transaction control language. DBMS interfaces and utilities are also summarized.
Ad
More from Dr. Thippeswamy S. (19)
Bacterial Examination of Water of different sources.ppt



Bacterial Examination of Water of different sources.pptDr. Thippeswamy S. Bacterial Examination of water is useful for:
(1) Detection of faecal pollution in potential water supply (very sensitive test).
(2) Assessment of water treatment plant performance.
(3) Confirmation of hygienic safety of final water entering supply.
(4) Surveillance of water quality throughout distribution.
(5) Indicator bacteria: give Quantitative results therefore used as basis for these standards:
(1) Raw Water Quality
(2) Treated Water Quality
(3) Distribution System Water Quality
(4) Bathing Water Quality
(5) Quality of Water for shellfish growing
(6) Quality of water for re-use in irrigation.
Seven QC Tools New approach.pptx



Seven QC Tools New approach.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Developed to organize verbal data diagrammatically.
Basic 7 tools effective for data analysis, process control, and quality improvement (numerical data)
Used together increases TQM effectiveness.
Soil Erosion.pptx



Soil Erosion.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Soil erosion is the movement and transport of soil by various natural processes and is responsible for the loss of an average of 30 tons per hectare of agricultural soils per year. The soil that is most affected by erosion is the topsoil layer. Soil erosion is accelerated by a sloped landscape, the removal of vegetation to create land space, soil tillage for agriculture, and drought. Wind and water play a monumental role in soil erosion.
Database Normalization.pptx



Database Normalization.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Third normal form (3NF) requires that there are no functional dependencies of non-key attributes on something other than a candidate key.
A table is in 3NF if all of the non-primary key attributes are mutually independent
That is, there are NO transitive dependencies
cloudapplications.pptx



cloudapplications.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. The document discusses using cloud computing for protein structure prediction and gene expression data analysis. Protein structure prediction is a computationally intensive task that helps design new drugs, but determining protein structures manually is difficult. Cloud computing enables scientists to submit protein structure prediction tasks to a cloud service without worrying about the complex predictions. It also discusses using gene expression profiling and classification algorithms like eXtended Classifier System (XCS) on cloud infrastructure to analyze large cancer and medical diagnosis datasets.
12575474.ppt



12575474.pptDr. Thippeswamy S. This document provides an overview of data intensive computing and some of the challenges it presents. It discusses how data intensive applications deal with large datasets ranging from terabytes to petabytes in size across various domains. Some of the key challenges in data intensive computing include developing scalable algorithms, metadata management technologies, and distributed file systems that can handle petabytes of data efficiently. Frameworks like MapReduce and cloud computing technologies help address these challenges by providing computation and storage at large scales.
djypllh5r1gjbaekxgwv-signature-cc6692615bbc55079760b9b0c6636bc58ec509cd0446cb...



djypllh5r1gjbaekxgwv-signature-cc6692615bbc55079760b9b0c6636bc58ec509cd0446cb...Dr. Thippeswamy S. This document discusses task-based distributed computing and the Aneka framework. It defines tasks as distinct units of code that can be executed remotely. Aneka uses a task programming model where tasks implement an interface and are wrapped in AnekaTask objects. Developers create application classes to control task submission and monitoring. Aneka supports various task types including embarrassingly parallel, parameter sweep, and workflows. It integrates with cloud infrastructures and provides APIs for developing distributed applications.
deploymentmodelsofcloudcomputing-230211123637-08174981.pptx



deploymentmodelsofcloudcomputing-230211123637-08174981.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. The document discusses the different deployment models of cloud computing:
- Private cloud is owned and operated by a single organization for its own use and is not shared. It provides security and customization but is less scalable and more costly than public clouds.
- Public cloud is owned by third parties and available to the general public over the internet in a pay-as-you-go model. It has minimal investment but is less secure and customizable.
- Hybrid cloud combines private and public clouds to meet specific needs, providing flexibility and enabling organizations to use the best solution for each workload.
- Community cloud is for specific communities and offers security and cost savings while maintaining private infrastructure control.
- Multi-cloud uses multiple
DBMS.pptx



DBMS.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. This document defines key database concepts like databases, database management systems (DBMS), and database applications. It describes the purpose of using a DBMS over file systems, which had drawbacks like data redundancy, integrity issues, and concurrent access problems. A DBMS provides solutions to these issues through its data definition language, data manipulation language, storage management, query processing, transaction processing, and concurrency control functions.
Normalization DBMS.ppt



