IPv6 Matrix presentation for World IPv6 Launch, June 2012
- 1. IPv6 Matrix Project Tracking IPv6 connectivity Worldwide http://www.ipv6matrix.org Dr. Olivier MJ Crépin-Leblond – [email protected] 4 June 2012 Update for World IPv6 Launch on 6 June 2012 Page 1 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 2. We are running out of IP addresses http://www.potaroo.net/tools/ipv4/index.html When we reach this point, it will be too late since there will be no more “free” IPv4 addresses! Real time data collected September 2011 Page 2 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 3. World IPv6 Launch Major Internet service providers (ISPs), home networking equipment manufacturers, and web companies around the world are coming together to permanently enable IPv6 for their products and services. http://www.worldipv6launch.org Page 3 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 4. IPv6 Matrix Project ISOC England was awarded a Community Grants Programme award in November 2009 Design and implementation of an “IPv6 Crawler,” software on a computer that crawls through the DNS at regular intervals in order to detect and test: IPv6 DNS servers IPv6 compliant Web servers IPv6 compliant SMTP mailers IPv6 compliant NTP servers. Page 4 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 5. Project Rationale Today, more than 95% of Internet traffic is generated by a small number of data sources – i.e. the world’s busiest Web Sites Without IPv6 accessible content, IPv6 has no chance of being used - ever. Take the 1 Million most popular Web site list from alexa.com as a starting point for the domains to be tested. Add more domains later. Test them for IPv6 connectivity This is equivalent to testing about 6.3 million hosts worldwide Use GeoIP database to estimate real host location Page 5 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 6. Project Teams London, UK: Project Management and support Hardware supply and installation Data Centre and IPv6 connectivity Nile University, Egypt: Software Programming Page 6 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 7. Crawler (back end) Crawler Model Name (eth0) HP DL360p turtle.ipv6matrix.org ; crawler.ipv6matrix.org turtle.ipv6matrix.com ; crawler.ipv6matrix.com turtle.ipv6matrix.net ; crawler.ipv6matrix.net IPv4 address 212.124.204.162 / 100 Mb/s (eth0) / speed IPv6 address 2a00:19e8:20:1::a2 / 100 Mb/s (eth0) / speed Name (eth1) shell.ipv6matrix.org IPv4 address 194.33.63.250 / 1 Gb/s (GIH (eth1) / private address space) speed CPU 2 x Dual Core Intel(R) Xeon(TM) CPU 3.60GHz RAM 4 Gb DDR2 SDRAM HD Storage 146 Gb hardware SATA 2-disk RAID (hot swappable) PSU 2 x hot-swappable redundant 535W. Operating CENTOS 5 Linux / updated System Page 7 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 8. Web Server (front end) Web Server Model Name (eth0) HP DL140 elephant.ipv6matrix.org ; www.ipv6matrix.org elephant.ipv6matrix.com ; www.ipv6matrix.com elephant.ipv6matrix.net ; www.ipv6matrix.net IPv4 address 212.124.204.170 / 100 Mb/s (eth0) / speed IPv6 address 2a00:19e8:20:1::aa / 100 Mb/s (eth0) / speed Name (eth1) tusk.ipv6matrix.org IPv4 address 194.33.63.251 / 1 Gb/s (GIH (eth1) / private address space) speed CPU 2 x Dual Core Intel(R) Xeon(TM) CPU 3.40GHz RAM 4 Gb DDR2 SDRAM HD Storage 2 x 1 Tb fast SATA PSU Single 500W Operating System Ubuntu 4.4 Linux / updated Page 8 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 9. Router Router Model CISCO 2811 Operating Advanced IP Services IOS System DRAM 64 Mb Ethernet Ports / 2 / 100 Mb/s speed Interface card / MN-16ESW 16 port / 100 speed Mb/s Page 9 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 10. Local Network Page 10 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 11. Software flowchart Page 11 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
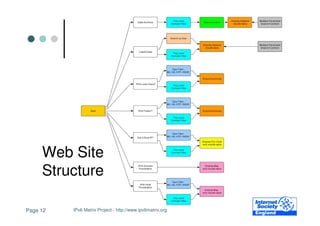
- 12. Web Site Structure Page 12 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 13. www.ipv6matrix.org Web Site Page 13 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 14. What are we tracking? Host IPv6 penetration Using IPv4 Geo-location coordinates Includes generic TLD (gTLDs, .com, .net, .org) and country code ccTLDs Two types of information: Infrastructure: DNS + Web + E-mail + Time server (NTP) This tracks all of the infrastructure required to run IPv6 Web services Web sites only (actual content) This tracks the Web services themselves. Usually this percentage is lower than the figure for the infrastructure Page 14 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 15. What are we archiving? Everything that we are tracking on the previous page, plus: Testing of connectivity to the above services in case IPv6 addresses are advertised but no service runs on them Tracing of route from London Docklands to each one of these hosts both using IPv4 and IPv6 – and archiving all of this information in text format A lot more data, accessible from the Web site archive In June 2012, the size of this database in text format is approx 140Gb and continually increasing (the testing software runs 24/7) Page 15 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 16. Data Archives Selecting Data Archives provides a link to the detailed information Table. Click on “Search”, to go directly to the Top Level Domain, or scroll down to the desired Top Level Domain. Page 16 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 17. Data Archives Example Data in Data Archives (stop at date) Click on the “+” to the left of the Top Level Domain to gain access the sub-menu containing the dates of all the data runs, and so on, to reveal results. year-month-day__hour-min-sec Page 17 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 18. Data Archives - results Click on the links to open a new window containing all of the detailed results formatted in a table. Page 18 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 19. Data Archives - results Basic IPv4/IPv6 connectivity table Domain penetration summary table Geographical IP database Type of IPv6 access (tunnels etc.) Trace path, hop count, MTU IPv4 & IPv6 Ping count IPv4 and IPv6 Reverse IPv4 and IPv6 SOA for Nameserver Service detection for SMTP, HTTP and HTTPs TLS detection for SMTP Page 19 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 20. Detailed Data for .AE Clicked on tcp80_WWW_ae: connection to http port Page 20 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 21. Using the filter Use the filter to select by Top Level Domain, or by type of service tested. Page 21 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 22. Results 4 June 2012 – pre-IPv6 Launch Page 22 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 23. Europe Data snapshot 2.02% 5.68% 2.77% 5.58% IPv6 Host Penetration Infrastructure 7.91% 8.24% - DNS 4.75% 2.13% 5.39% 5.06% 6.96% 5.20% - Web 13.70% 4.06% 9.34% 6.44% 13.52% 6.72% - E-mail 2.80% 2.66% 4.96% 11.87% 7.07% 7.44% 4.04% - NTP 3.88% 2.71% 0.83% 3.70% 0.16% Low Sample 15.14% 11.83% Low accuracy 15.81% 10.53% 0.64% 0.58% 18.54% 9.82% 0.65% 0.93% 18.36% December 2011 9.98% 16.26% 11.09% 6.14% 12.19% 8.87% 4 June 2012 6.92% 16.66% 16.73% 6.30% 2.67% 10.01% 2.33% 6.50% 3.51% 12.20% 2.71% 4.34% 4.04% Page 23 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 24. Europe Data snapshot 0.47% 2.60% 0.45% 2.85% IPv6 Host Penetration 0.51% Web only 0.51% 0.99% 1.17% 0.94% 1.11% 1.22% 1.08% 2.19% 0.71% 2.41% 1.68% 7.45% 1.68% 0.86% 0.75% 2.82% 1.83% 6.71% 0.93% 0.19% 0.16% 0.27% 0.95% 0.35% 0.17% Low Sample 1.00% 0.42% Low accuracy 1.08% 0.36% 0.32% 0.29% 26.70% 11.67% 0.34% 0.35% 23.86% December 2011 11.85% 12.29% 0.48% 4 June 2012 9.14% 12.43% 0.73% 10.35% 4.15% 3.90% 0.85% 1.30% 4.00% 0.65% 1.07% 1.41% 4.35% 0.64% 1.59% 1.80% Page 24 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