Normalization DBMS.pptDr. Thippeswamy S. The purpose of normailization
Data redundancy and Update Anomalies
Functional Dependencies
The Process of Normalization
First Normal Form (1NF)
Second Normal Form (2NF)
Third Normal Form (3NF)
Normalization Alg.ppt



Normalization Alg.pptDr. Thippeswamy S. The document describes the steps of the normalization algorithm to normalize a relational database schema into BCNF. The key steps are:
1. Identify functional dependencies to determine candidate keys.
2. Normalize to 1NF by removing non-atomic values.
3. Normalize to 2NF by removing non-prime attributes that are dependent on part but not all of a candidate key.
4. Normalize to 3NF by removing non-prime attributes dependent on non-candidate keys.
5. Normalize to BCNF by removing relations where determinants are not candidate keys. The process may require repeatedly splitting relations.
introduction to matlab.pptx



introduction to matlab.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Matlab is basically a high level language which has many specialized toolboxes for making things easier for us
How high?
Conceptual Data Modeling



Conceptual Data ModelingDr. Thippeswamy S. Considering Company as a Mini world Problem we need to design the Database.
Company Database consists of:
Company Info
Employee Info
Project Info
The Formulated Requirements are:
The company is organized into departments. Each department has a unique name, a unique number, and a particular employee who manages the department. We keep track of the start date when that employee began managing the department. A department may have several location
A department controls a number of projects, each of which has a unique name, a unique number, and a single location
We store each employee’s name, Social Security number, address, salary, sex (gender), and birth date. An employee is assigned to one department, but may work on several projects, which are not necessarily controlled by the same department. We keep track of the current number of hours per week that an employee works on each project. We also keep track of the direct supervisor of each employee (who is another employee).
We want to keep track of the dependents of each employee for insurance purposes
Chp-1.pptx



Chp-1.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Define Database Management System (DBMS) and database
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of DBMS to file based system.
Analyses structure models in Database
Mod-2.pptx



Mod-2.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. Module-2, Arithmetic and Logic information
Unsigned numbers are defined as data in which all the bits are used to represent data.Operand can be between 00 and FFH(0to255decimal)for 8-bitdata.
Between 0000 and FFFFH(0 to 65535decimal)for 16-bitdata.
The x86 uses internal adder circuitry to perform the subtraction command.
Hence,the 2'scomplement method isused by the microprocessor to perform the subtraction. The steps involved are–
Take the 2'scomplement of the subtrahend(source operand)
Add it to the minuend(destination operand)
Invert the carry.
module 5.1.pptx



module 5.1.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. This document provides an overview of the ARM instruction set, including data processing instructions, branch instructions, load-store instructions, and program status register instructions. It describes the basic types of ARM instructions and how they manipulate data in registers and memory. Examples are provided to illustrate key instruction types like data movement, arithmetic, logical operations, and loading constants using the barrel shifter. The summary focuses on the major topics and instruction categories covered in the document.
module 5.pptx



module 5.pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. This document provides an overview of the ARM instruction set, including data processing instructions, branch instructions, load-store instructions, and program status register instructions. It describes the basic types of ARM instructions and how they manipulate data in registers and memory. Examples are provided to illustrate key instruction types like data movement, arithmetic, logical operations, and loading constants using the barrel shifter. The summary focuses on the major topics and instruction types covered in the document.
Module 2 (1).pptx



Module 2 (1).pptxDr. Thippeswamy S. This document provides an overview of arithmetic and logic instructions in x86 assembly language. It discusses unsigned and signed addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It also covers logic instructions like AND, OR, XOR, shift, compare, and conversions between binary-coded decimal and ASCII. Finally, it explains interrupts and rotation instructions in x86, specifically covering ROR, ROL, RCR, and RCL.
23. Journal of Mycology and Plant pathology.pdf



23. Journal of Mycology and Plant pathology.pdfDr. Thippeswamy S. This document contains summaries of multiple studies related to fungi and plant pathogens. The first study characterized 11 isolates of Trichoderma virens using morphological and molecular techniques, finding a good correlation between the identification methods. The second studied the antimicrobial activity and phytochemical composition of Albiziaamara leaf extracts against bacteria and fungi. The chloroform extract showed the highest activity. A third study evaluated the compatibility of the fungus Nomuraea rileyi with various pesticides, finding several insecticides and fungicides that were most compatible.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)



AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)Vəhid Gəruslu Invited tutorial at the Istanbul Software Testing Conference (ISTC) 2025 https://iststc.com/
ADVXAI IN MALWARE ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK: BALANCING EXPLAINABILITY WITH SECURITY



ADVXAI IN MALWARE ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK: BALANCING EXPLAINABILITY WITH SECURITYijscai With the increased use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in malware analysis there is also an increased need to
understand the decisions models make when identifying malicious artifacts. Explainable AI (XAI) becomes
the answer to interpreting the decision-making process that AI malware analysis models use to determine
malicious benign samples to gain trust that in a production environment, the system is able to catch
malware. With any cyber innovation brings a new set of challenges and literature soon came out about XAI
as a new attack vector. Adversarial XAI (AdvXAI) is a relatively new concept but with AI applications in
many sectors, it is crucial to quickly respond to the attack surface that it creates. This paper seeks to
conceptualize a theoretical framework focused on addressing AdvXAI in malware analysis in an effort to
balance explainability with security. Following this framework, designing a machine with an AI malware
detection and analysis model will ensure that it can effectively analyze malware, explain how it came to its
decision, and be built securely to avoid adversarial attacks and manipulations. The framework focuses on
choosing malware datasets to train the model, choosing the AI model, choosing an XAI technique,
implementing AdvXAI defensive measures, and continually evaluating the model. This framework will
significantly contribute to automated malware detection and XAI efforts allowing for secure systems that
are resilient to adversarial attacks.
some basics electrical and electronics knowledge



some basics electrical and electronics knowledgenguyentrungdo88 This chapter discribe about common electrical divices such as passive component, the internaltional system unit and international system prefixes.
The Gaussian Process Modeling Module in UQLab



The Gaussian Process Modeling Module in UQLabJournal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering We introduce the Gaussian process (GP) modeling module developed within the UQLab software framework. The novel design of the GP-module aims at providing seamless integration of GP modeling into any uncertainty quantification workflow, as well as a standalone surrogate modeling tool. We first briefly present the key mathematical tools on the basis of GP modeling (a.k.a. Kriging), as well as the associated theoretical and computational framework. We then provide an extensive overview of the available features of the software and demonstrate its flexibility and user-friendliness. Finally, we showcase the usage and the performance of the software on several applications borrowed from different fields of engineering. These include a basic surrogate of a well-known analytical benchmark function; a hierarchical Kriging example applied to wind turbine aero-servo-elastic simulations and a more complex geotechnical example that requires a non-stationary, user-defined correlation function. The GP-module, like the rest of the scientific code that is shipped with UQLab, is open source (BSD license).
ELectronics Boards & Product Testing_Shiju.pdf



ELectronics Boards & Product Testing_Shiju.pdfShiju Jacob This presentation provides a high level insight about DFT analysis and test coverage calculation, finalizing test strategy, and types of tests at different levels of the product.
Introduction to FLUID MECHANICS & KINEMATICS



Introduction to FLUID MECHANICS & KINEMATICSnarayanaswamygdas Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. Originally applied to water (hydromechanics), it found applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical, and biomedical engineering, as well as geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology.
It can be divided into fluid statics, the study of various fluids at rest, and fluid dynamics.
Fluid statics, also known as hydrostatics, is the study of fluids at rest, specifically when there's no relative motion between fluid particles. It focuses on the conditions under which fluids are in stable equilibrium and doesn't involve fluid motion.
Fluid kinematics is the branch of fluid mechanics that focuses on describing and analyzing the motion of fluids, such as liquids and gases, without considering the forces that cause the motion. It deals with the geometrical and temporal aspects of fluid flow, including velocity and acceleration. Fluid dynamics, on the other hand, considers the forces acting on the fluid.
Fluid dynamics is the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion. It is a branch of continuum mechanics, a subject which models matter without using the information that it is made out of atoms; that is, it models matter from a macroscopic viewpoint rather than from microscopic.
Fluid mechanics, especially fluid dynamics, is an active field of research, typically mathematically complex. Many problems are partly or wholly unsolved and are best addressed by numerical methods, typically using computers. A modern discipline, called computational fluid dynamics (CFD), is devoted to this approach. Particle image velocimetry, an experimental method for visualizing and analyzing fluid flow, also takes advantage of the highly visual nature of fluid flow.
Fundamentally, every fluid mechanical system is assumed to obey the basic laws :
Conservation of mass
Conservation of energy
Conservation of momentum
The continuum assumption
For example, the assumption that mass is conserved means that for any fixed control volume (for example, a spherical volume)—enclosed by a control surface—the rate of change of the mass contained in that volume is equal to the rate at which mass is passing through the surface from outside to inside, minus the rate at which mass is passing from inside to outside. This can be expressed as an equation in integral form over the control volume.
The continuum assumption is an idealization of continuum mechanics under which fluids can be treated as continuous, even though, on a microscopic scale, they are composed of molecules. Under the continuum assumption, macroscopic (observed/measurable) properties such as density, pressure, temperature, and bulk velocity are taken to be well-defined at "infinitesimal" volume elements—small in comparison to the characteristic length scale of the system, but large in comparison to molecular length scale
railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forging



railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forgingJavad Kadkhodapour railway wheels, descaling after reheating and before forging
Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptx



Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptxRishavKumar530754 LiDAR-Based System for Autonomous Cars
Autonomous Driving with LiDAR Tech
LiDAR Integration in Self-Driving Cars
Self-Driving Vehicles Using LiDAR
LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars
"Feed Water Heaters in Thermal Power Plants: Types, Working, and Efficiency G...



"Feed Water Heaters in Thermal Power Plants: Types, Working, and Efficiency G...Infopitaara A feed water heater is a device used in power plants to preheat water before it enters the boiler. It plays a critical role in improving the overall efficiency of the power generation process, especially in thermal power plants.
🔧 Function of a Feed Water Heater:
It uses steam extracted from the turbine to preheat the feed water.
This reduces the fuel required to convert water into steam in the boiler.
It supports Regenerative Rankine Cycle, increasing plant efficiency.
🔍 Types of Feed Water Heaters:
Open Feed Water Heater (Direct Contact)
Steam and water come into direct contact.
Mixing occurs, and heat is transferred directly.
Common in low-pressure stages.
Closed Feed Water Heater (Surface Type)
Steam and water are separated by tubes.
Heat is transferred through tube walls.
Common in high-pressure systems.
⚙️ Advantages:
Improves thermal efficiency.
Reduces fuel consumption.
Lowers thermal stress on boiler components.
Minimizes corrosion by removing dissolved gases.
Avnet Silica's PCIM 2025 Highlights Flyer



Avnet Silica's PCIM 2025 Highlights FlyerWillDavies22 See what you can expect to find on Avnet Silica's stand at PCIM 2025.
Level 1-Safety.pptx Presentation of Electrical Safety



Level 1-Safety.pptx Presentation of Electrical SafetyJoseAlbertoCariasDel Level 1-Safety.pptx Presentation of Electrical Safety
Degree_of_Automation.pdf for Instrumentation and industrial specialist



Degree_of_Automation.pdf for Instrumentation and industrial specialistshreyabhosale19 degree of Automation for industrial and Instrumentation learners.
Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous Security



Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous SecurityMarc Hornbeek This presentation provides detailed guidance and tools for conducting Current State and Future State Value Stream Mapping workshops for Intelligent Continuous Security.
fluke dealers in bangalore..............



fluke dealers in bangalore..............Haresh Vaswani The Fluke 925 is a vane anemometer, a handheld device designed to measure wind speed, air flow (volume), and temperature. It features a separate sensor and display unit, allowing greater flexibility and ease of use in tight or hard-to-reach spaces. The Fluke 925 is particularly suitable for HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) maintenance in both residential and commercial buildings, offering a durable and cost-effective solution for routine airflow diagnostics.
Data Structures_Searching and Sorting.pptx