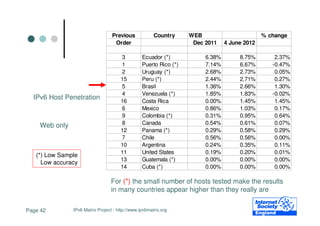
- 25. Previous Country DNS+WEB+E-mail+NTP % change Order Dec 2011 4 June 2012 1 Moldova (*) 18.54% 18.36% -0.18% 2 Switzerland 16.66% 16.73% 0.07% 4 France 15.14% 15.81% 0.67% 7 Slovenia 11.33% 13.69% 2.36% 5 Finland 13.70% 13.52% -0.18% 9 Czech Republic 10.01% 12.20% 2.19% 3 Slovakia 16.26% 12.19% -4.07% 11 Netherlands 9.34% 11.87% 2.53% 6 Ukraine 11.83% 10.53% -1.30% 10 Portugal 9.82% 9.98% 0.16% 8 Poland 11.09% 8.87% -2.22% 12 Denmark 7.91% 8.24% 0.33% 14 Latvia 6.72% 7.44% 0.72% 15 Germany 6.44% 7.07% 0.63% 32 Russia 2.13% 6.96% 4.83% IPv6 Host Penetration 17 Spain 6.14% 6.92% 0.78% 18 Estonia 6.14% 6.92% 0.78% 13 Bosnia and Herzegovina (*) 7.51% 6.54% -0.97% 16 Austria 6.30% 6.50% 0.20% 19 Croatia 5.83% 6.28% 0.45% Infrastructure 20 Norway 5.68% 5.58% -0.10% - DNS or 21 23 Sweden Belgium 4.75% 4.06% 5.06% 4.96% 0.31% 0.90% - Web or 26 Luxembourg 3.21% 4.80% 1.59% 22 Greece 4.34% 4.04% -0.30% - E-mail or 24 Lithuania 4.04% 3.88% -0.16% 29 United Kingdom 2.71% 3.70% 0.99% - NTP 30 Italy 2.67% 3.51% 0.84% 25 Macedonia 3.33% 3.33% 0.00% 33 Iceland 2.02% 2.77% 0.75% 31 Hungary 2.33% 2.71% 0.38% (*) Low Sample 28 Ireland 2.80% 2.66% -0.14% Low accuracy 27 Serbia (*) 3.06% 2.53% -0.53% 35 Romania 0.58% 0.93% 0.35% 36 Bulgaria 0.50% 0.81% 0.31% 34 Belarus 0.83% 0.16% -0.67% Page 25 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 26. Previous Country WEB % change Order Dec 2011 4 june 2012 1 Moldova (*) 23.70% 23.86% 0.16% 2 Slovakia 12.29% 12.43% 0.14% 3 Portugal 11.67% 11.85% 0.18% 5 Spain 9.14% 10.35% 1.21% 6 Germany 7.45% 6.71% -0.74% 9 Slovenia 4.77% 5.53% 0.76% 10 Czech Republic 4.00% 4.35% 0.35% 8 Switzerland 4.15% 3.90% -0.25% 7 Macedonia 4.23% 3.12% -1.11% 11 Norway 2.60% 2.85% 0.25% 14 Belgium 2.41% 2.82% 0.41% 16 Netherlands 1.68% 1.83% 0.15% 15 Greece 1.59% 1.80% 0.21% 13 Finland 2.19% 1.68% -0.51% 17 Croatia 1.63% 1.45% -0.18% 18 Italy 1.30% 1.41% 0.11% IPv6 Host Penetration 20 Russia 1.17% 1.22% 0.05% 19 Sweden 0.99% 1.11% 0.12% 4 Estonia 0.94% 1.08% 0.14% 22 France 1.00% 1.08% 0.08% Web only 23 21 Austria Latvia 0.85% 0.86% 1.07% 0.93% 0.22% 0.07% 24 Ireland 0.71% 0.75% 0.04% 28 Poland 0.48% 0.73% 0.25% 25 Hungary 0.65% 0.64% -0.01% 35 Serbia (*) 0.00% 0.59% 0.59% 31 Denmark 0.51% 0.51% 0.00% (*) Low Sample 26 Iceland 0.47% 0.45% -0.02% Low accuracy 29 Bulgaria 0.16% 0.45% 0.29% 27 Ukraine 0.42% 0.36% -0.06% 30 United Kingdom 0.27% 0.35% 0.08% 32 Romania 0.29% 0.35% 0.06% 12 Belarus 0.95% 0.17% -0.78% 33 Lithuania 0.19% 0.16% -0.03% 34 Bosnia and Herzegovina (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Page 26 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 27. Europe Trends Many countries see a significant rise in infrastructure Likely to be caused by a main hosting provider, installing dual-stack Name-servers Russia with biggest growth in infrastructure Slovakia & Portugal still leading with dual- stack Web sites Spain catching up. Country with largest number of dual stack Web sites in Europe: Germany Page 27 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 28. Asia Data snapshot IPv6 Host Penetration 2.13% 6.96% 12.90% Infrastructure 22.42% - DNS or - Web or - E-mail or 0.20% 1.83% 0.50% 0.22% 2.02% - NTP 0.47% 2.76% 0.25% 3.70% 0.54% 0.22% 0.90% 2.38% 2.21% 2.66% HK: 2.61% 2.51% HK: 2.49% Low Sample 0.00% 3.52% 0.00% 3.81% Low accuracy 0.64% 11.94% 1.84% 0.63% 12.79% 1.89% 3.12% 22.73% December 2011 3.12% 6.16% 26.32% 7.74% 1.22% 4.22% 0.10% 0.27% 4.57% 0.47% 3.47% 4.16% 4 June 2012 3.84% 4.32% SG: 25.52% SG: 24.52% Page 28 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 29. Asia Data snapshot IPv6 Host Penetration 1.17% 1.22% 3.49% 5.95% Web only 0.15% 0.28% 0.38% 0.18% 0.29% 0.40% 1.77% 0.13% 3.06% 0.14% 0.08% 0.40% 1.49% 0.38% 1.59% HK: 0.71% 0.69% HK: 0.77% Low Sample 0.00% 4.69% 0.00% 4.56% Low accuracy 0.65% 11.21% 3.57% 0.64% 11.85% 3.45% 3.12% 50.00% December 2011 3.12% 1.14% 50.00% 1.40% 1.22% 1.24% 0.11% 0.27% 1.55% 0.07% 0.91% 0.97% 4 June 2012 0.98% 0.89% SG: 0.65% SG: 0.90% Page 29 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 30. Previous Country DNS+WEB+E-mail+NTP % change Order Dec 2011 4 June 2012 1 Singapore 25.52% 24.52% -1.00% 2 Armenia (*) 12.90% 22.42% 9.52% 3 Sri Lanka (*) 11.94% 12.79% 0.85% 4 Indonesia 6.16% 7.74% 1.58% 12 Russia 2.13% 6.96% 4.83% 8 Malaysia 4.22% 4.57% 0.35% 6 New Zealand 4.16% 4.32% 0.16% 5 Australia 3.47% 3.84% 0.37% 7 Philippines (*) 3.52% 3.81% 0.29% IPv6 Host Penetration 10 Saudi Arabia (*) 2.76% 3.70% 0.94% 9 Oman (*) 3.12% 3.12% 0.00% 11 Taiwan 2.38% 2.66% 0.28% 14 Thailand 2.21% 2.51% 0.30% Infrastructure 24 Hong Kong 2.61% 2.49% -0.12% - DNS or 15 Japan 1.83% 2.02% 0.19% 13 Qatar (*) 1.84% 1.89% 0.05% - Web or 20 India 0.54% 0.90% 0.36% - E-mail or 17 United Arab Emirates (*) 0.64% 0.63% -0.01% - NTP 18 Iran 0.50% 0.47% -0.03% 22 Vietnam (*) 0.10% 0.47% 0.37% 16 Pakistan 1.22% 0.27% -0.95% (*) Low Sample 19 South Korea 0.25% 0.22% -0.03% Low accuracy 21 China 0.20% 0.22% 0.02% 23 Kuwait (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Page 30 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 31. Previous Country WEB % change Order Dec 2011 4 June 2012 1 Sri Lanka (*) 11.21% 11.85% 0.64% 3 Armenia (*) 3.49% 5.95% 2.46% 2 Philippines (*) 4.69% 4.56% -0.13% 4 Qatar (*) 3.57% 3.45% -0.12% 5 Oman (*) 3.12% 3.12% 0.00% 6 Saudi Arabia (*) 1.77% 3.06% 1.29% 7 Taiwan 1.49% 1.59% 0.10% 13 Malaysia 1.24% 1.55% 0.31% 9 Indonesia 1.14% 1.40% 0.26% IPv6 Host Penetration 12 Russia 1.17% 1.22% 0.05% 10 Australia 0.91% 0.98% 0.07% 22 Singapore 0.65% 0.90% 0.25% 11 New Zealand 0.97% 0.89% -0.08% Web only 24 Hong Kong 0.71% 0.77% 0.06% 15 Thailand 0.38% 0.69% 0.31% 14 United Arab Emirates (*) 0.65% 0.64% -0.01% 16 Iran 0.38% 0.40% 0.02% 20 India 0.14% 0.40% 0.26% (*) Low Sample 18 Japan 0.28% 0.29% 0.01% Low accuracy 8 Pakistan 1.22% 0.27% -0.95% 19 China 0.15% 0.18% 0.03% 17 South Korea 0.13% 0.08% -0.05% 21 Vietnam (*) 0.11% 0.07% -0.04% 23 Kuwait (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Page 31 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 32. Asia Trends Singapore still leading by far in infrastructure but trailing in dual-stack Web Site content Russia with biggest growth in infrastructure China results abnormally very low – content not dual stacked or IPv6 behind firewall? India also low both in infrastructure and most popular Web sites with dual stack Less reliability of results due to smaller sample size in many countries of the region Page 32 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 33. Africa Data snapshot IPv6 Host Penetration 36.61% 43.01% Infrastructure - DNS or - Web or - E-mail or - NTP 9.52% 9.38% 7.42% 7.17% Low Sample 10.20% Low accuracy 9.43% December 2011 4 June 2012 0.96% 1.01% Page 33 