Data Structures_Searching and Sorting.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Sorting Order and Stability in Sorting.
Concept of Internal and External Sorting.
Bubble Sort,
Insertion Sort,
Selection Sort,
Quick Sort and
Merge Sort,
Radix Sort, and
Shell Sort,
External Sorting, Time complexity analysis of Sorting Algorithms.
Introduction to SQL
- 1. 2-1 2-1 Chapter 2 DataBase System Concepts and Architecture 2.1 Data Models, Schemas, and Instances 2.2 DBMS Architecture and Data Independence 2.3 Database Languages and Interfaces 2.4 The Database System Environment 2.5 Classification of Database Management Systems 2.6 Summary
- 2. Introduction to SQL SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. *What is SQL? SQL stands for Structured Query Language SQL lets you access and manipulate databases SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard *What Can SQL do? SQL can execute queries against a database SQL can retrieve data from a database SQL can insert records in a database SQL can update records in a database SQL can delete records from a database SQL can create new databases SQL can create new tables in a database SQL can create stored procedures in a database
- 3. SQL can create views in a database SQL can set permissions on tables, procedures, and views SQL is a Standard - BUT.... Although SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard, there are many different versions of the SQL language
- 4. 2-2 2-4 Data Model: A set of concepts to describe the structure of a database, and certain constraints that the database should obey. ‧data types ‧relationships Provide data abstraction Data Model Operations: Operations for specifying database retrievals and updates by referring to the concepts of the data model. ‧generic operation: insert, delete, modify, retrieve ‧user-defined operations 2.1 Data Models, Schemas, and Instances
- 5. 2-2 2-5 2.1.1 Categories of Data Models: - Conceptual (high-level, semantic) data models: Provide concepts that are close to the way many users perceive data. (Also called entity-based or object-based data models.) ‧entity ‧attribute ‧relationship - Physical (low-level, internal) data models: Provide concepts that describe details of how data is stored in the computer. ‧record formats ‧record ordering ‧access paths - Implementation (record-oriented) data models: Provide concepts that fall between the above two, balancing user views with some computer storage details. ‧relational ‧network ‧hierarchical
- 6. 2-3 2-6 2.1.2 Schemas, Instances and Database State Database Schema (meta-data): The description of a database. Includes descriptions of the database structure and the constraints that should hold on the database. Schema Diagram: A diagrammatic display of (some aspects of ) a database schema. (refer to Fig 2.1 2-5) Database Instance: The actual data stored in a database at a particular moment in time. Also called database state ( or occurrence, snapshot) (refer to Fig 1.2 2-6) The database schema changes very infrequently. The database state changes every time the database is updated. Schema is also called intension, whereas state is called extension. Each schema construct has its own current set of instances. cf database
- 7. 2-4a 2-7 Figure 2.1 Schema diagram for UNIVERSITY database schema construct Known data: name of record types, data items
- 8. 2-4 2-8 Figure 1.2 UNIVERSITY Database
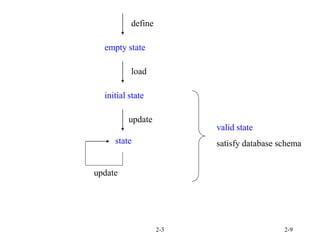
- 9. 2-3 2-9 define empty state initial state load state update update valid state satisfy database schema
- 10. 2-5 2-10 2.2 DBMS Architecture and Data Independence Proposed to support DBMS characteristics of: - Insulation of programs and data/program and operations (program-data and program-operation independence) - Support of multiple views of the data. - Use of catalog (database description) Defines DBMS schema at three levels: (see 2-9) - Internal schema at the internal level to describe data storage structures and access paths. Typically uses a physical data model. - Conceptual schema at the conceptual level to describe the structure and constraints for the whole database. Uses a conceptual or an implementation data model. - External schema at the external level to describe the various user views. Usually uses the same data model as the conceptual level or high-level data model. Mappings among schema levels are also needed. Programs refer to an external schema, and are mapped by the DBMS to the internal schema for execution 2.2.1 Three-Schema Architecture
- 11. 2-6 2-11 Figure 2.2 The Three-schema architecture 2-6
- 12. 2-7 2-12 2.2.2 Data Independence Logical Data Independence: The capacity to change the conceptual schema without having to change the external schemas and their application programs. Physical Data Independence: The capacity to change the internal schema without having to change the conceptual schema. When a schema at a lower level is changed, only the mappings between this schema and higher-lever schemas need to be changed in a DBMS that fully supports data independence. The higher-level schemas themselves are unchanged. Hence, the application programs need not be changed since they refer to the external schemas. By adding or removing a record type or data item to · expand the database (2-11) · reduce the database Reorganize physical files to improve performance e.g. List all sections offered in Fall 1998 Disadvantages of two levels of mappings: Overhead during compilation or execution of a query or program