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 34. Africa Data snapshot IPv6 Host Penetration 0.00% 0.00% Web only 10.00% 0.00% 2.78% 2.56% Low Sample 14.29% Low accuracy 14.29% December 2011 4 June 2012 0.41% 0.46% Page 34 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 35. Country DNS+WEB+E-mail+NTP % change Dec 2011 4 June 2012 Tunisia (*) 36.61% 43.01% 6.40% IPv6 Host Penetration Tanzania (*) 10.20% 9.43% -0.77% Senegal (*) 9.52% 9.38% -0.14% Kenya (*) 7.42% 7.17% -0.25% Infrastructure South Africa 0.96% 1.01% 0.05% - DNS or Algeria 0.00% 0.96% 0.96% - Web or - E-mail or - NTP The small number of hosts tested make the results for most of Africa appear higher than they really are (*) Low Sample Low accuracy Page 35 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 36. Country WEB % change Dec 2011 4 June 2012 IPv6 Host Penetration Tanzania (*) 14.29% 14.29% 0.00% Kenya (*) 2.78% 2.56% -0.22% Algeria 0.00% 1.28% 1.28% South Africa 0.41% 0.46% 0.05% Web only Senegal (*) 10.00% 0.00% -10.00% Tunisia (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% (*) Low Sample The small number of hosts tested make the results Low accuracy for most of Africa appear higher than they really are Page 36 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 37. Africa Trends Many countries now have IPv6 capability, some through tunnels Dual Stack Islands starting to appear Can be compared with the growth of Internet connectivity in the nineties Page 37 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 38. Compare Historical data on African Internet Connectivity June 1994 May 1997 Source: Internetology - http://www.nsrc.org/codes/bymap/ntlgy/ntlgy.htm Page 38 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 39. North/South America 2.42% 3.30% IPv6 Host Penetration Infrastructure 5.81% 3.57% 6.17% 3.57% - DNS or PR: 7.14% PR: 6.67% - Web or 0.53% 4.05% - E-mail or 0.80% 4.35% - NTP 0.00% 1.09% Low Sample 0.93% 2.32% 1.14% 5.89% Low accuracy 3.70% 4.44% December 2011 0.30% 0.72% 2.63% 5.41% 4 June 2012 3.42% 0.49% 5.36% 0.49% 0.57% 0.56% Page 39 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 40. North/South America 0.54% 0.61% IPv6 Host Penetration Web only 0.19% 0.20% PR: 7.14% PR: 6.67% 0.86% 1.85% 1.03% 1.83% 0.00% 1.45% Low Sample 0.29% 1.36% 0.58% 2.66% Low accuracy 6.38% December 2011 8.75% 0.31% 0.95% 0.24% 2.68% 4 June 2012 2.44% 0.35% 2.73% 2.71% 0.56% 0.56% Page 40 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 41. Previous Country DNS+WEB+E-mail+NTP % change Order Dec 2011 4 June 2012 2 Puerto Rico (*) 7.24% 6.67% -0.57% 4 United States 5.81% 6.17% 0.36% 9 Brasil 2.32% 5.89% 3.57% 3 Uruguay (*) 5.41% 5.36% -0.05% 7 Ecuador (*) 3.70% 4.44% 0.74% 5 Venezuela (*) 4.05% 4.35% 0.30% 6 Cuba (*) 3.57% 3.57% 0.00% IPv6 Host Penetration 15 Peru (*) 2.63% 3.42% 0.79% 8 Canada 2.42% 3.30% 0.88% 10 Panama (*) 0.93% 1.14% 0.21% Infrastructure 16 Costa Rica 0.00% 1.09% 1.09% - DNS or 11 Mexico 0.53% 0.80% 0.27% - Web or 14 Colombia (*) 0.30% 0.72% 0.42% 12 Chile 0.57% 0.56% -0.01% - E-mail or 13 Argentina 0.49% 0.49% 0.00% - NTP 1 Guatemala (*) 100.00% 0.00% -100.00% (*) Low Sample Low accuracy For (*) the small number of hosts tested make the results in many countries appear higher than they really are Page 41 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 42. Previous Country WEB % change Order Dec 2011 4 June 2012 3 Ecuador (*) 6.38% 8.75% 2.37% 1 Puerto Rico (*) 7.14% 6.67% -0.47% 2 Uruguay (*) 2.68% 2.73% 0.05% 15 Peru (*) 2.44% 2.71% 0.27% 5 Brasil 1.36% 2.66% 1.30% 4 Venezuela (*) 1.85% 1.83% -0.02% IPv6 Host Penetration 16 Costa Rica 0.00% 1.45% 1.45% 6 Mexico 0.86% 1.03% 0.17% 9 Colombia (*) 0.31% 0.95% 0.64% Web only 8 Canada 0.54% 0.61% 0.07% 12 Panama (*) 0.29% 0.58% 0.29% 7 Chile 0.56% 0.56% 0.00% 10 Argentina 0.24% 0.35% 0.11% 11 United States 0.19% 0.20% 0.01% (*) Low Sample 13 Guatemala (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Low accuracy 14 Cuba (*) 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% For (*) the small number of hosts tested make the results in many countries appear higher than they really are Page 42 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 43. America Trends USA leads in infrastructure but low on dual Stack Web site (although the figure is 1699 hosts). Brazil leading in Latin America with 204 Dual Stack Web Site hosts Elsewhere, data based on low number of Web sites, needs to be taken in moderation (the restricted number of hosting providers can make figures jump several percentage points) Page 43 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 44. Worldwide Trends We are seeing a slow growth in dual stack IPv4-IPv6 implementation A decrease in percentage in some countries, points to unstable peering agreements (the IPv6 network is less closely meshed than the IPv4 network) Germany leads the world in the number of Dual Stack Web sites among world’s most popular Web sites: 14636 hosts out of a sample size of 218 178 hosts tested Bearing in mind the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Registry has run out of IPv4 addresses, it is alarming to see so few Web sites up and running IPv6 in that region, especially in countries where Internet growth is high, such as in India. Page 44 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 45. Problems / Possible Errors Lots of errors in the DNS – commas, no A, no AAAA record, looping MX, etc. Firewalls and security software: Blocking of network segments detecting denial of service attack (DoS) by error: • Unusual UDP traffic. Trace-path / ping, SMTP, HTTP, Secure HTTP, NTP port testing. Internet snapshot from one location only Less accurate results with small input data size (small number of domains tested) Disputed accuracy of Geographical IP database Page 45 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 46. Example: fake IPv6 AAAA record Country specific results? /P2 These “ipv6” addresses are AAAA records which pretend to denote an IPv6 address, (examples from the report / finding but are actually IPv4 addresses. errors etc.) There are plenty of examples of such mis- configuration in the DNS. Worse problems are caused by commas in domain names, ie. www.domain,com as well as IP addresses returning localhost 127.0.0.1 or ::1 etc. Comma! Perform a search for ipv6 field starting with ::ffff Page 46 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
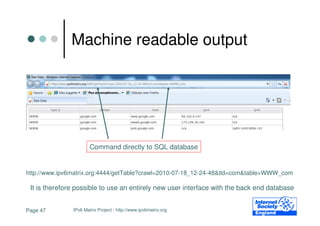
- 47. Machine readable output Command directly to SQL database http://www.ipv6matrix.org:4444/getTable?crawl=2010-07-18_12-24-48&tld=com&table=WWW_com It is therefore possible to use an entirely new user interface with the back end database Page 47 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 48. Future work / funding required Add more domains to be tested Add more features to be tested Current front end Web Pages are only an example of possible analysis Develop new data visualisation Perform further analysis Perform historical/time analysis from archives Develop an engine to write automated reports Duplicate Crawler to other regions Page 48 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org
- 49. Thank you Contact: ISOC England – [email protected] CTM International Page 49 IPv6 Matrix Project - http://www.ipv6matrix.org