- 13. 2-7a 2-13 UNIVERSITY Conceptual Schema STUDENT (Name, Student Number, Class, Major) COURSE (Course Name, Course Number, Credit, Dept) PREREQUISITE (Course Number, Prerequisite Number) SECTION (Section Id, Course Number, Semester, Year, Instructor) GRADE_REPORT(Student Number, Section Id , Grade) UNIVERSITY External Schema TRANSCRIPT(Student Name, Course Number, Grade, Semester, Year, Section Id) derived from STUDENT, SECTION, GRADE_REPORT PREREQUISITES(Course Name, Course Number, Prerequisites) derived from PREREQUISITE, COURSE Change GRADE-REPORT Schema Construct GRADE_REPORT (Student Number, Student Name, Section Id, Course Number, Grade) Change Mapping (& View Definition) TRANSCRIPT derived from SECTION, GRADE_REPORT
- 14. 2-8 2-14 2.3 Database Languages and Interfaces Data Definition Language (DDL): Used by the DBA and database designers to specify the conceptual schema of a database. In many DBMSs, the DDL is also used to define internal and external schemas (views). In some DBMSs, separate storage definition language (SDL) and view definition language (VDL) are used to define internal and external schemas. Data Manipulation Language (DML): Used to specify database retrievals and updates (insertion, deletion, modifications) - DML commands (data sublanguage) can be embedded in a general-purpose programming language (host language). - Alternatively, stand-alone DML commands can be applied directly (query language). provide appropriate languages and interfaces for each category of users. 2.3.1 DBMS Languages DDL Compiler
- 15. 2-9 2-15 Types of DML -Procedural DML: • Also called record-at-a-time (record-oriented) or low-level DML • Must be embedded in a programming language. • Searches for and retrieves individual database records and uses looping and other constructs of the host programming language to retrieve multiple records. -Declarative or non-procedural DML: • Also called set-at-a-time (set-oriented) or high-level DML. • Can be used as a stand-alone query language or can be embedded in a programming language. • Searches for and retrieves information from multiple related database records in a single command. - host language: general-purpose language - data sublanguage: DML - C++
- 16. 2-10 2-16 2.3.2 DBMS Interfaces - Stand-alone query language interfaces. (casual end user) - Programmer interfaces for embedding DML in programming languages: (programmer) -Pre-compiler Approach -Procedure (Subroutine) Call Approach - User-friendly interfaces: -Menu-based Interfaces for Browsing. -Forms-based Interfaces. -Graphical User Interfaces. -Natural language Interfaces -Combination of the above -Interfaces for Parametic Users (using function keys) - Interfaces for the DBA: -Creating accounts, granting authorizations -Setting system parameters -Changing schemas or access path
- 17. 2-11 2-17 2.4.1 DBMS Component Modules 2.4 The Database System Environment Figure 2.3
- 18. 2-12 2-18 2.4.2 Database System Utilities To perform certain functions such as: - Loading data stored in files into a database. Conversion tool - Backing up the database periodically on storage. - File reorganizing database file structures. - Report generation utilities. - Performance monitoring utilities. - Other functions, such as sorting, user monitoring, data compression, etc.
- 19. 2-12 2-19 Data dictionary utility: - Used to store schema descriptions and other information such as design decisions, application program descriptions, user information, usage standards, etc. (comment) -Active data dictionary is accessed by DBMS software and users/DBA. -Passive data dictionary is accessed by users/DBA only. Communications Facilities - Allow users at locations remote from the database system site to access the database. DB (DBMS)/DC (Data Communication System) 2.4.3 Tools, Application Environments, and Communications Facilities
- 20. 2-13 2-20 2.5 Classification of Database Management Systems Based on the data model used: •Data models -Traditional: Relational, Network (see 2-19), Hierarchical - Emerging: Object-oriented, Semantic, Entity- Relationship, other. Other classifications: •Number of users : Single-user (typically used with personal computers) vs. multi-user (most DBMSs) •Number of sites: Centralized (uses a single computer) vs. distributed (uses multiple computers). Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous • Cost of DBMS software. $10,000~100,000 $100~3,000 •Types of access paths used. (inverted file structures, …) •Purpose general purpose special purpose e.g. airline reservations, telephone directory, on-line transaction processing system
- 21. 2-14 2-21 Figure 2.4 A Network Schema









